DuoResp Spiromax por d/ing 160/4.5 mcg/dose 120 doses (Teva)
It is recommended to gradually reduce the dose of the drug before stopping treatment and it is not recommended to abruptly discontinue treatment. The drug DuoResp Spiromax is not used for the initial selection of therapy in the first stages of treatment of bronchial asthma. Taking formoterol may cause a prolongation of the QT interval. An increase in the frequency of taking bronchodilators as emergency medications indicates worsening of the course of the underlying disease and serves as a basis for revising the treatment tactics of bronchial asthma. An unexpected and progressive deterioration in the control of symptoms of bronchial asthma or COPD is a potentially life-threatening condition and requires urgent medical intervention. In this situation, you should consider increasing the dose of GCS or adding systemic anti-inflammatory therapy, for example, a course of oral GCS or antibiotic treatment in case of infection. Patients are advised to carry emergency medications (short-acting β2-agonists) with them at all times. The patient's attention should be drawn to the need to regularly take DuoResp Spiromax in accordance with the selected dose, even in cases of no symptoms of the disease. Treatment with DuoResp Spiromax should not be started during an exacerbation or significant worsening of bronchial asthma. As with any other inhalation therapy, the occurrence of paradoxical bronchospasm with an immediate increase in wheezing after taking a dose of the drug. In this regard, therapy with DuoResp Spiromax should be discontinued, treatment tactics should be reconsidered and, if necessary, alternative therapy should be prescribed. Systemic effects may occur when taking any inhaled corticosteroids, especially when taking high doses of drugs over a long period of time. Systemic effects are less likely to occur with inhalation therapy than with oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include adrenal suppression, decreased BMD, cataracts, and glaucoma. Based on limited data from studies of long-term corticosteroids, it can be assumed that most children and adolescents receiving inhaled budesonide therapy will eventually achieve normal adult growth rates. However, minor (approximately 1 cm), short-term growth retardation has been reported, mainly in the first year of treatment. Due to the potential effect of inhaled corticosteroids on BMD, special attention should be paid to patients taking high doses of the drug for a long period with the presence of risk factors for osteoporosis. Studies of long-term use of inhaled budesonide in children at an average daily dose of 400 mcg (metered dose) or adults at a daily dose of 800 mcg (metered dose) did not show a significant effect on BMD. There is no data regarding the effect of high doses of DuoResp Spiromax on BMD. If there is reason to believe that adrenal function was impaired due to previous systemic GCS therapy, precautions should be taken when transferring patients to treatment with DuoResp Spiromax. The benefits of inhaled budesonide therapy generally minimize the need for oral steroids, but patients who stop taking oral corticosteroids may experience long-term insufficient adrenal function. Patients who have previously required acute use of high-dose corticosteroids or have received long-term treatment with inhaled corticosteroids in high doses may also be in this risk group. It is necessary to provide additional administration of GCS during periods of stress or surgery. It is recommended to instruct the patient to rinse the mouth with water after inhalation in order to prevent the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa. Precautions should be taken when treating patients with a prolonged QTc interval. Taking formoterol may cause a prolongation of the QTc interval. The need for the use and dose of inhaled GCS should be reconsidered in patients with active or inactive forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system. When β2-adrenergic agonists are co-administered with drugs that can cause or enhance the hypokalemic effect, such as xanthine derivatives, steroids or diuretics, the hypokalemic effect of β2-agonists may be enhanced. Special precautions should be taken in patients with unstable bronchial asthma using short-acting bronchodilators to relieve attacks during exacerbation of severe bronchial asthma, because the risk of developing hypokalemia increases against the background of hypoxia and in other conditions when the likelihood of developing a hypokalemic effect increases. In such cases, it is recommended to monitor serum potassium levels. During treatment, the concentration of glucose in the blood should be monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus. Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machines. The drug DuoResp Spiromax does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and machines. May have a minor effect if side effects occur. Caution must be exercised when operating vehicles and machinery due to the possibility of side effects.
DuoResp Spiromax, 1 piece, 320 mcg+9 mcg/dose, dosed powder for inhalation
Inhalation.
