The female hormone estrogen is a substance that determines a woman’s health. There are more than 30 estrogen-like substances, but the most significant are estradiol, estrone and estriol. The mechanism of action of these fractions is to support the reproductive, cardiovascular, nervous systems and musculoskeletal system.
What is the hormone estrogen responsible for?
Estrogen in women is produced from androgen as a result of enzymatic reactions.
The role of estrogens in the functioning of the female body is as follows:
- building a silhouette according to the female type, a special accumulation of fat in the lower part of the body;
- growth of the uterus, tubes, ovaries;
- breast growth in teenagers;
- female-pattern hair growth, pigmentation of nipples and external genitalia;
- uterine tone during ovulation, contractile movements of the tubes to promote sperm;
- regular menstrual cycle, possibility of conception;
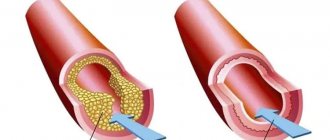
- inhibition of the growth of cholesterol plaques, timely removal of “bad” cholesterol (maintaining normal lipid metabolism);
- reducing the risk of osteoporosis;
- maintaining the balance of ferrates and copper in the blood;
- normalization of cognitive abilities - memorization, concentration;
- ensuring an adequate course of pregnancy;
- maintaining healthy nails, hair and skin.
Estrogens, derivatives of progesterone, have a complex effect on a woman’s body. They take part in the work of the heart muscle, support the body’s thermoregulation and the process of calcium absorption. It is under their influence that secondary sexual characteristics are formed in teenage girls - a feminine voice, figure.
Just as estrogen is responsible for femininity, testosterone (a steroid hormone) is responsible for masculinity. If a man has more estrogen than testosterone, he will exhibit feminine characteristics.
Menstrual cycle and hormones
The level of female sex hormones, including estrogen, depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. There are 4 of them in total.
Menstrual phase
It begins the female cycle in the absence of pregnancy. At the end of the cycle, a thickened mucous layer of the endometrium, necessary for the fetus, is formed in the uterus. When pregnancy does not occur, the layer is rejected and comes out along with the blood. Hormone levels are low during this period. During menstruation, pain may occur in the groin area and lower back.
How genetic testing helps with family planning
Follicular phase
It begins on the first day of the cycle and continues until ovulation. In a woman's ovary, follicles containing eggs begin to form and gradually mature. Estrogen levels gradually rise and reach a peak around ovulation. During this phase, the endometrium in the uterus begins to thicken, which provides nutrition for the embryo if fertilization occurs.
Ovulatory phase
The egg is released from the mature follicle into the fallopian tubes, which are connected to the uterus. This is where the fusion of sperm and egg occurs during conception, and then the embryo moves into the uterus and attaches to a special layer. If fertilization does not occur, the egg dies in the fallopian tube.
Luteal phase
After the follicle ruptures and the egg is released into the fallopian tubes, the corpus luteum remains in the ovary. It produces estrogen and progesterone, a hormone that also regulates the cycle and is necessary during pregnancy. Together they prepare the uterus for fertilization. If this does not happen, the corpus luteum stops functioning, and the level of estrogen and progesterone decreases. Then menstruation begins.
If the cycle is 28 days, then ovulation occurs approximately on the 14th day - the middle of the cycle. Typically the cycle length is 25–30 days, but it can be shorter or longer.
Types of female hormone
Three basic factions:
- Estradiol is the most important hormone. Before the onset of puberty in boys and girls, its concentration in the blood is the same; the content changes at approximately 12–13 years. Participates in the accumulation of fatty tissue on the chest, hips, development of the mammary glands, and maintains skin tone. In the pubertal phase, it forms sexual characteristics, in adult women it maintains the health of the skin and hair, slows down cellular aging, participates in the construction of bone tissue, utilizes harmful cholesterol, and affects emotional stability. During the gestational period, it helps to increase the size of the uterus along with the growth of the fetus, increases the metabolic rate, forms the bone tissue of the fetus and provides it with nutrients and oxygen.
- Estrone. Synthesized by the adrenal cortex, ovaries and fat cells. It is an “intermediate” hormone, used by the body as a raw material for the production of estradiol.
- Estriol. It has virtually no effect on hormone levels in women, is inactive in the body, and is found in small quantities. But immediately after conception, its level increases under the influence of gonadotropin to prepare the uterus for growth with an enlarged fetus. It also forms ducts in the breast for lactation, reduces the risk of uterine tone, prevents spasms, and increases blood flow in the uterine cavity. Produced by placental tissue.
