Author
: Grachev Ilya Illarionovich
Editor
: Efremov Mikhail Mikhailovich
Publication date: 05/13/2014 Update date: 12/16/2021
Atopic dermatitis (neurodermatitis) is a disease that causes skin lesions, itching and burning. Those affected may include both adults and children. It occurs most easily in childhood. The danger in this case is not the skin disease itself, but concomitant infections.
In most cases, the disease develops before the age of 12 years. 60% of cases are children under 1 year of age. Only 10% of those diagnosed with the disease are adults and adolescents over 12 years of age. Timely treatment helps to get rid of the disease without consequences for health.
Causes of Neurodermatitis (Atopic Dermatitis)
The main cause of the disease is the increased sensitivity of the immune system to certain factors. Foods (chocolate, honey, nuts, citrus fruits, strawberries, fish, caviar), medications, plant pollen, animal hair, bird feathers, dry fish food, mold, dust, tobacco smoke and many other substances can act as provoking factors.
Usually, a hereditary predisposition is enough to cause neurodermatitis. If manifestations of the disease are detected in both parents, then the probability of its development in the baby reaches 81%. If one parent is sick, then this figure is 55%, and it is also higher if the mother has the pathology.
Sometimes, in addition to genetic predisposition, an additional “trigger” is required, which can be:
- toxicosis;
- infections or smoking during pregnancy;
- artificial feeding;
- allergic reactions to food irritants;
- unfavorable environmental or climatic conditions;
- poor nutrition;
- physical and mental stress;
- stressful situations;
- infectious and parasitic diseases;
- diseases of the digestive and endocrine system.
Causes
Atopic dermatitis is a disease with a hereditary predisposition. The main factors in the development of the disease:
- Atopic constitutional abnormality (the body's predisposition to an excessive response when in contact with allergens).
- Features of the skin condition, weakening of its barrier function.
- Unfavorable course of pregnancy, childbirth (a factor in the development of the disease in the child).
- Irrational feeding in the first year of life (including early cessation of breastfeeding).
- Disorders of the digestive system: dysbiosis, biliary dyskinesia.
- Dysregulation of the central nervous system.
- Stress, traumatic situations.
- Overwork.
- Bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse)1.
The risk of developing neurodermatitis in a child whose both parents suffer from allergic diseases (bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, urticaria) can reach 75%, so it is very important to monitor the condition of his skin from the first days of life. Various allergens provoke exacerbations of neurodermatitis:
- pet hair;
- antibacterial drugs;
- flavorings;
- plant pollen;
- house dust mites.
Atopic dermatitis is also exacerbated by upper respiratory tract infections during seasonal outbreaks of ARVI.
Neurodermatitis. Symptoms
There are 2 stages of neurodermatitis: acute and chronic.
During the acute stage, the skin becomes inflamed, red spots and papules, erosions, weeping areas and crusts form on it. The rash is accompanied by severe itching. If a secondary infection occurs, then pustular lesions are detected.
The chronic stage is characterized by the following symptoms of neurodermatitis:
- The lower eyelids are covered with multiple deep wrinkles (Denny-Morgan fold)
- The nail plates acquire a “polished” shine due to constant scratching of the skin;
- The skin around the eyes darkens and peels;
- The skin on the sole becomes puffy and flaky, turns red and becomes cracked;
- Temporary hair loss on the eyebrows due to scratching the skin of the eyelids (pseudo-Hertog symptom)
- In places of the most pronounced inflammation in the acute stage, the skin is thickened, skin folds are more clearly visible (skin pattern)
Symptoms
Symptoms of neuroderma are an itchy rash on the skin. When scratching the skin, there is a risk of violating its integrity. Because of this, there are risks of bacterial penetration and the development of inflammation. In such cases, it is necessary to use antiseptic drugs, which can now be purchased in pharmacies or ordered online with delivery to the specified address.
The pathology can affect small areas of the skin, but in severe cases, large areas of damage are observed. If they occur in several places, then widespread atopic dermatitis is diagnosed. On the skin, when neurodermatitis develops, photos confirm this; plaques first appear, which consist of small papules. Additionally, there is a feeling of increased dryness, and visually it seems that the skin is sprinkled with flour.
Since the skin rash is constantly itchy, scratch marks may appear over time. This can be avoided if you use special medications. Today they are often sold in pharmacies on promotions, so they are cheap.
Forms of neurodermatitis
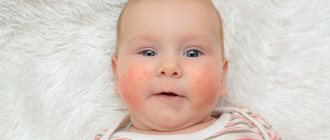
Clinical manifestations of neurodermatitis vary depending on the age of the patient, which is clearly visible in the photo. There are 3 forms of the disease: infant, child and adult.
The infantile form occurs in children in the first one and a half years of life and is known as diathesis.
