Thrombosis and various diseases of the heart and blood vessels can cause serious complications and even lead to the death of the patient. The vitamin complex “Angiovit” allows you to reduce the risk and alleviate the course of serious diseases. It normalizes blood composition and protects against thrombosis. It is prescribed for many cardiovascular diseases.
Characteristic
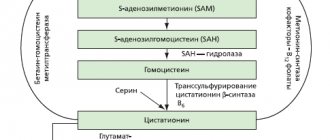
Vitamin complex for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases associated with increased levels of homocysteine, which is one of the factors of damage to the walls of blood vessels.
Elevated levels of homocysteine in the blood (hyperhomocysteinemia) are found in 60–70% of cardiac patients and are one of the main risk factors for atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis, incl. for myocardial infarction, ischemic stroke, diabetic vascular damage. The occurrence of hyperhomocysteinemia is promoted by a deficiency of folic acid and vitamins B6 and B12 in the body.
In addition, hyperhomocysteinemia is one of the factors in the formation of chronic (habitual) miscarriage and congenital fetal pathology. A relationship has been established between hyperhomocysteinemia and the occurrence of various types of depressive states, senile dementia (dementia), and Alzheimer's disease.
Composition and release form
"Angiovit" are small white tablets protected by a thin coating. They must be swallowed whole without chewing. Pharmacies sell cardboard boxes of 60 pieces each.
The tablet contains three main active ingredients - B vitamins and their derivatives:
- B6 (pyridoxine hydrochloride) - 4 mg;
- B9 (folic acid) - 5 mg;
- B12 (cyanocobalamin) - 6 mcg.
The medicine is made from forms of several B vitamins. This vitamin complex thins the blood and improves the condition of blood vessels.
Indications for use
After ingestion, the medicine is quickly absorbed into the blood and begins to act. "Angiovit" is included in the treatment of various diseases.
Indications for taking "Angiovit":
- angina pectoris 2 and 3 degrees;
- IHD;
- diabetic angiopathy;
- any thrombosis;
- atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels and the circulatory failure caused by it;
- myocardial infarction.
"Angiovit" is taken to prevent and treat these dangerous diseases. In addition, it is often prescribed to pregnant women to improve blood circulation between the placenta and the fetus. Thanks to this medicine, the fetus receives a sufficient amount of blood. Moreover, the drug provides the fetus with B vitamins, which are vital for the development of the child’s nervous system. Folic acid plays a particularly important role in this. Due to its deficiency, the fetus may develop pathologies such as anencephaly and spina bifida.
Can I take it during pregnancy?
Doctors recommend taking Angiovit already at a time when a woman is just about to become a mother. This medicine will help avoid the tragic consequences of a lack of B vitamins for newborns. "Angiovit" is prescribed to avoid the following intrauterine pathologies:
- splitting of the spinal cord (spina bifida);
- heart defects;
- weak immunity;
- anencephaly;
- developmental delay;
- underdevelopment of blood vessels.
The medicine must be taken during all periods of pregnancy, especially at the very beginning, when the child’s nervous system is being formed.
Angiovitis. The use of the drug Angiovit in pregnancy pathologies
An important role in the pathogenesis of pregnancy complications is played by disorders of the hemostatic system, caused by a predisposition to thrombosis (thrombophilia) due to genetic or acquired defects in the anticoagulant and fibrinolytic blood system, as well as the coagulation process itself. The central place in the development of thrombophilia in obstetric pathology is occupied by damage to the vascular wall with the subsequent development of endothelial dysfunction. Many markers of endothelial dysfunction are involved in the formation of thrombogenic potential and thromboresistance of blood vessels. The development of thrombophilia largely depends on an imbalance between pro- and anticoagulant factors. The predominance of procoagulant factors leads to increased thrombus formation, adhesion and aggregation of platelets. The risk group for the development of thromboembolic disorders includes women with genetic forms of thrombophilia, patients whose pregnancy is complicated due to the development of gestosis, arterial hypertension, purulent-septic and infectious diseases, diabetes mellitus, etc. [1]. One of the important factors leading to dysfunction of the vascular endothelium and stimulation of thrombus formation is hyperhomocysteinemia, which causes its negative impact on the course of pregnancy. Free penetration of homocysteine acid and homocysteine through the fetoplacental barrier can lead to the development of secondary autoimmune reactions and cause various complications of pregnancy, leading to such severe consequences for the fetus as anencephaly, spinal canal cleft, etc. It has been shown that hyperhomocysteinemia has an adverse effect on the course of pregnancy. gestosis [2, 3]. In the early stages of pregnancy, hyperhomocysteinemia, contributing to the development of fetoplacental circulatory disorders, may be one of the leading causes of miscarriage. The purpose of our study was to determine the content of homocysteine in blood plasma during recurrent miscarriage and the possibility of correcting hyperhomocysteinemia using the drug "Angiovit" (pharmaceutical), which has proven itself in the treatment of hyperhomocysteinemia observed in myocardial infarction, ischemic cerebral stroke and diabetic angiopathy [4] and has found wide application in practice. As a comparison group, pregnant women with manifestations of late gestosis were examined. Along with the determination of homocysteine in the blood, some other markers of hemostasis disorders in pathological pregnancy (D-dimers, protein C, antithrombin III and von Willebrand factor) were studied.