Bronchial asthma
The drug DuoResp Spiromax is not intended for the initial treatment of intermittent and mild persistent bronchial asthma. Selection of the dose of the drugs included in the drug DuoResp Spiromax occurs individually and depending on the severity of the disease. This must be taken into account not only when starting treatment with combination drugs, but also when changing the maintenance dose of the drug.
In the event that individual patients require a different combination of doses of active components than in the drug DuoResp Spiromax, β2-adrenergic agonists and/or corticosteroids should be prescribed in separate inhalers.
Patients should visit their doctor regularly to monitor the optimal dose of DuoResp Spiromax. The dose should be reduced to the lowest dose that maintains optimal control of asthma symptoms. After achieving optimal control of bronchial asthma when taking the drug 2 times a day, it is recommended to titrate the dose to the minimum effective, up to taking the drug 1 time per day, in cases where, in the opinion of the doctor, the patient requires maintenance therapy in combination with a long-acting bronchodilator .
Adults (18 years and older):
DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose as maintenance therapy 1-2 inhalations 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 4 inhalations 2 times a day. The patient must always have with him a separate inhaler with a short-acting β2-agonist to relieve attacks. An increase in the frequency of use of short-acting β2-agonists is an indicator of deterioration in overall disease control and requires a review of anti-asthmatic therapy.
The drug DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks.
The drug DuoResp Spiromax can be prescribed both as continuous maintenance therapy and as on-demand therapy when attacks occur. As a maintenance therapy and to relieve attacks, the following is especially indicated for patients:
- with insufficient control over bronchial asthma and the need for frequent use of drugs to relieve attacks;
- a history of exacerbations of bronchial asthma that required medical intervention.
Careful monitoring of dose-related side effects is required in patients using large numbers of inhalations to relieve attacks. The recommended dose for maintenance therapy is 2 inhalations per day, taken no 1 inhalation in the morning and evening, or 2 inhalations once - only in the morning or only in the evening. For some patients, a maintenance dose of DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose 2 inhalations 2 times a day may be prescribed. If symptoms occur, 1 additional inhalation is necessary. With a further increase in symptoms within a few minutes, 1 additional inhalation is prescribed, but no more than 6 inhalations to relieve 1 attack. Usually, more than 8 inhalations per day are not required, but the number of inhalations can be increased to 12 inhalations per day for a short time.
Patients receiving more than 8 inhalations per day are advised to seek medical help to review therapy.
The drug DuoResp Spiromax 320/9 mcg/dose.
1 inhalation 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 2 inhalations 2 times a day.
After achieving optimal control of bronchial asthma symptoms while taking the drug 2 times a day, it is possible to reduce the dose to the lowest effective dose, up to once a day.
COPD
Adults (18 years and older):
DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose 2 inhalations of the drug 2 times a day. DuoResp Spiromax 320/9 mcg/dose 1 inhalation of the drug 2 times a day.
Special patient groups
There is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients.
There is no data on the use of DuoResp Spiromax in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Since budesonide and formoterol are eliminated primarily by the kidneys, with the participation of hepatic metabolism, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected in patients with severe cirrhosis.
Mode of application
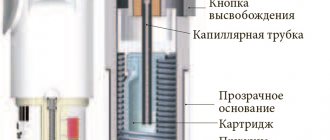
DuoResp Spiromax is a breath-activated drug, which means that the active substance enters the respiratory tract when the patient inhales it from the mouthpiece. Patients with moderate to severe asthma are able to develop sufficient inspiratory flow rates to receive a therapeutic dose of DuoResp Spiromax.
To ensure effective treatment, DuoResp Spiromax must be used correctly. Therefore, patients should be advised to carefully read the directions for use of the drug and follow the instructions for medical use.
The use of the drug DuoResp Spiromax includes 3 stages.
1. Open the mouthpiece cover by turning it down until you hear a click and it opens.
2. Place the mouthpiece between your teeth, closing your lips around it, without biting the mouthpiece of the inhaler. Take a deep breath from the dispenser. Remove the mouthpiece from your mouth and hold your breath for 10 seconds or longer - as long as is comfortable for the patient.
3. Carefully exhale and close the dispenser lid.
It is important not to shake the inhaler before use, exhale into the mouthpiece, or hold your breath while preparing to inhale.
