Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
Delivery on Sundays and holidays does not work!
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2022 Pharmacy 84.
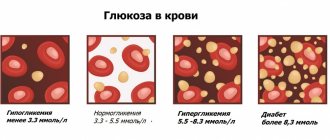
Glucose 5% 200 ml solution for inf.fl.
Instructions for medical use of the drug GLUCOSE Trade name Glucose International nonproprietary name No Dosage form Solution for infusion 5%, 10% 200 ml, 400 ml Composition 1 liter of solution contains the active substance: dextrose monohydrate (glucose, in terms of anhydrous dextrose) – 50 , 0 g or 100.0 g excipients: sodium chloride, 0.1 M hydrochloric acid, water for injection. Osmolality From 266 to 326 mOsm/kg (for a concentration of 5%) From 541 to 662 mOsm/kg (for a concentration of 10%) Description Colorless transparent liquid Pharmacotherapeutic group Plasma replacement and perfusion solutions. Solutions for parenteral nutrition. Carbohydrates. ATC code B05BA03 Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics Absorbed completely by the body, not excreted by the kidneys (appearance in urine is a pathological sign). Pharmacodynamics Glucose enhances redox processes in the body, improves the antitoxic function of the liver, and covers part of the body's energy costs. Infusion of glucose solutions quickly replenishes water deficiency. Entering the tissues, it is phosphorylated, turning into glucose-6-phosphate, which is actively involved in many parts of the body’s metabolism. An isotonic 5% glucose solution has a detoxifying, metabolic effect, restores the volume of circulating blood, and is a source of valuable, easily digestible nutrients. When glucose is metabolized in tissues, a significant amount of energy is released, which is necessary for the functioning of the body. A hypertonic 10% glucose solution increases the osmotic pressure of the blood, improves metabolism, and increases myocardial contractility; improves the antitoxic function of the liver, dilates blood vessels, increases diuresis. Indications for use - hypoglycemia, carbohydrate deficiency - toxic infections, intoxication in liver diseases (hepatitis, liver dystrophy and atrophy, including liver failure) - hemorrhagic diathesis - dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea, postoperative period) - collapse, shock - for the preparation of drug solutions for intravenous administration. Method of administration and dosage. Isotonic glucose solution (5%) is administered intravenously (drip) at a maximum speed of up to 150 drops/min, the maximum daily dose is 2000 ml. A hypertonic solution (10%) is administered intravenously at a dose of 60 drops/min; the maximum daily dose for adults is 1000 ml. Intravenous bolus - 10-50 ml of 5% and 10% solutions. In adults with normal metabolism, the daily dose of administered glucose should not exceed 4-6 g/kg/day, that is, about 250-450 g/day (with a decrease in metabolic rate, the daily dose is reduced to 200-300 g), while the volume administered fluid - 30-40 ml/kg/day. For parenteral nutrition, along with fats and amino acids, children are given 6 g of glucose/kg/day on the first day, and subsequently up to 15 g/kg/day. When calculating the dose of glucose when administering 5% and 10% solutions, it is necessary to take into account the permissible volume of injected fluid: for a body weighing 2-10 kg - 100-165 ml/kg/day, for children weighing 10-40 kg - 45-100 ml/kg/day Rate of administration: in a normal metabolic state, the maximum rate of administration for adults is 0.25-0.5 g/kg/h (with a decrease in metabolic rate, the rate of administration is reduced to 0.125-0.25 g/kg/h). In children, the rate of administration should not exceed 0.5 g/kg/day; which for a 5% solution is about 10 ml/min - 200 drops/min (20 drops = 1 ml). In cases of severe dehydration, it is possible to administer 3-5 liters of isotonic glucose solution. For diabetic patients, glucose is administered under the control of its content in the blood and urine. Side effects - hyperglycemia, ion imbalance - fever - hypervolemia, acute left ventricular failure - when the rate of administration is increased - osmotic diuresis with loss of water, electrolytes and the development of hyperosmolar coma - at the injection site - development of infection, thrombophlebitis - depletion of the insular apparatus of the pancreas Contraindications - hypersensitivity - hyperglycemia - hyperlacticacidemia - hyperhydration - postoperative disorders of glucose utilization - cerebral edema - pulmonary edema - acute left ventricular failure - hyperosmolar coma With caution - decompensated chronic heart failure - diabetes mellitus under control of blood sugar levels - chronic renal failure (oligo-, anuria ) - hyponatremia Drug interactions Glucose solutions should not be mixed with alkaloids (they decompose) or with general anesthetics (decreased activity). Glucose weakens the effect of analgesics and adrenomimetic drugs. When combining with other drugs, it is necessary to visually monitor compatibility (invisible chemical or therapeutic incompatibility is possible). Glucose is incompatible in solutions with aminophylline, soluble barbiturates, hydrocortisone, kanamycin, soluble sulfonamides, cyanocobalamin. Due to the fact that glucose is a fairly strong oxidizing agent, it should not be administered in the same syringe with hexamethylenetetramine. Do not use in the same system simultaneously, before or after blood transfusion due to the possibility of pseudoagglutination. When used simultaneously with thiazide diuretics and furosemide, their ability to influence the level of glucose in the blood serum should be taken into account. Insulin promotes the entry of glucose into peripheral tissues. Glucose solution reduces the toxic effect of pyrazinamide on the liver. The administration of a large volume of glucose solution contributes to the development of hypokalemia, which increases the toxicity of simultaneously taken digitalis preparations. Glucose solution is incompatible with the following combinations: - bevacizumab - benfotiamine + pyridoxine - cladribine - causes increased degradation of cladribine - pyridoxine + thiamine + cyanocobalamin + [lidocaine] - thioctic acid A solution of iron (III)-dextran hydroxide can be mixed with a 5% dextrose solution. Linezolid solution for infusion is compatible with 5% dextrose solution. Special instructions For more complete and rapid absorption of glucose, you can administer 4-5 units of short-acting insulin per 4-5 g of glucose subcutaneously. When administering glucose solutions, monitoring of electrolyte balance and glucose levels in the blood and urine is necessary. With repeated administration of the solution, disturbances in the functional state of the liver and depletion of the insular apparatus of the pancreas are possible. For diabetic patients, glucose is administered with caution, under the control of sugar levels in the blood and urine. To increase osmolarity, a 5% glucose solution can be combined with a 0.9% sodium chloride solution. Pregnancy and lactation The use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation is possible only when the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus (adequate and strictly controlled studies have not been conducted). Peculiarities of the drug's influence on the ability to drive a vehicle or operate potentially dangerous machinery. The drug does not affect the ability to drive a vehicle or operate potentially dangerous machinery. Overdose Symptoms: hyperglycemia, glycosuria, hyperglycemic hyperosmolar coma, hyperhydration, water-electrolyte imbalance, increased liponeogenesis with increased production of carbon dioxide, which leads to a sharp increase in minute tidal volume, and, as a consequence, respiratory rate; fatty infiltration of the liver. Treatment: stop administering glucose, administer short-acting insulin, symptomatic therapy. Release form and packaging Solution for infusion 5%, 10%. 200 ml and 400 ml of the drug in glass bottles for blood, transfusion and infusion drugs with a capacity of 250 ml and 450 ml, respectively, sealed with rubber stoppers and crimped with aluminum caps. A label made from label or writing paper or self-adhesive paper is placed on each bottle. 24, 28 bottles of 200 ml or 12, 15 bottles of 400 ml with an equal number of instructions for use in the state and Russian languages are placed in corrugated cardboard boxes with gaskets and grids (for hospitals). Storage conditions Store at temperatures from 5 °C to 30 °C. Keep out of the reach of children! Freezing the drug, provided the bottle remains sealed, is not a contraindication to its use. Non-wetting of the inner surface of the bottle is not a contraindication to the use of the drug. Shelf life 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies By prescription. , Russian Federation. 440033, Penza, st. Druzhby, 4, tel/fax e-mail Name and country of the owner of the registration certificate JSC Biosintez, Russian Federation. Address of the organization that accepts claims from consumers on the quality of products (products) on the territory of the Republic of Kazakhstan: JSC Biosintez, Russian Federation 440033, Penza, st. Druzhby, 4, tel/fax e-mail
Glucose-SOLOpharm
Intravenously (drip). The drug is usually administered into a peripheral or central vein.
