Action of Thiogamma
Thiogamma is not originally intended for facial skin. This is a pharmaceutical solution for intravenous administration. How did he get into the beauty industry and arouse such increased interest among women? One of the famous beauty bloggers shared the recipe for a miracle anti-aging serum, which was made with Tiogamma. The blogger discovered this solution due to the content of such an active substance as alpha-lipoic acid (ALA). Users were hooked by the visible positive results using a product with a low price.
Now more and more girls prefer a budget alternative to expensive ALA products. Let's remember how this acid is for the face:
- the protective function of the skin from UV rays is enhanced;
- cell and tissue restoration processes are improved;
- the functioning of the sebaceous glands is regulated;
- the skin is less exposed to pollution;
- premature aging is prevented;
- the skin becomes more elastic, wrinkles are smoothed out.
Lipoic acid is synthesized in our body independently, however, with age, its reserves are gradually depleted. Therefore, the substance is most often used as an anti-aging agent against wrinkles. In order to prolong youth and beauty, ALA is also consumed internally with the help of specially developed dietary supplements.
In cosmetology for the face, Thiogamma is taken with a concentration of 1.2%. This is a weak solution that is safe for the skin.
Thiogamma is not stable
When you buy a cosmetic product, you are dealing with stabilized alpha lipoic acid.
When you buy Thiogamma, you are dealing with an unstabilized formula that is sensitive to literally everything: to the chlorinated tap water you wash your face with, to metals present in the water, to temperature, sugar, light, air, etc.
This means that if you washed your face with water that contains metals, applied a cream with minerals to your face (no matter before or after Thiogamma), alpha-lipoic acid will bind with them and settle on the skin in the form of a complex, and the effectiveness will tend to zero.
Application in cosmetology
It is recommended to think about purchasing Thiogamma for skin in the following cases:
- Unhealthy complexion.
- The presence of facial and pronounced wrinkles.
- Pimples, acne.
- Dermis with increased fat content or dryness.
- Redness and other damage.
The substance is sold in almost any pharmacy at an affordable price. It has three release forms:
- Tableted. This is a drug for oral administration. To use it in cosmetology, the tablets must first be crushed.
- In ampoules.
- Injection. Available in 50 ml bottles.
In cosmetology, it is advisable to use solutions with a concentration of 1.2%. They have simple instructions and a convenient release form.
The packaging with Thiogamma usually comes with specialized bags in which the bottles are stored after opening. One bottle is completely enough for the course, so the substance is often purchased individually. The duration of sessions is from 10 to 30 days. If necessary, the course is repeated one more time during the year.
Apply the solution as a toner using a cotton pad in the morning and evening. The face is wiped with massage movements. You can also pour the liquid into a spray bottle and apply it to the skin by spraying. The face is first cleaned. Tap water contains metals, and therefore destroys the properties of the active substance of the solution. To avoid this, wash your face with micellar or rose water before the procedure. Some time after the session, moisturize your skin with your usual cream.
Thiogamma is also used to care for eyelids. To do this, make lotions from cotton pads soaked in a solution. The compresses are kept for 5 minutes.
Important information! After the first session, the skin may turn red. A tingling sensation may also occur. This is a normal reaction. In subsequent times, the skin will tolerate the substance more calmly.
Currently, the incidence of stroke in high-income countries is 94 per 100 thousand people, while in countries with middle and low income levels (this group includes the Russian Federation) this figure is 117 per 100 thousand people. For a large number of people over the age of 50, the processes of the so-called. normal aging are quickly replaced by pathological changes associated primarily with insufficiency of cerebral blood flow due to atherosclerotic damage to the vessels supplying blood to the brain, with changes in the rheological properties of the blood, leading to dysregulation and a decrease in neurotransmitter activity. Clinically, these neurotransmitter and morphological dysregulations are manifested by severe symptom complexes of acute and/or chronic cerebral ischemia, requiring constant and effective correction.
Pathomorphological disorders in patients with acute and chronic cerebral ischemia are based on a variety of pathogenetic factors, such as atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, as well as their combinations, cardiac pathology, changes in the condition of the spine with compression of the vertebral arteries, hormonal disorders leading to changes in the blood coagulation system, other types of disorders of the hemostatic system and physicochemical properties of blood, leading to the formation of functional and morphological ischemic disorders.