Estrogen norm
Normal hormone levels are determined by periods of the menstrual cycle:
| Type of estrogen | 1 phase | 2 phase | Pregnancy | Climax |
| Estradiol | 15-60 ng/l | 27-246 ng/l | 17-18 thousand ng/l | 5-30 ng/l |
| Estrone | 5-9 ng% | 3-25 ng% | 1500-3000 ng% | — |
| Estriol | — | — | 0.7-110 nmol/l | — |
Estriol is produced only by the placenta, from the moment of conception to 40 weeks. It is first synthesized from maternal cholesterol by the adrenal glands, then by the fetal liver.
During the gestational period, important values are not only the content of estriol in the mother, but also in the fetus. In the amniotic fluid in the 2nd trimester it should be in the range of 3.5–27.1 nmol/l, in the 3rd trimester – 7.3–69 nmol/l.
Symptoms of Imbalance
Estrogens actively influence the female body from the first menstruation to the development of menopause. Both an increase and a decrease in their volume inhibit reproductive function, spoil a woman’s appearance, the condition of the cardiovascular system, and the structure of bones and cartilage.
Signs of hormone excess in women
Normally, estrogen synthesis increases during puberty and during pregnancy, if it occurs without pathologies. In other periods, an increase in concentration is often caused by improper functioning of the body or the intake of the hormone from food and the environment.
Reasons for estrogen dominance:
- consumption of foods high in phytoestrogens;
- incorrectly selected hormone replacement therapy;
- frequent drinking of alcohol;
- excess weight;
- vascular diseases, heart disease, diabetes, hypertension;
- uncontrolled use of OK (oral contraceptives).
Symptoms of excess estrogen are:
- Excessive weight gain
. With increased levels of female hormones, adipose tissue accumulates mainly in the waist, buttocks, and thighs. - Irregular cycle
- scanty or, conversely, heavy discharge, breakthrough bleeding, hyperpolymenorrhea, amenorrhea and other disorders. - Breast tenderness and swelling
. Normally, this condition is observed a few days before the onset of menstruation and during pregnancy. If the mammary glands hurt in the middle of the cycle, this may indicate an increase in estrogen levels. - Increased emotionality
. PMS, sudden mood swings, depression, anxiety, panic attacks, and insomnia may develop. - Regular headaches
. Most often they are associated with approaching menstruation. - Hair loss
, baldness, deterioration of nails and hair. - Memory impairment
. Some scientists associate Alzheimer's disease with low levels of female estrogen. - Chronic fatigue
.
Important!
Complications of hyperestrogenism - endometrial hyperplasia, increased risk of bleeding, fibroids, endometriosis, cycle disorders. There are relative and absolute forms:
- relative hyperestrogenism
- a decrease in progesterone levels with the same amount of estrogen; - absolute hyperestrogenism
- an increase in estrogen with the same concentration of progesterone.
In adult women, hyperestrogenism can cause a condition similar to the manifestations of menopause - sweating, hot flashes, irritability, frequent headaches.
Symptoms of hormone deficiency
Estrogen deficiency can be caused by the following factors: taking hormonal drugs, thyroid pathologies, therapy for estrogen-dependent tumors in women, taking nootropics or antidepressants, sudden weight loss, pituitary gland diseases, unbalanced nutrition.
Estrogen deficiency can be determined by the following symptoms:
- During puberty, there may be a delay in the formation of secondary sexual characteristics - absence of menarche until 15–16 years of age, irregular periods, formation of a male-type figure in girls with a narrow pelvis, broad shoulders and developed muscles. The imbalance is also manifested by a decrease in the size of the uterus, underdevelopment of both external and internal reproductive organs.
- During menopause, a decrease in estrogen is normal. If the concentration of hormones falls at the age of 40–45 and earlier, the symptoms of menopause appear more clearly - rapid heartbeat, profuse sweating, hot flashes, dizziness, migraines.
- After the age of 35–40, the main symptoms are weight gain, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, the appearance of wrinkles, cellulite, stretch marks, moles and papillomas in large numbers, decreased libido, high heart rate, and impaired blood circulation in the brain.
- In young women, estrogen deficiency leads to frequent colpitis, vaginitis, cycle disruptions, pronounced PMS, decreased performance, joint pain, changes in blood pressure, and lack of lubrication in the vagina.
