What is caffeine?
Caffeine is a substance that is found naturally in the leaves and seeds of many plants.
Man also learned to create an artificial analogue, the formula of which is C8H10N4O2, and use it in food. Caffeine has medicinal properties and is used as a stimulant of the central nervous system, causing increased activity. Most people respond to this substance with increased energy and improved mood.
Caffeine is found in tea, coffee, chocolate, various soft drinks, and is also part of painkillers. Natural caffeine has a bitter taste, but in many products this bitterness is masked by processing.
Content:
- What is caffeine?
- Metabolism
- Effect on the body
- Caffeine overdose
- How does it get into the blood?
- Caffeine and pregnancy
- Effect on the stomach
- Side effects
- Harmful properties
- Effects of quitting caffeine
- How to safely quit caffeine
- Benefit for health
- Invigorating springs
The main sources of this substance for teenagers are energy drinks and other soft drinks. Their “work” is noticeable, as a rule, for 6 hours. True, sensitivity to caffeine is an individual indicator. Typically, the younger the person, the less of the substance is needed to feel its effects. Individuals who regularly consume caffeinated beverages become less sensitive to this energizing component over time. This means that they will need to increase the dose again and again to achieve the effect.
Best Caffeine Supplements
In most cases, caffeine is part of a comprehensive supplement. But this can be a disadvantage if you only need to use caffeine to stimulate performance. Also, supplements that contain only caffeine are significantly less expensive, which has financial benefits.
Among the popular and high-quality caffeine supplements, it is worth highlighting:
- Scitec Nutrition Caffeine is a great supplement that can be used for any purpose. It can be used both in sports and to gain vigor and improve mental performance. The dosage per capsule is 100 mg, which may not be enough for heavy training;
- Olimp's Caffeine Kick is a powerful supplement that rivals fat burners and pre-workout supplements. Contains 300 mg of caffeine, which is enough to stimulate activity even for professional athletes.
Metabolism
Once in the body, caffeine is metabolized into dimethylxanthine derivatives (paraxanthine, theobromine, theophylline), then into monoxanthine, and then into the xanthine molecule. Other metabolic products are di- and trimethyl allantoin, uric acid and uracil derivatives.
Caffeine is easily distributed in plasma, intercellular fluid and inside cells. It also circulates in extracellular adipose tissue. By the way, people who smoke metabolize caffeine faster. Also, differences in the speed of the process may occur among people of different nationalities, which is explained by a genetic factor. But there is practically no difference in the rate of absorption between women and men.
Our body is able to absorb these “energizing molecules” quite quickly. But it also quickly gets rid of them. Caffeine is metabolized primarily by the liver and has a relatively short half-life. Usually 5-7 hours are enough to get rid of half of the resulting substance. For this reason, the cup of coffee you enjoyed before lunch will definitely not prevent you from falling asleep in the evening.
Caffeine can be synthetic or natural (obtained from plants). It is possible to determine the difference between them only in the laboratory. The concentration of any of these substances in the body can be measured by examining saliva, since this substance accumulates primarily in liquids in the body. Caffeine can enter the body through the mucous membranes of the cheeks. Chewing gum containing the substance is characterized by faster absorption compared to drinking coffee, since in the form of a drink, caffeine must first pass through the stomach and intestines, and only then enters the blood.
Effect on the body
Caffeine is a product of plant origin, the highest concentration of which is found in coffee beans, tea leaves, soft drinks, chocolate, and cocoa beans.
Also found in some medications (painkillers, allergies, colds and weight loss). In fact, from a chemical point of view, caffeine is a pain reliever and also a substance that enhances the effects of other pain-relieving drugs.
Modern data on caffeine is very contradictory regarding its beneficial and negative effects on the human body.
