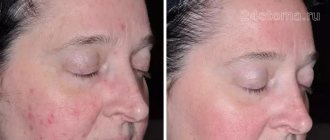
Dental periodontitis is an inflammation of an infectious nature that occurs at the membrane of the tooth root and affects the tissues of the oral cavity located next to it. Periodontitis is difficult to confuse with other dental diseases, because it has a clear symptom – severe and constantly increasing pain, which cannot be relieved by taking tablets from the pharmacy.
Treatment of periodontitis must be carried out urgently, because you risk not only losing a tooth, but also acquiring complications that are dangerous to the overall health of the body! How periodontitis occurs, what signs will help to identify the disease in a timely manner, how periodontitis is treated in dentistry, at what prices the service is offered in Moscow - we will talk about this in detail in this article.
Symptoms of periodontitis
Despite the fact that experts distinguish several types and stages of periodontitis, there are a number of symptoms, the presence of which most likely indicates the development of this disease.
Clinical manifestations of periodontitis:
- pain due to periodontitis;
- weakness;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the temperature may increase by 1 - 2 degrees;
- tooth mobility;
- affected teeth often change color.
Almost all complaints with periodontitis are associated with the occurrence of pain, but patients often go to the doctor only with very severe pain, when the disease is in an advanced stage.
Prevention
Prevention of periodontitis is not much different from the prevention of caries. To prevent the development of the disease, it is necessary to pay increased attention to the following factors:
- Proper brushing of teeth. Maintaining oral hygiene helps prevent the appearance of plaque, which is an optimal environment for the development and growth of microorganisms that cause damage to enamel and hard tissues.
- Regular visits to the dental clinic. By detecting periodontitis in a timely manner, it can be cured with minimal surgical intervention. During preventive examinations, the doctor will perform a professional teeth cleaning, removing hard deposits in the form of tartar, which will reduce the risk of developing the disease.
- Your own diet. Sweet foods rich in carbohydrates promote the growth of microorganisms responsible for the appearance of plaque, which provokes the appearance of periodontal disease. An excellent preventive measure would be to include in your diet a large amount of vegetables, fruits, and foods high in calcium, which strengthen tooth enamel.
Following these recommendations does not imply serious costs, but it allows you to avoid serious problems in the future.
Diagnostics
Almost all methods for diagnosing periodontitis are associated with x-ray examination, since it is quite difficult to visually determine the disease. The most obvious signs:
- change in tooth color;
- the presence of carious cavities;
- fistula due to periodontitis;
- pus during periodontitis (purulent discharge from the gums in the place where the root tip is located).
Be that as it may, the stage of periodontitis can only be accurately diagnosed using x-rays: this is crucial, since the treatment plan is drawn up depending on the type of disease.
Causes
Complications of oral diseases
As a consequence of untreated gingivitis, periodontal disease, tooth root cysts and pulpitis.
Infection
Bacteria penetrate the gums through the bloodstream during inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx and upper respiratory tract (sore throat, sinusitis, etc.).
Deep caries
As a rule, it leads to the occurrence of granulosa or fibrous forms of periodontitis due to decay products that accumulate daily in the dental canals of severely damaged teeth.
Dentist mistakes
Poorly performed treatment of tooth canals, when fragments of dental instruments, etc. accidentally remain there.
Injuries
The bad habit of constantly pressing on the tooth with a ballpoint pen, a smoking pipe, or a filling that is too high and injures the periodontium can also provoke non-infectious periodontitis.
Professional factor
In professions such as a brass musician or a tailor, pathological pressure on the tooth occurs on a regular basis: in the first case when playing an instrument, and in the second due to the habit of biting off the thread with teeth instead of cutting with scissors.
Attention!!
Patients with reduced immunity and chronic diseases of the endocrine system are also at risk.
Treatment of the tooth and its canals in the treatment of periodontitis
- Anesthesia of the area of the diseased tooth. It is impossible to do without the use of anesthetics in the treatment of periodontitis, since the inflammation has gone deep into the tooth and affected the nerve endings. Without local anesthesia, the process of treating periodontitis will be very unpleasant and painful for the patient.
- When the anesthetic takes effect, the doctor will begin working with the diseased tooth. Treatment of periodontitis involves the removal of all destroyed dental tissues, depulpation of the tooth, as well as treatment of the dental canals.
- Treatment of canals for periodontitis involves their expansion and washing with antiseptic solutions. In order to eliminate inflammation and destroy infection, the dentist will place an antibacterial drug in the cavity of the canals.
- The drilled tooth is covered with a temporary filling and after that a break is taken in the treatment of periodontitis. The doctor sends the patient home, but before that he prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, and provides detailed advice on the care of his teeth and oral cavity. You must follow all the dentist’s recommendations exactly, otherwise the treatment of periodontitis will either take longer or, what is much worse, be completely ineffective.
Next time you will need to see the doctor in 3-4 days to continue treatment of periodontitis.
Classification of periodontitis
It is believed that the main cause of periodontitis is complications from caries (pulpitis), when the inflammatory process moves to the apex of the root and tooth root periodontitis occurs. This is indeed one of the most common reasons, but this does not always happen.
Classification of periodontitis by reason of occurrence
| Type of periodontitis | Price for installation of one implant |
| Infectious | The most common type of disease when a chain of caries occurs is pulpitis - periodontitis. Appears both after primary and secondary caries. It can be difficult to detect visually (especially periodontitis under a crown or filling). |
| Medication | