Compound
One dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler includes 320 mcg of micronized budesonide and 9 mcg of formoterol fumarate dihydrate or 160 mcg of micronized budesonide and 4.5 mcg of formoterol fumarate dihydrate or 80 mcg of micronized budesonide and 4.5 mcg of formoterol fumarate dihydrate .
Additional components: lactose monohydrate .
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
Two-component drug for the treatment of bronchial asthma . There is no INN. Includes budesonide and formoterol , which have different effects and exhibit a mutually stimulating effect in reducing the frequency of asthma attacks.
Budesonide is a glucocorticosteroid that has a dose-dependent and rapid anti-inflammatory effect on the respiratory tract, reducing the severity of symptoms and the frequency of attacks of bronchial asthma . When using inhaled budesonide, there is a reduced incidence of serious negative effects than when using systemic glucocorticosteroids Reduces swelling of the bronchial mucosa, secretion of mucus and sputum.
Formoterol is the second component, a selective stimulator of β2-adrenergic receptors . Causes rapid and long-term relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles in patients with reversible narrowing of the airway lumen. This effect is dose-dependent and occurs 2-3 minutes after inhalation and lasts at least 12 hours.
With the combined use of formoterol and budesonide , the severity of symptoms of bronchial asthma is reduced, lung function is stimulated and the frequency of attacks of the disease is reduced. The drug is well tolerated by patients.
Pharmacokinetics
Studies have found no evidence of an interaction between budesonide and formoterol. Inhaled budesonide is actively absorbed and reaches its maximum concentration after 30 minutes. Bioavailability is 49%. Pharmacokinetics in children 6-16 years of age and in adult patients does not differ.
Inhaled formoterol is also actively absorbed after inhalation and reaches its maximum concentration after 10 minutes. Systemic bioavailability – 61%. Plasma protein binding of formoterol is 50%, budesonide is approximately 90%.
Budesonide undergoes active biotransformation during the “first pass” through the liver with the synthesis of metabolites that have weak hormonal activity.
Formoterol is metabolized in the liver by conjugation to form active metabolites. Budesonide is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites and only in small quantities in its original form.
After use, up to 13% of the delivered amount of formoterol is excreted in its original form by the kidneys. The half-life is 17 hours.
Buy Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for inhalation 320mcg+9mcg/dose 60doses in pharmacies
Symbicort Turbuhaler Buy Symbicort Turbuhaler in pharmacies Symbicort Turbuhaler in the medicine directory DOSAGE FORMS powder for inhalation 320mcg/9mcg 60dz
MANUFACTURERS AstraZeneca AB (Sweden)
GROUP Combined products containing glucocorticosteroids
COMPOSITION Budesonide + Formoterol.
INTERNATIONAL NON-PROPENTED NAME Budesonide + Formoterol
SYNONYMS Foradil Combi
PHARMACOLOGICAL ACTION The drug contains formoterol and budesonide, which have different mechanisms of action and exhibit an additive effect in reducing the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma. Budesonide is an inhaled glucocorticosteroid. When used in recommended doses, it has an anti-inflammatory effect in the bronchi, reducing the severity of symptoms and the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma with a lower frequency of side effects than when using systemic glucocorticosteroids. Reduces the severity of swelling of the bronchial mucosa, mucus production, sputum formation and airway hyperactivity. Formoterol is a selective b2-adrenergic receptor agonist. Causes relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles in patients with reversible airway obstruction. The bronchodilator effect occurs quickly, within 1-3 minutes after inhalation, and persists for 12 hours after taking a single dose. The addition of formoterol to budesonide reduces the severity of symptoms of bronchial asthma, improves bronchial function and reduces the frequency of exacerbations of the disease.
INDICATIONS FOR USE Bronchial asthma is insufficiently controlled by taking inhaled glucocorticosteroids and short-acting beta-adrenergic stimulants or adequately controlled by inhaled glucocorticosteroids and long-acting beta-adrenergic stimulants. Symptomatic therapy in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and a history of repeated exacerbations who have severe symptoms of the disease despite therapy with long-acting bronchodilators.
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to budesonide, formoterol or inhaled lactose; children under 6 years of age. Carefully. Pulmonary tuberculosis (active or inactive form; fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, diabetes mellitus, uncontrolled hypokalemia, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, severe arterial hypertension, aneurysm of any location or other severe cardiovascular diseases (ischemic heart disease, tachyarrhythmia or severe heart failure), prolongation of the QT interval (taking formoterol may cause prolongation of the QTc interval
SIDE EFFECTS Since the drug contains budesonide and formoterol, you can expect the same side effects that are noted when these drugs are used separately. There was no increase in the incidence of adverse reactions observed during the concomitant administration of the two drugs. The most common adverse reactions associated with taking the drug are such pharmacologically expected undesirable side effects for b2-agonists, such as tremor and rapid heartbeat. These symptoms are usually of moderate severity and disappear after a few days.
INTERACTION No data available.
OVERDOSE No data available.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS It is recommended to instruct the patient on the need to rinse the mouth with water after inhalation in order to prevent the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa. During pregnancy, Symbicort Turbuhaler should be prescribed only in cases where the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Symbicort Turbuhaler can be prescribed to nursing women if the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the potential risk for the child. Symbicort Turbuhaler does not affect the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery.
STORAGE CONDITIONS Store at a temperature below 30 degrees C out of the reach of children.
Indications for use
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (symptomatic therapy in persons with a severe form of the disease and with a history of recurrent exacerbations and severe symptoms, despite treatment with long-acting bronchodilators).
- Bronchial asthma (poorly controlled by the use of inhaled glucocorticosteroids and short-acting beta2-agonists glucocorticosteroids and long-acting beta2-agonists
Symbicort turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg 60 doses (AstraZeneca)
Pharmacodynamics Symbicort Turbuhaler contains formoterol and budesonide, which have different mechanisms of action and exhibit an additive effect in reducing the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma. Budesonide. Budesonide, an inhaled glucocorticosteroid, in recommended doses has an anti-inflammatory effect in the bronchi, reducing the severity of symptoms and the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma with a lower incidence of side effects than when using systemic glucocorticosteroids. Reduces the severity of edema of the bronchial mucosa, mucus production, sputum formation and airway hyperreactivity. Formoterol. Formoterol is a selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist that causes relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle in patients with reversible airway obstruction. The bronchodilator effect occurs quickly, within 1-3 minutes after inhalation and persists for 12 hours after taking a single dose. Budesonide + Formoterol. Bronchial asthma The addition of formoterol to budesonide reduces the severity of symptoms of bronchial asthma, improves bronchial function and reduces the frequency of exacerbations of the disease. The effect of Symbicort Turbuhaler on bronchial function corresponds to the effect of the combination of budesonide and formoterol alone and exceeds the effect of budesonide alone. The drug is well tolerated. Symbicort Turbuhaler improves bronchial function and is well tolerated in children aged 6 to 11 years when taking the drug for 12 weeks (two inhalations of 80/4.5 mcg/inhalation twice a day). Chronic obstructive diseases lungs (COPD) In patients with severe COPD, while taking Symbicort Turbuhaler, there was a significant reduction in the frequency of exacerbations of the disease compared to patients receiving only formoterol or placebo as therapy (average frequency of exacerbations 1.4 but compared with 1.8-1.9 in the placebo/formoterol group) . There were no differences noted between taking Symbicort and formoterol on the forced expiratory volume in the first minute (FEV). Pharmacokinetics Absorption. Symbicort Turbuhaler is bioequivalent to the corresponding monotherapy drugs in terms of the systemic action of budesonide and formoterol. Despite this, a slight increase in cortisol suppression was noted after taking Symbicort Turbuhaler compared to monotherapy. This difference does not have an impact on clinical safety. There is no evidence of pharmacokinetic interaction between budesonide and formoterol. Pharmacokinetic parameters for the corresponding substances are comparable after the administration of budesonide and formoterol as single drugs and as part of Symbicort Turbuhaler. For budesonide, when administered as part of a combination drug, the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is slightly larger, the drug is absorbed faster and the maximum plasma concentration is higher. For formoterol, when administered as part of a combination drug, the maximum concentration in blood plasma coincides with that for the single drug. Iigalated budesonide is rapidly absorbed and reaches maximum plasma concentration 30 minutes after inhalation. The average dose of budesonide that enters the lungs after inhalation through Turbuhaler is 32-44% of the delivered dose. Systemic bioavailability is approximately 49% of the delivered dose. In children aged 6 to 16 years, the average dose of budesonide that enters the lungs after inhalation through Turbuhaler does not differ from those in adult patients (the final concentration of the drug in the blood plasma was not determined). Inhaled formoterol is quickly absorbed and reaches a maximum concentration in plasma blood 10 minutes after inhalation. The average dose of formoterol that enters the lungs after inhalation through Turbuhaler is 28-49% of the delivered dose. Systemic bioavailability is approximately 61% of the delivered dose. Distribution and metabolism. Approximately 50% of formoterol and 90% of budesonide are bound to plasma proteins. The volume of distribution for formoterol is about 4 l/kg and for budesonide 3 l/kg. Formoterol is inactivated by conjugation (active O-demethylated metabolites are formed, mainly in the form of inactivated conjugates). Budesonide undergoes intense biotransformation (about 90%) during the first passage through the liver with the formation of metabolites with low glucocorticosteroid activity. The glucocorticosteroid activity of the main metabolites 6-beta-hydroxybudesonide and 16-alpha-hydroxyprednisolone does not exceed 1% of the similar activity of budesonide. There is no evidence of metabolite interactions or substitution reactions between budesonide and formoterol. The bulk of the dose of formoterol is metabolized in the liver and then excreted by the kidneys. After inhalation, 8-13% of the delivered dose of formoterol is excreted unchanged in the urine. Formoterol has a high systemic clearance (approximately 1.4 l/min.); The half-life of the drug averages 17 hours. Budesonide is metabolized primarily with the participation of the CYP3A4 enzyme. Budesonide metabolites are excreted in the urine unchanged or in the form of conjugates. Only a small amount of unchanged budesonide is found in the urine. Budesonide has a high systemic clearance (approximately 1.2 l/min). The pharmacokinetics of formoterol in children and in patients with renal failure have not been studied. Plasma concentrations of budesonide and formoterol may be increased in patients with liver disease.
Contraindications
- Age up to 6 years (for all forms of release).
- Age up to 12 years (for release forms 320/9 mcg).
- Sensitization to formoterol, budesonide or inhaled lactose.
Use with caution in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis ; with viral, bacterial or fungal infections of the respiratory system ; with thyrotoxicosis , diabetes mellitus , severe arterial hypertension aneurysm or severe cardiovascular disease
Symbicort Rapihaler, 1 piece, 80 mcg+4.5 mcg/dose, dosed aerosol for inhalation
It is recommended to gradually reduce the dose of the drug before stopping treatment and it is not recommended to abruptly discontinue treatment.
Symbicort® Rapihaler is not intended for the initial selection of therapy for bronchial asthma.
If therapy is insufficiently effective, a doctor's consultation is necessary. Sudden and progressive deterioration in control of COPD symptoms is a potentially life-threatening condition and requires urgent medical attention. In this situation, you should consider increasing the dose of GCS, for example, prescribing a course of oral GCS, or treatment with antibiotics in case of infection.
A large US study assessed the safety of the use of salmeterol, another β2-adrenergic agonist, compared with placebo in addition to usual therapy. An increase in the incidence of deaths due to bronchial asthma was shown in patients receiving salmeterol compared with patients receiving placebo (13/13176 (0.1%) vs 3/13179 (0.02%). However, to date There are currently no studies available to assess the incidence of asthma-related deaths in patients receiving formoterol, the active ingredient in Symbicort® Rapihaler.It is possible that the increased risk of asthma-related deaths during treatment with salmeterol is due to the class-specific effect of β2 agonists -adrenergic receptors, which include formoterol.
Patients are recommended to always carry an inhaled drug with them to relieve attacks.
The patient's attention should be drawn to the need to regularly take a maintenance dose of Symbicort® Rapihaler in accordance with the doctor's prescription, even in cases where there are no symptoms of the disease.
If the symptoms of bronchial asthma can be controlled, the dose of Symbicort® Rapihaler can be gradually reduced, and it is important to constantly monitor the patient's condition. The lowest effective dose of Symbicort®Rapihaler should be prescribed (see “Dosage and Administration”).
Treatment with Symbicort® Rapihaler should not be started during periods of exacerbation or significant worsening of bronchial asthma.
During therapy with Symbicort® Rapihaler, exacerbations of bronchial asthma and serious adverse events associated with bronchial asthma may develop. Patients should continue treatment but seek medical attention if asthma symptoms are not controlled or if symptoms worsen after starting therapy.
Data from clinical studies of Symbicort® in patients with COPD with pre-bronchodilator FEV1 <50% predicted and post-bronchodilator FEV1 <70% predicted are not available (see “Pharmacodynamics”).
As with any other inhaled therapy, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with an immediate increase in wheezing and shortness of breath after taking a dose of the drug. In this case, you should stop therapy with Symbicort®, reconsider treatment tactics and, if necessary, prescribe alternative therapy. In case of paradoxical bronchospasm, it is necessary to immediately use a fast-acting inhaled bronchodilator.
Systemic effects may occur when taking any inhaled corticosteroids, especially when using drugs in high doses over a long period of time. Systemic effects are less likely to occur with inhalation therapy than with oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include suppression of adrenal function, growth retardation in children and adolescents, decreased BMD, cataracts and glaucoma.
It is recommended to regularly monitor the growth of children receiving inhaled corticosteroids for a long time. In case of established growth retardation, therapy should be reconsidered in order to reduce the dose of inhaled GCS. It is necessary to carefully evaluate the balance between the benefits of glucocorticosteroid therapy and the possible risk of growth retardation. Based on the limited data from studies of long-term corticosteroid use, it can be assumed that most children and adolescents receiving inhaled budesonide therapy will eventually achieve normal adult growth rates. However, slight short-term growth retardation has been reported, mainly in the first year of treatment.
Children taking immunosuppressants, incl. GCS are more susceptible to infectious diseases than healthy children. For example, chickenpox and measles can be very severe and sometimes fatal. Particular care must be taken not to expose children and adults with weakened immune systems to the risk of contracting viruses. If there is a risk of infection with chickenpox, treatment with Ig is prescribed locally or with an Ig mixture intravenously. If signs and symptoms of chickenpox are present, antiviral treatment should be given. It is necessary to continue anti-asthma therapy in case of a viral upper respiratory tract infection. For those patients who experience severe exacerbations of asthma due to a viral respiratory tract infection, short-term oral corticosteroid treatment should be prescribed.
Due to the potential effect of inhaled corticosteroids on BMD, special attention should be paid to patients with risk factors for osteoporosis who are taking high doses of the drug for a long period. Studies of long-term use of inhaled budesonide in children at an average daily dose of 400 mcg (metered dose) or adults at a daily dose of 800 mcg (metered dose) did not show a significant effect on BMD. There is no data regarding the effect of higher doses of Symbicort® on BMD.
If there is reason to believe that adrenal function has been impaired due to previous systemic GCS therapy, precautions should be taken when transferring patients to treatment with Symbicort®.
The benefits of inhaled budesonide therapy generally minimize the need for oral corticosteroids, but patients who discontinue oral corticosteroids may experience long-term adrenal insufficiency. Patients who in the past required urgent use of high doses of corticosteroids or received long-term treatment with inhaled corticosteroids in high doses may also belong to this risk group. It is necessary to provide additional administration of GCS during periods of stress or surgery.
It is recommended to instruct the patient on the need to rinse the mouth with water after inhalation to reduce the risk of developing candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx. It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhalation in case of development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
Precautions should be taken when treating patients with a prolonged QTc interval. Taking formoterol may cause a prolongation of the QTc interval.
The need for the use and dose of inhaled corticosteroids should be reconsidered in patients with active or inactive forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system.
When β2-adrenergic agonists are co-administered with drugs that can cause or enhance the hypokalemic effect, such as xanthine derivatives, steroids or diuretics, the hypokalemic effect of β2-agonists may be enhanced. Special precautions should be taken in patients with unstable bronchial asthma using short-acting bronchodilators, since the risk of developing hypokalemia increases against the background of hypoxia. In such cases, it is recommended to monitor the serum potassium concentration.