It is believed that for healthy people, 300 mg of an invigorating substance per day is a normal portion that is not harmful to health. Meanwhile, in some cases it is important to limit the consumption of the substance. Large portions (more than 700 mg per day) help remove calcium and magnesium from the body. It was previously believed that caffeine was one of the causes of osteoporosis. Meanwhile, recent studies have shown that calcium losses caused by caffeine from 1 cup of coffee can be easily compensated for by 2 tablespoons of milk. But in people who are especially sensitive to even minor calcium losses, caffeine can actually cause bone problems. For this reason, women after menopause should not abuse caffeine-containing products, since they are already at risk of developing osteoporosis.
It also acts on the body as a mild diuretic. But again, don't worry that foods containing this substance can cause dehydration.
When talking about caffeine, many people think of coffee first. But this is far from the only source of the substance. Tea, cola and other drinks also contain caffeine. And this explains why, according to research, children aged 6-9 years consume approximately 25 mg of the energizing substance daily, and their parents may not even realize it. Meanwhile, children sensitive to it develop irritability and anxiety.
Caffeine acts as a stimulant, affecting the central nervous system. In the body, this substance begins to act approximately 15 minutes after administration and this effect lasts up to 6 hours.
Application in sports
In sports, caffeine is considered one of the most consumed additives. It is contained in all complexes that are aimed at stimulating physical and mental activity. It is the basis for all fat burners, pre-workout complexes, and is also included in some amino acid supplements to increase vigor and energy.
In the sports industry, caffeine sodium benzoate is most often used; it is more useful and does not harm the gastrointestinal tract, like liquid drinks. Average dosages are from 120 to 350 mg. It is not recommended to take supplements that contain more than 350 mg of the substance; they can cause significant consequences from the cardiovascular system, insomnia and other negative effects.
Caffeine overdose
Consuming moderate doses (up to 250 mg of brewed coffee or 500 mg of cola) helps people concentrate and relieve drowsiness. But higher doses increase heart rate, raise body temperature, increase blood flow to the skin and extremities, increase blood pressure and blood sugar levels, and also stimulate the secretion of stomach acid, acting as a diuretic.
With excessive consumption of the substance, people may experience dizziness, hypoglycemia, nausea, rapid breathing and heart rate, confusion, irritability, insomnia, changes in appetite, dry mouth and other side effects. But contrary to popular belief, caffeine cannot neutralize alcohol in the body.
How does it get into the blood?
Once in the body, caffeine is absorbed in the intestines by almost 99%. And the concentration of the substance in the body can reach up to 10 mg per 1 kg of weight. The entire absorption process occurs within approximately 45 minutes after ingestion, and caffeine reaches its peak level in the blood within 15-20 minutes. But these are rough estimates, since in each case the rate of absorption of substances depends on physiology and the source. Caffeine is absorbed slowest from chocolate and cola, while caffeine from coffee drinks and substances in tablet form is absorbed faster. But still, it is absorbed most quickly from chewing gum - through the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
Contents in green and black tea
Caffeine in tea is present along with tannin. When brewing a drink, the substance is not released entirely, so the drink has a gentler effect on the body. Tannin prevents the psychostimulant from being quickly absorbed and promotes its rapid elimination.
Black tea contains approximately 70 mg of alkaloid per 200 ml. Green tea contains more psychostimulants, containing approximately 85 mg per cup.
One cup of jasmine green tea contains 60-70 mg of caffeine.
The amount of alkaloid in tea depends on:
- From the type of tea
- Growing conditions
- From flavoring additives
Side effects
Consuming caffeine in moderate doses generally does not have any harmful side effects on the body. Although some researchers convince that regular consumption of 100 mg of coffee daily can subsequently cause infertility, heartburn and intestinal dysfunction.
Consuming high doses of caffeine deprives you of sleep, and a person stops noticing the body's signals about the need for rest. Meanwhile, it is important to understand that caffeine does not replenish energy reserves or prevent emotional fatigue. It simply blocks the body's physiological needs for rest. Over time, this condition leads to the development of depression, causing anxiety, excessive nervousness, sweating and tremors.
Caffeine Web
An interesting study was conducted by Dr. Mervyn G. Hardinge at the Institute of Public Health at Loma Linda University.
Dr Hardinge studied two species of spiders using large numbers of specimens. He discovered that one of the varieties of spiders weaves a beautiful, symmetrical web of large size. This is what he used for his experiments. Very skillfully, he measured out infinitesimal doses of caffeine, which he injected into the spider’s body with a very thin needle. Each spider received a dose equivalent to two cups of coffee for an adult. Then the webs woven by these spiders were studied. They all turned out to be completely deformed. They were small in size, contained few rays, and had an ugly shape.
Before the caffeine dose, the web contained 30 to 35 concentric rings. The web, woven even 48 hours after the administration of one dose of caffeine, still remained deformed and contained only 12-13 rings. The same picture was observed after 72 hours. Only 96 hours after the injection, the size and shape of the web returned to normal.
Drugs are not a cure for fatigue. The cure is a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and rest.
Harmful properties
Some studies suggest that caffeine may be harmful to your health. Here are some arguments in favor of this.
- Consuming more than 4 cups of coffee per day leads to early death. Research shows that this dose, taken daily, is enough to increase the risk of sudden death by 21%.
- Increases blood pressure. In people suffering from arterial hypertension, after 2 cups of coffee, blood pressure rises over the next 2-3 hours.
- Increases the risk of cardiac diseases at a young age. Drinking 4 cups of coffee daily is enough to quadruple your risk of heart attack.
- Caffeine can trigger the development of gout.
- Provokes the formation of cysts in the mammary glands in women. It is enough to consume 30 mg of coffee per day to increase the chances of fibrocystic mastopathy by one and a half times. And women who drink 500 mg of coffee are 2-3 times more at risk of cystitis.
- Causes urinary incontinence. People who consume the drink regularly and in large doses are 70% more likely to experience incontinence than others.
- Causes insomnia.
- Causes stomach upset. Especially if you drink coffee on an empty stomach.
- Excessive caffeine consumption provokes headaches.
- Caffeine leads to impaired fertility in women: the chances of getting pregnant are reduced by 27%.
- The risk of miscarriages increases: it is enough to drink 2 servings of coffee daily for several weeks before conception.
- It worsens the health of diabetics because it disrupts glucose metabolism.
- May cause overdose or allergy symptoms.
- Accelerates heart contraction.
- Exacerbates the symptoms of menopause.
- Increases anxiety and depression.
- Caffeine lovers consume more glucose, which is fraught with obesity and diabetes.
- It suppresses collagen production in the skin.
- Makes bone tissue more fragile, which increases the risk of fractures.
Antioxidant action
Free radicals are substances formed as a result of unfavorable environmental factors affecting humans (ultraviolet radiation, high temperatures, radiation), which are characterized by strong chemical activity, enter into unwanted interactions, and cause damage or cell death. The ability of radicals to act on DNA (genetic material) leads to its breakdown and the development of tumors.
Caffeine has powerful antiradical properties - it removes hydroxyl compounds, modulates the synthesis of nitric oxide in cells, while reducing the damaging effects of radicals. Moreover, the caffeine-free drink contains the same amount of antioxidants.
Drinking antioxidant-rich coffee daily reduces the risk of developing:
Effects of quitting caffeine
People who stop drinking caffeinated drinks may experience discomfort and deterioration in the first 12-24 hours. Typically, the first side effects of caffeine withdrawal include headaches, irritability, nausea, nervousness, and muscle tension. But these symptoms last no longer than a week. Then the body finally adapts to a new way of life.
In order to avoid side effects, experienced people advise switching to a caffeine-free life gradually - reducing the amount of substance consumed every day.