After inhalation, it is necessary to rinse the mouth with water.
When using the drug DuoResp Spiromax, the patient may experience a specific taste due to the presence of an excipient - lactose.
Duoresp Spiromax instructions for use
Clinical and pharmacological group Drug with anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator effects Release form, composition and packaging Dosed powder for inhalation of white or almost white color, without visible lumps and inclusions; the dosing indicator window should show No. 120.1 delivered dose of budesonide (micronized) 160 mcg formoterol fumarate dihydrate (micronized) 4.5 mcg Excipients: lactose monohydrate - 5 mg*. 120 doses - plastic inhalers (1), placed in foil - cardboard packs. 120 doses - plastic inhalers (3), placed in foil - cardboard packs.
Powder for inhalation, dosed, white or almost white, without visible lumps or inclusions; the dosing indicator window should show No. 60.1 delivered dose of budesonide (micronized) 320 mcg formoterol fumarate dihydrate (micronized) 9 mcg Excipients: lactose monohydrate - 10 mg*. 60 doses - plastic inhalers (1), placed in foil - cardboard packs. 60 doses - plastic inhalers (3), placed in foil - cardboard packs. * the target amount in the delivered dose is indicated (is approximate).
Indications : bronchial asthma, insufficiently controlled by taking inhaled corticosteroids and short-acting beta2-agonists or adequately controlled by inhaled corticosteroids and long-acting beta2-agonists; - COPD - symptomatic therapy in patients with severe COPD (FEV1 <50% of the estimated calculated level) and with a history of repeated exacerbations, who have severe symptoms of the disease, despite therapy with long-acting bronchodilators.
Contraindications : hypersensitivity to budesonide, formoterol or inhaled lactose; - children and adolescents up to 18 years of age. With caution: pulmonary tuberculosis (active or inactive form), fungal, viral or bacterial respiratory infections, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, diabetes mellitus, uncontrolled hypokalemia, idiopathic hypertrophic subaortic stenosis, severe arterial hypertension, aneurysm of any location or other severe cardiovascular diseases (CHD, tachyarrhythmia or severe heart failure), prolongation of the QT interval (taking formoterol may cause prolongation of the QTc interval), lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Dosage Bronchial asthma The drug DuoResp Spiromax is not intended for the initial treatment of intermittent and mild persistent bronchial asthma. Selection of the dose of the drugs included in the drug DuoResp Spiromax occurs individually and depending on the severity of the disease. This must be taken into account not only when starting treatment with combination drugs, but also when changing the maintenance dose of the drug. In the event that individual patients require a different combination of doses of active components than in the drug DuoResp Spiromax, beta2-agonists and/or corticosteroids should be prescribed in separate inhalers. Patients should visit their doctor regularly to monitor the optimal dose of DuoResp Spiromax. The dose should be reduced to the lowest dose that maintains optimal control of asthma symptoms. After achieving optimal control of bronchial asthma when taking the drug 2 times a day, it is recommended to titrate the dose to the minimum effective, up to taking the drug 1 time a day, in cases where, in the opinion of the doctor, the patient requires maintenance therapy in combination with a long-acting bronchodilator . Adults (18 years and older) DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose as maintenance therapy 1-2 inhalations 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 4 inhalations 2 times a day. The patient must always have with him a separate inhaler with a short-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist to relieve attacks. An increase in the frequency of use of short-acting beta2-agonists is an indicator of deterioration in overall disease control and requires a review of anti-asthmatic therapy. The drug DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose as maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks DuoResp Spiromax can be prescribed both as continuous maintenance therapy and as on-demand therapy when attacks occur. As a maintenance therapy and for the relief of attacks, it is especially indicated for patients with: - insufficient control over bronchial asthma and the need for frequent use of drugs to relieve attacks; - a history of exacerbations of bronchial asthma that required medical intervention. Careful monitoring of dose-related side effects is required in patients using large numbers of inhalations to relieve attacks. The recommended dose for maintenance therapy is 2 inhalations/day: 1 inhalation in the morning and evening, or 2 inhalations 1 time/day only in the morning or only in the evening. For some patients, a maintenance dose of DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose may be prescribed - 2 inhalations 2 times a day. If symptoms occur, 1 additional inhalation is necessary. With a further increase in symptoms within a few minutes, 1 additional inhalation is prescribed, but no more than 6 inhalations to relieve 1 attack. Usually it is not necessary to prescribe more than 8 inhalations per day, but you can increase the number of inhalations to 12 per day for a short time. Patients receiving more than 8 inhalations per day are advised to seek medical help to review therapy. The drug DuoResp Spiromax 320/9 mcg/dose Prescribe 1 inhalation 2 times a day. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 2 inhalations 2 times a day. After achieving optimal control of the symptoms of bronchial asthma while taking the drug 2 times a day, it is possible to reduce the dose to the lowest effective dose, up to 1 time a day. COPD Adults (18 years and older) DuoResp Spiromax 160/4.5 mcg/dose 2 inhalations 2 times/day. DuoResp Spiromax 320/9 mcg/dose 1 inhalation 2 times/day.