The concentration and dose of the administered solution depend on the age, body weight and clinical condition of the patient.
The use of the drug should be carried out under regular medical supervision. Clinical and biological parameters should be carefully monitored, in particular blood glucose concentrations, as well as water and electrolyte balance.
In adults with normal metabolism, the daily dose of administered glucose should not exceed 4-6 g/kg, that is, about 250-450 g (with a decrease in metabolic rate, the daily dose is reduced to 200-300 g), while the daily volume of administered fluid is 30 -40 ml/kg.
For parenteral nutrition, along with fats and amino acids, children are given 6 g of glucose/kg/day on the first day, and subsequently up to 15 g/kg/day.
Rate of administration: in a normal metabolic state, the maximum rate of administration for adults is 0.25-0.5 g/kg/h (with a decrease in metabolic rate, the rate of administration is reduced to 0.125-0.25 g/kg/h). In children, the rate of glucose administration should not exceed 0.5 g/kg/h.
To ensure complete absorption of dextrose administered in large doses, short-acting insulin is simultaneously prescribed at the rate of 1 unit of insulin per 4-5 g of dextrose.
With total parenteral nutrition, the administration of glucose should always be accompanied by the introduction of a sufficient amount of amino acid solutions, an emulsion of lipids, electrolytes, vitamins and microelements.
For patients with diabetes mellitus, glucose is administered under the control of its content in the blood and urine.
5% glucose solution : Recommended dose as a source of carbohydrate (alone or as part of parenteral nutrition if necessary):
For adults: 500-3000 ml per day.
For children, including newborns:
- with a body weight of 0-10 kg - 100 ml/kg per day;
- with a body weight of 10-20 kg - 1000 ml + additional 50 ml for each kg of body weight over 10 kg per day;
- with body weight over 20 kg - 1500 ml + additional 20 ml for each kg of body weight over 20 kg per day.
The rate and volume of infusion depend on the age, body weight, clinical condition and metabolism of the patient, as well as concomitant therapy. In children, they should be determined by the attending physician who has experience in the use of intravenous drugs in this category of patients.
The threshold for glucose utilization in the body must not be exceeded in order to avoid hyperglycemia, so the maximum dose of dextrose varies from 5 mg/kg/min for adults and 10-18 mg/kg/min for newborns and children, depending on age and total body weight.
The recommended dose when used for dilution and dissolution of parenterally administered drugs is usually 50-250 ml per dose of the administered drug, but the required volume should be determined based on the instructions for use of the added drugs. In this case, the dose and rate of administration of the solution are determined by the properties and dosage regimen of the diluted drug.
10% glucose solution:
Adults and elderly people
The recommended doses in Table 1 serve as a guideline for use in adults weighing approximately 70 kg.
Table 1. Dosing recommendations for adults (70 kg)*
| Indications for use | Initial daily dose | Infusion rate | Recommended duration of use |
| As a source of carbohydrates (alone or as part of parenteral nutrition if necessary) | 500-3000 ml per day (7-40 ml/kg per day) | The maximum recommended infusion rate should not exceed the patient's glucose utilization threshold, as this may lead to hyperglycemia: 5 mg/kg/min (3 ml/kg/h) | The duration of treatment depends on the clinical condition of the patient |
| Prevention and treatment of hypoglycemia | |||
| Rehydration in case of fluid loss and dehydration in patients with high carbohydrate needs | |||
| For dilution and dissolution of parenterally administered drugs | 50-250 ml per dose of administered drug | Depending on the drug being diluted | Depending on the drug being diluted |
*Maximum volumes within recommended doses should be administered within 24 hours to avoid hemodilution.