How to safely quit caffeine
Try drinking plain water instead of cola first. Stick to this principle for a week. Have your caffeine cravings decreased? This means that the “treatment” must be continued. Now is the time to replace traditional coffee with a similar decaffeinated drink. It is also important to track portions of food consumption. Continue until your daily caffeine dose drops to 100 mg or less. Gradually giving up caffeine-containing drinks will protect you from unpleasant physiological sensations and will also be less “painful” on a psychological level.
Without caffeine, do you feel tired? Make sure you are getting enough rest per day? Better yet, check the vitamin and mineral balance in the body? Drowsiness and chronic fatigue may indicate vitamin deficiency or other health problems. But caffeine does not cure this.
Substance abuse
The effects of caffeine determine a person's psychological need for daily intake.
Chronic intoxication is the main reason for the formation of substance abuse. In severe cases, it resembles amphetamine addiction, but, fortunately, it occurs much more easily without life-threatening consequences. As the period of abuse increases, household stimulants no longer provide such a euphoric effect. Most addicts develop tolerance; daily doses of the substance can reach 500-1000 mg. For the development of substance abuse, the patient’s personality traits play an important role.
Stopping stimulants leads to withdrawal symptoms. During withdrawal (“withdrawal”), signs of nervous exhaustion come to the fore: unbearable fatigue, apathy, irritability. Often the mood decreases to the point of depression. Using the substance slightly alleviates the painful condition, which confirms the fact of addiction.
Benefit for health
People who regularly consume caffeine (in adequate doses) report improved concentration and cognitive function. For some people it is a remedy for headaches.
According to some data, it can reduce the risk of Parkinson's disease, liver disease, dementia, and type 2 diabetes. But despite the possible positive effects, do not forget that consuming this substance in large doses can have adverse effects.
In addition, caffeine tablets serve as a cure for migraines. Take 1-2 tablets for a week, and then 1 tablet for a month. It also has benefits for bodybuilders, as it helps increase performance by almost 20%. Bodybuilders consume approximately 3 mg of the substance for every kilogram of body weight half an hour before a planned workout.
By the way, depression of the central nervous system, decreased activity (physical and mental), a state close to loss of consciousness, cerebral vascular spasms (migraine), hypotension and asthma can also be reasons to drink a cup of coffee or a tablet containing caffeine. Even infants are also prescribed this substance as a medicine for certain diseases.
Advantages:
- Reduces pain. Two cups of coffee can reduce post-workout pain by 48%.
- Source of fiber. Two cups of brewed coffee provides 1.8 g of fiber.
- Protection against diabetes. Coffee drinkers (1 cup per day) have a 9% lower risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Immunity from Alzheimer's. There is an assumption that caffeine can protect against the development of Alzheimer's disease.
- Cure for depression. A 10-year study involving 86 thousand women showed that coffee drinkers were 20% less likely to suffer from depression.
- Protection against Parkinson's. Researchers from Sweden claim that caffeine reduces the chances of developing Parkinson's disease. Incredibly, scientists suggest that this substance can even affect the genetic factor.
- Protection against cardiac diseases. This generally sounds like science fiction, since traditional medicine prohibits people with heart problems from consuming caffeine. But Korean researchers say 3 cups of coffee a day improves health and reduces the chances of heart disease.
- Stronger DNA. The European Journal of Nutrition once reported that the DNA of coffee drinkers is more stable and without damage. They say that this is again due to caffeine.
- Less chance of multiple sclerosis – 4 cups of caffeinated beverage per day can protect against multiple sclerosis, preventing neuronal damage that causes the disease. At least that's what researchers from Sweden think.
- Reduces the risk of cancer. Moderate caffeine consumption reduces the risk of colon cancer by 26%. This was stated by scientists from California after a study involving 5,100 people. And another group of scientists from a cancer center in Southern California noticed that coffee drinkers were 29% less likely to get liver cancer.
- No gout. A study involving more than 50 thousand people allowed scientists to conclude that coffee protects men from gout. It is believed that this is the “work” of caffeine. Although no one can give a 100% guarantee of this yet. Moreover, there is a completely opposite opinion that it is precisely this that causes gout.
