A cluster of disorders affecting the neuropsychic sphere of a person and arising due to sudden or chronic mental trauma. In general, it is characterized by the absence of constructive changes in mental activity. In other words, this nervous disorder is a peculiar response of the body to stress, permanent experiences and internal conflict of the individual, which arise in the event of frustration, that is, a discrepancy between real possibilities and a person’s desires. Neurotic conditions are graded according to level and severity. They can be chronic or situational in nature. According to WHO, 400 million people experience some form of mental illness. Neuroses and neurotic conditions are considered the most common mental disorder.
Diagnosis of neuroses
According to clinical statistics, almost every person, one way or another, at a certain period of his life has encountered states of neurotic instability of varying degrees of severity. The easiest, primary stage of such conditions is defined as neurotic and represents a reaction of the psyche to certain external events: sudden grief, difficulties with adaptation, prolonged stress, and so on. It is these conditions that are also designated as borderline (non-psychotic) and lie in the field of study of minor psychiatry. A psychologist or neurologist can diagnose mild situational neurosis, as well as prescribe therapy, but if the situation becomes more protracted and complex, then the help of a psychiatrist is necessary.
Why does the disease develop?
The World Health Organization notes that 10-20% of the world's population is diagnosed with various neurotic disorders. However, these are only officially confirmed diagnoses. Many more people live with their fears and anxieties for years without seeking medical help.
Among the common reasons:
- constant overwork;
- information overload;
- monotonous work;
- features of upbringing in a family with frequent traumatic situations;
- asthenic physique;
- long-term chronic diseases;
- frequent drinking of alcohol.
Psychologists say that individual characteristics of the psyche and physiology are of great importance. People with different character types may experience the same situations differently. For example, some perceive monotonous work as normal, while others perceive it as stress.
Neurosis in women is observed 2 times more often than in men. The explanation is the so-called emotional lability (instability, mobility). Women enter a state of passion much more easily when exposed to even weak external stimuli (events, situations).
Women experience neurosis more often than men. Photo by Andrea Piacquadio from Pexels
Symptoms of neurosis
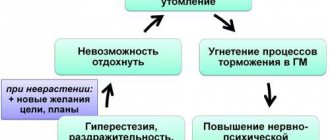
Most often, neurotic disorders are characterized by mixed clinical symptoms. The prevalence of certain characteristics is associated with the specific location of the lesion in the nervous system.
The general possible symptoms of neurotic disorders are quite multifaceted and can manifest themselves both at the somatic level (physiologically) and at the psychological or psychopathic level.
Symptoms of psychopathy include: sleep disturbances (insomnia), loss of appetite or overeating, various panic states (fears, nightmares, phobias, hypochondria) and so on. At the physiological level, the patient can experience a wide range of ailments: pain in different parts of the body (psychalgia), migraines (headaches), a feeling of numbness, coldness or sweating of the extremities, fainting, tachycardia, a feeling of a lump in the throat, a feeling of suffocation, frequent urination, diarrhea. Disturbances in the functioning of body systems without visible organic changes are defined as somatoform disorders.
Somatoform disorders are a group of diseases of a mental nature in which somatic symptoms mask the original neurotic nature of the disease. Thus, the patient has somatic complaints, but there are no pathological changes in the internal organs that could explain these complaints.
The causes of neuroses, as will be discussed in detail below, can be absolutely any traumatic situation that provokes sudden or chronic emotional exhaustion. The symptoms of the disease themselves are determined by the general background of predisposition: the situation in the family, the level of socialization and self-realization, genetic predisposition, and so on. However, the general history of the disease coincides in the following parameters.
Important symptoms of incipient neurosis:
- Hypersensitivity to stress . Violent emotional reaction to minor events: despair, anger, etc.
- Increased levels of anxiety.
- Total focus on the traumatic situation (obsession).
- Tearfulness.
- Excessive vulnerability and touchiness.
- Asthenia (fatigue syndrome) , fatigue, decreased concentration, absent-mindedness.
- Misophonia (sensitivity to loud sounds) , as well as bright light or sudden changes in temperature.
