Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The drug Fibrinolysin is a plasma component of human blood obtained by enzymatic activation of plasma profibrinolysin with trypsin . In clinical practice, it is used in the form of clear, colorless solutions prepared before injections. The activity of fibrinolysin is determined biologically by determining its ability to lyse a standard fresh fibrin at a temperature of 37 ° C for 30 minutes and is expressed in units of action.
Fibrinolysin is a therapeutic agent that counteracts blood clotting . fibrin protein strands , that is, it has an effect similar to a proteolytic enzyme . The maximum effectiveness of the drug is observed with its early use, at the time of the loss of fibrin clots and the formation of blood clots . Further effectiveness decreases in proportion to the time the clot .
Pharmacological properties of the drug Fibrinolysin
fibrinolysin (plasmin) is a component of human blood that is obtained by enzymatic activation of profibrinolysin (plasminogen) in blood plasma with trypsin. Fibrinolysin is a drug that affects blood clotting and is a physiological component of the body's natural anticoagulant system. The mechanism of action of fibrinolysin is associated with its ability to break down fibrin threads (acts as a proteolytic enzyme). The greatest effect is achieved with its early use in the case of pathological processes accompanied by the loss of fibrin clots and the formation of blood clots. The effectiveness of fibrinolysin decreases after thrombus retraction.
Indications for use
For vials:
- thromboembolism of peripheral and pulmonary arteries;
- acute thrombophlebitis;
- thromboembolism of cerebral vessels;
- chronic thrombophlebitis in the acute phase;
- myocardial infarction.
For ampoules:
- hemorrhages in the organs of vision of a traumatic nature (no earlier than 4 days from the time of intraocular trauma );
- hemorrhages in the vitreous body , anterior chamber or retina of the eye ;
- thrombosis of the central ophthalmic vessels (vein/artery) and their branches.
Contraindications
For vials:
- hemorrhagic diathesis ;
- open wounds;
- bleeding;
- pregnancy:
- acute hepatitis ;
- hypersensitivity;
- gastrointestinal ulcer;
- lactation;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- nephritis;
- acute form of pulmonary tuberculosis ;
- fibrinogenopenia;
- childhood;
- radiation sickness;
- history of anaphylactic reactions
- surgery, biopsy, trauma, puncture of large vessels undergone in the recent past (10 days);
- excessively high blood pressure due to brain damage.
For ampoules:
- pregnancy;
- hypersensitivity;
- lactation;
- history of anaphylactic reactions
- childhood;
- contraindications to Dicaine , due to its use before Fibrinolysin.
Contraindications to the use of the drug Fibrinolysin
Hemorrhagic diathesis, bleeding, open wounds, acute hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, nephritis, fibrinogenopenia, acute pulmonary tuberculosis, radiation sickness. A relative contraindication is hypertension (arterial hypertension) with brain damage (systolic blood pressure - 220 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure - 120 mm Hg). At higher blood pressure, fibrinolysin can be prescribed only for health reasons. There are no contraindications for subconjunctival administration.
Side effects
For vials:
- allergic manifestations (including facial flushing fever , urticaria );
- decrease in blood pressure (monitoring required during administration);
- chest and/or abdominal pain;
- bleeding;
- changes/pain at the injection site.
If these symptoms are detected, the injection rate should be reduced, and in case of severe reactions, stop the injection. To relieve side effects, depending on their direction, Promedol , cardiovascular or antihistamines .
For ampoules:
- allergic manifestations (including facial hyperemia local edema , urticaria );
- changes/pain at the injection site.
If these symptoms are detected, the dose of the drug should be reduced, and if reactions are severe, stop using it. To relieve side effects, depending on their direction, Promedol or antihistamines .
Side effects of the drug Fibrinolysin
With intravenous administration, allergic reactions are possible (chills, fever, erythema, urticaria, etc.). Sometimes a decrease in blood pressure may occur, and therefore repeated measurement during infusion is recommended. To eliminate side effects, it is necessary to reduce the rate of fibrinolysin administration, and if the reaction is more pronounced, stop the administration, administer promedol, antihistamines and, if necessary, cardiovascular drugs. With subconjunctival injection of fibrinolysin, short-term pain at the injection site is possible.
Fibrinolysin, instructions for use
For vials:
For thrombosis of cerebral vessels and myocardial infarction, it is advisable to use Fibrinolysin during the first 6 hours; with thrombosis of peripheral arteries for 12 hours; with thrombosis of peripheral veins for 5-7 days, counting from the detection of thrombosis .
Fibrinolysin should be administered by infusion . Immediately before starting the infusion, the contents of the bottle are diluted in a solution of sodium chloride (9%) in a ratio of 100-160 IU per 1 ml of solvent. Then Heparin at the rate of 10,000 units of Heparin per 20,000 units of Fibrinolysin. The start of administration is carried out at a rate of 10-12 drops in 60 seconds. It is possible to increase the speed to 15-20 drops in 60 seconds (with good tolerance). The total daily dosage varies between 20,000-40,000 units, with an infusion of at least 3 hours. It should be remembered that Fibrinolysin does not contain a stabilizer, which is why the prepared solution quickly loses its activity.