MATERIALS AND METHODS OF RESEARCH
Quantitative analysis of homocysteine was performed in plasma samples (EDTA) by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with fluorometric detection (Shimadzu RF-535). Chromatographic separation of homocysteine was carried out on a Reprosil 80 ODS-2 column (100×4 mm, 3 µm, Dr Maish GMBH, Germany). Detection was performed at 385 nm (excitation) and 515 nm (emission) [5]. The activity of antithrombin and protein C was determined on an automatic coagulometer ACL-200 (USA) using reagents (ACL-200 Operator's Manual). The activity of von Willebrand factor was determined by the rate of aggregation of a standard suspension of human platelets under the influence of ristomycin in the presence of plasma from the patient being examined. The measurements were carried out on an AR-2110 aggregometer (Solar, Belarus). Platelet-free pooled donor plasma was used to construct a standard curve [6].
To determine D-dimers, which are specific degradation products during fibrinolysis, a latex agglutination test (kits) was used. The principle of the method is based on the fact that in the presence of fibrin degradation products (D-dimers), agglutination of latex particles coated with monoclonal antibodies to them occurs. The concentration of D-dimers is expressed in μg/ml fibrinogen equivalent; the normal value for plasma is less than 0.5 μg/ml. The range of 0.5–3.0 indicates predominantly low concentrations of D-dimers, while the level of 0.5–3.0 indicates the opposite picture, i.e., characterizes the presence of predominantly high concentrations of D-dimers [7].
Angiovit was prescribed 1 tablet 2 times a day for three weeks, regardless of food intake, to all patients with miscarriage and gestosis, whose homocysteine levels exceeded the physiological norms for pregnant women: 6 µmol/l in the first trimester, 4 µmol/l - in the second trimester and 3 µmol/l in the third trimester. For patients whose plasma homocysteine level exceeded 10 µmol/l, the drug was prescribed 2 tablets 2 times a day until the homocysteine level decreased to physiological values corresponding to pregnancy.
After completing the course of taking Angiovit, a control examination of all patients was carried out, which included, in addition to clinical observation carried out throughout the entire period of treatment, determination of homocysteine and some other markers of endothelial dysfunction in the blood: D-dimers, protein C, antithrombin III and von Willebrand factor.
RESULTS AND ITS DISCUSSION
Clinical observations
As part of the study of the effect of the drug Angiovit on some indicators of the hemostatic system, 92 pregnant women were examined, of which 32 women with signs of threatened miscarriage, 30 women with manifestations of late gestosis and 30 pregnant women without a clinical picture of gestosis and threatened miscarriage.
The average age of patients in the group with threatened miscarriage was 27.8 years; 41% had a first pregnancy, and 59% had a repeat pregnancy. Signs of impending miscarriage were observed in 44% of those examined in the first trimester, and in 19% in the second trimester; the clinical picture of threatening premature birth in the third trimester was observed in 38% of women.
Among patients with gestosis, the average age was 29.3%; The first pregnancy was in 40%, and the second pregnancy was in 60% of patients. 18 pregnant women (60%) had mild late gestosis, 8 (27%) had moderate gestosis, and 4 women (13%) had severe gestosis. In 24 patients (80%), the clinical picture of gestosis developed in the third trimester of pregnancy, and in only 6 women - at the end of the second trimester.