- Insomnia and other sleep disorders : inability to fall asleep, intermittent, shallow sleep, drowsiness during the day
- Autonomic disorders : pressure changes, rapid breathing, arrhythmia or tachycardia, sweating, diarrhea, nausea and others.
- Decreased libido and potency in certain cases.
If you experience two or more of the above conditions on a long-term basis, then you should not ignore them. You should listen to your body, seek help in time and take the necessary measures.
Neurotic depression
Neurotic depression is typically characterized by a depressed state with some inhibition of psychomotor reactions and thinking. There are monotonous depressive memories, pessimistic views of the future, and fixation on the traumatic situation. There is a tendency to tearfulness, irritability, decreased appetite, sleep disturbance, sensitivity (excessive emotional sensitivity).
Neurotic depression does not reach the depth of psychosis, is reversible, and goes away when a traumatic situation is analyzed or under the influence of treatment.
Forms and types of neuroses
In a general clinic, based on symptoms, neuroses are divided into two groups: physical and mental. At the physical (physiological) level, a neurotic disorder manifests itself specifically in the human body and can affect any system of the body: muscular (facial neurosis, neuralgia), respiratory (choking attacks), cardiovascular (tachycardia), pharyngeal neurosis, gastrointestinal (diarrhea) and other species.
As for neuroses of a mental nature, emotional reactions are affected. Mental neuroses are divided into 4 subtypes:
Depressive neurosis
Usually manifests itself in a bad mood, a decrease in intellectual function and volitional resource, and an inability to concentrate. From a physical point of view, it is characterized by a lack of appetite or, conversely, overeating, often a decrease in sexual activity.
Hypochondriacal or anxiety neurosis
Another name is neurosis of fear or obsessive states. Characteristic signs: excessive anxiety for minor or non-existent reasons, unreasonable fear, general depression, obsessive negative thoughts. Disturbances in the body are associated with disruption of the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, when a person begins to inadequately assess his health. For example, there is excessive fear for one’s physical condition and a tendency to attribute to oneself illnesses that do not exist. But the danger is that symptoms eventually begin to appear, although the disease itself is in fact absent.
The underlying conflict lies in the plane of contradictions between one’s own desires, needs and sense of duty.
Asthenic neurosis or neurasthenia
With this disorder, symptoms such as asthenia and psychasthenia come to the fore, namely fatigue, frequent mood swings, fixation on negative thoughts, lack of focus, difficulties with concentration and intellectual activity, abilities, insomnia and decreased libido, discomfort in the body ( pain, numbness, cramps, etc.). Usually arises as a result of frustration, that is, a long-term conflict (contradiction) between the real capabilities of the individual and his desires.
Hysterical neurosis
In certain cases it may be associated with narcissistic personality disorder. Among the key signs, it is worth noting inflated or changeable self-esteem, a constant high need for the attention of others, mannerisms, etc. In connection with the above, the motivating factor of hysteria is a neurotic conflict, characterized by unreasonably inflated demands of the patient on the environment without taking into account the moods and wishes of other people. Optionally, there may be an inability to empathize.
According to the duration and nature of the course, neurotic conditions can be situational and chronic. Situational neurosis is a reaction of the human nervous system to stress, the duration of which is related to the duration of the stress factor. Once the negative situation is over, self-healing occurs automatically. A more complex situation is chronic neurosis, a state in which the patient can remain throughout his life, which is due to general unconstructive patterns of response to the surrounding reality. For such a person, life itself and its details are the causes of constant stress. Why is this happening? What is a psychogenic factor?
ICD 10 code
Stress-related and somatoform neurotic disorders in ICD 10 are classified in categories F40-F48. Neurosis is a disease with reversible mental disorders. The disease is caused by exposure to traumatic factors. Neurotic disorder is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- disturbances of well-being, somato-vegetative, emotional functions;
- mental exhaustion;
- the patient’s awareness of the fact of his illness;
- absence of disruption of the reflection of the real world.
Psychiatrists distinguish the following clinical forms of neurotic conditions: asthenic neurosis (astheno-neurotic disorder or neurasthenia), obsessive-compulsive neurosis, hysterical neurosis, neurotic depression (depressive neurosis).