The use of formoterol at a dose of 90 mcg for 3 hours in patients with acute bronchial obstruction was safe. During treatment, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Clinical studies and meta-analyses have shown that the use of inhaled corticosteroids in COPD may lead to an increased risk of developing pneumonia. However, the absolute risk with budesonide is small. A meta-analysis of 11 double-blind studies involving 10,570 patients with COPD did not demonstrate a statistically significant increase in the risk of developing pneumonia in patients receiving budesonide (including in combination with formoterol) compared with patients receiving therapy without budesonide (placebo or formoterol) . The incidence of such a serious adverse event as pneumonia was 1.9% per year with therapy including budesonide and 1.5% per year with therapy without budesonide. The pooled hazard ratio comparing therapy containing budesonide to therapy without budesonide was 1.15 (95% CI: 0.83, 1.57). The pooled hazard ratio comparing budesonide/formoterol with formoterol or placebo was 1 (95% CI: 0.69, 1.44). The cause-and-effect relationship between the development of pneumonia and the use of drugs containing budesonide has not been established.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery. Symbicort® Rapihaler is not expected to affect the ability to drive vehicles or use machinery.
Side effects
- Reactions from the central nervous system: nausea, headache , anxiety, psychomotor agitation, depression , sleep disturbances , taste disturbances.
- Reactions from the circulatory system: atrial fibrillation , tachycardia, extrasystole, angina pectoris, pressure changes.
- Reactions from the musculoskeletal system: convulsions, tremor.
- Reactions from the respiratory system: mild irritation in the throat, candidiasis of the mucous membranes of the mouth and pharynx, hoarseness, cough, bronchospasm.
- Dermatological reactions: exanthema , itching , bruising, dermatitis .
- Allergic reactions: Quincke's edema , urticaria , anaphylactic reactions.
- Metabolic disorders: hyperglycemia, hypokalemia , symptoms of generalized action of glucocorticosteroids.
Symbicort turbuhaler 160mcg/4.5mcg 120doses dosed powder for inhalation
pharmachologic effect
Combined bronchodilator (selective beta2-adrenergic agonist + local glucocorticosteroid)
Composition and release form Symbicort turbuhaler 160 µg/4.5 µg 120 doses dosed powder for inhalation
Powder – 1 dose:
- Active ingredients: micronized budesonide 160 mcg and formoterol fumarate dihydrate 4.5 mcg;
- Excipients: lactose monohydrate 730 mcg.
60 doses and 120 doses in a plastic inhaler with tamper-evident control (protective film indicating the location of opening), consisting of a dosing device, a powder storage tank, a desiccant tank, a mouthpiece and a screw cap. Each inhaler is placed in a cardboard box with instructions for use.
Description of the dosage form
Inhaler: A red rotating dispenser with a Braille code imprinted on it. The lid is white. On the inside of the lid there are 5 ribbed thickenings in the form of longitudinal stripes. The dosage indicator window shows the number “60” or “120” for a 60-dose or 120-dose inhaler, respectively. The mouthpiece has four longitudinal ribs and can rotate. Contents: white to almost white granules, mostly round in shape.
Directions for use and doses
Bronchial asthma
Symbicort Turbuhaler is not intended for the initial treatment of intermittent and mild persistent bronchial asthma. The dose of the drugs included in Symbicort is selected individually and depending on the severity of the disease. This must be taken into account not only when starting treatment with combination drugs, but also when changing the maintenance dose of the drug. In the event that individual patients require a different combination of doses of active components than in Symbicort Turbuhaler, β2-adrenergic agonists and/or glucocorticosteroids should be prescribed in separate inhalers. The dose should be reduced to the lowest dose that maintains optimal control of asthma symptoms. Patients should be under constant medical supervision to ensure adequate dosage adjustment of Symbicort Turbuhaler. Once complete control over the symptoms of bronchial asthma is achieved on the background of the minimum recommended dose of the drug, at the next stage you can try prescribing monotherapy with inhaled glucocorticosteroids.
There are two approaches to prescribing therapy with Symbicort Turbuhaler:
A. Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy: Symbicort Turbuhaler is prescribed for ongoing maintenance therapy in combination with a separate short-acting beta2-agonist agonist to relieve attacks.
B. Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks: Symbicort Turbuhaler is prescribed both for continuous maintenance therapy and on demand when symptoms appear.
A. Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy
The patient must always have with him a separate inhaler with a short-acting beta2-agonist agonist to relieve attacks.
Adults (18 years and older): Symbicort Turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg/dose and 160/4.5 mcg/dose: 1 - 2 inhalations twice a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 4 inhalations twice a day.
Adolescents (12-17 years): Symbicort Turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg/dose and 160/4.5 mcg/dose: 1 - 2 inhalations twice a day.
Children over 6 years of age: Symbicort Turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg/dose: 1 - 2 inhalations twice a day.
After achieving optimal control of asthma symptoms with twice daily dosing, it is recommended to titrate the dose to the lowest effective dose, up to once daily dosing in cases where, in the opinion of the physician, the patient requires maintenance therapy in combination with a long-term bronchodilator actions.
An increase in the frequency of use of short-acting beta2-agonists is an indicator of deterioration in overall disease control and requires a review of anti-asthmatic therapy.
B. Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks
Symbicort Turbuhaler can be prescribed both as continuous maintenance therapy and as on-demand therapy when attacks occur. The patient must always have Symbicort with him to relieve attacks.
Symbicort as a maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks is especially indicated for patients with:
- insufficient control over bronchial asthma and the need for frequent use of drugs to relieve attacks;
- a history of exacerbations of bronchial asthma that required medical intervention.
- carefully study the instructions for use of Turbuhaler
- inhale forcefully and deeply through the mouthpiece to ensure that the optimal dose of the drug reaches the lungs
- never exhale through the mouthpiece
- rinse your mouth with water after inhaling maintenance doses to reduce the risk of developing candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx. It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhalation to relieve symptoms in case of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
- Careful monitoring of dose-related side effects is required in patients using large numbers of inhalations to relieve attacks.
Adults (18 years and older): Symbicort Turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg/dose and 160/4.5 mcg/dose: recommended dose for maintenance therapy 2 inhalations per day, taken 1 inhalation in the morning and evening, or 2 inhalations once only in the morning or only in the evening. For some patients, a maintenance dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler 160/4.5 mcg/dose 2 inhalations twice a day may be prescribed. If symptoms occur, 1 additional inhalation is necessary. With a further increase in symptoms within a few minutes, 1 additional inhalation is prescribed, but no more than 6 inhalations to relieve 1 attack. Usually it is not necessary to prescribe more than 8 inhalations per day, but you can increase the number of inhalations to 12 per day for a short time. Patients receiving more than 8 inhalations per day are advised to seek medical help to review therapy.
Children and adolescents under 18 years of age: Symbicort Turbuhaler is not recommended for children and adolescents as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks.
COPD
Adults: 2 inhalations of Symbicort Turbuhaler 160/4.5 mcg/dose twice a day.
Special groups of patients: there is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients. There is no data on the use of Symbicort in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Since budesonide and formoterol are primarily eliminated by hepatic metabolism, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected in patients with severe cirrhosis.
Children under 6 years of age: Symbicort Turbuhaler is not recommended for children under 6 years of age.
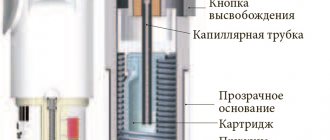
Instructions for correct use of Turbuhaler:
The mechanism of action of Turbuhaler: when inhaled by the patient through the mouthpiece, the drug enters the respiratory tract. The patient must be instructed:
The patient may not taste or feel the drug after using Turbuhaler, which is due to the small amount of the substance delivered.
Turbuhaler is a multi-dose inhaler that allows you to dose and inhale the drug in very small doses.
When you inhale, Turbuhaler powder is delivered to your lungs. Therefore, it is important that you inhale strongly and deeply through the mouthpiece.
Preparing Turbuhaler for first use:
Before using Turbuhaler for the first time, it must be prepared for use.
Unscrew and remove the cover.
Hold the inhaler vertically with the red dispenser facing down. Do not hold the inhaler by the mouthpiece when turning the dispenser.
Turn the dispenser all the way in one direction (it doesn’t matter clockwise or counterclockwise), and then also all the way in the opposite direction. You will hear a click as you turn the dispenser. Follow the described procedure twice.
The inhaler is now ready for use, and you do not have to repeat this procedure for preparing Turbuhaler for use before each use. To take the drug, follow the instructions below.
How to use SYMBICORT® TURBUHALER®
To take one dose, follow the procedure described below.
- Unscrew and remove the cover.
- Hold the inhaler vertically with the red dispenser facing down. Do not hold the inhaler by the mouthpiece when turning the dispenser. In order to measure the dose, turn the dispenser all the way in one direction (no matter clockwise or counterclockwise), and then also all the way in the opposite direction. You will hear a click as you turn the dispenser.
- Exhale. Do not exhale through the mouthpiece.
- Gently place the mouthpiece between your teeth, purse your lips and inhale forcefully and deeply through your mouth. Do not chew or squeeze the mouthpiece with your teeth.