Special groups of patients There is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients. There is no data on the use of DuoResp Spiromax in patients with renal or hepatic impairment. Because Budesonide and formoterol are eliminated primarily by the kidneys, with the participation of hepatic metabolism; in patients with severe cirrhosis, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected.
Rules for using the drug DuoResp Spiromax is a breath-activated drug, which means that the active substance enters the respiratory tract when the patient inhales it from the mouthpiece. Patients with moderate to severe asthma are able to develop sufficient inspiratory flow rates to receive a therapeutic dose of DuoResp Spiromax. To ensure effective treatment, DuoResp Spiromax should be used correctly. Therefore, patients should be advised to carefully read the directions for use of the drug and follow the instructions for medical use.
The use of DuoResp Spiromax includes three stages. 1. Open the mouthpiece cover by turning it down until you hear a click and it opens. 2. Place the mouthpiece between your teeth, closing your lips around it, without biting the mouthpiece of the inhaler. Take a deep breath from the dispenser. Remove the mouthpiece from the mouth and hold your breath for 10 seconds or longer, as long as is comfortable for the patient. 3. Carefully exhale the air and close the dispenser lid. It is important not to shake the inhaler before use, exhale into the mouthpiece, or hold your breath while preparing to inhale. After inhalation, it is necessary to rinse the mouth with water. When using the drug DuoResp Spiromax, the patient may experience a specific taste due to the presence of an excipient - lactose.
Side effects During the co-administration of budesonide and fenoterol, there was no increase in the incidence of adverse reactions. The most common adverse reactions associated with taking the drug are such pharmacologically expected undesirable side effects for beta2-agonists, such as tremor and rapid heartbeat. Symptoms are usually mild and disappear within a few days of starting treatment. During a 3-year clinical trial of budesonide in COPD, skin bruising and pneumonia occurred at rates of 10% and 6%, respectively, compared with 4% and 3% in the placebo group (p<0.001 and p<0.01). respectively). Determination of the frequency of adverse reactions: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100, <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000, <1/100), rarely (≥1/10,000, <1 /1000), very rare (<1/10,000) and unknown (cannot be estimated from available data). Frequency Adverse reactions From the immune system Rarely immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions (exanthema, urticaria, itching, dermatitis, angioedema and anaphylactic reaction) From the endocrine system Very rarely Cushing's syndrome adrenal suppression growth retardation decreased bone mineral density Metabolism Rarely hypokalemia Very rare hypoglycemia signs or symptoms of systemic glucocorticoid effects (including hypoadrenal gland dysfunction) Nervous system disorders Common headache tremor Uncommon dizziness Very rare taste disturbances Psychiatric disorders Uncommon agitation psychomotor agitation anxiety sleep disturbances Very rare depression behavioral disorders Visual disorders Very rare cataract glaucoma From the cardiovascular system Often palpitations Uncommon tachycardia Rarely arrhythmia (for example, atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole) Very rarely angina pectoris prolongation of the QT interval blood pressure fluctuations From the respiratory system Often candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx pharyngeal irritation cough hoarseness Rarely bronchospasm Very rarely paradoxical bronchospasm From the digestive system Uncommon nausea From the skin and subcutaneous tissues Uncommon bruising From the musculoskeletal system Uncommon muscle cramps Systemic effects of inhaled corticosteroids can occur when taken in high doses for a long time. The use of beta2-agonists can lead to an increase in the blood levels of insulin, free fatty acids, glycerol and ketone derivatives.