Causes and pathogenesis of neurotic conditions
As mentioned above, the cause of the development of the disorder is an intrapersonal conflict caused by the influence of macro (environmental factors) or micro factors (internal experiences and predisposition of a person). Often, factors can influence complexly.
Classical psychiatry divides the factors that are prerequisites for the occurrence of neuroses into three groups:
- Exogenous factor (traumatic circumstances) . By these we mean a difficult life situation, job loss, divorce, loss of a loved one, abusive relationships, moving, and so on.
- Endogenous factor (disturbances in the functioning of neurotransmitters).
- Somatogenic factor (various somatic diseases) . Somatic diseases of various human organs and systems. Prolonged illness, intoxication of the body, hormonal disorders, and so on.
The development of the disease and its course depend on the interaction of two phenomena: the functional state of the central nervous system and the strength, as well as the duration of external influences affecting it. The causes of chronic neurotic disorder (when a person always feels bad) can be very different, and only a qualified specialist can identify them. In clinical psychology, it is customary to look for the causes of deviations in childhood. For example, factors such as an anxious family, children's attitudes, narcissistic parents, the need to constantly meet given standards - all this can determine the development of internal conflict, and, accordingly, mental illness. Temporary neurotic states are more often associated with situational stress factors: dismissal, bankruptcy, divorce, loss of a loved one, moving to another city, and so on. Sometimes, to neutralize a traumatic situation, you just need to change the environment, immerse yourself in your comfort zone and remove from your life those moments that cause irritation. But if the main reason is internal conflict, then a change in atmosphere is only a temporary measure.
Risk factors
Although there are many manifestations of this disease, what they have in common is a stress factor or a traumatic situation. These can be difficult experiences, stress, strong excitement, emotional turmoil.
Video 1. What is neurosis? Source: YouTube channel “TASS Science”
However, constant stressful situations are not a necessary risk factor. Among the potential “victims” of neuroses are people with an unstable psyche that reacts sharply to an atypical situation. For suspicious, impressionable, sentimental people, one strong shock is enough. For example, for a woman it may be a difficult birth. The disease can be provoked by:
- loss of a large sum of money;
- difficult divorce proceedings;
- separation from a loved one;
- dismissal;
- disaster, accident;
- death of a loved one.
star fever
People leading an active public lifestyle are susceptible to neurosis. Johnny Depp, Emma Stone, Bella Hadid, David Beckham, Mariah Carey are just a small part of the list of show business stars who have publicly admitted to treating neurosis. For 12-year-old Prince Harry, the death of his mother, Princess Diana, was a stress factor for protracted neurosis. For Ariana Grande - the terrorist attack in Manchester. The world-famous singer Adele experiences fear in front of a large audience. And actress Kim Bassinger suffers from panic attacks.
Treatment and prevention of neuroses
In our ultra-fast times, in the rhythm of big cities, it is quite difficult to remain in harmony and balance. But, as they say, saving drowning people is their own business, which is why the prevention of neurotic conditions is our personal responsibility. Standardized working hours, minimizing stress, dosed rest, physical activity (running, swimming, yoga), separation of work and personal life, sports, hobbies, the opportunity to be in nature, walks - all these simple little things help to increase the volitional threshold and reduce the stress factor. As they say, “a healthy mind in a healthy body,” which is why it is very important to keep yourself in shape and your body in balance. A physically strong person and nervous system are more or less fine. Most neurotic disorders develop unnoticed, simply due to ordinary life circumstances, such as an uncontrolled information field, time pressure, and the inability to disconnect from work processes in the evening.
In addition to the above recommendations, you can use traditional medicine for treatment at home.
The use of folk remedies in the treatment of neurotic disorders
It is no secret that from time immemorial people have been treated with herbs, and the result, oddly enough, was not long in coming. Regular use of decoctions and infusions based on medicinal herbs in some cases can be an excellent alternative to classical therapy and will help get rid of neurosis.
After such treatment, many patients noted a decrease in neurotic syndrome, felt general calm, normalization of sleep patterns and quality, and emotional harmonization. The most effective herbs in the treatment of nervous disorders include chamomile, oregano, lemon balm, mint, valerian, peony flowers, hop cones, angelica root and others.
All these herbs have a very beneficial effect on the body and reduce anxiety levels. Aromatherapy can be an alternative method: using essential oils or aroma sticks, using herbal compresses or regularly eating honey. By the way, following a special diet and the presence of certain foods in the diet is also an excellent preventive and therapeutic agent.
How to eat with neurosis
In the treatment of all types of neurosis, an important place is occupied by adherence to a special balanced diet. The patient’s daily diet simply needs to include foods enriched with nutrients and vitamins of certain groups.
By nutrients in this aspect we mean: fatty oils and acids, proteins and vitamins of groups C, B, E, P, as well as carotene salt, iron, folic acid, magnesium.
A balanced complex of the substances described above is found in foods such as raisins, cheese, walnuts, beets, cabbage, bananas, sorrel, lemons and others.
Regular consumption of them will direct the work of the nervous system receptors in the right direction and balance the overall emotional state. To lift your mood and improve your well-being, it makes sense to start consuming sunflower seeds, boiled chicken pulp, shrimp, and salmon fish more often. These products will compensate for the lack of vitamin B6 in the body, which is responsible for the stability of the emotional background.
Classification
The main types of neurosis include:
- Neurasthenia. Develops against the background of difficulties in interpersonal relationships. It is also called “irritable weakness”, such people show dissatisfaction with any reason, they are bothered by headaches and heart pain, tachycardia, heartburn and sleep disturbances;
- Hysteria or conversion neurosis. It is observed more often in females. Such people play along with the created image. Often this is the role of a seriously ill patient, simulating seizures or loss of vision. An attack of hysteria occurs spontaneously, usually after a provoking situation, in order to get what is what. However, the symptoms do not appear at the request of the patient and leave him tormented. Hysteria is observed in spoiled people and people with high self-esteem who are not accustomed to being denied anything;
- Obsessive-compulsive neurosis. The condition manifests itself through the emergence of fear and anxious thoughts even in the absence of a provoking agent. These include fear of society, fear of infection with some kind of disease. To alleviate their condition, patients may resort to special rituals that cause inconvenience and suffering. This group includes phobic neurosis and panic attacks;
- Somatoform disorders. This is the name given to the appearance of complaints that resemble a somatic disease, but no organ pathology is objectively detected.
- This group of neuroses is classified as general, in the clinic of which emotional disorders predominate.
- According to the duration of their course, neuroses are divided into:
- Spicy. They develop in response to short-term stimuli and can go away on their own, without specific therapy. This type of neurosis is also called situational;
- Chronic. They arise under the influence of a long-term stimulus, leading to disadaptation in society and changes in the psycho-emotional background.
- Other types of neurotic disorders:
- Bulimia is an eating disorder. It often occurs in teenage girls with complexes and lack of self-confidence. There are two forms of bulimic neurosis: with and without purging. In the first case, a person periodically overeats, then artificially induces vomiting so as not to gain weight. People suffering from bulimia without purging exhaust their bodies with strict diets and excessive exercise;
- Hypochondriacal neurosis is classified as a somatoform disorder. Such people concentrate their attention even on minor deteriorations in their well-being. They regard any symptoms as a sign of a dangerous disease. Such people usually come to the doctor with a stack of reports from other specialists and the results of many examinations. The diagnosis is made by excluding somatic pathology based on examination data, treatment is carried out by a psychotherapist;
- Autonomic neurotic disorder or VSD is a complex of symptoms caused by dysfunction of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. Depending on the predominance of the tone of the nervous system, VSD can occur as sympathicotonia or vagotonia. In the first case, symptoms of activation of the sympathetic nervous system (increased blood pressure, tachycardia, pallor) dominate, in the second - parasympathetic (low blood pressure, slow pulse, dizziness, redness of the skin). A separate category is vegetative crisis, which is characterized by increased symptoms and is accompanied by dizziness, weakness, sweating and decreased blood pressure. Against the background of an imbalance in the functioning of the nervous system, muscular or respiratory neurosis may occur;
- Noogenic neurosis has recently become increasingly widespread due to a sedentary lifestyle and the emergence of a virtual network. At the same time, a person loses his life values and regards his existence as meaningless, he has no incentive to work, he is not satisfied with his life and is unable to overcome life’s difficulties;
- Neurogenic bladder syndrome is a neurosis characterized by a fear of voiding in a public place. Such a person takes a long time to adjust to urination, eventually avoids leaving the house, and tries to drink less liquid in a public place;
- Cardioneurosis or cardiac neurosis is a disorder of cardiac activity in response to a mental disorder. A person feels a “fading” heart, pain in the chest, attacks of palpitations or pulsations throughout the body. During an attack, a person is bothered by a feeling of fear and anxiety. After ruling out cardiac pathology, such patients are prescribed a consultation with a psychotherapist;
- Sexual neurosis is a mental disorder that affects a person’s sex life. Sexual disorders are manifested by either an increase or decrease in sexual desire. With increased desire, sexual desire is directed towards another object, and sexual perversion occurs. A decrease in desire leads to the fact that a person avoids sexual contacts, and sometimes even people of the opposite sex;
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder is characterized by the presence of intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and actions (compulsions).