During a control examination of pregnant women taking Angiovit, in the group with threat of miscarriage, pregnancy progressed in 31 patients (97%), and only one woman had a non-developing pregnancy at 12 weeks. Clinical manifestations of the threat of miscarriage completely disappeared in 24 women (75%), in 8 pregnant women (25%) the manifestations of the threat of miscarriage decreased significantly.
In the group with gestosis, during the control examination, pregnancy progressed in all women. At the same time, in 16 patients (53%) there was a decrease in the clinical manifestations of late gestosis, in 14 pregnant women (47%) the severity of gestosis remained at the same level, but there was no increase in the severity of the clinical picture.
Laboratory research
The results obtained showed that the most informative test characterizing endothelial dysfunction in the obstetric pathology under study (recurrent miscarriage, preeclampsia) is the determination of homocysteine (Table 1). We obtained especially clear data regarding miscarriage, in which the level of homocysteine in the blood of patients was 50% higher compared to the control, and after a course of taking Angiovit (1 tablet 2 times a day for 3 weeks) not only reached the control level level, but was almost 2 times lower. With gestosis, the level of homocysteine did not undergo such significant changes as with recurrent miscarriage, but even in this case, after a course of taking Angiovit, a slight decrease in the level of homocysteine in the blood was noted (Table 1).
Table 1 Table 1. Homocysteine content (µmol/l) in blood plasma during pregnancy Note: p1 - compared to control; p2 - compared to the indicators before taking Angiovitis
Along with homocysteine, we identified distinct changes in the content of D-dimers, which are products of fibrin degradation, the level of which increases as a result of activation of fibrinolysis (Table 2). Table 2. Content of D-dimers in blood plasma during pregnancy (%) Note: less than 0.5 μg/ml is normal; 0.5–3.0 mcg/ml - a slight increase in the indicator; 0.5–3.0 μg/ml—elevated D-dimer levels
As can be seen from the data presented in table. 2, the level of D-dimers in the pathology we are studying is either significantly reduced compared to the norm (miscarriage) or they are absent (preeclampsia). After a course of use of Angiovit, the content of D-dimers increases sharply.
It is known that von Willebrand factor is one of the factors leading to an increase in the thrombogenic potential of the endothelium with its subsequent damage. According to our data (Table 3), with recurrent miscarriage and preeclampsia, there is a tendency to increase its content (p > 0.05), and after treatment with Angiovit it normalizes.
Table No. 3 Table 3. Activity of von Willebrand factor in blood plasma during pregnancy (%) Note: p1 - compared to control; p 2—compared to the values before taking Angiovitis
Other indicators of the functional state of the endothelium that we studied (protein C and antithrombin III) did not undergo noticeable changes in the studied pathology of pregnancy and during treatment with Angiovit.
The results obtained indicate the diagnostic value of determining such markers of endothelial dysfunction as homocysteine and D-dimers in obstetric pathology and the beneficial effect of the drug Angiovit as a therapeutic agent that helps correct these indicators during pregnancy complications - recurrent miscarriage and preeclampsia.
In women of reproductive age, the normal level of homocysteine in the blood plasma is slightly lower than in men, amounting to 8–9 µmol/l [8]. During pregnancy, homocysteine levels decrease by more than 50%, especially low values are observed in the second and third trimesters (4–3 μmol/l). This is due to an increase in the rate of its metabolism, an increase in glomerular filtration and the metabolism of fetal homocysteine.
Our data indicate a significant increase in homocysteine content in the blood plasma of women with recurrent miscarriage, which is confirmed in a number of works by other authors [9–11]. Of particular importance in the increase in homocysteine levels that we discovered during miscarriage is a deficiency of vitamins, primarily folic acid and B vitamins (B6 and B12). It is unlikely that an increase in homocysteine levels can be caused by congenital defects in the enzymes of homocysteine metabolism (cystathionine beta-synthetes and methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase), which leads to persistent and more significant hypercysteinemia (homocysteine content in the blood can range from 15 to 100 µmol/l) and is accompanied by severe clinical symptoms. manifestations. It has been established that such significant hyperhomocysteinemia leads to the appearance of secondary autoimmune reactions and may be one of the important factors in the pathogenesis of severe fetal malformations, such as anencephaly, spinal canal cleft, etc. [3].