Overdose Symptoms: in case of formoterol overdose - tremor, headache, rapid heartbeat. In isolated cases, the development of tachycardia, hyperglycemia, hypokalemia, prolongation of the QTc interval, arrhythmia, nausea and vomiting was reported. In case of acute overdose of budesonide, even in significant doses, no clinically significant effects are expected. With chronic use of excessive doses, systemic effects of GCS, such as hypercortisolism and suppression of adrenal function, may occur. Treatment: supportive and symptomatic therapy is provided. If it is necessary to discontinue the drug DuoResp Spiromax due to an overdose of formoterol, the issue of prescribing an appropriate GCS should be considered. Formoterol at a dose of 90 mcg over 3 hours is safe for patients with acute bronchial obstruction.
Drug interactions Taking ketoconazole at a dose of 200 mg 1 time/day increases the plasma concentration of budesonide when administered orally (single dose 3 mg) when administered together by an average of 6 times. When ketoconazole was prescribed 12 hours after taking budesonide, the plasma concentration of the latter increased, on average, 3 times. There is no information about such an interaction with budesonide when administered inhaled, but a noticeable increase in the concentration of the drug in the blood plasma should be expected. Because There are no data for dose selection recommendations; the above combination of drugs should be avoided. If possible, the time interval between the administration of ketoconazole and budesonide should be increased as much as possible. A dose reduction of budesonide should also be considered. Other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors are also likely to significantly increase budesonide plasma concentrations. β2-adrenergic receptor blockers can reduce the intensity of the action of formoterol. The combination of formoterol + budesonide should not be prescribed simultaneously with beta-blockers (including eye drops), except in cases of emergency. Co-administration of a combination of formoterol + budesonide and quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide, phenothiazines, antihistamines (terfenadine), MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants may prolong the QT interval and increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias. In addition, levodopa, levothyroxine, oxytocin and alcohol can reduce the tolerance of the heart muscle to beta2-agonists. The simultaneous use of MAO inhibitors, as well as drugs with similar properties, such as furazolidone and procarbazine, may cause an increase in blood pressure. There is an increased risk of developing arrhythmias in patients undergoing general anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbon preparations. With simultaneous use of the combination of formoterol + budesonide and other beta-adrenergic drugs, the side effects of formoterol may be increased. As a result of the use of beta2-adrenergic agonists, hypokalemia may develop, which may be exacerbated by concomitant treatment with xanthine derivatives, corticosteroids or diuretics. Hypokalemia may increase the susceptibility to the development of arrhythmias in patients taking cardiac glycosides. There was no interaction between budesonide and formoterol with other drugs used to treat bronchial asthma.
Special instructions Before stopping treatment, it is recommended to gradually reduce the dose of the drug. It is not recommended to abruptly cancel treatment. DuoResp Spiromax is not used for the initial selection of therapy in the first stages of treatment of bronchial asthma. Taking formoterol may cause QT prolongation. An increase in the frequency of taking bronchodilators as emergency medications indicates a worsening of the underlying disease and serves as a basis for revising the treatment tactics for bronchial asthma. Sudden and progressive deterioration in control of symptoms of asthma or COPD is a potentially life-threatening condition and requires urgent medical attention. In this situation, you should consider increasing the dose of GCS or adding systemic anti-inflammatory therapy, for example, a course of oral GCS or antibiotic treatment in case of infection. Patients are advised to carry emergency medications (short-acting beta2-agonists) with them at all times. The patient's attention should be drawn to the need to regularly take DuoResp Spiromax in accordance with the selected dose, even in cases where there are no symptoms of the disease. Treatment with DuoResp Spiromax should not be started during periods of exacerbation or significant worsening of bronchial asthma. As with any other inhaled therapy, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur with an immediate increase in wheezing after taking a dose of the drug. In this regard, therapy with DuoResp Spiromax should be discontinued, treatment tactics should be reconsidered and, if necessary, alternative therapy should be prescribed. Systemic effects may occur when taking any inhaled corticosteroids, especially when taking drugs in high doses over a long period of time. Systemic effects are less likely to occur