- There is alcoholic neurosis, which occurs against the background of severe alcohol dependence and can become chronic. Symptoms of this condition vary and may include insomnia, fatigue, aggression or depression, headaches and heart pain. The main goal of treatment is to get rid of addiction.
Professional treatment and anti-anxiety therapy
As for the nosological (more advanced) stages, it is very important to notice a change in your condition in time and take appropriate measures, that is, to prevent the development of a chronic form. Professional treatment of neurosis has two main directions: psychotherapeutic (psychoanalytic) and pharmacological (medicinal). Medication is prescribed at the affective stages, before which the emphasis is on psychotherapeutic work and anti-anxiety therapy.
At the initial level of a neurotic state, anti-anxiety therapy is possible on an outpatient basis, and without the use of medications. Excellent methods of reducing anxiety, in addition to those described above, are such non-drug procedures as: massage, balneological treatment (hydrotherapy, mud therapy, aromatherapy, galvanization of the collar areas, acupuncture, Charcot's shower, physical therapy, breathing practices, etc. However, if the patient is long-term being in a state of anxiety for a period of time (more than two weeks, for example) and experiencing a complex of symptoms, this may already indicate the chronification of neurosis and its affective level. The chronic form occurs if a person neglects the recommendations and does not modify his lifestyle. Overwork, overwork , excessive responsibility, as a consequence, alcohol abuse - all this contributes to the development of chronic neurotic conditions. This condition is dangerous and requires qualified assistance from a specialist, the prescription of psychotherapeutic and, quite possibly, drug treatment!
Drug therapy
The course of neurosis is associated with a simultaneous decrease in the level of brain serotonin, therefore long-term use of antidepressants - selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors - is prescribed for treatment. At the initial stage of treatment with antidepressants, their adverse reactions may occur, and the patient’s condition may worsen. In view of this, it is important not to stop taking the prescribed treatment, but only to reduce the dose of the drugs. Then, as tolerance improves, the dosage is gradually increased to the recommended values. Over time, the symptoms of neurosis decrease and the patient's condition improves.
Important: the antidepressant must be selected by a doctor! The selection takes into account the individual tolerability of the drug and its effectiveness for specific neurotic symptoms.
For the treatment of neuroses accompanied by insomnia or poor sleep, sedative and hypnotic antidepressants are prescribed. Sometimes, with great caution and in small doses, in short courses (to avoid addiction), tranquilizers are prescribed. When treating neuroses with concomitant weakness, memory loss, and asthenia, nootropic drugs are used. The duration of treatment is usually several months; if necessary, the course must be repeated.
Psychotherapeutic treatment
Neurosis, as a combination of functional mental disorders, can have a long course and progress. In this aspect, the most effective method of treatment is psychotherapy. The choice of the direction of psychotherapy and the selection of methods is carried out by the doctor individually, taking into account the specifics of each specific case. To eliminate panic attacks or fears of space, for example, tools such as hypnosis, family psychotherapy, body-oriented therapy, Gestalt therapy, gradual involvement in some interesting activity are used to eliminate feelings of sadness, melancholy and loneliness, create a positive attitude and positive emotions. Social addiction is treated with cognitive therapy and behavior correction. The goal of any method is to bring the individual into the zone of awareness.
