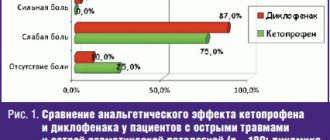
Artrosilene, 1 pc., 50 g, 5%, gel for external use
Capsules
Suction.
When administered orally, ketoprofen is quite completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and its bioavailability exceeds 80%. Cmax in plasma when taking Artrosilene capsules is observed 4–10 hours after oral administration, its value directly depends on the dose taken and is 3–9 μg/ml. T1/2 is 6.5 hours. The maximum therapeutic effect is observed over a period of 4 to 24 hours. Food helps to reduce Cmax values and increase Tmax without changing AUC.
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd - 0.1–0.2 l/kg. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolism.
Ketoprofen is primarily metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form esters with glucuronic acid.
Excretion.
Metabolites are excreted in the urine. Less than 1% is excreted in feces. The drug does not accumulate.
Solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
Tmax for parenteral administration is 20–30 minutes. The effective concentration lasts 24 hours. Therapeutic concentration in synovial fluid lasts 18–20 hours.
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd - 0.1–0.2 l/kg. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolized by microsomal liver enzymes. Excreted by the kidneys, 60–80% in the form of glucuronide in 24 hours.
Suppositories
Suction.
Ketoprofen lysine salt is rapidly absorbed: Tmax after rectal administration is 45–60 minutes. The plasma concentration depends linearly on the dose taken.
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd - 0.1–0.2 l/kg. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolism.
Ketoprofen is primarily metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form esters with glucuronic acid.
Excretion.
Metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine (up to 76% after 24 hours). The drug does not accumulate.
Gel, aerosol
When applied cutaneously, it is absorbed slowly; a dose of 50–150 mg over 5–8 hours produces a plasma concentration level of 0.08–0.15 mcg/ml. Practically does not accumulate in the body. Bioavailability is about 5%.
Artrosilene gel for external use 5% tubes 50g
Compound
Active substance: ketoprofen lysine (ketoprofen lysine salt) - 5 g. Excipients: carbomer - 1 g, trolamine - 1.9 g, polysorbate 80 - 0.8 g, ethanol 96% - 5 g, methyl parahydroxybenzoate - 0.1 g, lavender-nerolium flavor - 0.2 g, purified water - 86 ml.
Pharmacokinetics
Ketoprofen is absorbed very slowly and practically does not accumulate in the body. Bioavailability is 5%. Ketoprofen penetrates into the subcutaneous tissue, ligaments and muscles, synovial fluid and reaches therapeutic concentrations there. The concentration of the drug in the blood plasma is extremely low. Ketoprofen is metabolized in the liver to form conjugates, which are mainly excreted in the urine. Ketoprofen is characterized by slow excretion in urine.
Indications for use
Symptomatic treatment of painful and inflammatory processes of various origins, including:
- rheumatoid arthritis and periarthritis;
- ankylosing spondylitis (ankylosing spondylitis);
- psoriatic arthritis;
- reactive arthritis (Reiter's syndrome);
- osteoarthritis of various localizations;
- tendonitis, bursitis;
- myalgia;
- neuralgia;
- radiculitis;
- injuries of the musculoskeletal system (including sports), bruises of muscles and ligaments, sprains, ruptures of ligaments and muscle tendons.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to ketoprofen;
- hypersensitivity to salicylates, tiaprofenic acid or other NSAIDs, fenofibrate, UV blockers, fragrances;
- violation of the integrity of the skin (eczema, weeping dermatitis, open or infected wound);
- indications in the anamnesis of attacks of bronchial asthma caused by taking NSAIDs and salicylates;
- history of photosensitivity reactions;
- exposure to sunlight, incl. indirect sunlight and UV irradiation in a solarium throughout the entire treatment period and for another 2 weeks after stopping treatment;
- III trimester of pregnancy; children under 15 years of age.
Carefully
Impaired liver and/or kidney function, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, blood diseases, bronchial asthma, chronic heart failure.
Directions for use and doses
Externally.
Use 1-1.5 g of the drug (the volume of cherries) once. The drug is applied to the surface of the skin 2 times a day in accordance with the size of the treated area and the doctor’s instructions, gently rubbing until completely absorbed. With iontophoresis, the drug is applied to the negative pole.
The dosage in children aged 6 to 12 years corresponds to that in adults and depends on the area of application and the doctor’s recommendations.
Duration of treatment - the drug is used for both acute and chronic diseases for a period varying from a few days to 3-4 weeks.
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Best before date
3 years. Do not use the drug after the date indicated on the package.
special instructions
It is necessary to avoid contact of this product with the eyes, the skin around the eyes, and mucous membranes.
Ketoprofen can be used externally in combination with oral administration. The total daily dose, regardless of the dosage form, should not exceed 200 mg.
To reduce the risk of developing photosensitivity, it is recommended to protect skin areas treated with ketoprofen with clothing from exposure to ultraviolet radiation throughout the entire treatment period and for another 2 weeks after stopping use of the gel.
