The drug Glucose is a very necessary remedy for many patients. First of all, the medicine is necessary as a source of energy necessary to nourish tissues and cells. Cell activity depends on how well the body is able to metabolize the compounds.
First of all, glucose enters the body through consumed food. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, the substance breaks down into simple molecules, which enter the bloodstream and are distributed throughout the body.
There is no need to worry about what dose of a substance is needed, because the excretory system removes excess from the body.
Where does glucose come from?
Blood glucose reserves appear not only from food consumed.
If glucose levels begin to fall, the body will launch mechanisms to break down strategic reserves. Certain enzymes remove glucose molecules from the glycogen chain (stored in the liver) and send them into the bloodstream. Thanks to this process, normal glucose levels are maintained in the body.
It is important to know that after hypoglycemia, sharp jumps in plasma glucose levels often occur, which are very difficult to deal with.
The body also extracts glucose from fat reserves, but this process is lengthy. This method is used during heavy exercise or prolonged fasting.
Usefulness, value for the body
When eating, few people think about the benefits of a certain product. Meanwhile, glucose, this “fast” carbohydrate, is simply necessary for a person. There was once a popular belief that sweets were harmful, but modern research suggests otherwise.
The substance has been assigned the role of the main source of energy and an indispensable participant in metabolic processes.
This is the most important of all carbohydrates for humans, since monosaccharides are completely digestible, easily absorbed in the intestines. Glucose is very nutritious and safe for a healthy body. It is during the oxidation of this substance that energy is released, which is necessary for the functioning of our organs. Glucose is also the only source of energy for brain function. As soon as we eat something sweet, we immediately feel a surge of energy. When oxidized, “fast” carbohydrate releases more than a third of the energy used in the body.
Glucose is so important for the body that the body constantly maintains its amount at the same level. With its deficiency in the blood, a person loses concentration and becomes lethargic. An increase in concentration leads to increased production of the pancreatic hormone - insulin, which reduces its content in the blood. It is important that the delivery of glucose into cells is carried out thanks to insulin, and without it, “fast carbohydrate” does not enter the cell. When the hormone is no longer produced in the required quantities, diabetes develops.
Glucose is an essential unit for the construction of many dietary di- and polysaccharides, such as starch and glycogen. It is polysaccharides that form the basis of cartilage tissue, ligaments and hair. Glycogen is the carbohydrate reserves that the body makes in anticipation of heavy physical activity. It is also part of DNA and RNA, a number of enzymes
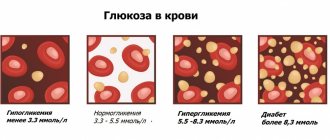
In the body, glucose is found in muscles, blood and in small quantities in all cells. Glucose concentration in the blood of a healthy person: 3.33 -5.55 µmol/l. This is approximately 0.1% to 0.12% of the total. 100 ml of blood contains 80-100 mg of glucose. Its level rises after eating and falls during hunger and physical work. When glucose levels decrease, a pathological condition is formed - hypoglycemia, which is accompanied by agitation, anxiety, muscle tremors, and fainting.
Composition of the drug
One tablet of the drug contains 1 g of glucose monohydrate. The auxiliary ingredients are:
- Calcium stearate
- Potato starch
- Talc
- Stearic acid
Glucose tablets are produced in a round shape, their surface is flat.
If the drug is produced in a “set” with ascorbic acid, a chamfer and a dash are applied to the tablets.
The drug is placed in 10 pieces in blister packs. The cardboard package may contain 1 or 2 blisters and instructions for use.
Chemical composition
Glucose is found in large quantities in fruits and berries.
Glucose is a monosaccharide with a hexose. The composition includes starch, glycogen, cellulose, lactose, sucrose and maltose. Once in the stomach, grape sugar is broken down into fructose.
The crystallized substance is colorless, but with a pronounced sweet taste. Glucose can dissolve in water, especially in zinc chloride and sulfuric acid.
This makes it possible to create medical preparations based on grape sugar to compensate for its deficiency. Compared to fructose and sucrose, this monosaccharide is less sweet.
pharmachologic effect
Glucose (dextrose) belongs to the category of monosaccharides. The substance is found in the juice of various berries (in particular grapes), which is why it is sometimes called grape sugar.
Oligosaccharides and disaccharides consist of glucose units.
Once in the digestive system, complex saccharides break down into fructose and glucose.
Glucose, as a monosaccharide, is found in:
- Lymph
- Blood
- Myocardium
- Skeletal muscles
Glucose is a participant in carbohydrate metabolism and affects metabolism.
Dextrose is necessary for carbohydrate nutrition of muscles and brain; the substance is well and quickly absorbed and helps improve human performance.
Properties
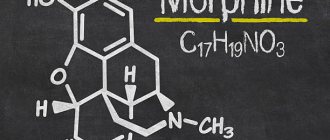
Glucose is a colorless crystalline powder, highly soluble in water, with a sweet taste. The melting point of this substance is 146º C. Formula of glucose: C6H12O6.
Glucose is formed during photosynthesis and is found in all parts of green plants.
Most of it is found in grape juice, which is why this carbohydrate is also called “grape sugar.” There is a lot of it in all ripe berries and fruits. In addition, it is part of regular sugar and honey. Today, the chemical properties of glucose are well studied. It belongs to polyhydric alcohols, and is also classified as a monosaccharide. These are carbohydrates that, when exposed to water (scientifically called hydrolysis), do not break down into simpler molecules.
Based on the rate of decay, they are usually divided into fast (simple) and slow (complex). Glucose is a “fast carbohydrate” because it is absorbed by the body in a short time. Let us add that glycogen is synthesized from glucose. By binding to a substance such as creatine phosphate, glycogen is converted into adenosine triphosphoric acid (ATP), which is the main supplier of energy for cells.