Psychotherapy methods
- Group therapy . In such classes, a collective analysis of various situations and conflicts that provoked is carried out. Each patient tells how he manages to cope with the disease. Patients are taught that the disorder is treatable.
- Individual therapy . Personal work of a doctor - psychiatrist, psychotherapist or psychologist with a patient using the techniques necessary in a particular case.
- Art therapy . This is treatment using creativity for the purpose of sublimation, aimed at the constructive use of energy resources and the transformation of negative energy into positive energy through the means of substitution. Drawing, singing, theater arts, poetry reading.
- Autogenic training . They use methods of self-hypnosis, hypnosis, and elements of neurolinguistic programming.
- Psychodrama, psychoanalysis . Based on the study of the patient’s inner world.
Psychotherapy
In order to alleviate neurotic symptoms (by taking antidepressants), psychotherapy is carried out:
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy – formation in the patient of the correct reaction to the situation, strengthening his adequate assessment of his behavior in a traumatic situation, changing the way he responds to it;
- group psychotherapy – takes place for 1.5 hours daily or weekly, in the form of discussions. Topics are determined in advance; they relate to the biography, behavior of group members, and life situations. Group therapy has rules: strict confidentiality, sincerity of participants, experience “here and now,” specificity of topics. Groups can be closed - with a constant composition of participants, or open - someone comes, someone stops visiting;
- hypnotherapy - suggestion is carried out in a special state of the patient, hypnotic. The session includes 4 stages: hypnotization, therapeutic suggestion, therapeutic rest, dehypnotization;
- autogenic training;
- breathing exercises for relaxation and concentration;
- non-verbal methods of psychotherapy - music therapy, art therapy, dancing and pantomime.
The most effective treatment is a combination of antidepressant medication and cognitive behavioral therapy.
Symptoms and treatment of neurosis in children
Unfortunately, children are often also susceptible to neurotic disorders. And the reasons can also be quite varied. First of all, it is worth noting psychotraumatic circumstances, but the trigger for the development of conditioning depending on the traumatic situation is the constitutional initial characteristics and genetic determination of the child. In other words, basic factors are a trigger mechanism - a trigger for the development of neurosis. However, family situation and upbringing are also strong motivating factors. For example, excessive spoiling, exaltation of the child in the family, permissiveness, overprotection, hypoprotection (the opposite state, when the child is not taken care of on the contrary), non-acceptance, failure to meet parental expectations, breakdowns on the child, harsh upbringing, and so on. All these gaps in relationships with children can lead to neurotic states without initial visible deviations.
The most common symptoms in childhood include:
- nervous tics, facial neuroses (blinking, twitching);
- enuresis (stomach upset);
- stuttering;
- nervous cough;
- sleep disorder;
- ADHD (Attention deficit disorder and hyperexcitability).
It is important to note that the main therapeutic target in the treatment of childhood neurotic disorders is the parent. The main goal of child therapy is to influence the parent through the prism of the child’s condition. In most cases, adults do not realize that the problem concerns, first of all, their condition, which is projected onto the child. The symptoms exhibited by the child are the symptoms of the family. This needs to be remembered from a psychological point of view. As for specific methods of treatment: this is supportive therapy, the use of various projective techniques (sand therapy, art, body-oriented, fairy tale therapy). An excellent method in the case of children is physiotherapy: balneological treatment and acupuncture.
Of course, we must not forget about observing basic balancing standards at home, such as maintaining a daily routine, reducing or eliminating the child’s interaction with a smartphone or social networks, and walking in the fresh air. Additional recommendations include physical activity (children's yoga, swimming, dancing), placing an aquarium in the apartment, listening to classical music.
In certain cases, a neurologist may prescribe sedative homeopathic medications. But, as noted above, the cause of childhood neuroses lies in the behavior of the parent.