- Remove the inhaler from your mouth before exhaling.
- If inhalation of more than one dose is required, repeat steps 2-5.
- Close the inhaler cap and check that the inhaler cap is securely screwed on.
- Rinse your mouth with water without swallowing.
IMPORTANT!
Do not attempt to remove the mouthpiece as it is attached to the inhaler and cannot be removed.
The Turbuhaler's mouthpiece rotates, but do not turn it unless necessary.
Because the amount of powder inhaled is very small, you may not feel the taste of the powder after inhalation. However, if you followed the instructions, you can be sure that you inhaled (inhaled) the required dose of the drug.
If you mistakenly repeat the procedure for loading the inhaler more than once before taking the drug, you will still receive one dose of the drug when inhaling. While the dose indicator will show the total number of doses measured.
The sound you hear when you shake the inhaler is made by the drying agent, not the medicine.
How do you know when your inhaler needs to be changed?
The dose indicator shows the approximate number of doses remaining in the inhaler; the count of doses of filled Turbuhaler starts from the 60th or 120th dose (depending on the total number of doses of Turbuhaler you purchased).
The indicator shows an interval of 10 doses, so it does not show every dispensed (loaded) dose. You can be sure that Turbuhaler delivers the required dose of the drug, even if you do not notice a change in the dose indicator window.
The appearance of a red background in the dose indicator window means that there are 10 doses of the drug left in Turbuhaler. When the number 0 appears on a red background in the middle of the dose indicator window, the inhaler must be replaced with a new one.
Note that even when the dose indicator window shows 0, the dispenser continues to rotate. However, the dose indicator stops recording the number of doses (stops moving) and the number 0 remains in the dose window of the inhaler.
Cleaning
Clean the outside of the mouthpiece regularly (once a week) with a dry cloth.
Do not use water or other liquids to clean the mouthpiece.
Disposal
Be careful with your used inhaler; remember that some medication may remain inside the inhaler.
Pharmacodynamics
Symbicort contains formoterol and budesonide, which have different mechanisms of action and exhibit an additive effect in reducing the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma.
The special properties of budesonide and formoterol make it possible to use their combination simultaneously as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks, or as maintenance therapy for bronchial asthma.
Budesonide. Budesonide is a glucocorticosteroid that, after inhalation, has a rapid (within several hours) and dose-dependent anti-inflammatory effect on the airways, reducing the severity of symptoms and the frequency of exacerbations of bronchial asthma. When prescribing inhaled budesonide, there is a lower incidence of serious adverse effects than when using systemic glucocorticosteroids. Reduces the severity of edema of the bronchial mucosa, mucus production, sputum formation and airway hyperreactivity.
The exact mechanism of the anti-inflammatory effect of glucocorticosteroids is unknown.
Formoterol. Formoterol is a selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist, after inhalation of which rapid and long-lasting relaxation of bronchial smooth muscles occurs in patients with reversible airway obstruction. The dose-dependent bronchodilator effect occurs within 1 to 3 minutes after inhalation and persists for at least 12 hours after taking a single dose.
Symbicort Turbuhaler: Budesonide + Formoterol
Bronchial asthma
Clinical efficacy of Symbicort as maintenance therapy
The addition of formoterol to budesonide reduces the severity of asthma symptoms, improves lung function and reduces the frequency of exacerbations of the disease.
The effect of Symbicort Turbuhaler on lung function corresponds to the effect of the combination of budesonide and formoterol monotherapy and exceeds the effect of budesonide alone. In all cases, a short-acting beta2-agonist agonist was used to relieve attacks. There was no decrease in the anti-asthmatic effect over time. The drug is well tolerated.
Symbicort Turbuhaler as maintenance therapy in combination with a short-acting beta2-agonist agonist to relieve attacks was prescribed to patients aged 6 to 11 years for 12 weeks (two inhalations of 80/4.5 mcg/inhalation twice a day). Improvement in pulmonary function and good tolerability of therapy were noted in comparison with the corresponding dose of Turbuhaler budesonide.
Clinical effectiveness of Symbicort as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks.
During the observation of 4447 patients receiving Symbicort therapy as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks for 6 to 12 months, a statistically and clinically significant decrease in the number of severe exacerbations was noted, an increase in the period of time until the onset of the first exacerbation compared with the combination of Symbicort or budesonide as maintenance therapy and a beta2-agonist to relieve attacks. Effective control of disease symptoms, pulmonary function, and a decrease in the frequency of inhalation prescriptions to relieve attacks were also noted. There was no development of tolerance to the prescribed therapy. In patients who sought medical help due to the development of an acute attack of bronchial asthma, after inhalation of Symbicort, relief of symptoms (relief of bronchospasm) occurred as quickly and effectively as after the administration of salbutamol and formoterol.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
In patients with severe COPD (FEV1 = 36% before initiation of Symbicort therapy), a significant reduction in the frequency of exacerbations of the disease was observed while taking Symbicort Turbuhaler compared with patients receiving formoterol or placebo alone as therapy (mean exacerbation frequency 1.4 compared with 1 .8 - 1.9 in the placebo/formoterol group). There were no differences observed between the use of Symbicort and formoterol on the forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1).
Pharmacokinetics
Suction. Symbicort Turbuhaler is bioequivalent to the corresponding monotherapy drugs in terms of the systemic action of budesonide and formoterol. Despite this, a slight increase in cortisol suppression was noted after taking Symbicort Turbuhaler compared to monotherapy. This difference does not have an impact on clinical safety. There is no evidence of a pharmacokinetic interaction between budesonide and formoterol.
Pharmacokinetic parameters for the corresponding substances are comparable after the administration of budesonide and formoterol in the form of single drugs and as part of Symbicort Turbuhaler. For budesonide, when administered as part of a combination drug, the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) is slightly larger, the drug is absorbed faster and the maximum plasma concentration is higher. For formoterol, when administered as part of a combination drug, the maximum concentration in blood plasma coincides with that for the monopreparation.
Inhaled budesonide is rapidly absorbed and reaches maximum plasma concentration 30 minutes after inhalation. The average dose of budesonide that enters the lungs after inhalation through Turbuhaler is 32-44% of the delivered dose. Systemic bioavailability is approximately 49% of the delivered dose. In children aged 6 to 16 years, the average dose of budesonide that entered the lungs after inhalation through Turbuhaler does not differ from those in adult patients (the final concentration of the drug in the blood plasma was not determined). Inhaled formoterol is rapidly absorbed and reaches maximum concentration in blood plasma 10 minutes after inhalation. The average dose of formoterol that enters the lungs after inhalation through Turbuhaler is 28-49% of the delivered dose. Systemic bioavailability is approximately 61% of the delivered dose.
Distribution and metabolism. Approximately 50% of formoterol and 90% of budesonide are bound to plasma proteins. The volume of distribution for formoterol is about 4 l/kg and for budesonide - 3 l/kg. Formoterol is inactivated by conjugation (active O-demethylated metabolites are formed mainly in the form of inactivated conjugates). Budesonide undergoes intense biotransformation (about 90%) during the first passage through the liver with the formation of metabolites with low glucocorticosteroid activity. The glucocorticosteroid activity of the main metabolites - 6-β-hydroxybudesonide and - 16α-hydroxyprednisolone - does not exceed 1% of the similar activity of budesonide. There is no evidence of metabolite interactions or substitution reactions between budesonide and formoterol.
The bulk of the dose of formoterol is metabolized in the liver and then excreted by the kidneys: after inhalation, 8-13% of the delivered dose of formoterol is excreted unchanged. Formoterol has a high systemic clearance (approximately 1.4 L/min); The half-life of the drug averages 17 hours.
Budesonide is metabolized primarily through the enzyme CYP3A4. Budesonide metabolites are excreted by the kidneys unchanged or in the form of conjugates. Only a small amount of unchanged budesonide is found in the urine. Budesonide has a high systemic clearance (approximately 1.2 L/min).
The pharmacokinetics of formoterol and budesonide in patients with renal failure have not been studied. Plasma concentrations of budesonide and formoterol may be increased in patients with liver disease.
Indications for use Symbicort turbuhaler 160 µg/4.5 µg 120 doses dosed powder for inhalation
Bronchial asthma, as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks (insufficiently controlled by taking inhaled corticosteroids and short-acting beta2-agonists as on-demand therapy, or adequately controlled by inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta2-agonists).
COPD (Symptomatic therapy in patients with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (FEV1
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to budesonide, formoterol or inhaled lactose.
