In the modern world, there is a great choice of everything and everyone, including contraceptives. Moreover, each manufacturer praises its means of protection, usually emphasizing only the advantages and keeping silent about the disadvantages.
It is quite difficult to independently understand such a flow of diverse and sometimes contradictory information, but in this article we will try to objectively highlight all the pros and cons of the main means of contraception.
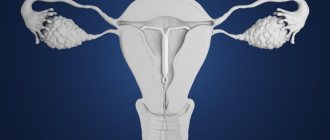
To begin with, it is worth noting that there are quite a few methods of contraception, but only 2 of them are used for long-term protection against pregnancy: intrauterine devices and hormonal contraceptives .
The principle of operation of intrauterine devices.
Basically, the effect of the IUD is due to a mechanical obstacle to the passage of sperm.
In addition, under the influence of the hormonal IUD (Mirena), cervical mucus thickens and ovulation is suppressed. In some cases, fertilization still occurs, BUT in this case, the IUD prevents implantation.
The hormonal IUD can be used not only for contraception, but also for therapeutic purposes, for example, for endometriosis.
With the use of a hormonal IUD, menstruation becomes less abundant and may subsequently disappear completely. This is an expected reaction of the endometrium, and not a side effect. After the IUD is removed, the cycle is restored.
Benefits of using Mirena
During the conservative treatment of adenomyosis, various hormonal drugs are used, but Mirena has its own advantages:
- Installation is carried out once every 5 years. Unlike hormonal pills, which must be taken strictly according to schedule, after inserting an intrauterine device, a woman does not need to follow any rules or treatment regimens. The IUD remains effective throughout its stay in the body.
- Allows you to achieve a therapeutic effect with a minimal dosage of the hormone. The hormone levonorgestrel, which is part of the drug, enters directly into the uterine cavity, exerting a localized effect.
- Minimal risk of side effects. The drug does not pass through the digestive system, so it does not affect other internal organs.
- No risk of overdose. During the day, a strictly fixed dose of levonorgestrel is released - 20 mcg.
- Reliable contraception. After implantation of an intrauterine device, a woman is reliably protected from unwanted pregnancy.
- Normalization of hormonal levels.
Patients are often prescribed the drug Visanne for uterine adenomyosis. The active ingredient of the product is micronized dienogest - a synthetic hybrid gestagen of the third generation. The drug is available in tablet form and is used for internal and external endometriosis. The doctor must decide which is better - Visanne or Mirena for adenomyosis, taking into account the nature of the disease, the degree of neglect, the presence of indications and contraindications.
When is an IUD installed?
With a regular menstrual cycle, a copper-containing IUD is installed in the first 12 days after the start of menstrual bleeding, and a hormonal IUD in the first 7 days. In the case of a hormonal IUD, the contraceptive effect occurs 7 days after installation, so during these days it is necessary to use an additional method of contraception. After installing a copper-containing IUD, you can have open sex life from the moment of installation.
If the menstrual cycle is irregular, an IUD can be installed on any day, provided that the woman is definitely not pregnant! The IUD can be used during breastfeeding (4 or more weeks after birth).
Features of use during pregnancy and lactation
Any means of contraception cannot be used while carrying a child. If pregnancy occurs while using the Mirena system (this can happen if the IUD is installed incorrectly or falls out), then it must be taken out, as the likelihood of an unplanned abortion or premature birth increases. If the system is removed incorrectly, spontaneous abortion can also occur.
You can use this method of contraception only 1.5 months after the birth of the child. The IUD will not affect the quantity and quality of breast milk in any way.
How is an IUD installed?
Before installing an IUD, you must undergo the following examinations:
1. Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and ultrasound of the breast
2. Tests for STIs
3. PAP TEST
The installation process itself takes about 20 minutes and takes place on the gynecological chair during the examination. The IUD is inserted into the uterine cavity, leaving control antennae in the vagina (for which the IUD is later removed). They will not cause you discomfort, BUT you need to be more careful when using tampons and removing them, since as a result of lightly tugging on the mustache, the spiral may shift and there will be no contraceptive effect.