The mechanism of development of hypoxia, which is a discrepancy between tissue demand for oxygen and its delivery, is the same for any form of cerebrovascular pathology. It is associated primarily with impaired oxidation of substrates in body tissues as a result of difficulty or blockade of electron transport in the mitochondrial respiratory chain, which leads to damage to lysosome membranes with the release of utilitarian enzymes into the intercellular space.
Treatment of cerebral stroke consists of general and specific methods. The first include measures to ensure adequate oxygenation, correction of blood pressure, relief of complications, possible seizures, monitoring the condition of vital organs, patient care measures, as well as the use of specific therapy methods that stimulate the protective mechanisms of brain tissue in conditions of acute ischemia and hypoxia. The same applies to the processes of correction of chronic forms of cerebral circulatory disorders. The treatment strategy for ischemic stroke is based on clarifying the leading pathogenetic mechanism and its correction, aimed at compensating for the deficiency of cerebral hemodynamics, and improving metabolic processes in brain tissue [1–3]. The problem of improving care for this pathology is the most important in clinical medicine due to its widespread prevalence, high mortality rate, significant disability and social maladaptation of patients who have suffered a stroke. One of the most promising methods of nonspecific therapy for cerebral stroke and chronic forms of cerebral circulatory disorders currently includes the use of antioxidants, which are a specific corrector of brain energy metabolism, acting specifically under conditions of ischemia and hypoxia.
Modern scientific and technological advances have made it possible to reconsider the pessimistic opinion that existed until recently about the possibilities of treating acute cerebral ischemia. The introduction of modern technologies has significantly improved the diagnosis of ischemic stroke: it has made it possible to visualize not only the area of structural damage, but also the characteristics of the blood supply, as well as the functional state of brain tissue, to objectify vascular factors leading to impaired cerebral circulation, which has modified views on the strategy of pathogenetic treatment of various subtypes of ischemic stroke. stroke. Analysis of the dynamics of the deployment of molecular and biochemical mechanisms “triggered” by acute cerebral ischemia has established a clear temporal sequence of their “switching on.” During the first 3 hours from the moment of acute cerebrovascular accident, the energy deficit of ischemic tissue is maximal; after 3–6 hours, glutamate excitotoxicity, disturbances of calcium homeostasis and lactic acidosis are expressed, fading by the end of the first day. Long-term consequences of ischemia begin to appear at 2–3 hours, reach a maximum after 12–36 hours (oxidative stress and local inflammation) and on days 2–3 (apoptosis), but persist for a long time (for several months), promoting in the post-stroke period, the progression of atherogenesis and diffuse damage to brain tissue [3, 5, 7].
To systematize the complex reactions of the ischemic cascade, a conditional and simplified scheme for the development of its successive stages was proposed:
1. Decreased cerebral blood flow. 2. Glutamate excitotoxicity. 3. Intracellular accumulation of calcium. 4. Activation of intracellular enzymes. 5. Increased nitric oxide synthesis and development of oxidative stress. 6. Expression of early response genes. 7. Long-term consequences of ischemia (local inflammatory reaction, microcirculatory disorders, damage to the blood-brain barrier). 8. Apoptosis [8, 12].
Each stage of the ischemic cascade is a potential target for therapeutic intervention. The nature of reperfusion therapy (impact on the 1st stage of the cascade) is determined by the pathogenetic variant of the development of stroke and the possibility of its implementation only in a hospital after a neuroimaging study (computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain), which makes it possible to exclude the hemorrhagic component of the lesion and determine the pathogenetic variant of the stroke. The advantages of another line of therapy, neuroprotection (impact on stages 2–8 of the cascade), lie in the possibility of its use at the prehospital stage when the first symptoms of a stroke appear, even if it is possibly hemorrhagic. According to experimental and clinical studies [13–15], early use of neuroprotectors makes it possible to increase the proportion of transient ischemic attacks and “minor” strokes among acute ischemic cerebrovascular accidents; significantly reduce the size of cerebral infarction; lengthen the period of the therapeutic window, expanding the possibilities for thrombolytic therapy; protect against reperfusion injury.