Advantages of treatment at the clinic of JSC "Medicine"
The course of neurosis does not lead to disability, but often disrupts the full life of the patient and people close to him. In modern medicine, there are 3 stages of development of neuroses. The later the stage, the more difficult the treatment; this must be clearly understood. Medical specialists (academician Roitberg’s clinic) successfully treat neuroses in adults and children at any stage of complexity.
Remember: it is impossible to cure neurosis on your own, but in the conditions of the clinic of JSC “Medicine” it is absolutely possible to recover completely! Leading specialists of domestic medicine, including academicians, professors, doctors and candidates of medical sciences, conduct receptions here. Modern material and technical base, coupled with the professionalism of doctors, allows patients with neuroses to recover in the shortest possible time!
Neurosis and its consequences
Do not underestimate the destructive impact of neurotic conditions on the body and psyche. The consequences of a disease that has entered the chronic stage can be very destructive, even leading to disability of the individual. The greatest risk in this aspect is caused by psychosomatic abnormalities, when a disorder of the nervous system still has a significant impact on the functioning of the body's systems. The range of diseases was described above, and it is quite wide: strokes, heart attacks, heart failure, asthma, asthma attacks, reduced immunity and high susceptibility to infections, hormonal disorders up to anorexia or bulimia, chondrosis of varying severity, and so on.
On the psychopathic side, the disorder can:
- Lead to loss of levels of performance and concentration, as well as deterioration of memory properties and decreased mental activity. In other words, in neurosis a person loses his former resourcefulness and becomes unable to perform hitherto familiar tasks. It is important to note that decreased performance can also be affected by lack of sleep and lack of proper rest.
- The next problem associated with this disorder is difficulties in communicating with family, friends, and colleagues. The patient's destructive personality traits become aggravated, leading to conflicts. For example, excessive emotionality, inappropriate stubbornness, hyper touchiness, suspicion.
- Neurosis also provokes obsessive states: fears, phobias, negative memories. In an advanced stage, the development of paranoid syndrome is possible. The patient begins to double-check everything many times: whether the iron is turned off, whether the door is locked, whether he is being followed, etc.
Timely professional treatment of a complex condition and properly selected therapy can completely relieve a person of the symptoms described in this article.
Causes
The formation of neurotic disorders is provoked by the influence of many factors. This may be a short-term reactor or chronic stress. Currently, there are two main causes of neuroses:
- insufficient functionality of the body's neurotransmitter and neurophysiological systems, which leads to a pronounced response to stress;
- mental characteristics, personality type and relationships with other people.
- The most common causes for the development of neurological disorders are:
- long-term illnesses, especially those accompanied by intoxication;
- addiction to drinking alcohol or smoking tobacco;
- chronic or acute stress: death or serious illness of a loved one, divorce, dismissal;
- mental overload;
- influence of family and others. Children adopt the habits and behavior of their parents; if the mother or father behaves aggressively, there is a high probability of neurotic disorders in the child.
Which doctor should I contact?
Depending on the stage and symptoms, different specialists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of neurotic disorder. A team of specialists is involved in restoring the activity of the nervous system weakened by the disease: psychologists, neurologists, endocrinologists; in certain cases, the help of a psychotherapist or psychiatrist is necessary. As for the harmonization of the mental state, this problem lies in the field of activity of the psychotherapist and psychiatrist. There are also related specializations, such as, for example, psychoneurologist; this specialist combines the knowledge and techniques of a psychologist and a neurologist, which allows him to work simultaneously in several areas.
What is the diagnosis based on?
The diagnosis is made by a neurologist or psychiatrist. The specialist interviews and examines the patient and conducts a psychological examination.
It is very important to exclude somatic diseases when diagnosing neurosis, because many of its symptoms are similar to manifestations of pathologies of internal organs. For this, the patient is prescribed a series of laboratory and instrumental examinations: ultrasound, X-ray, CT, MRI, vascular examination, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
After excluding such diseases, differential diagnosis is carried out with other mental illnesses: psychopathy, schizophrenia, manic-depressive disorder. An important assessment criterion is the person’s awareness of his illness and the desire to get rid of it.