During pregnancy, such a pathology is fraught with disruptions in the development of the placenta, abruption, miscarriage, abnormalities in the formation of the child’s nervous and cardiac systems, and uterine bleeding. The risk of genetic abnormalities in the fetus, in particular Down syndrome, also increases.
Estrogen deficiency - symptoms
Menopause is associated with menopause. During this period of life, a woman may develop somatic or vasomotor disorders. The latter - hot flashes and excessive sweating - occur in certain situations - at high air temperatures, under conditions of mental stress.
Vaginal dryness is also a common problem, leading to vaginal itching and more frequent intimate infections. In addition, a woman stops enjoying sex life, because irritation and burning often lead to dyspareunia - pain during sexual intercourse. There may even be slight bleeding after sexual intercourse.
Low estrogen levels may also be associated with psychological symptoms. Depression is a common companion to menopause (perimenopausal depression). Patients complain of increased anxiety, sleep problems, and decreased psychomotor skills.
How to check your estrogen levels?
A basic estrogen test is a blood test.
It contains all 3 fractions of the hormone, the ratio of each type is determined in accordance with the following factors:
- age;
- presence or absence of pregnancy;
- taking medications containing any hormones;
- weight.
It is important to take the test in accordance with the duration of the cycle:
- if the cycle is 20–21, blood is taken 2–3 days from the start of the first bleeding;
- with a cycle of 28 days – 3–5 days;
- more than 28 days – in the range of 5–7 days from the start of menstruation.
If the cycle is irregular, an ovulation test is first performed.
Within 24 hours of its onset, the concentration of estrogen reaches its peak. Before taking tests, a woman is recommended to limit her intake of hormone-containing drugs, exclude sexual activity, and physical activity. The last meal is possible no later than 10 hours. You can find out the answer in 20–30 minutes.
Postmenopause - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of postmenopausal disorders should begin with general recommendations for lifestyle changes : proper nutrition, physical activity, adequate sleep and rest, elimination of negative environmental factors.
In recent decades, hormonal drugs have been actively used to treat menopausal disorders . They have a number of positive effects:
- reduce the frequency and severity of hot flashes;
- normalize mood, reduce anxiety and feelings of depression;
- slow down the aging process of the skin, improve its appearance;
- help prevent osteoporosis and fractures;
- reduce the likelihood of developing metabolic disorders and some cancers [10].
Hormonal treatment is carried out for at least one year (on average lasts 3-5 years). If hot flashes do not return, then taking hormonal medications should be stopped.
In general, the need for hormone therapy exists up to 60 years of age. At an older age, somatic diseases dominate in patients, so the need to take hormonal drugs is replaced by the need for special treatment of emerging diseases. The exception is hormonal ointments and suppositories for local treatment of urogenital problems - if necessary, they can be used for life [3].
Hormonal medications should be prescribed taking into account their contraindications . These include the presence of diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, bleeding disorders, thrombophlebitis, gallbladder disease, neoplasms of the uterus and ovaries (including fibroids), breast tumors and severe liver diseases. In some cases, hormonal drugs increase the risk of cancer. Studies have also shown that long-term hormone replacement therapy slightly increases the risk of developing Alzheimer's disease, which the patient should be warned about [14].
Among the drugs for hormonal treatment of postmenopausal disorders, biphasic drugs are distinguished: cycloprogynova, divina, klimen, klimonorm and femoston. They are recommended for women starting from premenopause, i.e. when menstruation has not yet ended, but occurs irregularly. Upon the onset of postmenopause, drugs for continuous regimen are indicated: femoston conti, femoston mini, Angelique, Indivina, Climodien and Cliogest.
Recently, the drug Livial (tibolone, ledidon) has been used to treat postmenopausal climacteric disorders and prevent osteoporosis. It has an estrogen-like effect on those organs and tissues that are deficient in estrogen. This drug is especially suitable for patients with depression. It can be taken for a long time.
Estrogen monotherapy is indicated for women with a removed uterus. They can be used in the form of tablets (Proginova, Estrofem), gels (Divigel, Estrogel) or patches (Klimara, Dermestril). If the uterus is not removed, then monoestrogens can also be used, but under the guise of gestagens.
For urogenital disorders, estrogens are prescribed in the form of a cream or suppository for topical use, as they stimulate the growth of the urethral epithelium. Such drugs include Orniona, Ovestin, Gynoflor E, Ovipol Clio, etc. Local treatment can be used for a long time, but an indispensable condition should be annual monitoring of smears for oncocytology, transvaginal ultrasound of the uterus and its appendages [11].