The IUD can also be used by nulliparous girls, but there is a risk of the IUD falling out, since the uterus of nulliparous women is smaller.
Complications, side effects
The IUD does not cause the typical unpleasant symptoms caused by contraceptives. Women should not suffer from irritability, mood swings, water retention, weight gain or severe PMS symptoms. This is due to the fact that the IUD does not contain estrogen and does not cause hormonal disorders.
But, like any method of contraception, it has its drawbacks. These include:
- lack of protection against sexually transmitted diseases;
- cramps in the lower abdomen during menstruation;
- irregular menstruation (may even be absent);
- migraine.
Advantages of contraception using the IUD.
- Long-term contraception: IUD is effective for 5 years
- Reliable method of contraception
- There is no need to monitor the regularity of taking pills, or the position of the patch or vaginal ring
- There are not as many side effects as when taking CHCs, including the IUD does not affect libido and does not increase the risk of thrombosis
- The hormonal IUD has a therapeutic effect in some gynecological pathologies (endometriosis, heavy menstruation, recurrent endometrial polyps)
- The IUD can be used during breastfeeding
- Quite an economical method of contraception
How it works?
The contraceptive device causes inflammation in the uterus, which makes fertilization impossible. The body begins to produce white blood cells that destroy sperm. Therefore, conception is impossible, pregnancy is impossible.
There are also hormone-releasing IUDs on the market that change the texture of cervical mucus, making it thicker, which is important for protection against pregnancy and infections. Therefore, the sperm loses its viability and moves more slowly.
The spirals are effective from the moment of “insertion” and remain fully effective for a long time, up to 5 years. Their advantage is that you can refuse them at any time and quickly return the body to its original state.
Disadvantages of using an intrauterine device.
- After installing the IUD, pain in the lower abdomen may persist for some time, 1-3 months. During this period, NSAIDs can be used.
- With a copper-containing IUD, menstruation may become more profuse, so much so that the IUD has to be removed.
- There is a risk of the spiral falling out or dislodging; this usually occurs within the first 3 months after installation. Therefore, if you feel that the IUD has fallen out or has shifted, consult a doctor immediately!
- Intermenstrual bleeding often appears, which causes inconvenience, but usually disappears in the first 2-3 months after installation.
- A common side effect during the first time after installation of a hormonal IUD is breast tenderness, headaches and slight weight gain.
- There are risks of pelvic inflammatory disease, so it is important to be screened for STIs before inserting an IUD. If you are concerned about persistent pain in the lower abdomen or pain during sexual intercourse, fever or abnormal discharge from the genital tract, then immediately contact your gynecologist.
- Although the IUD is a reliable method of contraception, BUT a low percentage of the probability of pregnancy still exists!
- It is extremely rare, but when installing an IUD, perforation of the uterus occurs - this is damage to the muscular layer of the uterus by the spiral! To avoid this situation, an OMT ultrasound and measurement of the length of the uterine cavity are performed before installation, and also after installation of the IUD, ultrasound control is necessary!
Birth control pills: advantages and disadvantages
Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) are the most common method of hormonal contraception.
Oral contraceptives use synthetic hormones that are similar in action to those produced by the body itself.
The composition of birth control pills must include the hormone gestagen , which provides protection against pregnancy.
Based on their composition, oral contraceptives are divided into:
- gestagenic (contain only the hormone gestagen)
- combined (contain two hormones: gestagen and estrogen (needed to control the menstrual cycle))
Principles of action of oral contraceptives
Birth control pills:
- suppress or inhibit ovulation
- affect the composition of the cervical mucus of the cervix, making it more viscous and thick, which prevents the passage of sperm into the uterus
- affects the endometrium (mucous lining) of the uterus so that a fertilized egg cannot implant in it
- progestin tablets additionally reduce the mobility of the fallopian tubes , which slows down the movement of the egg through them and, as a result, the likelihood that the sperm will have time to fertilize decreases
Benefits of birth control pills
- High degree of protection – up to 99% when used correctly
- It is possible to become pregnant in the next cycle after stopping oral contraceptives, but it is recommended to wait 3 months
- Can be used by nulliparous women
- Can be used to treat hormonal imbalances and some gynecological diseases
Disadvantages of birth control pills
Many disadvantages of oral contraceptives arise from their principle of action:
- mood swings
- nausea , sometimes vomiting
- breast tenderness
- weight gain (may be caused by fluid retention or changes in carbohydrate-fat metabolism)
- decreased libido
- worsening acne (quite rare)
- increased removal of microelements from the body . If there is a lack of microelements in the body, serious diseases can occur. When taking oral contraceptives, it is important to take vitamin complexes .