Children's age up to 6 years.
Lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
With caution: pulmonary tuberculosis (active or inactive form); fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, diabetes mellitus, uncontrolled hypokalemia, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, severe arterial hypertension, aneurysm of any location or other severe cardiovascular diseases (coronary heart disease, tachyarrhythmia or severe heart failure) , prolongation of the QT interval (taking formoterol may cause prolongation of the QTc interval).
Application of Symbicort turbuhaler 160 µg/4.5 µg 120 doses dosed powder for inhalation during pregnancy and lactation
There are no clinical data on the use of Symbicort or the combined use of formoterol and budesonide during pregnancy. During pregnancy, Symbicort should be used only in cases where the benefits of the drug outweigh the potential risk to the fetus. The lowest effective dose of budesonide needed to maintain adequate control of asthma symptoms should be used. Inhaled budesonide is excreted in breast milk, however, when used in therapeutic doses, no effects on the child were noted. It is not known whether formoterol passes into women's breast milk. Symbicort should only be prescribed to breastfeeding women if the expected benefit to the mother is greater than any possible risk to the baby.
special instructions
It is recommended to gradually reduce the dose of the drug before stopping treatment and it is not recommended to abruptly discontinue treatment.
Symbicort (80/4.5 mcg/dose) Turbuhaler is not intended for patients with severe bronchial asthma.
Symbicort Turbuhaler is not intended for initial selection of therapy in the first stages of treatment of bronchial asthma.
If therapy is insufficiently effective or the maximum recommended doses of Symbicort are exceeded, it is necessary to reconsider treatment tactics. Sudden and progressive deterioration in control of symptoms of asthma or COPD is a potentially life-threatening condition and requires urgent medical attention. In this situation, the possibility of increasing the dose of glucocorticosteroids should be considered, i.e. prescribing a course of oral glucocorticosteroids or antibiotic treatment in case of infection.
Patients are advised to carry emergency medications with them at all times, either Symbicort Turbuhaler (for patients with bronchial asthma using Symbicort Turbuhaler for maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks), or short-acting beta2-agonists (for all patients using Symbicort Turbuhaler only for maintenance therapy ).
The patient's attention should be drawn to the need to regularly take a maintenance dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler in accordance with the selected therapy, even in cases where there are no symptoms of the disease. Inhalations of Symbicort Turbuhaler to relieve attacks should be carried out only when symptoms occur, but are not indicated for regular preventive use, i.e. before physical activity. In such cases, the use of a separate short-acting bronchodilator is indicated.
If the symptoms of bronchial asthma are controllable, the dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler can be gradually reduced, and it is important to constantly monitor the patient's condition. The lowest effective dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler should be prescribed (see section “Dosage and Administration”).
Treatment with Symbicort Turbuhaler should not be started during periods of exacerbation or significant worsening of bronchial asthma.
During therapy with Symbicort Turbuhaler, exacerbations and the development of serious adverse events associated with bronchial asthma may be observed. Patients should continue treatment but seek medical attention if asthma symptoms are not controlled or if symptoms worsen after starting therapy.
As with any other inhalation therapy, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with an immediate increase in wheezing after taking a dose of the drug. In this regard, Symbicort therapy should be discontinued, treatment tactics should be reconsidered and, if necessary, alternative therapy should be prescribed. Systemic effects may occur when taking any inhaled glucocorticosteroids, especially when taking high doses of drugs over a long period of time. Systemic effects are less likely to occur with inhaled therapy than with oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include adrenal suppression, growth retardation in children and adolescents, decreased bone mineral density, cataracts, and glaucoma.
It is recommended to regularly monitor the growth of children receiving long-term inhaled glucocorticosteroid therapy. In case of established growth retardation, therapy should be reconsidered in order to reduce the dose of inhaled glucocorticosteroid. It is necessary to carefully evaluate the ratio of the benefits of glucocorticosteroid therapy to the possible risk of growth retardation. When choosing therapy, it is recommended to consult a pediatric pulmonologist.
Based on limited data from studies of long-term corticosteroid use, it can be assumed that most children and adolescents treated with inhaled budesonide will eventually achieve normal adult height. However, minor short-term growth retardation has been reported, mainly in the first year of treatment.
Due to the potential effect of inhaled corticosteroids on bone mineral density, special attention should be paid to patients taking high doses of the drug for a long period with risk factors for osteoporosis. Studies of long-term use of inhaled budesonide in children at an average daily dose of 400 mcg (metered dose) or adults at a daily dose of 800 mcg (metered dose) did not show a significant effect on bone mineral density. There is no data regarding the effect of high doses of Symbicort Turbuhaler on bone mineral density.
If there is reason to believe that adrenal function has been impaired due to previous systemic glucocorticosteroid therapy, precautions should be taken when transferring patients to treatment with Symbicort.
The benefits of inhaled budesonide therapy generally minimize the need for oral corticosteroids, but patients who discontinue oral corticosteroid therapy may experience long-term adrenal insufficiency. Patients who have previously required acute high-dose corticosteroids or have received long-term treatment with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids may also be at risk. It is necessary to provide additional administration of glucocorticosteroids during periods of stress or surgery. It is recommended to instruct the patient to rinse the mouth with water after inhaling maintenance doses in order to prevent the risk of developing candidiasis of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa. It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhalation to relieve symptoms in case of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
Precautions should be taken when treating patients with a prolonged QTc interval. Taking formoterol may cause a prolongation of the QTc interval.
The need for the use and dose of an inhaled glucocorticosteroid should be reconsidered in patients with active or inactive forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system.
When β2-adrenergic agonists are co-administered with drugs that can cause or enhance the hypokalemic effect, for example, xanthine derivatives, steroids or diuretics, the hypokalemic effect of β2-adrenergic agonists may be enhanced. Special precautions should be taken in patients with unstable bronchial asthma using short-acting bronchodilators to relieve attacks during exacerbation of severe bronchial asthma, since the risk of developing hypokalemia increases against the background of hypoxia and in other conditions when the likelihood of developing a hypokalemic effect increases. In such cases, it is recommended monitor serum potassium levels.
Taking formoterol at a dose of 90 mcg per 1 hour for 3 hours is safe for patients with acute bronchial obstruction. During treatment, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Symbicort Turbuhaler contains lactose (
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Symbicort Turbuhaler does not affect the ability to drive a car or operate machinery. May affect the ability to drive and operate machinery if side effects develop.
Overdose
Symptoms of formoterol overdose: tremor, headache, rapid heartbeat. In isolated cases, the development of tachycardia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, prolongation of the QTc interval, arrhythmia, nausea and vomiting was reported. Supportive and symptomatic treatment may be prescribed.
If it is necessary to discontinue Symbicort Turbuhaler due to an overdose of formoterol, which is part of the combination drug, the issue of prescribing an appropriate glucocorticosteroid should be considered.
In case of acute overdose of budesonide, even in significant doses, no clinically significant effects are expected. With chronic use of excessive doses, systemic effects of glucocorticosteroids, such as hypercortisolism and suppression of adrenal function, may occur.
Side effects Symbicort turbuhaler 160mcg/4.5mcg 120doses dosed powder for inhalation
There was no increase in the incidence of adverse reactions observed during the concomitant administration of the two drugs.
The most common adverse reactions associated with taking the drug are such pharmacologically expected adverse events for β2-adrenergic agonists, such as tremor and rapid heartbeat; symptoms are usually mild and disappear within a few days of starting treatment. During the use of budesonide in COPD, bruising and pneumonia occurred at an incidence of 10% and 6%, respectively, compared with 4% and 3% in the placebo group (p
Frequent (>1/100,
Central nervous system: Headache
Cardiovascular system: Heartbeat
Musculoskeletal system: Tremor
Respiratory tract: Candidiasis of the oral and pharyngeal mucosa, cough, hoarseness, mild irritation in the throat
Uncommon (>1/1000,
Cardiovascular system: Tachycardia
Musculoskeletal system: Muscle cramps
Central nervous system: Psychomotor agitation, anxiety, nausea, dizziness, sleep disturbances
Skin: Bruising
Rare (>1/10000,
Skin: Immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. dermatitis, exanthema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, anaphylactic reaction
Airway: Bronchospasm
Metabolic disorders: Hypokalemia
Cardiovascular system: Arrhythmia (eg, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole)
Very rare (
Metabolic disorders: Hyperglycemia, signs or symptoms of systemic corticosteroid effects (including adrenal hypofunction)
Psychiatric symptoms: Depression, behavioral disorders (mainly in children)
Central nervous system: Taste disturbances
Cardiovascular system: Angina pectoris, blood pressure fluctuations
Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids may occur when high doses are taken over a long period of time.