In our study, Angiovit turned out to be an effective means of preventing the development of moderate hyperhomocysteinemia, which was most likely due to the balanced ratio of these vitamins in its composition (0.005 g of folic acid, 0.004 g of vitamin B6 and 0.000006 g of vitamin B12). It should be noted that the use of Angiovit led to a decrease in the relatively low (compared to women with miscarriage) level of homocysteine in the blood of pregnant women with preeclampsia.
In addition, the therapeutic effect of Angiovit was accompanied by a decrease in the thrombogenic potential of the vascular wall and the risk of subsequent development of endothelial dysfunction, which can be judged by the decrease in the formation of D-dimers and the activity of von Willebrand factor in the blood of patients with recurrent miscarriage and preeclampsia. This was manifested in a noticeable improvement in the overall clinical picture: a decrease in the severity of clinical manifestations of the threat of miscarriage and preeclampsia in the majority of subjects. In almost all women in the study group who took Angiovit, pregnancy progressed, and in 75% of pregnant women with recurrent miscarriage, the clinical manifestations of threatened miscarriage completely disappeared.
The good tolerability and pronounced effectiveness of Angiovit allow us to recommend it as an effective treatment for recurrent miscarriage and preeclampsia. To assess the effectiveness of using Angiovit for the purpose of preventing pregnancy pathologies, further research on its effect at different stages of gestation (in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester) should be continued.
CONCLUSIONS
1. The effectiveness of Angiovit has been shown in the treatment of recurrent miscarriage and gestosis.
2. Taking Angiovit when there is a threat of miscarriage leads to an improvement in the clinical picture, progression of pregnancy and in most cases (75% of patients) to the complete disappearance of signs of a threat of premature birth.
3. Angiovit was noted to be well tolerated, lack of side effects and the possibility of its use in obstetric practice.
4. Angiovit is a promising drug that helps reduce the risk of hyperhomocysteinemia and the development of thrombolytic conditions in obstetric pathology.
Overdose symptoms
Medicine does not know of cases of overdose with Angiovit. But if the patient drinks this medicine uncontrollably and in large quantities, he will develop signs of hypervitaminosis. It manifests itself in the form of a number of symptoms:
- numbness of the limbs and other parts of the body;
- tremor of hands and feet;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- prolonged cramps, most often in the calf muscles;
- capillary thrombosis;
- anaphylactic shock.
Particularly severe consequences (thrombosis and shock) are caused by excessive consumption of vitamin B12, so you must take the tablets very carefully.
It is necessary to comply with the dosage and regimen of taking medications.
Interaction with other drugs
"Angiovit" should not be taken together with medications that increase blood clotting. The consequences of such a treatment can be unpredictable: the blood becomes viscous, which causes blood clots to form.
Allergies can occur when Angiovit is combined with thiamine; this effect is created by cyanocobalamin, which is part of the drug. The absorption of vitamin B12 in the stomach is reduced if Angiovit was taken together with antiepileptic drugs, colchicine, aminoglycoside antibiotics, salicylates and potassium-based drugs.
If “Angiovit” was prescribed along with glycosides for the heart, then the myocardium will be well protected from hypoxia. This effect is created by pyridoxine: thanks to its action, contractile proteins of the heart muscle are actively formed. It goes well with Asparkam and glutamic acid.
Pyridoxine weakens the effect of the drug Levodopa for Parkinson's disease, but enhances the effect of thiazide diuretics.
There are drugs that reduce the effect of vitamin B6. These include cycloserine, penicillamine, contraceptives containing estrogen and isonicotine hydrazide.
Vitamin B9 weakens the effects of Phenytoin and Carbamazepine (for epilepsy and arrhythmia), so the dosage has to be increased. Only the attending physician can correct it.
"Angiovit" should not be taken by those patients who are prescribed Methotrexate, Pyrimethamine, Trimethoprim or Triamterene. Also, "Angiovit" is incompatible with sulfonamines, "Kolestyramine" and anti-ulcer antacids based on magnesium and aluminum. Because of this combination, the therapeutic effects of both drugs disappear.
Contraindications and side effects
"Angiovit" should not be taken by patients who have been found to be hypersensitive to the substances that make up the medicine. Side effects manifest themselves in the form of allergic reactions:
- hives;
- headache;
- angioedema;
- dizziness;
- redness and itching of the skin;
- sleep disorders;
- nausea, vomiting;
- abdominal pain.
Most patients tolerate Angiovitis well, especially in spring and autumn, when the lack of vitamins is especially acute.