- deterioration in glucose absorption (rare)
- headache
- spotting (especially typical for oral contraceptives with one progestogen hormone)
- the hormone estrogen in combined birth control pills increases blood clotting (hypercoagulation), which leads to unpleasant consequences: the risk of thrombophlebitis, heart attack, stroke , and existing cardiovascular problems are aggravated.
- the need to take pills at the same time according to a strictly established schedule , otherwise the risk of becoming pregnant increases sharply
- To avoid negative consequences,
a gynecologist should
prescribe
birth control pills after conducting all the necessary studies
Depending on the type of gestagen (about a dozen different gestagens are used in pharmaceuticals) and on the presence or absence of estrogens (ethinyl estradiol is usually used) various side effects may be observed in oral contraceptives. The list of all side effects is indicated in the instructions for the tablets.
Contraindications to the use of birth control pills
- pregnancy
- presence of malignant tumors
- thrombosis or thromboembolism - the occurrence of blood clots in blood vessels
- previous heart attacks, strokes
- bleeding disorders
- cardiovascular diseases
- diabetes
- liver diseases
- smoking
- postpartum period less than 6 months
Conclusion
The use of birth control pills requires increased responsibility and self-organization, because the effectiveness of this method depends on the regularity of use.
The contraceptive effect does not occur immediately, but within a week after starting treatment.
Oral contraceptives affect hormonal levels, which leads to both simply unpleasant and dangerous side effects. However, they can be used in the treatment of certain gynecological diseases.
Intrauterine devices do not affect a woman’s hormonal background; their contraceptive effect is based on the physical properties of the components and appears immediately after installation.
Spontaneous loss of the IUD is possible, so it is necessary to check the presence of IUD threads in the vagina. It is also quite common to experience increased menstrual flow in the first months after installation. In addition, intrauterine devices increase the risk of developing inflammatory processes.
Both methods of contraception are highly effective.
The installation and removal of the IUD is carried out by a gynecologist. After some time, a re-examination is required, and if nothing worries you, further observation by a gynecologist is not necessary.
The selection and prescription of contraceptive pills should be carried out only by a gynecologist. Taking the wrong pills can lead to serious side effects. It is advisable to constantly monitor the condition of the body in order to promptly identify a lack of microelements or the development of concomitant diseases and correct their negative manifestations.
Contraindications to the installation of an IUD.
- Presence of a sexually transmitted infection
- Inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs (including in the postpartum period and the period after termination of pregnancy)
- Cervical cancer, uterine cancer, breast cancer
- Anomalies of the uterus - bicornuate uterus, septum in the uterine cavity
- Submucous uterine fibroids
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology
- Pregnancy
- Allergy to copper, Wilson-Konovalov disease - in the case of copper-containing IUDs
- Liver diseases and tumors, hypersensitivity to levonorgestrel - in the case of a hormonal IUD
Author: obstetrician-gynecologist Tarakanova M.Yu.
Complications associated with IUD insertion
During installation of an intrauterine device, there is a risk of developing the following complications:
- Perforation of the uterus. Injury leads to heavy bleeding and a sharp deterioration of the condition. Perforation mainly occurs due to deformation of the reproductive organ or congenital developmental anomalies.
- Expulsion of the system. If the coil falls out, you need to consult a doctor who will replace the drug.
- Endometritis. The main cause is an untreated genital tract infection.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Follicular atresia. After implantation of the IUD, the hormonal background changes, so the maturation of the egg is possible, but the follicle does not always mature completely. It increases in size and becomes similar to an ovarian cyst. Often, such a follicle resolves on its own within 2.5 – 3 months. If this does not happen, the patient's treatment plan changes.