The use of β2-adrenergic agonists can lead to an increase in the blood levels of insulin, free fatty acids, glycerol and ketone derivatives.
Drug interactions
Taking ketoconazole 200 mg once a day increases the plasma concentration of oral budesonide (single dose 3 mg) when administered together by an average of 6 times. When ketoconazole was prescribed 12 hours after taking budesonide, the plasma concentration of the latter increased by an average of 3 times.
There is no information about such an interaction with inhaled budesonide, however, a noticeable increase in the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma should be expected. Since there are no data for dosage recommendations, the combination of drugs described above should be avoided. If this is not possible, the time interval between the administration of ketoconazole and budesonide should be increased as much as possible. A dose reduction of budesonide should also be considered. Other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors are also likely to significantly increase budesonide plasma concentrations. The use of Symbicort as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks is not recommended for patients receiving potent CYP3A4 inhibitors.
Blockers (beta-adrenergic receptors) may weaken the effect of formoterol. Symbicort should not be prescribed simultaneously with beta-blockers (including eye drops), except in cases of emergency.
Co-administration of Symbicort Turbuhaler and quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide, phenothiazines, antihistamines (terfenadine), monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO) and tricyclic antidepressants may prolong the QTc interval and increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. In addition, levodopa, levothyroxine, oxytocin and alcohol can reduce the tolerance of the heart muscle to β2-agonists.
Co-administration of MAO inhibitors, as well as drugs with similar properties, such as furazolidone and procarbazine, may cause an increase in blood pressure.
There is an increased risk of developing arrhythmias in patients undergoing general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbon preparations.
When taking Symbicort Turbuhaler and other β-adrenergic drugs together, the side effects of formoterol may be increased. As a result of the use of β2-agonists, hypokalemia may occur, which may be exacerbated by concomitant treatment with xanthine derivatives, mineral derivatives of glucocorticosteroids or diuretics. Hypokalemia may increase the susceptibility to the development of arrhythmias in patients taking cardiac glycosides.
There was no interaction between budesonide and formoterol with other drugs used to treat bronchial asthma.
Instructions for use Symbicort Turbuhaler (Method and dosage)
Instructions for use of Symbicort Turbuhaler indicate that this drug is not used for the initial treatment of mild bronchial asthma.
The dose is selected individually, taking into account the severity of the disease. Before the first use, the inhaler must be prepared, in order to understand how this is done and how to use the inhaler, you need to watch the video.
Video on how to use Symbicort Turbuhaler:
Bronchial asthma
Patients taking the drug should undergo regular examinations with the doctor who prescribed the drug to ensure that the dosage remains optimal.
Recommended doses. Adults (18 years and older) can take up to two inhalations twice a day. Some patients may need up to four inhalations twice a day. Children (12-17 years old) should also use up to two inhalations twice a day.
After control of asthma symptoms, the dose is adjusted to the lowest effective dose, up to using the drug once a day. In children (6-12 years old), the dosage form with the lowest dosage is used, up to two inhalations twice a day.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
The recommended dose for adults is two inhalations twice a day.
Symbicort Turbuhaler, powder 160 mcg / 4.5 mcg / dose, 120 doses
Inhalation.
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® 80+4.5 mcg/dose
Bronchial asthma
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® is not intended for the initial treatment of bronchial asthma. The dose of the drugs included in the Symbicort® drug is selected individually and depending on the severity of the disease. This must be taken into account not only when starting treatment with combination drugs, but also when changing the maintenance dose of the drug.
Patients should be under constant medical supervision to ensure adequate dose selection of Symbicort® Turbuhaler®.
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® can be used in accordance with various treatment approaches:
B. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect.
C. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy (fixed dose).
B. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effect
If maintenance therapy with a combination of inhaled corticosteroids and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist is necessary, the patient can take Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and in addition to relieve attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect. The patient must carry Symbicort® with him at all times to relieve symptoms.
Symbicort® as a maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect is especially indicated for patients:
— with insufficient control over bronchial asthma and the need for frequent use of drugs to relieve attacks/symptoms;
- a history of exacerbations of bronchial asthma that required medical intervention.
Adults and teenagers (12 years and older):
The recommended dose for maintenance therapy is 2 inhalations/day, taken 1 inhalation in the morning and evening or 2 inhalations once only in the morning or only in the evening. If symptoms occur, take 1 additional inhalation. With a further increase in symptoms within a few minutes, 1 additional inhalation is prescribed, but no more than 6 inhalations to relieve 1 attack.
Usually, more than 8 inhalations per day are not required, but you can increase the number of inhalations to 12 per day for a short time. Patients receiving more than 8 inhalations/day are advised to seek medical help to review therapy.
Careful monitoring of dose-related side effects is required in patients using a large number of inhalations to relieve attacks.
Children under 12 years old:
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effect is not recommended for children under 12 years of age.
C. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy (fixed dose)
If maintenance therapy with a combination of inhaled corticosteroids and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist is necessary, the patient can take Symbicort® Turbuhaler® in a fixed daily dose and use a separate short-acting bronchodilator to relieve symptoms.
Adults (18 years and older):
1–2 inhalations 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 4 inhalations 2 times a day.
Teenagers (12–17 years):
1–2 inhalations 2 times a day.
Children 6–11 years old:
1–2 inhalations 2 times a day.
Children under 6 years old:
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® is not recommended for children under 6 years of age.
The dose should be reduced to the lowest dose that maintains optimal control of asthma symptoms. After achieving optimal control over the symptoms of bronchial asthma when taking the drug 2 times a day, it is recommended to titrate the dose to the minimum effective, up to taking the drug 1 time per day in cases where, in the opinion of the doctor, the patient requires maintenance therapy with a long-acting bronchodilator in combination with inhaled GCS.
If individual patients require a different combination of doses of active substances than in Symbicort® Turbuhaler®, beta2-adrenergic agonists and/or corticosteroids should be prescribed in separate inhalers.
An increase in the frequency of use of short-acting beta2-agonists is an indicator of deterioration in overall disease control and requires a review of anti-asthma therapy.
Special patient groups:
there is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients. There is no data on the use of Symbicort® in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Since budesonide and formoterol are primarily eliminated through hepatic metabolism, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected in patients with severe cirrhosis.
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® 160+4.5 mcg/dose
Bronchial asthma
The dose of the drugs included in the Symbicort® drug is selected individually and depending on the severity of the disease. This must be taken into account not only when starting treatment with combination drugs, but also when changing the maintenance dose of the drug.
Patients should be under constant medical supervision to ensure adequate dose selection of Symbicort® Turbuhaler®.
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® can be used in accordance with various treatment approaches:
A. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® for relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effect (patients with mild bronchial asthma).
B. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect.
Alternatively, Symbicort® Turbuhaler® can be used as a fixed dose therapy:
C. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy (fixed dose).
A. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® for relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effect (patients with mild bronchial asthma)
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® is taken on demand to relieve symptoms of bronchial asthma as they develop and to prevent bronchoconstriction caused by allergens or exercise (or to prevent symptoms in situations assessed by the patient as likely to provoke an attack of bronchial asthma). Formoterol, the active ingredient in Symbicort® Turbuhaler®, provides a rapid onset of action (within 1–3 minutes) with prolonged bronchodilation (at least 12 hours after a single dose) with reversible airway obstruction. The patient must carry Symbicort® Turbuhaler® with him at all times to relieve symptoms.
The physician should discuss allergen exposure and the amount of physical activity with the patient and take them into account when recommending the frequency of dosing.
Adults and teenagers (12 years and older):
patients should take 1 inhalation on demand when symptoms develop and to prevent bronchoconstriction caused by allergens or exercise, to control bronchial asthma. With a further increase in symptoms within a few minutes, 1 additional inhalation is prescribed, but no more than 6 inhalations to relieve 1 attack.
Usually, more than 8 inhalations per day are not required, but you can increase the number of inhalations to 12 per day for a short time. Patients receiving more than 8 inhalations/day are advised to seek medical help to re-evaluate their condition and review their asthma therapy.
Careful monitoring of dose-related side effects is required in patients using large numbers of on-demand inhalations.
Children under 12 years old:
The effectiveness and safety of Symbicort® Turbuhaler® for the relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effects in children under 12 years of age have not been studied.
B. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effect
If maintenance therapy with a combination of inhaled corticosteroids and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist is necessary, the patient can take Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and in addition to relieve attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect. The patient must carry Symbicort® with him at all times to relieve symptoms.