Primary neuroprotection is distinguished, aimed at interrupting the rapid reactions of the glutamate-calcium cascade, free radical mechanisms, which should begin from the first minutes of ischemia and continue throughout the first 3 days of stroke (especially active in the first 12 hours). Secondary neuroprotection is aimed at reducing the severity of long-term consequences of ischemia: blocking pro-inflammatory cytokines, cell adhesion molecules, inhibition of pro-oxidant enzymes, enhancing trophic supply, interrupting apoptosis. It can be started 3–6 hours after the onset of stroke and should continue for at least 7 days. Starting from the first days of the disease after the formation of morphological infarct changes in the brain, reparative therapy aimed at improving the plasticity of healthy tissue surrounding the infarction, activating the formation of polysynaptic connections, and increasing the density of receptors is becoming increasingly important. Secondary neuroprotectors, which have trophic and modulatory properties, enhance regenerative and reparative processes, helping to restore impaired functions.
The use of antioxidant drugs that can protect brain tissue from ischemic damage is an important area of secondary neuroprotection. When choosing a drug for antioxidant therapy, it is necessary to take into account that there is no universal compound that blocks all pathways of generation of reactive oxygen species, since, based on its chemical structure and mechanism of action, each antioxidant more or less effectively affects individual parts of the pathological process, not being at the same time a universal remedy.
According to the mechanism of action, drugs with antioxidant properties are divided into primary (true), which prevent the formation of new free radicals (these are mainly enzymes that work at the cellular level), and secondary, capable of capturing already formed radicals. Medicines based on antioxidant enzymes (primary antioxidants) are represented mainly by substances of natural origin obtained from bacteria, plants, and animal organs. Some of them are at the stage of preclinical trials, for others the path to neurological practice remains closed. Among the objective reasons for the clinical unpopularity of enzyme preparations, one should note the high risk of side effects, rapid inactivation of enzymes, their high molecular weight and inability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier [18, 19].
There is no generally accepted classification of secondary antioxidants. A wide variety of synthetic drugs with claimed antioxidant properties can be divided into two classes based on the solubility of the molecules - hydrophobic, or fat-soluble, acting inside the cell membrane (for example, α-tocopherol, coenzyme Q10, β-carotene), and hydrophilic, or water-soluble, acting on the interface between aqueous and lipid environments (ascorbic acid, carnosine, acetylcysteine). Every year, the voluminous list of synthetic antioxidants is replenished with new drugs, each of which has its own pharmacodynamic characteristics.
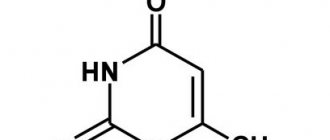
A wide therapeutic potential has been noted for α-lipoic acid (thioctic acid, Thiogamma), which affects energy metabolism and the reduction of oxidative stress, which is the pathogenetic rationale for the use of this drug by people with cerebral ischemia. The results of the experiment confirmed the ability of this antioxidant to reduce the volume of the infarct zone and improve neurological functioning in mice subjected to transient focal ischemia in the middle cerebral artery territory [20]. The effectiveness of the use of a combination of α-lipoic acid (Thiogamma) and vitamin E has been proven, which was used in two therapeutic regimens both for prophylactic administration and for intensive treatment in a model of thromboembolic cerebral infarction in rats. In addition, the effect of antioxidants on neurological deficits, glial reactivity and neuronal remodeling in the ischemic penumbra zone was studied. The results of the experiment demonstrated the undeniable advantage of the preventive administration of the studied antioxidants in terms of the degree of improvement of neurological functions, and the suppression of astrocytic and microglial reactivity was noted both with the prophylactic use of α-lipoic acid with vitamin E, and in the intensive therapy of already developed ischemic brain damage [19, 20] .
Combinations of thiamine and α-lipoic acid are gaining great importance today, which plays an important coenzyme role in the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic acid and α-keto acids [20, 21]. Alpha lipoic acid oxidizes the “active aldehyde” associated with thiamine; the acyl residue formed during the oxidative decarboxylation of the keto acid is added to it and then transferred to acetyl coenzyme A. The pronounced coenzyme value of thiamine is explained by the activity of thiamine diphosphate (cocarboxylase), which allows thiamine to take part in the functioning of several enzyme systems [22]. In addition, thiamine diphosphate is necessary for the functioning of pyruvate dehydrogenase and 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complexes, which provide oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic and α-ketoglutaric acids with the release of metabolic energy, important for the regulation of carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism. The functioning of the tricarboxylic acid cycle also depends on thiamine diphosphate, and thanks to the activity of transketolase, the functioning of the pentose phosphate cycle, which is a supplier of ribose-5-phosphate, necessary for the synthesis of nucleic acids and a number of amino acids, is ensured [23]. The reactions mediated by thiamine diphosphate are α-cleavage resulting in the formation of a thiamine-bound “active aldehyde.” Non-coenzyme functions of thiamine (especially in the form of thiamine triphosphate) are involved in the synaptic transmission of nerve impulses, affecting the release of acetylcholine from nerve cells and exhibiting anticholinesterase activity, which causes an increase in neuromuscular conduction [20–23].