with inhalation therapy than with oral corticosteroids. Possible systemic effects include adrenal suppression, decreased bone mineral density, cataracts, and glaucoma. Based on the limited data from studies of long-term corticosteroid use, it can be assumed that most children and adolescents receiving inhaled budesonide therapy will eventually achieve normal adult growth rates. However, slight (approximately 1 cm), short-term growth retardation has been reported, mainly in the first year of treatment. Due to the potential effect of inhaled corticosteroids on bone mineral density, special attention should be paid to patients taking high doses of the drug for a long period with the presence of risk factors for osteoporosis. Studies of long-term use of inhaled budesonide in children at an average daily dose of 400 mcg (metered dose) or adults at a daily dose of 800 mcg (metered dose) did not show a significant effect on bone mineral density. There is no data regarding the effect of high doses of DuoResp Spiromax on bone mineral density. If there is reason to believe that adrenal function has been impaired due to previous systemic GCS therapy, precautions should be taken when transferring patients to treatment with DuoResp Spiromax. The benefits of inhaled budesonide therapy generally minimize the need for oral steroids; however, patients who discontinue oral corticosteroid therapy may experience long-term adrenal insufficiency. Patients who in the past required acute use of high doses of corticosteroids or received long-term treatment with high-dose inhaled corticosteroids may also be at this risk. It is necessary to provide additional administration of GCS during periods of stress or surgery. It is recommended to instruct the patient to rinse the mouth with water after inhalation in order to prevent the development of candidiasis of the oral mucosa. Precautions should be taken when treating patients with a prolonged QTc interval. Taking formoterol may cause a prolongation of the QTc interval. The need for the use and dose of inhaled GCS should be reconsidered in patients with active or inactive forms of pulmonary tuberculosis, fungal, viral or bacterial infections of the respiratory system. When beta2-agonists are co-administered with drugs that can cause or enhance the hypokalemic effect, for example, xanthine derivatives, steroids or diuretics, the hypokalemic effect of beta2-agonists may be enhanced. Special precautions should be taken in patients with unstable bronchial asthma using short-acting bronchodilators to relieve attacks during exacerbation of severe bronchial asthma, because the risk of developing hypokalemia increases against the background of hypoxia and in other conditions when the likelihood of developing a hypokalemic effect increases. In such cases, it is recommended to monitor serum potassium levels. During treatment, blood glucose concentrations should be monitored in patients with diabetes mellitus. Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery The drug DuoResp Spiromax does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. May have a minor effect if side effects occur. Caution must be exercised when operating vehicles and machinery due to the possibility of side effects. Pregnancy and lactation There are no clinical data on the use of DuoResp Spiromax or the combined use of formoterol and budesonide during pregnancy. During pregnancy, DuoResp Spiromax should be used only in cases where the benefit of treatment with the drug outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Budesonide should be used at the minimum effective dose necessary to maintain adequate control of asthma symptoms. Inhaled budesonide is excreted in breast milk, however, when used in therapeutic doses, no effects on the child were noted. It is not known whether formoterol is excreted into breast milk in women. DuoResp Spiromax can be prescribed to breastfeeding women only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs any possible risk to the baby. In case of renal impairment There is no data on the use of DuoResp Spiromax in patients with renal failure. Because Budesonide and formoterol are excreted mainly by the kidneys, with the participation of hepatic metabolism, then in patients with severe liver cirrhosis, a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected. In case of impaired liver function, there is no data on the use of the drug DuoResp Spiromax in patients with liver failure. Because Budesonide and formoterol are eliminated primarily by the kidneys, with the participation of hepatic metabolism, then in patients with severe cirrhosis of the liver a slower rate of elimination of the drug can be expected Diagnoses Status asthmaticus Bronchitis Cough Cystic fibrosis
Use in the elderly There is no need for special selection of the drug dose for elderly patients.
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies The drug is dispensed with a prescription.
Conditions and periods of storage The drug should be stored out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life: 2 years. The shelf life of the drug after opening the foil wrapper is 6 months.