Children and Adolescents: The rate and volume of infusion depend on the age, body weight, clinical condition and metabolism of the patient, as well as concomitant therapy. They should be determined by a physician experienced in the use of intravenous drugs in children.
The recommended doses in Table 2 serve as a guideline for use in children and adolescents and are based on body weight and age.
Table 2. Dosing recommendations for children and adolescents
| Indications for use | Initial daily dose | Initial infusion rate* | |||
| Newborns and premature babies | Infants and young children (1-23 months) | Children (2-11 years old) | Teenagers (from 12 to 16-18 years old) | ||
| As a source of carbohydrates (alone or as part of parenteral nutrition if necessary) | — with body weight 2-10 kg 100 ml/kg/day — with body weight from 10 to 20 kg — 1000 ml + additional 50 ml for each kg of body weight over 10 kg/day - with body weight over 20 kg - 1500 ml + additional 20 ml for each kg of body weight over 20 kg/day | 6-11 ml/kg/h (10-18 mg/kg/min) | 5-11 ml/kg/h (9-18 mg/kg/min) | 4-8 ml/kg/h (7-14 mg/kg/min) | From 4 ml/kg/h (7-8.5 mg/kg/min) |
| Prevention and treatment of hypoglycemia | |||||
| Rehydration in case of fluid loss and dehydration in patients with high carbohydrate requirements | |||||
| For dilution and dissolution | Initial dose: from 50 to 100 ml per dose of the administered drug. Regardless of age. Infusion rate: depending on the drug being diluted. Regardless of age. | ||||
| parenterally administered drugs | |||||
*The rate, volume of infusion and duration of treatment depend on the age, body weight, clinical condition and metabolism of the patient, as well as concomitant therapy. They should be determined by a physician experienced in the use of intravenous drugs in children.
Note: Maximum volumes within recommended doses should be administered within 24 hours to avoid hemodilution.
The maximum infusion rate should not exceed the threshold for glucose utilization in the patient's body, as this may lead to hyperglycemia.
Depending on the patient's clinical condition, the rate of administration may be reduced to reduce the risk of osmotic diuresis.
When using the drug for diluting and dissolving medications for infusion, the required volume is determined based on the instructions for use of the added medications.
20% glucose solution:
Administration of a 20% glucose solution is carried out only through the central vein. The rate of solution administration is up to 30-40 drops/min (1.5-2 ml/min). The maximum daily dose for adults is 500 ml.
For more complete absorption of dextrose administered in large doses, short-acting insulin is simultaneously prescribed at the rate of 1 unit of insulin per 4-5 g of dextrose.
With total parenteral nutrition, the administration of glucose should always be accompanied by the introduction of a sufficient amount of amino acid solutions, an emulsion of lipids, electrolytes, vitamins and microelements.
The procedure for working with the Polyflak EH bottle (a bottle with a head designed to connect to a standard infusion system):
1. Place the bottle vertically on a horizontal surface.
2. Remove the cap.
3. Treat the bottle port with a disinfectant.
4. Prepare the infusion system.
5. Insert the spike (or injection needle) into the marked chamfer on the port at a right angle until it tightly touches the dropper skirt (or the butterfly of the injection needle).
6. Turn the bottle over and secure the system to the infusion stand (tripod).
Note
— If it is necessary to administer a drug, administer the drug only through the marked chamfer on the port of the bottle.
— The infusion system cannot be inserted into the bottle suspended (or on an infusion stand (tripod)).
— When forming a “lake” in the infusion system, you cannot press on the bottle (this manipulation is carried out by pressing on the dropper).