It is characterized by an acute course. The skin becomes swollen, covered with bright pink spots, blisters and crusts, and pronounced weeping is observed. Most often, the disease manifests itself on the face, but can affect the scalp, buttocks, legs, and hands. Children's
In children aged 2-12 years, papules and red spots form on the back of the hands, on the flexor surfaces and in skin folds.
The skin becomes dry, becomes cracked, and a pattern appears on it. A characteristic feature of childhood neurodermatitis is an “atopic face”: the skin becomes dull in color, darkens around the eyes, and an additional fold forms on the lower eyelid. Adult
Adults are usually diagnosed with a chronic form of neurodermatitis with rare exacerbations. The skin thickens, becomes very dry and cracks, and a pronounced pattern is visible on it. A pale pink rash covers the face and neck, back and chest, hands and feet.
What it is
Neurodermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease that occurs due to its increased reactivity to allergens or some nonspecific irritants.
Many people know it under another name: atopic dermatitis. Neurodermatitis is not as rare as we would like. Up to 12% of people suffer from its manifestations, with women more often than men².
Most often, the disease is observed in infants and young children, but sometimes symptoms remain with a person for life. In this case, coping with dermatitis can be difficult, but with the help of modern medications, patients with a chronic form of the disease can achieve stable remission and live a full life.
It should be noted that despite its frightening appearance (the disease manifests itself as a rash, dryness and wounds on the skin), neurodermatitis is not contagious and does not pose a threat to life, although it can cause a lot of trouble, mainly due to itching.
Treatment of neurodermatitis
Treatment of neurodermatitis should be comprehensive. Only in this case will it be possible to get a positive result.
To cope with the disease, you need to:
- stop the patient's contact with the substance that provokes the allergy;
- carry out desensitization - reduce sensitivity to the allergen;
- suppress the inflammatory process in the skin;
- relieve unpleasant symptoms;
- prevent exacerbations;
- cure concomitant diseases;
- cleanse the body of toxins;
Treatment should be carried out at any stage of neurodermatitis (acute and chronic). If there are concomitant chronic diseases, the dermatologist recommends that the patient consult with other specialists (generalist, pediatrician, allergist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist, pulmonologist).
Treatment of neurodermatitis depends on the symptoms and cause of the disease, the age of the patient and the severity of clinical manifestations. It consists of taking medications, conducting physiotherapeutic procedures, and psychotherapy.
Drug treatment includes taking:
- antihistamines;
- immunosuppressive drugs for severe disease;
- enterosorbents
- medications that improve digestive processes in the presence of gastrointestinal pathology;
- vitamin complexes (vitamins A and D are most often used);
- sedatives.
Drug therapy (antihistamines and immunosuppressive drugs) is usually prescribed for a short period to quickly relieve the inflammatory process, relieve itching and stop the appearance of new rashes.
Quite often the disease is complicated by pathological changes in the gastrointestinal tract. Enterosorbents, probiotics, prebiotics, enzymes, bacteriophages and hepaprotectors will help remove metabolic products, destroy pathogenic microflora and normalize digestion.
Vitamin deficiency is often detected in people suffering from neurodermatitis. Vitamins and minerals can be washed out of the body or poorly absorbed due to disruptions in the functioning of the digestive system. Vitamin and mineral complexes will help correct the situation, as well as activate metabolism and speed up regeneration.
Neurodermatitis causes not only physical, but also psychological discomfort. A person feels unattractive, tries to avoid society, his self-esteem decreases, and an inferiority complex develops. Particularly sensitive people may experience psychosis and neuroses, which requires the help of a psychotherapist. The specialist will teach you how to relax and control the situation, and will correct your psychological mood, which will facilitate a quick recovery. For depression, excessive irritability, insomnia, and fear, he will select sedatives, sleeping pills, antidepressants, and tranquilizers.
The most widely used external preparations in the treatment of neurodermatitis are hormonal and non-hormonal agents.
When choosing hormonal ointments, the doctor takes into account the patient’s age, the severity of the disease and the location of the rash. For children, as well as in cases where the rashes are located on the face, weak-acting products are recommended. Stronger medications will be needed for severe disease and severe thickening of the skin.
Glucocorticosteroid drugs have a powerful effect, quickly relieve inflammation and itching, but they can cause side effects with long-term use. Therefore, they can usually be used for no more than 2-3 weeks.
For long-term maintenance therapy, doctors prefer non-hormonal agents, among which are drugs from the Losterin line (cream, shampoo, shower gel, zinc-naphthalan paste, foot cream, hand cream soap). They contain a balanced combination of active substances that provide maximum therapeutic effect and are intended for daily skin care for neurodermatitis and other dermatological diseases. They do not contain hormones or dyes. They are not addictive and do not cause side effects. Products from the Losterin line reduce inflammation and itching, eliminate weeping, have an exfoliating effect, eliminate pathogenic microflora, and restore damaged skin.