Alternative to hormone therapy
Hormone replacement therapy is not the only way to treat postmenopausal menopause. In addition to it, there are non-hormonal drugs. They are usually prescribed for mild to moderate menopause or the presence of contraindications to hormone therapy [8]. Such non-hormonal agents include:
- antimenopausal drugs and dietary supplements : climalanin, climaxan, climadinon, climactoplan, feminal, inoklim, etc. - they eliminate hot flashes, but do not prevent the development of late complications of postmenopause;
- antidepressants (Asentra, paroxetine, fluoxetine, Prozac), painkillers (Lyrica, gabapentin) and sleeping pills are symptomatic drugs, prescribed together with a psychotherapist. The dose of the drugs used should be gradually reduced, but if the symptoms of menopause reappear, the dose is increased.
Bisphosphonates are used to treat osteoporosis in postmenopause: Fosamax, Bivalos, Bonviva, Forosa. They slow down the “resorption” of bone tissue and increase bone density. It is also necessary to take vitamin D and calcium supplements [6].
Psychotherapy is also used in the complex treatment of postmenopausal disorders. It helps the patient cope with the psychological difficulties that arise during postmenopause and prevent the development of certain psychosomatic complications.
Treatment of hormonal imbalance
The main goal of therapy is to normalize the stages of estrogen production, increase or decrease concentrations to normal.
During the pubertal phase, menopause and or pregnancy, treatment with hormones (gestagens and estrogens) is not carried out.
Medicines
If, in case of hormone deficiency, it is necessary to take drugs that can restore estrogen, then in case of its excess it is strictly forbidden to be treated with such drugs.
To increase estrogen levels
If estrogen is synthesized in a woman in small quantities, the following drugs are prescribed:
| Name | Action |
| Premarin | Conjugated estrogen. Contains natural estrogens. Used for estrogen deficiency, after surgery on the uterus, ovaries, to prevent osteoporosis during the menopause phase. |
| Proginova | Contains estradiol valerate, restores the volume of steroid hormones, improves the condition of cartilage and bone tissue, removes symptoms of menopause, improves skin condition, and slows down aging. |
| Veroshpiron | Includes spironolactone, which has an estrogen-like effect. It has a diuretic effect, reduces testosterone concentrations, and is used in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome and menstrual disorders. Reduces the manifestations of female alopecia, skin problems, male pattern hair growth. |
| Hemafemin | Contains deer pantohematogen, increases the concentration of estrogen in the female body, additionally includes vitamins C, E. Affects the functioning of the ovaries, eliminates hot flashes and pressure surges. Not used during pregnancy, with caution - in case of impaired blood clotting or thrombosis. |
| Stella | Stimulates the production of estrogen, reduces the activity of papillomavirus, reduces the risk of developing tumors that produce estrogen. Contains broccoli extract, silicon dioxide, green tea, lactose, soy extract. |
| Ovestin | Contains estriol. Used to reduce the brightness of menopause, in the treatment of infertility, after surgical extirpation of the uterus, ovaries, and tubes. |
| OK (Estrogenolite, Janine, Aktivel, Lindinet, Femoden) | Monophasic contraceptives contain synthetic estrogens in small doses. They enhance the natural process of hormone production and stop ovulation. |
Remedies of this type are often produced in tablets, replenishing the lack of estrogen. Hormone replacement therapy drugs are used for menopause, estrogen deficiency, and infertility. Oral contraceptives are often prescribed to normalize the cycle, for endometriosis, and breakthrough bleeding.
To reduce estrogen levels
In this case, antiestrogenic drugs are used.
Prescribed depending on the cause of low levels of female hormones:
- Antitumor drugs: Arimidex, Femara.
- For uterine, ovarian and anovulatory infertility: Tamoxifen.
- For breast cancer: Letrozole.
Review of tablets containing estrogen →
Estrogen in food
{banner_banstat9}
The effect of drug treatment can be improved with the help of properly selected nutrition.
To increase performance
The activity of estrogen production can be increased by including foods that are rich in hormone-like substances in the menu:
- vegetables
- eggplants, tomatoes, carrots, pumpkin, beets; - greens, herbs
- celery, parsley, asparagus, spinach, basil; - fruits and berries
- pomegranates, dates, cherries, melons, apricots, papaya, grapes, raspberries; - dairy products
- cheese, butter, sour cream, cottage cheese, kefir; - sunflower seeds
, flax seeds, pumpkin seeds, peanuts, sesame seeds; - garlic
, mustard.