In addition, some experiments have shown that caffeine can stimulate sexual desire in women, protect against early death (according to Japanese scientists), prevent tooth decay, retinal damage and even melanoma.
Caffeine: how much and where?
The problem of energy drink consumption is a constant topic in the media and in the medical community. A number of food industry specialists, doctors and commodity producers turned to the National Consumer Protection Fund with a request to look into this problem at an independent expert level.
Tea and coffee are the main sources of caffeine
The National Fund for the Support of Manufacturers decided to create a working group to implement the expert-analytical project “Analysis of the risks of consuming caffeine-containing food products presented on the Russian consumer market.”
The products were tested by authoritative specialists from VTsIOM and the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. Among other things, samples of non-alcoholic tonic drinks from the most famous brands were analyzed and evaluated.
Today, the caffeine content in so-called “energy” drinks is most strictly regulated and controlled, experts say. At the same time, other segments of caffeine-containing drinks are not regulated or standardized by the state to the proper extent. However, expertise suggests that the main sources of caffeine in food products are tea and coffee.
According to scientists from the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, caffeine contained in food products, drinks and medicines should be considered as a source of risks that must be assessed and taken into account.
During the study, various methods were used, including analytical chemistry (high-performance liquid chromatography), computational and statistical methods of analysis. Please note that the study was conducted using data available as of November 2013.
Where is there more caffeine?
The selection of product samples was carried out by a commission of the fund with the involvement of specialists from interested parties. The collected samples were delivered to the accredited laboratory of the Research Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, where they were handed over to authorized persons for examination under an agreement with the foundation.
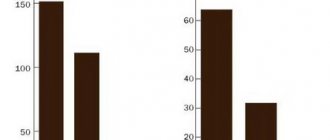
In accordance with the results obtained, the highest caffeine content of all the presented types of food products was found in coffee samples. Depending on the type and manufacturer, the spread of the data obtained ranged from 272 mg/l, that is, slightly more than in some types of tea, to 3105 mg/l.
Thus, latte coffee can contain 272-398 mg/kg of caffeine, and black tea can contain 244-301 mg/kg. But at the same time: Such a “heavyweight” as espresso can contain 1295-3105 mg/kg, and mate tea – only 92 mg/kg.
In general, the caffeine content in the tea samples ranged from 58 mg/L to 301 mg/L. In cocoa and hot chocolate from 37 mg/l. up to 397 mg/l.
The level of caffeine in chocolate depended on its type, milk content and other components. The amount of caffeine ranged from 103 mg/kg in milk chocolate with whole hazelnuts to 665 mg/kg in dark chocolate. You need to understand that the caffeine content in the same dark chocolate, but from different manufacturers, may vary.
Energy drinks contained the least amount of caffeine in the results. The highest caffeine content in energy drinks is 321 mg/l, and the lowest is 218.6 mg/l.
The caffeine content of the most popular carbonated soft drinks ranged from 87 mg/L to 130 mg/L.
Experts: safe level has definitely been exceeded
In parallel with determining the caffeine content in various caffeine-containing food products, at the request of the National Fund for Consumer Protection, VTsIOM conducted a survey of consumers in 131 localities in 46 constituent entities of the Russian Federation, in order to study the structure, levels and sources of caffeine consumption in the diet of certain categories of the population of the Russian Federation.
The survey involved 3,600 consumers, including 1,600 adult respondents aged 18-44 years and 2,000 teenage respondents aged 12-17 years.
As expected, tea became the most consumed caffeine-containing product among Russians. This drink is consumed by 95% of adults and 98% of adolescents aged 12-17 years. The lowest share of consumers (both adults and teenagers) is for energy drinks: 23% are teenagers 12-17 years old, 20% are adults.
The average Russian teenager (12-17 years old) drinks 916 servings of tea, 236 servings of coffee, 96 servings of cola drinks, 26 servings of energy drinks (250 ml can), consumes 103 servings of chocolate and 9 tablets of caffeine-containing medications per year.