After completing the infusion of Fibrinolysin with Heparin , intravenous or intramuscular injections of Heparin at 40,000-60,000 units per 24 hours for 2-3 days, with a consistent reduction in its dosage and a transition to taking indirect anticoagulants .
For ampoules:
Fibrinolysin 300 units is administered exclusively subconjunctivally . To do this, the contents of one ampoule are diluted in 0.5 ml of injection water . The prepared solution should be injected under the conjunctiva of the lower transitional fold or sclera after a preliminary injection of Dicaine (0.5%) into the conjunctival sac for the purpose of anesthesia . Repeated administration procedures are carried out after 24-48 hours. The total number of injections ranges from 3 to 10, depending on the indications.
Instructions for use Tranexam tablets 250 mg 10 pcs
Inside, regardless of food intake.
Short-term treatment of bleeding caused by increased fibrinolysis:
The recommended standard dose of tranexamic acid is 15-25 mg/kg body weight, on average 1000-1500 mg 2-3 times a day.
- For prostatectomy and surgical interventions on the bladder:
1000 mg 6 hours before surgery, then 1000 mg 3-4 times a day until gross hematuria disappears. It is not recommended to use the drug for more than 2 weeks after surgery. - For menorrhagia:
the recommended dose is 1000 mg 3 times a day until menorrhagia stops, but not more than 4 days. In case of profuse bleeding, the dose of the drug can be increased, but the total daily dose should not exceed 4000 mg. Treatment with tranexamic acid should not be started before menstrual bleeding occurs. In clinical studies, tranexamic acid was not used for more than three consecutive menstrual cycles. - For recurrent nosebleeds:
1000 mg 3 times a day for 7 days. - After cervical conization surgery:
1500 mg 3 times a day for 12 days after surgery. - For traumatic hyphema:
1000-1500 mg 3 times a day (target dose 25 mg/kg body weight) for 7 days. - Patients with hemophilia:
the drug is prescribed orally at a dose of 25 mg/kg body weight 2 hours before tooth extraction, and then 1000-1500 mg 3 times a day for 6-8 days. Coagulation factors VIII or IX should be prescribed simultaneously. - For hereditary angioedema:
1000-1500 mg 2-3 times a day. If the patient can foresee an exacerbation of the disease, the drug can be taken intermittently depending on the presence of prodromal symptoms. In other cases, the drug should be taken continuously. - Bleeding during pregnancy:
250-500 mg 3-4 times a day until bleeding stops completely. The average duration of treatment is 7 days.
Use of the drug in special groups of patients
Renal dysfunction
In patients with mild to moderate impairment of renal excretory function, adjustment of the dose and frequency of tranexamic acid administration is necessary:
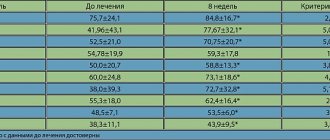
| Serum creatinine concentration | Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) | Tranexamic acid dose | Frequency of reception |
| 120-249 µmol/l (1.36-2.82 mg/dl) | 60-89 ml/min/1.73m2 | 15 mg/kg body weight | 2 times a day |
| 250-500 µmol/l (2.83-5.66 mg/dl) | 30-59 ml/min/1.73m2 | 15 mg/kg body weight | 1 time per day |
Liver dysfunction
In patients with impaired liver function, no dose adjustment is required.
Elderly age
In elderly patients in the absence of renal failure, no dose adjustment is required.
Childhood
Data regarding the effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in children are limited.
In children, tranexamic acid is prescribed at a rate of 25 mg/kg body weight 2-3 times a day.
What to do if you miss a dose
If you miss one dose, you must take the next dose of the drug at the prescribed time. You should not take a double dose of the drug after missing the next dose.
special instructions
For vials:
Therapy should be carried out under close monitoring of blood clotting . Caution must be exercised when treating patients over 70 years of age. Immediately after infusion administration, it is necessary to determine the level of prothrombin (indicators should not decrease by more than 30-40%), blood clotting time (indicators should not more than double), and the amount of fibrinogen (indicators should not be less than 100%).
For ampoules:
Therapy should be carried out under close monitoring of blood clotting . Care must be taken when treating patients after 70 years of age, as well as with hemorrhagic diathesis , open wounds, bleeding, acute hepatitis, gastrointestinal ulcer , liver cirrhosis , nephritis, tuberculosis , fibrinogenopenia, radiation sickness , recent injuries, surgeries, biopsies, punctures of large vessels, excessive blood pressure against the background of brain lesions.
Fibrinolysin analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Biostrepta
Aktilise
Gemaza
Dystreptase
Thrombovazim
Streptokinase
- Dystreptase;
- Aktilise;
- Sigris;
- Streptokinase;
- Metalize;
- Thrombovazim;
- Celiasis;
- Eberkynase;
- Gemaza;
- Tobarpin;
- Biostrepta;
- Elaxim.