Early therapy with antioxidants is currently considered as a real, pathogenetically determined method for correcting cerebral metabolism in cerebral ischemia.
Thiogamma is an antioxidant with three therapeutic pathways, as it is available in the form of ampoules, amber glass bottles that do not need to be diluted, and tablets. This ensures continuity of therapy both at the stage of inpatient treatment and subsequent follow-up treatment in an outpatient setting. Thiogamma is able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier, work as part of the cell membrane and in the cytoplasm of the cell. The antioxidant effect of the drug is due to the presence of two thiol groups in the molecule, resulting in the binding of free radical molecules and free tissue iron, preventing its participation in the formation of reactive oxygen species (Fenton reaction), and providing support for the work of other antioxidant systems (glutathione, ubiquinone). Thiogamma participates in the metabolic cycles of vitamins C and E, is a cofactor for the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvic and ketoglutaric acids in the mitochondrial matrix, playing an important role in the energy supply of the cell, and helps eliminate metabolic acidosis, facilitating the conversion of lactic acid into pyruvic acid [26, 27].
Thus, the therapeutic potential of Thiogamma is realized through its influence on the energy metabolism of neurons and the reduction of oxidative stress in nervous tissue.
Reviews from experts
Reviews from cosmetologists about Tiogamma for the face are different. And yet, most specialists are inclined to abstain from the pharmaceutical drug. No, not because of harm. It's all about ineffectiveness. The most common opinion of cosmetologists is not to save money and purchase high-quality cosmetics containing ALA.
The fact is that you need to know how to properly use Thiogamma for the face, observing all the nuances of the capricious alpha-lipoic (thioctic) acid. Otherwise, the result will be zero. In professional products from the world of cosmetology, the acid is stabilized, so its properties are not destroyed during use.
Reviews from many cosmetologists are collected into a single opinion, which is expressed by Olga Fem in the following video:
Thiogamma for the Face - another Beauty Myth?
Cosmetics are still more effective
Even if we assume that you can meet all the conditions and alpha-lipoic acid retains its properties, the effectiveness of the pharmaceutical drug will still be several times lower than that of a cosmetic product.
The point is not only that in cosmetics alpha-lipoic acid is hidden in some kind of delivery system, for example, in a liposome.
There is another important nuance - alpha-lipoic acid works better in combination, so in cosmetics it is often used together with vitamins C and E, coenzyme Q10 and squalene.
In other words, it takes a whole team to achieve a good result! And the effectiveness of the cosmetic product is achieved not only due to the presence of alpha-lipoic acid, but thanks to a complex of components that work together much better.
For example, alpha lipoic acid extends the antioxidant life of vitamins C and E, making the cream or serum more effective.
Therefore, to say that a pharmaceutical drug will not only be cheaper, but also no worse than a cosmetic product, is, to put it mildly, naive.
Alpha lipoic acid works better when combined!
Storage of the solution
The substance is stored in the refrigerator. Once opened, the solution should not be used for longer than 30 days. According to the instructions, the product has a longer shelf life. However, for cosmetic purposes, it is not advisable to store Thiogamma for a long time, since its beneficial properties disappear over time.
Some people do not open the bottle completely, but make a kit using a syringe. Also, after opening, the bottles are packed into bags.
Interesting to know! Did the solution thicken during storage? Dilute with saline solution.
What harm can a pharmaceutical product cause?
The substance may cause harm in rare cases. It is enough not to resort to frequent use of the solution (2 times a day, 2 courses per year - maximum). It is also worth studying the contraindications:
- children under 18 years of age;
- dehydration;
- allergy;
- individual intolerance;
- liver and kidney diseases;
- pregnancy and lactation period.
Before use, do an allergy test. Apply a little product to the inner elbow area. Observe your skin's reaction throughout the day.
Tiogamma solution for inf. 1.2% 50ml n10
from 1550 ₽
More details
Thiogamma 600 tablets p/o 600 mg No. 10x3
Name
Thiogamma 600 tablets, coated, 600 mg, blister pack No. 10x3
Description
Capsule-shaped, film-coated tablets, light yellow in color, with possible white inclusions, scored on both sides.