Symbicort® as a maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with an anti-inflammatory effect is especially indicated for patients:
— with insufficient control over bronchial asthma and the need for frequent use of drugs to relieve attacks/symptoms;
- a history of exacerbations of bronchial asthma that required medical intervention.
The physician should discuss allergen exposure and the amount of physical activity with the patient and take them into account when recommending the frequency of dosing.
Adults and teenagers (12 years and older):
Patients should take 1 inhalation on demand when symptoms develop and to prevent bronchoconstriction caused by allergens or exercise, to control bronchial asthma. With a further increase in symptoms within a few minutes, 1 additional inhalation is prescribed, but no more than 6 inhalations to relieve 1 attack. Patients also take the recommended maintenance dose - 2 inhalations/day, 1 inhalation in the morning and evening, or 2 inhalations once only in the morning or only in the evening. For some patients, a maintenance dose of 2 inhalations 2 times a day may be prescribed.
Usually, more than 8 inhalations per day are not required, but you can increase the number of inhalations to 12 per day for a short time. Patients receiving more than 8 inhalations/day are advised to seek medical attention for re-evaluation and review of maintenance therapy.
Careful monitoring for dose-related side effects is required in patients using large numbers of on-demand inhalations.
Children under 12 years old:
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks/symptoms with anti-inflammatory effect is not recommended for children under 12 years of age.
C. Symbicort® Turbuhaler® as maintenance therapy (fixed dose)
If maintenance therapy with a combination of inhaled corticosteroids and a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist is necessary, the patient can take Symbicort® Turbuhaler® in a fixed daily dose and use a separate short-acting bronchodilator to relieve symptoms.
Adults (18 years and older):
1–2 inhalations 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 4 inhalations 2 times a day.
Teenagers (12–17 years):
1–2 inhalations 2 times a day.
Children aged 6–11 years:
For children aged 6–11 years, the drug is available in a lower dosage (80/4.5 mcg/dose).
Children under 6 years old:
Symbicort® Turbuhaler® is not recommended for children under 6 years of age.
The dose should be reduced to the lowest dose that maintains optimal control of asthma symptoms. After achieving optimal control over the symptoms of bronchial asthma when taking the drug 2 times a day, it is recommended to titrate the dose to the minimum effective, up to taking the drug 1 time per day in cases where, in the opinion of the doctor, the patient requires maintenance therapy with a long-acting bronchodilator in combination with inhaled GCS.
If individual patients require a different combination of doses of active substances than in the drug Symbicort® Turbuhaler®, a beta2-adrenergic agonist and/or corticosteroids should be prescribed in separate inhalers.
An increase in the frequency of use of short-acting beta2-agonists is an indicator of deterioration in overall disease control and requires a review of anti-asthma therapy.
COPD
Adults:
2 inhalations 2 times a day.
Special patient groups:
there is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients. There is no data on the use of Symbicort® in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Since budesonide and formoterol are primarily eliminated through hepatic metabolism, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected in patients with severe cirrhosis.
Instructions for the correct use of Turbuhaler®
Mechanism of action of Turbuhaler®:
when inhaled by the patient through the mouthpiece, the drug enters the respiratory tract.
It is important to instruct the patient about the following:
— you must carefully study the instructions for use of Turbuhaler®;
- you should inhale strongly and deeply through the mouthpiece to ensure that the optimal dose of the drug reaches the lungs;
- never exhale through the mouthpiece;
— it is necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhaling maintenance doses to reduce the risk of developing candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx. It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhalation to relieve symptoms in case of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
The patient may not taste or feel the drug after using Turbuhaler®, which is due to the small amount of the substance delivered.
Instructions for use of Turbuhaler®
Turbuhaler® is a multi-dose inhaler that allows you to dose and inhale the drug in very small doses. When the patient inhales, Turbuhaler® powder is delivered to the lungs. Therefore, it is important that the patient inhales forcefully and deeply through the mouthpiece.
Preparing Turbuhaler® for first use
Before using Turbuhaler® for the first time, it is necessary to prepare it for use.
1. Unscrew and remove the cap.
2. Hold the inhaler vertically with the red dispenser facing down. Do not hold the inhaler by the mouthpiece when turning the dispenser. Turn the dispenser all the way in one direction (no matter clockwise or counterclockwise), and then also all the way in the opposite direction. When turning the dispenser, the patient will hear a click. Perform the described procedure twice.
The inhaler is now ready for use, and the patient does not have to repeat this procedure for preparing Turbuhaler® for use before each use. In order to take the drug, you must follow the instructions given below.
How to use Symbicort® Turbuhaler®
To take a single dose, you must follow the procedure described below.
1. Unscrew and remove the cap.
2. Hold the inhaler vertically with the red dispenser down (Fig. 2). Do not hold the inhaler by the mouthpiece when turning the dispenser. In order to measure the dose, turn the dispenser all the way in one direction (no matter clockwise or counterclockwise), and then also all the way in the opposite direction. When turning the dispenser, the patient will hear a click.
3. Exhale. Do not exhale through the mouthpiece.
4. Carefully place the mouthpiece between your teeth, purse your lips and inhale forcefully and deeply through your mouth. Do not chew or squeeze the mouthpiece with your teeth.
5. Before exhaling, remove the inhaler from your mouth.
6. If inhalation of more than one dose is required, steps 2–5 must be repeated.
7. Close the inhaler with the cap and check that the inhaler cap is screwed on tightly.
8. Rinse your mouth with water without swallowing.
Important!
You should not attempt to remove the mouthpiece as it is attached to the inhaler and cannot be removed. The Turbuhaler® mouthpiece rotates, but should not be turned unless necessary.
Since the amount of powder inhaled is very small, the patient may not be able to taste the powder after inhalation.
However, if the patient followed the instructions, then he can be sure that he inhaled (inhaled) the required dose of the drug.
If the patient mistakenly repeated the procedure for loading the inhaler more than 1 time before taking the drug, he will still receive one dose of the drug during inhalation. While the dose indicator will show the total number of doses measured.
The sound the patient hears when shaking the inhaler is produced by the drying agent, not the medication.
How to know when your inhaler needs to be changed
The dose indicator shows the approximate number of doses remaining in the inhaler; the dose count of filled Turbuhaler® begins with the 60th or 120th dose (depending on the total number of doses of Turbuhaler® purchased).
The indicator shows an interval of 10 doses, so it does not show every dispensed (loaded) dose.
The patient can be confident that Turbuhaler® delivers the required dose of the drug, even if he does not notice a change in the dose indicator window.
The appearance of a red background in the dose indicator window means that there are 10 doses of the drug left in Turbuhaler®. When the number 0 appears on a red background in the middle of the dose window, the inhaler should be thrown away.
It should be noted that even when the dose indicator window shows the number 0, the dispenser continues to rotate. However, the dose indicator stops recording the number of doses (stops moving) and the number 0 remains in the dose window of the inhaler.
Cleaning
Regularly (once a week) it is necessary to clean the outside of the mouthpiece with a dry cloth.
Do not use water or other liquids to clean the mouthpiece.
Disposal
You must be careful with the used inhaler; you should remember that some amount of the drug may remain inside the inhaler.
Interaction
Beta blockers weaken the effect of formoterol .
When used together with disopyramide, quinidine, procainamide, antihistamines, phenothiazines, MAO inhibitors and tricyclic antidepressants ventricular arrhythmia increases .
L-thyroxine, L-dopa, oxytocin and ethyl alcohol may impair the cardiovascular tolerance of beta-2 sympathomimetics .
The combined use of MAO inhibitors, furazolidone and procarbazine can cause allergic reactions.
Analogues of Symbicort Turbuhaler
Level 4 ATX code matches:
Tevacomb
Foster
Foradil Combi
Seretide
The following analogues of Symbicort exist: Foracort 200 (complete analogue), Airtrek, Berodual, Seretide.
Reviews about Symbicort Turbuhaler
Reviews of Symbicort on Internet forums and reviews from doctors indicate that this drug helps many people cope with attacks of bronchial asthma and significantly improve their quality of life.
Which is better Seretide or Symbicort?
The choice between Seretide and Symbicort should be made based on the individual characteristics of the patient. There are often cases when one of the drugs turns out to be ineffective, then it is replaced with an analogue.