To preserve the maximum benefits of products, subject them to minimal heat treatment, include them in the menu every day, choose only fresh vegetables and fruits, and cook them once.
To reduce performance
{banner_banstat10}
The purpose of the diet: weight loss, normalization of the digestive tract:
- exclude canned food, fatty meats, sausage, coffee, beer and alcohol in general;
- consume more: mushrooms, citrus fruits, green tea;
- Replace cow's milk with coconut or rice milk.
Folk remedies that increase estrogen
Estrogen metabolism, as well as hormone concentrations, can be normalized using folk remedies:
- Take 20 fresh raspberry leaves and pour 200 ml of boiling water for one hour. Drink instead of regular tea 2 times a day, first strain and cool. Start taking it in the middle of your menstrual cycle.
- Pour 100 ml of boiling water over 5 hop cones, simmer for 5 minutes, then add 5 mint leaves, leave for 40 minutes. Drink half a glass three times a day for 1 month.
- Pour 100 g of plantain seeds with 50 ml of fresh flaxseed oil. Leave it for a day. Then take one teaspoon before meals three times a day.
- Grind 100 g of fresh nettle leaves, squeeze the juice from half a lemon, grate the peel, mix everything. Boil with 300 ml of water over low heat for 10 minutes, leave under a closed lid for half an hour. Then strain, take up to 3 glasses a day instead of tea.
- Take equal amounts of dried lemon balm and rose hips, add water so that it covers the dry ingredients. Boil for about half an hour, cool, strain and drink 1 glass in the morning and before bed instead of tea.
You can increase the synthesis of natural hormones in the female body using aromatherapy. Use oil of cypress, rose, lavender, mint, bergamot, orange, birch buds. They can also be used for bathing and massage.
How to increase estrogen?
If you notice the above signs of hormone deficiency, consult your doctor. Depending on the test results, he selects an individual way to increase hormones.
Doctors often prescribe tocopherol (vitamin E) to patients. It is also possible to take hormonal medications (oral contraceptives). Each tablet of combined oral contraceptives contains estrogen and progesterone (in different ratios).
You can also increase hormone levels in women with the help of food. They contain phytoestrogens - these are non-steroidal plant hormones, the structure of which is similar to human hormones. They contain:
- soybeans and soy products (milk, cheese, butter, flour, yogurt);
- other types of legumes (beans, peas, beans);
- products of animal origin (meat, fish oil, dairy products);
- some vegetables and fruits (carrots, red grapes, eggplants, tomatoes, pumpkin, cauliflower and Brussels sprouts);
- coffee.
If there is a lack of these hormones in the body, try to eat a dosed amount of these foods. Excessive portions can cause excess hormones.
Possible consequences and complications
If estrogens are secreted in insufficient quantities, there is no therapy, and pathological conditions develop:
- obesity;
- bone destruction;
- thrombosis;
- infertility;
- mastopathy;
- breast tumors;
- metabolic disorders;
- thyroid pathology;
- mental and nervous disorders;
- ovarian cysts;
- menstrual cycle disorders.
With excess estrogen, weight also increases, skin condition worsens, breast sensitivity increases, and blood pressure rises. Sleep, gastrointestinal function, and psycho-emotional background suffer.
The main task of estrogen is to provide a woman with the opportunity to become pregnant and bear a fetus. It is also thanks to this hormone that girls develop a typically female figure, thinner and more elastic skin than men, and no hair in the chest and abdomen. With an excess or deficiency of all fractions of estrogen, hormonal levels are disrupted, which is fraught with health complications and difficulties in conceiving and bearing a fetus.
Excess estrogen
With an increased amount of these hormones in the body, the following side effects may occur:
- nausea, vomiting;
- headache and dizziness;
- insomnia;
- irritability;
- soreness of the mammary glands;
- swelling, including bloating;
- high blood pressure;
- irregular periods;
- cold extremities (arms, legs);
- weight gain;
- fatigue;
- acne;
- hair loss;
- blood clot formation;
- tumors (uterus, breast, endometrium).
Both excess and deficiency of these hormones immediately manifest themselves externally and internally. In Russia, a lack of female hormones is rare, but an excess of them is very common. This is why Russian women are often diagnosed with breast cancer, mastopathy, and severe premenstrual syndrome.
If you experience the symptoms described, contact your doctor immediately. Adjust your hormonal levels before the situation gets worse.
hormone, estrogen, hormones