Main active ingredient
Thioctic acid
Release form
Pills
Dosage
600mg
pharmachologic effect
Thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid is an endogenous antioxidant that functions as a coenzyme in the oxidative decarboxylation of alpha-keto acids. In diabetes mellitus, as a result of hyperglycemia, the content of advanced glycation end products increases. This process contributes to a decrease in endoneural blood flow and the development of endoneurial hypoxia. At the same time, along with an increase in the production of free radicals, the content of antioxidants, in particular glutathione, decreases. In clinical studies in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy, the administration of thioctic acid led to a decrease in sensory disturbances accompanying diabetic polyneuropathy, such as dysesthesia, paresthesia, pain, and numbness.
Indications for use
Paresthesia in diabetic polyneuropathy.
Directions for use and doses
The basis of treatment for diabetic polyneuropathy is optimal treatment of diabetes mellitus. For diabetic polyneuropathy in adults, the daily dose is 1 tablet per day (600 mg of thioctic acid), taken as a single dose on an empty stomach approximately 30 minutes before meals. The tablets are taken without chewing, with a small amount of liquid. The score on both sides of the tablet is intended only to facilitate patient administration and not to divide into doses. For severe polyneuropathy, treatment can be started with intravenous administration of thioctic acid. Concomitant food intake may interfere with the absorption of thioctic acid, so patients with a long gastric emptying time should take the tablets half an hour before breakfast. Because diabetic neuropathy is a chronic disease, long-term treatment may be required.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Due to the lack of sufficient clinical data, the use of the drug during pregnancy is not recommended. There is no information on the penetration of thioctic acid into breast milk. A decision must be made to either stop breastfeeding or discontinue therapy, taking into account the benefits of breastfeeding for the child and the benefits of therapy for the mother.
Precautionary measures
Regular alcohol consumption is an important risk factor for the onset and progression of polyneuropathy and may affect the results of treatment with thioctic acid. Patients taking Thiogamma® 600 should avoid drinking alcohol. In patients with diabetes mellitus, constant monitoring of blood glucose concentrations is necessary, especially at the initial stage of therapy. In some cases, it is necessary to reduce the dose of insulin or oral hypoglycemic drug to avoid the development of hypoglycemia. The medicine contains lactose; patients with hereditary galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption should not take this medicine. Information for patients with diabetes: 1 tablet contains less than 0.0041 XE (bread units). Cases of autoimmune insulin syndrome (AIS) have been reported during treatment with thioctic (alpha-lipoic) acid. Patients with certain alleles, such as HLA-DRB1*04:06 and HLA-DRB1*04:03, are more susceptible to developing AIS when treated with thioctic acid. The HLA-DRB1*04:03 allele (predisposition to AIS, odds ratio: 1.6) is more common in Caucasians (more common in Southern Europe than in Northern Europe). The HLA-DRB1*04:06 allele (susceptibility to AIS, odds ratio: 56.6) is mainly found in individuals from Japan and Korea. Autoimmune insulin syndrome should be considered in the differential diagnosis of spontaneous hypoglycemia in patients receiving thioctic acid (see section "Side effects")
Interaction with other drugs
When Thiogamma® 600 is used simultaneously with cisplatin, the effect of the latter is reduced, because thioctic acid (alpha-lipoic acid) forms ionic complexes with metals. For these reasons, simultaneous use with iron and magnesium supplements, and with dairy products containing calcium is not recommended. When taking the daily dose 30 minutes before breakfast, iron and magnesium supplements can be taken at lunchtime or in the evening. When used simultaneously, thioctic acid enhances the effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents. In some cases, it is necessary to reduce the dose of insulin or oral hypoglycemic drug to avoid the development of hypoglycemia. Alcohol (ethanol) reduces the therapeutic activity of thioctic acid. Patients taking the drug Thiogamma®600 should refrain from drinking alcohol, including during intervals free from taking the drug.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to thioctic acid or other components of the drug. Children and youth under 18 years of age (efficacy and safety of use have not been established).
Compound
1 film-coated tablet contains the active ingredient: thioctic acid - 600 mg; excipients: hypromellose, anhydrous colloidal silicon dioxide, microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, carmellose sodium, talc, simethicone (consisting of dimethicone and colloidal silicon dioxide 94:6), magnesium stearate. Film shell composition: hypromellose, macrogol 6000, talc, sodium lauryl sulfate.