Symbicort Turbuhaler price, where to buy
Buying a drug containing the lowest dosage in Russia will cost 1025-1910 rubles. And the price of Symbicort Turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg in Ukraine reaches 360 hryvnia.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for injection.
dosage 160/4.5 mcg/dose 120 dosesAstra Zeneca AB/LLC Astra Zeneca Industries RUB 1,948 order - Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for injection. dosage 160/4.5 mcg/dose 60 doses AstraZeneca AB/ AstraZeneca Industries LLC
RUB 1,039 order
- Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for injection. 80 µg + 4.5 µg/dose 60 doses AstraZeneca AB / ZiO-Zdorovye / Astra Zeneca Industries LLC
RUB 1,066 order
- Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for injection. dosage 80/4.5 mcg/dose 120 dosesAstra Zeneca AB/LLC Astra Zeneca Industries
RUB 2,069 order
- Symbicort turbuhaler por. d/inhal. 320mcg+9mcg/dose 60doses n1Astra Zeneca AB/LLC Astra Zeneca Industries
RUR 2,138 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for inhalation 80 µg 60 dosesAstra Zenesa/ZiO-Zdorovye
RUR 1,028 order
- Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for inhalation 80 µg 120 dosesAstra Zeneсa/AstraZeneca Industries
RUB 1,902 order
- Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for inhalation 320 mcg 60 dosesAstra Zeneсa/AstraZeneca Industries
RUB 2,064 order
- Symbicort turbuhaler (portable for inhalation 320 mcg 60 doses)Astra Zeneca/ZIO Zdorovye
RUB 2,115 order
- Symbicort turbuhaler (portion d/inhalation 160 mcg 120 doses) Astra Zenesa/AstraZeneca Industries
RUB 2,163 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Symbicort Turbuhaler 80/4.5 mcg/dose 60 doses powder for inhalation Astra Zeneca AB, Sweden
363 UAH.order - Symbicort Turbuhaler 160/4.5 mcg/dose N60 powder for inhalation Astra Zeneca AB, Sweden
454 UAH. order
- Symbicort Turbuhaler 320 mcg N60 powder for inhalation
1054 UAH. order
PaniPharmacy
- Symbicort Symbicort turbuhaler por. d/ing. 160mcg/dose+4.5mcg/dose 60doses Sweden, AstraZeneca
492 UAH order
- Symbicort Symbicort Turbuhaler powder for inhalation 320 mcg/dose + 9 mcg/dose 60 doses Sweden, AstraZeneca
1116 UAH order
- Symbicort Symbicort turbuhaler por. d/ing. 80mcg/dose+4.5mcg/dose 60doses Sweden, AstraZeneca
393 UAH. order
show more
Symbicort® Turbuhaler®
Bronchial asthma
Symbicort Turbuhaler is not intended for the initial treatment of intermittent and mild persistent bronchial asthma. The dose of the drugs included in Symbicort is selected individually and depending on the severity of the disease. This must be taken into account not only when starting treatment with combination drugs, but also when changing the maintenance dose of the drug. In the event that individual patients require a different combination of doses of active components than in Symbicort Turbuhaler, β2-adrenergic agonists and/or glucocorticosteroids should be prescribed in separate inhalers.
Patients should visit their doctor regularly to monitor the optimal dose of Symbicort Turbuhaler. The dose should be reduced to the lowest dose that maintains optimal control of asthma symptoms. Once optimal control of asthma is achieved with twice daily dosing, it is recommended to titrate the dose to the lowest effective dose, up to once daily dosing, in cases where, in the opinion of the physician, the patient requires maintenance therapy in combination with a long-acting bronchodilator . Adults (18 years and older): Symbicort Turbuhaler 320/9 mcg/dose: 1 inhalation twice daily. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 2 inhalations twice a day. After achieving optimal control of asthma symptoms while taking the drug twice a day, it is possible to reduce the dose to the lowest effective dose, up to once a day. Adolescents (12-17 years): Symbicort Turbuhaler 320/9 mcg/dose: 1 inhalation twice daily. Children under 12 years of age: Symbicort Turbuhaler 320/9 mcg/dose is not recommended for children under 12 years of age due to the lack of clinical data. Symbicort Turbuhaler 320/9 mcg/dose is intended for maintenance therapy only. COPD Adults: 1 inhalation of Symbicort Turbuhaler 320/9 mcg/dose twice a day. Special groups of patients: there is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients. There is no data on the use of Symbicort Turbuhaler 320/9 mcg/dose in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Since budesonide and formoterol are eliminated primarily by the kidneys, with the participation of hepatic metabolism, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected in patients with severe cirrhosis.
Instructions for correct use of Turbuhaler:
The mechanism of action of Turbuhaler: when inhaled by the patient through the mouthpiece, the drug enters the respiratory tract. The patient must be instructed:
- carefully study the instructions for use of Turbuhaler
-inhale strongly and deeply through the mouthpiece to ensure that the optimal dose of the drug reaches the lungs
-never exhale through the mouthpiece
- rinse your mouth with water after inhaling maintenance doses to reduce the risk of developing candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx. It is also necessary to rinse your mouth with water after inhalation to relieve symptoms in case of candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx.
The patient may not taste or feel the drug after using Turbuhaler, which is due to the small amount of the substance delivered.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF TURBUHALER
Turbuhaler is a multi-dose inhaler that allows you to dose and inhale the drug in very small doses (Fig. 1).
When you inhale, Turbuhaler powder is delivered to your lungs. Therefore, it is important that you inhale strongly and deeply through the mouthpiece.
Preparing Turbuhaler for first use:
Before for the first time , it must be prepared for use.
Unscrew and remove the cover.
Hold the inhaler vertically with the red dispenser facing down (Fig. 2). Do not hold the inhaler by the mouthpiece when turning the dispenser.
Turn the dispenser all the way in one direction (it doesn’t matter clockwise or counterclockwise), and then also all the way in the opposite direction. You will hear a click as you turn the dispenser. Follow the described procedure twice.
The inhaler is now ready for use, and you do not have to repeat this procedure for preparing Turbuhaler for use before each use. To take the drug, follow the instructions below.
How to use SYMBICORT® TURBUHALER®
To take one dose, follow the procedure described below.
1. Unscrew and remove the cover.
2. Hold the inhaler vertically with the red dispenser facing down (Fig. 2). Do not hold the inhaler by the mouthpiece when turning the dispenser. In order to measure the dose, turn the dispenser all the way in one direction (no matter clockwise or counterclockwise), and then also all the way in the opposite direction. You will hear a click as you turn the dispenser.
3. Exhale. Do not exhale through the mouthpiece.
4. Gently place the mouthpiece between your teeth, purse your lips and inhale forcefully and deeply through your mouth (Figure 3). Do not chew or squeeze the mouthpiece with your teeth.
5. Before exhaling, remove the inhaler from your mouth.
6. If inhalation of more than one dose is required, repeat steps 2-5.
7. Close the inhaler with the cap and check that the inhaler cap is screwed on tightly.
8. Rinse your mouth with water without swallowing.
IMPORTANT!
Do not attempt to remove the mouthpiece as it is attached to the inhaler and cannot be removed.
The Turbuhaler's mouthpiece rotates, but do not turn it unless necessary.
Because the amount of powder inhaled is very small, you may not feel the taste of the powder after inhalation. However, if you followed the instructions, you can be sure that you inhaled (inhaled) the required dose of the drug.
If you mistakenly repeat the procedure for loading the inhaler more than once before taking the drug, you will still receive one dose of the drug when inhaling. While the dose indicator will show the total number of doses measured.
The sound you hear when you shake the inhaler is made by the drying agent, not the medicine.
How do you know when your inhaler needs to be changed?
The dose indicator (Fig. 4) shows the approximate number of doses remaining in the inhaler; the count of doses of filled Turbuhaler begins with the 60th or 120th dose (depending on the total number of doses of Turbuhaler you purchased).
The indicator shows an interval of 10 doses, so it does not show every dispensed (loaded) dose. You can be sure that Turbuhaler delivers the required dose of the drug, even if you do not notice a change in the dose indicator window.
The appearance of a red background in the dose indicator window means that there are 10 doses of the drug left in Turbuhaler. When the number 0 appears on a red background in the middle of the dose indicator window (Fig. 5), the inhaler must be replaced with a new one.
Note that even when the dose indicator window shows 0, the dispenser continues to rotate. However, the dose indicator stops recording the number of doses (stops moving) and the number 0 remains in the dose window of the inhaler.
Cleaning
Clean the outside of the mouthpiece regularly (once a week) with a dry cloth.
Do not use water or other liquids to clean the mouthpiece.
Disposal
Be careful with the used inhaler and remember that some medication may remain inside the inhaler.