Contrary to popular belief, the average consumption levels of energy drinks (by both adolescents and adult consumers) are noticeably lower than the consumption levels of other caffeine-containing products, experts emphasize.
The safe daily level of caffeine consumption recommended by Russian hygiene standards is 150 mg per day. As shown by the results of the analysis of caffeinated drinks, this amount of caffeine is contained in approximately two consumer servings of energy drinks (250 ml can) and two servings of coffee (medium cup).
Less than 1% of teenagers (0.6% to be exact) consume energy drinks in quantities exceeding the safe level of 2 servings (1 serving is a 250 ml can) per day. At the same time, 12.4% of teenagers (not to mention 32.4% of adults) consume more than 2 cups of coffee (which contain about 180 mg of caffeine) daily, the study found.
However, it should be noted that total caffeine intake (from all sources) for all population groups significantly exceeds the safe maximum daily intake (150 mg). The overwhelming amount of caffeine in the diet of all categories of the population (both adults and adolescents) comes from coffee and tea (more than 90%).
The average daily level of caffeine consumption in the Russian Federation is: for adults 18-44 years old - 344.9 mg, for adolescents 12-14 years old - 225.8 mg, for adolescents 15-17 years old - 256.6 mg. These levels significantly exceed the maximum level of safe daily caffeine consumption established in the Russian Federation (150 mg), although they are less than the safe level of caffeine consumption (400 mg/day) adopted abroad.
The consumer must be informed
To reduce caffeine consumption, consumers should be more actively informed about the recommended safe daily intake, experts say. It is also necessary to include warning labels such as “High caffeine content”, “Not recommended for children, pregnant women and nursing mothers, and persons sensitive to caffeine” on the labeling of all products containing a high concentration of caffeine, for example, ready-to-drink beverages with a caffeine content above 150 mg/l, packages of all types of dry coffee and tea (except decaffeinated coffee), as well as the corresponding range of menus and layouts of public catering establishments offering such products to consumers.
For reference: Caffeine is one of the most commonly consumed biologically active substances in the world and is found in common beverages (coffee, tea, soft drinks), products containing cocoa or chocolate, tonic (energy) drinks, medications, including analgesics and stimulants sold over-the-counter in dietary supplements and sports nutrition products.
Caffeine has the ability to increase blood pressure. This mainly occurs due to the so-called positive inotropic effect, that is, an increase in the strength and frequency of heart contractions. As a result, systolic blood volume (the amount of blood ejected from the ventricles in one heartbeat) increases. In addition, blood vessels narrow (though not all), which also contributes to an increase in blood pressure. Thus, caffeine has a direct effect on the cardiovascular system and increases the load on the heart.
Therefore, caffeine in large quantities should not be consumed by people suffering from hypertension or other pathologies associated with increased blood pressure. Also, the use of products containing caffeine should be approached with great caution by patients with coronary heart diseases, especially considering the fact that caffeine narrows the coronary vessels (the very vessels that feed the heart muscle and from the spasm of which myocardial infarction occurs). Since caffeine stimulates the production of gastrointestinal juice, you should not abuse drinks based on it (this also includes cocoa, cappuccino and even some types of tea) for patients with hyperacid gastritis and ulcerative processes in the stomach and duodenum. People who have decreased blood clotting should remember that caffeine impairs the aggregation activity (the ability to stick together) of platelets, which is one of the main mechanisms in stopping bleeding.
The vast majority of the adverse effects of caffeine do not occur with chronic caffeine consumption at a dose of about 150-400 mg/day. This assessment is valid for adult men and women of young and middle age. Caffeine consumption at a dose above 400 m g/day. undesirable, since in some cases it can negatively affect the human body, its cardiovascular, genitourinary, nervous systems, and gastrointestinal tract.
Ilya Yurukin
Based on materials from the National Consumer Protection Fund