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, headache. In case of accidental or suicidal use of oral doses of 10 to 40 g of thioctic acid together with alcohol, severe intoxication may develop with a fatal outcome. The picture of a severe overdose is manifested by psychomotor agitation, impaired consciousness, generalized convulsions, and lactic acidosis. Hypoglycemia, shock, rhabdomyolysis, hemolysis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, bone marrow suppression, and multiple organ failure may result from this intoxication. Treatment is symptomatic. There is no specific antidote. Treatment of severe intoxication is carried out in the intensive care unit. Therapeutic measures If thioctic acid intoxication is strongly suspected (e.g., more than 10 tablets containing 600 mg thioctic acid in adults and more than 50 mg/kg in children), immediate hospitalization is necessary and measures taken in accordance with general methods of treating intoxications (e.g., induced vomiting, gastric lavage, taking activated charcoal, etc.). When treating attacks of generalized seizures, lactic acidosis and other life-threatening consequences of overdose, one should be guided by the principles of modern intensive care. The benefits of hemodialysis, hemoperfusion or hemofiltration methods for the forced elimination of thioctic acid have not yet been confirmed.
Side effect
When assessing side effects, the following gradation of the frequency of their occurrence is taken as a basis: - very often (> 1/10); - often (> 1/100 - 1/1000 - 1/10,000 -
Storage conditions
Store in a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Buy Thiogamma 600 tablets p/o 600 mg No. 10x3 in the pharmacy
Price for Thiogamma 600 tablets p/o 600 mg No. 10x3
Instructions for use for Thiogamma 600 tablets p/o 600 mg No. 10x3
Cosmetics or pharmaceutical product
Why do some people prefer to purchase products with thioctic acid, if they can buy the same substance much cheaper? The pharmaceutical product Tiogamma, which is taken for the face, has a price much lower than any cosmetic product.
Yes, the active ingredient is the same - ALA. However, how effective is it in the Thiogamma solution from the pharmacy? ALK is a very capricious molecule that is poorly adapted to many external factors:
- metals (often found in tap water);
- ambient temperature;
- sugar;
- light;
- air.
It is enough to wash your face before applying Thiogamma for the skin or after - and there will be no effect. You are wasting the substance. The thing is that ALA in a pharmaceutical solution is not stabilized.
In cosmetics, the acid is hidden in liposomes (most often), so the capricious molecule is adapted and ready to enrich the dermis with all its beneficial properties. And this confirms that cosmetic preparations are more effective than drugs from the pharmacy.
Interesting to know! The maximum concentration of ALA in cosmetics is 1%.
If you know the rules for using Thiogamma for the face, follow all the conditions, taking into account the vagaries of the active substance, then the result is possible. Only a-lipoic acid behaves much better together with other components. Therefore, it is advisable to make facial masks using Tiogamma.
Thiogamma for face
Since there are cosmetics with alpha-lipoic acid, why do women use Thiogamma?
The answer in such cases is usually one - to save money.
A cream or serum from a well-known cosmetic brand can cost 30, 50, 100 euros or more. And one bottle of Thiogamma in Ukraine can be bought individually and will cost about 3 euros.
But some members of the “Pharmacy for the Service of Beauty” club believe that a product from a pharmacy will be even more effective than cosmetic products. They believe that the cosmetics industry, along with developers, manufacturers and cosmetologists, are simply making money out of the blue.
After all, the active ingredient is the same - so why pay more?
Although, in my opinion, before applying a drug intended for intravenous administration to treat patients with diabetes, women should have asked other questions:
- Is the alpha lipoic acid form of Thiogamma suitable for topical use?
- How safe is it?
- Will it be effective?
For clarification, I turned to a well-known expert in the field of cosmetic chemistry, chemist-technologist Yulia Gagarina, whom many of you know very well from a series of interesting interviews on my channel.
I asked Yulia what pitfalls those who use pharmaceutical preparations with alpha-lipoic acid may encounter. After all, they are not intended for application to the skin.
Yulia Gagarina: Alpha-lipoic acid is used in cosmetics both in pure form (yellow powder) and in the form of salts or compounds with peptides.
In any case, these are good active molecules, an excellent antioxidant. But since this is an active substance and it is capricious, it does not like literally everything: high temperature, light, metals, sugar.
That is, if the formula or preparation that is applied contains residual metal compounds, or if before or after using alpha lipoic acid you use water that contains metals: iron, copper, etc., or bleach, alpha lipoic acid will bind to them and the form of the complex will settle on the skin.