Do not use as occlusive dressings.
Description
NSAIDs for external use.
Dosage form
The gel for external use is transparent, light yellow in color, with a characteristic odor.
Use in children
Contraindication: children under 15 years of age.
Pharmacodynamics
NSAIDs. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-edema effects. Inhibits the activity of COX, which leads to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. In addition, ketoprofen inhibits lipoxygenase, bradykinin synthesis, stabilizes lysosomal membranes and prevents the release of enzymes involved in the inflammatory process.
Ketoprofen does not have a negative effect on the condition of articular cartilage.
Side effects
Allergic reactions: very rarely - angioedema, anaphylaxis.
From the skin and subcutaneous fat: infrequently - erythema, itching, burning, eczema, mild transient dermatitis; rarely - urticaria, rash, photosensitivity, bullous dermatitis, purpura, erythema multiforme, lichenoid dermatitis, skin necrosis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome; very rarely - a single case of severe contact dermatitis (due to poor hygiene and insolation), a single case of severe generalized photodermatitis, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
From the respiratory system: very rarely - asthmatic attacks (as a variant of an allergic reaction).
From the urinary system: very rarely - deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic renal failure.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Use is contraindicated in the third trimester of pregnancy. Use in the first and second trimesters is possible in cases where the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the potential risk for the fetus.
Use during lactation (breastfeeding) is not recommended.
Interaction
- Since the concentration of ketoprofen in the blood plasma is extremely low, symptoms of interaction with other drugs (similar symptoms with systemic use) are possible only with frequent and prolonged use.
- The simultaneous use of other topical products containing ketoprofen or other NSAIDs is not recommended.
- Simultaneous administration of acetylsalicylic acid reduces the degree of binding of ketoprofen to plasma proteins.
- Ketoprofen reduces the excretion of methotrexate and increases its toxicity.
- Patients taking coumarin-containing anticoagulant drugs are advised to undergo treatment under medical supervision.
Overdose
The extremely low systemic absorption of the active components of the drug when used externally makes overdose almost impossible. If large quantities of gel (more than 20 g) are accidentally ingested, systemic adverse reactions characteristic of NSAIDs may occur. It is necessary to lavage the stomach and take activated charcoal.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no data on the negative effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially hazardous activities that require concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Artrosilene gel for external use 5%, 50 g
Manufacturer
Doppel Pharmaceuticals, Italy
Compound
1 g of gel contains ketoprofen lysine salt 50 mg
pharmachologic effect
It has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. By inhibiting COX-1 and -2, it inhibits the synthesis of PG. It has anti-bradykinin activity, stabilizes lysosomal membranes and delays the release of enzymes from them that contribute to tissue destruction during chronic inflammation. Reduces the release of cytokines, inhibits the activity of neutrophils.
Reduces morning stiffness and swelling of joints, increases range of motion.
Ketoprofen lysine salt, unlike ketoprofen, is a rapidly soluble molecule with a neutral pH and is almost non-irritating to the gastrointestinal tract.
When applied topically, it has local anti-inflammatory, antiexudative and analgesic effects. In the form of a spray or gel, it provides a local therapeutic effect on affected joints, tendons, ligaments, and muscles.
In case of articular syndrome, it causes a decrease in joint pain at rest and during movement, a decrease in morning stiffness and swelling of the joints. The lysine salt of ketoprofen does not have a catabolic effect on articular cartilage.
Indications
- Diseases of the musculoskeletal system (including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis of peripheral joints and spine, rheumatic lesions of soft tissues).
- Muscle pain of rheumatic and non-rheumatic origin.
- Traumatic injuries of soft tissues.
- Weeping dermatoses.
- Eczema.
- Violation of the integrity of the skin.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Cannot be used in the third trimester of pregnancy.
There is no experience with the use of Artrosilene during lactation.
Use in the first and second trimesters is possible only after consultation with a doctor.
Contraindicated for children under 6 years of age.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity, incl. to other NSAIDs.
- Aspirin asthma.
- Lactation period.
- Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase, peptic ulcer.
- Ulcerative colitis in the acute phase.
- Crohn's disease.
- Diverticulitis.
- Hemophilia and other blood clotting disorders.
- Chronic renal failure.
- Weeping dermatoses.
- Eczema.
- Violation of the integrity of the skin.
Side effects
From the gastrointestinal tract: abdominal pain, diarrhea, stomatitis, esophagitis, gastritis, duodenitis, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, hematomesis, melena.
From the liver: increased bilirubin levels, increased activity of liver enzymes, hepatitis, liver failure, increased liver size.
From the nervous system: dizziness, hyperkinesia, tremor, vertigo, mood swings, anxiety, hallucinations, irritability, general malaise.
From the senses: conjunctivitis, visual impairment.
From the skin: urticaria, angioedema, erythematous exanthema, itching, maculopapular exanthema, increased sweating, exudative erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
From the genitourinary system: painful urination, cystitis, edema, hematuria, menstrual irregularities.