Physiotherapeutic procedures can speed up recovery and increase the effectiveness of treatment:
- plasmapheresis;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- balneotherapy;
- heliotherapy;
- climatotherapy;
- thalassotherapy;
- acupuncture;
With a combination of physiotherapy and sanatorium-resort treatment, long-term remission lasting several years can be achieved.
When treating neurodermatitis, important attention should be paid to diet. It is necessary to completely exclude from the diet foods that cause exacerbation of the disease. The basis of the diet should be vegetable dishes, cereals, fermented milk products, and boiled meat.
Complications
Without proper treatment, atopic dermatitis progresses and causes serious complications. A severe form of the disease, in addition to skin disorders, is characterized by a general deterioration in general condition. Patients experience rapid fatigue and weakness with minimal exertion. Against this background, apathy develops. Weight loss and decreased blood pressure may also occur.
With the development of neurodermatitis, the following complications may most often occur:
- Atopic march, which is characterized by the occurrence of allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and asthma. Most often the condition is observed in childhood.
- Hill's erythroderma. In this case, inflammation of the skin occurs, which is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling. In severe cases, more than 90% of the skin may be affected.
Diet for neurodermatitis
Food is often responsible for exacerbating neurodermatitis. Which product caused the allergic reaction is determined in the laboratory. Based on the results of the study, a specific elimination diet is prescribed, in which foods harmful to his health are limited in the patient’s diet. The most allergenic dishes are fish and fish broths, fried meat and meat broths, chocolate, citrus fruits, sweet berries, honey, nuts, caviar, mushrooms, spicy, pickled, smoked foods, as well as food colorings. If the disease worsens, you need to completely abandon dangerous foods; in the future, in consultation with your doctor, they can be gradually added to the daily diet. In addition, short-term therapeutic fasting is possible under the supervision of a doctor. The basis of the diet of a patient with neurodermatitis should be vegetables, cereals, boiled meat, and dairy products. Also, the diet can be compiled based on the presence of concomitant diseases.
The most allergenic foods
The basis of the diet of a patient with neurodermatitis
Prognosis and prevention
Children's neurodermatitis often goes away as they grow older. But if it becomes chronic, there is a high probability that symptoms will appear periodically throughout life. However, complex treatment can significantly improve the quality of life of such patients, reducing the risk of relapse to a minimum.
Prevention of neurodermatitis in children includes careful planning of pregnancy, monitoring the use of medications throughout the entire gestation period, as well as following a diet that excludes the consumption of highly allergenic foods. After the baby is born, breastfeeding is preferable with a gentle diet for the nursing mother.
Means to improve the functioning of the digestive system
Since the course of the pathology is often complicated by concomitant diseases of the digestive system, treatment of neurodermatitis is combined with therapy aimed at normalizing the functioning of the stomach and, mainly, the intestines. It has been proven that with the normalization of digestive processes, treatment of neurodermatitis occurs faster, since the level of toxicoderma in the body decreases and tissue regeneration processes are accelerated.
To regulate the functioning of the digestive organs, drugs with multidirectional effects are used:
- Enterosorbents are used to remove metabolic products and remove harmful microflora. However, taking them can lead to the leaching of vitamins and microelements, so it is necessary to artificially compensate for their deficiency. A course of taking enterosorbents is carried out before a course of taking drugs to regulate intestinal function. For neurodermatitis, activated carbon and preparations with the following active ingredients are most often used: attapulgite, diosmectite, polymethylsiloxane polyhydrate, hydrolytic lignin, povidone;
- preparations for normalizing intestinal microflora , which contain prebiotics (inulin, lactitol, lactulose, lysozyme), probiotics (bifidumbaterin, bactisubtil, linex, probifor), synbiotics (laminolact, normoflorin, maltodophyllus), enzymes (pancreatin), hepatoprotectors (phospholipids, beatin, glycyrrhizic acid, ademetionine), bacteriophages (pseudomonas, staphylococcal, coliproteus).
Psychotherapy for neurodermatitis
Neurodermatitis is not only a physical, but also a psychological disease that can lead to negative consequences for the patient’s daily life, for example, secondary psychoses and neuroses. The psyche is affected by both constant physical discomfort, itching, pain, and inappropriate attention or even condemnation from society. In addition to the main treatment, the patient requires the help of a psychotherapist, psychologist or psychoneurologist (depending on the severity of the disease), who will teach the patient self-control, relaxation methods, and also, if necessary, prescribe medications:
- sedative herbal medicines;
- drugs against insomnia;
- mild tranquilizers and antidepressants.
To prescribe psychotropic drugs, good reasons are needed, such as fear, insomnia, increased irritability, depression. The drugs are prescribed in small or medium doses for a certain period of time.