They always try to stabilize alpha-lipoic acid. It must be packaged in delivery systems, such as liposomes. And we must take into account that this molecule is very active, it is used in limited quantities - a maximum of 1% of the input.
If you buy a drug at a pharmacy, then you need to pay attention to the fact that it is not stabilized, it is capricious, it can quickly decompose under the influence of the same salts, heat, air and everything else.
Therefore, there is a high probability that, as a result, pharmaceutical alpha-lipoic acid, or rather its salt, will be used in vain. This will be a placebo effect, and not a real active compound.
Thus, we found out that alpha lipoic acid is an effective component that is successfully used in cosmetics. Recommended concentration is 1% maximum.
Anti-aging masks at home
Drugs with ALA are in particular demand among older women. However, it is permissible to use the product from an adult age for prevention purposes.
Check out super recipes for anti-aging masks at home. Prepare all the ingredients for future use; do not store leftovers.
With oils
This mask not only helps you rejuvenate, but also gets rid of acne and blackheads. Suitable for oily skin.
Compound:
- almond oil - 1.5 tsp;
- avocado oil - 1.5 tsp;
- tea tree oil - 1 ml;
- Thiogamma - 1-2 ml;
- cranberry juice - 3 ml;
- silk protein - 2 ml.
The mixture of oils must be slightly heated by steam, then combined with the rest of the components. The mixture is kept for min. 15. Frequency - 2-3 times a week.
With cognac and caffeine
Thiogamma is great for wrinkles. And in combination with other components it can eliminate other shortcomings. This mask not only rejuvenates, but also tightens pores and improves skin color.
Compound:
- drug in tablets - 4-5 pcs.;
- caffeine ampoule;
- 15 ml of weight loss product from Grandma Agafya’s Recipes;
- 20 ml cognac.
The tablets are crushed and combined with the other components. The mass is kept for up to 20 minutes.
With sea salt
An excellent remedy against facial wrinkles. Suitable for all derma types.
Compound:
- pair of tables aspirin;
- wheat germ oil;
- sea salt + some water;
- 2-3 ml of solution.
Salt is mixed with water until it becomes mushy. Then it is applied to the face for about 10 minutes. After that, it is washed off and a mass of crushed aspirin, oil and the drug is prepared. The mixture is kept for the same amount of time. Finally, the skin is wiped with chamomile infusion.
The most effective facelift procedures
There are many techniques used to perform a facelift:
- Radiesse
- RF needle lifting
- Laser resurfacing
- Thermolifting
- Temporal thread lifting
- Correction with liquid threads
- Massage
- SMAS lifting
The Idealist Clinic uses only proven technologies with proven effectiveness and safety. It is better to choose the method by which a non-surgical facelift will be performed with an experienced cosmetologist who will first assess the condition of your skin. Sign up for a consultation on anti-age therapy and aging prevention by calling the number, the consultation will be free for you.
Radiesse
Radiesse is a specific dermal filler that is used for non-surgical face lifting and provides long-term results. The drug replenishes lost volume on the face and stimulates the production of its own collagen. The procedure lasts from 30 to 60 minutes and does not cause discomfort to the client. A distinctive feature of this technique is that the drug does not cause swelling, since it does not contain hyaluronic acid.
Principles of the drug:
- instant smoothing of wrinkles due to volume replenishment
- stimulating the production of your own collagen, leaving the skin smooth
- the formation of a new dermal matrix, which is supported by the drug, due to which the effect lasts for 1-2 years
The Idealista clinic will help determine whether this procedure is suitable for the client. Cosmetologists will select the optimal method only after carefully studying the structure of the skin.
RF needle lifting
Needle radiofrequency fractional lifting is a technique using radio frequencies that penetrate the skin and have a stimulating effect on collagen. By heating the deep layers of the skin, metabolism improves and fibroblasts are activated to produce collagen. The technique does not give an immediate visible effect, but helps to obtain a lasting result using the body’s own strength.
Positive changes:
- improvement of skin tone
- restoration of elasticity
- smoothing skin texture
- wrinkle smoothing
In Idealist cosmetology, the micro-needle RF lifting procedure is carried out using the Scarlet S device. This is one of the three top devices in the micro-needle RF lifting technique, which allows you to accurately predict the depth of penetration and achieve an ideal result.
Laser resurfacing
Laser resurfacing is a procedure using a fractional erbium laser that allows you to renew the upper layers of the skin and stimulate the production of your own collagen.