Carbohydrates have been used by humans since ancient times, but only in 1811 the Russian scientist K. Kirchhoff isolated “grape sugar” in its pure form by hydrolysis of starch. By the way, glucose is still produced using this method to this day. The formula for this substance was derived by the Swedish chemist J.Ya. Berzelius in 1837.
Why is Glucose useful?
Glucose is widely used for the treatment of various pathologies, as it has a good effect on metabolic processes.
Pregnant women are prescribed glucose:
- If you suspect that the intrauterine fetus is smaller than the required size
- To reduce the chance of miscarriage
- To prevent premature birth
After consuming glucose, you feel better and fatigue goes away.
During pregnancy and lactation, it is necessary to constantly monitor plasma sugar levels.
Don't forget about the diet
Svetlana Filippovna, could you finally suggest a diet option for people suffering from diabetes?
Diet (one option): For diabetics - 50-60% carbohydrates, 20-25% fats and 15-20% proteins, and carbohydrates are complex carbohydrates (starches), fats only of plant origin (cholesterol control), proteins 1 g per 1 kg of weight – no more (kidney damage) – daily dose. Diabetes is a serious disease, the compensation of which requires regular self-monitoring of sugar at home (self-monitoring). The Center for Human Physical Health (Borisovskie Prudy, 29) can offer a wide range of glucometers and test strips.
Indications for use
The appearance of the pharmaceutical product depends on the manufacturing company and the presence of other components.
Doctors prescribe regular glucose in tablets, as well as its combination with ascorbic acid, for:
- During pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Avitaminosis and hypovitaminosis
- Increased need for vitamin C and glucose
In addition, the medication is necessary for children during periods of intensive growth.
Glucose is excellent for recovery after severe pathology and physical activity.
Contraindications to the use of Glucose
Glucose solution is contraindicated in patients who suffer from:
- hyperglycemia
- decompensated diabetes mellitus
- hyperosmolar coma
- impaired glucose utilization in the postoperative period
- hyperlactic acidemia
Intravenous administration of Glucose is carried out with caution when:
- chronic renal or heart failure
- hyponatremia
- Glucose tablets are contraindicated for:
- diabetes mellitus
- overhydration
- cerebral edema
- pulmonary edema
- circulatory diseases in which there is a high risk of pulmonary or cerebral edema
- acute left ventricular failure
Glucose in ampoules, can I drink it?
Glucose can be taken orally, as its regular solution does not contain substances that can be harmful. The medicinal liquid tastes quite pleasant, reminiscent of ordinary sweet water.
You can drink glucose in ampoules if there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure or if a diabetic has exceeded the dosage of insulin. However, for these problems, it is wiser to drink strong, sweet tea.
In case of poisoning, glucose is often prescribed, but its oral use during intoxication can provoke additional vomiting.
Mode of application
Children over three years of age and adults can take the classic form of the drug, 0.5-1 tablets three times a day. If the doctor considers it necessary to prescribe a combined form of the drug (with ascorbic acid), the dosage must be recalculated, taking into account the content of vitamin C in the tablet. Typically, the dose for treatment varies from 50 to 100 mg per day 3-5 times a day.
For preventive purposes, adult patients are allowed to take up to 100 mg of the drug per day. Children 6-14 years old should not take more than 50 mg of the drug per day.
It is important to understand that the dosage and duration of therapy must be adjusted by the attending physician.
Important tests
What additional studies need to be performed to diagnose diabetes mellitus?
Equally important is the determination of C-peptide. Insulin and C-peptide are the end products of proinsulin conversion in the beta cells of the pancreatic islets. Determination of C-peptide provides control over the functioning of pancreatic beta cells and insulin production. Diagnostically significant is that it is the C-peptide that allows one to assess the level of insulin and more clearly select the required (missing) dose of insulin. If the C-peptide in the blood decreases, this indicates a lack of insulin produced by special cells of the pancreas. Normally, the level of C-peptide is 0.5 - 2.0 μg/l. Currently, much attention is paid to the determination of antibodies to beta cells of the islets of Langerhans, the presence of which leads to the destruction of the cells themselves and disruption of insulin synthesis, which results in the appearance of type 1 diabetes. Autoimmune mechanisms of cell destruction can be hereditary in nature, as well as can be triggered by a number of external factors, such as viral infections, various forms of stress and exposure to toxic substances. Thus, the determination of antibodies to beta cells can be used for early diagnosis and identification of predisposition to type 1 diabetes. Patients with autoantibodies experience a progressive decline in beta cell function and insulin secretion. Antibodies to insulin are found in 35-40% of patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes. Antibodies to insulin can be observed in the stage of prediabetes. An antigen has also been found that represents the main target for autoantibodies associated with the development of insulin-dependent diabetes. This antigen turned out to be glutamic acid decarboxylase (gad), a very informative marker for diagnosing prediabetes. Antibodies to GAD can be detected in a patient 5-7 years before the clinical manifestation of the disease. The following is important: the determination of these markers allows in 97% of cases to differentiate type 1 diabetes from type 2, when the clinical picture of type 1 diabetes is disguised as type 2. And finally, the signal marker of body weight is leptin, which is formed in fat cells. It signals the brain to stop eating and increase energy expenditure. However, this mechanism is disrupted with large excess weight. These people have too many fat cells that secrete leptin, and its levels increase significantly with every extra gram of weight. When there is too much leptin in the blood, it stops playing its signaling function. Always remember that timely diagnosis will allow you to avoid health problems. The clinical and biochemical laboratory of MK CELT performs a wide range of tests, and the modern level of equipment, the qualifications of specialists and the timing of research guarantee high quality and reliability.