From the hematopoietic organs: leukocytopenia, leukocytosis, lymphangitis, decreased PV, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, enlarged spleen, vasculitis.
From the respiratory system: bronchospasm, dyspnea, sensation of laryngeal spasm, laryngospasm, laryngeal edema, rhinitis.
From the cardiovascular system: hypertension, hypotension, tachycardia, chest pain, syncope, peripheral edema, pallor.
Allergic reactions: anaphylactoid reactions, swelling of the oral mucosa, pharyngeal edema, periorbital edema.
Interaction
Inducers of microsomal oxidation in the liver (phenytoin, ethanol, barbiturates, flumecinol, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants), when used simultaneously with the drug Artrosilene, increase the metabolism of ketoprofen (increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites).
During simultaneous use with the drug Artrosilene, the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs decreases, the effect of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, fibrinolytics, ethanol, and the side effects of mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and estrogens are enhanced; the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs and diuretics decreases.
The simultaneous use of the drug Artrosilene with other NSAIDs, corticosteroids, ethanol, corticotropin can lead to the formation of ulcers and the development of gastrointestinal bleeding, increasing the risk of developing renal dysfunction.
The simultaneous administration of Artrosilene with oral anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, antiplatelet agents, cefoperazone, cefamandole and cefotetan increases the risk of bleeding.
The drug Artrosilene, when used simultaneously, enhances the hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs (dose recalculation is necessary).
The combined administration of Artrosilene with sodium valproate causes a violation of platelet aggregation.
Ketoprofen, when used simultaneously, increases the plasma concentration of verapamil and nifedipine, lithium, and methotrexate.
Antacids and cholestyramine, when taken orally with Artrosilene, reduce the absorption of ketoprofen.
How to take, course of administration and dosage
A single dose of gel is 3–5 g (the volume of a large cherry), an aerosol is 1–2 g (the volume of a walnut).
Depending on the size of the damaged area, the drug should be applied 2-3 times a day or as prescribed by the doctor, gently rubbing until completely absorbed.
With iontophoresis, the drug is applied to the negative pole.
The duration of treatment without consulting a doctor should not exceed 10 days.
Overdose
Currently, no cases of overdose with Artrosilene have been reported.
Special instructions
The drug should be applied only to intact skin. Avoid contact with eyes and mucous membranes.
To avoid hypersensitivity and photosensitivity, it is recommended to avoid exposure of the skin to sunlight during the course of treatment.
Release form
Gel
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Best before date
3 years
Active substance
Ketoprofen
Dosage form
gel for external use
Purpose
For adults, Children over 6 years old, Pregnant women in the 1st and 2nd trimester as prescribed by a doctor
Indications
Arthrosis, Gout, Myositis, Sciatica, Bruises, Arthritis, Swelling after injuries and operations, Bursitis, Rheumatoid arthritis, Osteochondrosis, Lumbago, Osteoarthritis, Trigeminal neuralgia
Barcode and weight
Barcode: 8024825000139 Weight: 0.069 kg
Artrosilene, 5%, gel for external use, 50 g, 1 pc.
Capsules
Suction.
When administered orally, ketoprofen is quite completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and its bioavailability exceeds 80%. Cmax in plasma when taking Artrosilene capsules is observed 4–10 hours after oral administration, its value directly depends on the dose taken and is 3–9 μg/ml. T1/2 is 6.5 hours. The maximum therapeutic effect is observed over a period of 4 to 24 hours. Food helps to reduce Cmax values and increase Tmax without changing AUC.
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd - 0.1–0.2 l/kg. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolism.
Ketoprofen is primarily metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form esters with glucuronic acid.
Excretion.
Metabolites are excreted in the urine. Less than 1% is excreted in feces. The drug does not accumulate.
Solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
Tmax for parenteral administration is 20–30 minutes. The effective concentration lasts 24 hours. Therapeutic concentration in synovial fluid lasts 18–20 hours.
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd - 0.1–0.2 l/kg. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolized by microsomal liver enzymes. Excreted by the kidneys, 60–80% in the form of glucuronide in 24 hours.
Suppositories
Suction.
Ketoprofen lysine salt is rapidly absorbed: Tmax after rectal administration is 45–60 minutes. The plasma concentration depends linearly on the dose taken.
Distribution.
Up to 99% of absorbed ketoprofen is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Vd - 0.1–0.2 l/kg. Easily penetrates histohematic barriers and is distributed in tissues and organs. Ketoprofen penetrates well into synovial fluid and connective tissue. Although the concentration of ketoprofen in synovial fluid is slightly lower than in plasma, it is more stable (lasts up to 30 hours).
Metabolism.
Ketoprofen is primarily metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes glucuronidation to form esters with glucuronic acid.
Excretion.
Metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine (up to 76% after 24 hours). The drug does not accumulate.
Gel, aerosol
When applied cutaneously, it is absorbed slowly; a dose of 50–150 mg over 5–8 hours produces a plasma concentration level of 0.08–0.15 mcg/ml. Practically does not accumulate in the body. Bioavailability is about 5%.