Effects of the technique:
- facial contour restoration
- improving skin elasticity and tone
- wrinkle correction
- elimination of sagging in the area of the upper and lower eyelids
- restoration of skin relief
- smoothness improvement
Thanks to the use of a premium Palomar erbium laser made in the USA and highly qualified cosmetologists, the procedure is painless and safe and does not have a long rehabilitation period.
Temporal thread lifting
A facelift with special threads is an effective procedure for improving facial contours. For this, safe, hypoallergenic materials are used, which not only support the facial frame, but also trigger the processes of producing your own collagen.
Only a doctor can determine the need for such a procedure. Therefore, sign up for a consultation at Idealista so that experienced cosmetologists can choose the optimal facelift method for you.
Infrared thermolifting
The essence of infrared thermolifting (IR lifting) is similar to radio frequency. The effect is achieved by heating the deep layers of the skin. Only for this purpose infrared rays are used. To avoid overheating of the skin, the cosmetologist uses a special cooling gel. The effect of thermolifting becomes noticeable gradually, since the processes of collagen and elastin production take time.
Face massage
Facial massage is an affordable method of rejuvenation that does not require large financial costs, and also has a general healing effect. A course of professional facial massage helps improve skin tone, reduce the severity of wrinkles and creases, and improve complexion.
There are several techniques for rejuvenating facial massage, which include:
- modeling lymphatic drainage
- deep plasticizing
- modeling author's
- classical
- Chinese jar and others
Facial massage to tighten facial skin is carried out strictly along massage lines. To improve the effect, anti-aging oils or serums are applied to previously cleansed skin. The advantage of the procedure is painlessness, lack of trauma to the skin, versatility, and the ability to combine massage with other injection or hardware techniques. After the session, redness of the skin is noted, but after 30 minutes the shade returns to normal and you can return to everyday activities.
Liquid threads
Liquid face lift threads are a mixture of hyaluronic acid and zinc, which makes it more durable and dense. They are injected into the subcutaneous fat using thin needles at predetermined locations.
SMAS lifting
SMAS lifting is an ultrasound method aimed at tightening the superficial muscular aponeurotic system of the face (Superficial muscular aponeurotic system). The essence of the procedure is to warm up the connective tissue to 60-70 degrees, which, under the influence of heat, begins to produce its own collagen.
Consumer Opinions
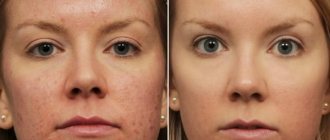
There are quite a lot of responses on review sites about using the substance on the face. There are more pros than cons. The skin is moisturized, smoothed and rejuvenated. Another significant advantage of the product is its cost.
Disadvantages include inconvenient use. Some write that they expected more, however, they are happy with this result.
Would you like to leave your opinion? Fill out the special form:
| Leave your review | |
| 1 2 3 4 5 | |
| Send Cancel | |
Send your review
Thiogamma for face
Average rating: Number of reviews: 0
Cosmetologists care about results
Of course, as is usually the case with such videos, I foresee reviews like:
You are deceiving us! It is simply not profitable for you cosmetologists when women use cheap products from the pharmacy. I use Tiogamma and even with the mistakes you are talking about here, I see excellent results!
I will immediately respond to such comments.
You can use whatever you want as long as you believe it helps you. My goal is not to dissuade anyone. I shoot videos, write articles and books for my subscribers who doubt the effectiveness of such drugs and who are interested in my opinion and the opinion of experts in the field of cosmetic chemistry.
You shouldn’t think that cosmetologists are not interested in inexpensive but effective products. Very interesting. And I am sure that many cosmetologists read this article with curiosity.
However, cosmetologists are primarily interested in the result - otherwise clients will no longer come to them. And if the effectiveness of the product is in great doubt, cosmetologists are not interested in such a drug.
Analogs
Tiagamma solution has analogues. Check out the TOP 3 drugs with identical active ingredients.
Octolipen
Octolipene conc.d/inf. 30mg/ml 10ml n10
from 385 ₽
More details
Smoothes out fine wrinkles, ideal at the initial stage of skin aging. Before use, the drug is diluted in other liquids. It is prohibited to use octopylene on the face in its pure form.
Berlition 300
Berlition 300 concentration d/inf. 25mg/ml 12ml n5
from 576 ₽
More details
A popular and effective anti-wrinkle product. It has a minimum of contraindications and side effects.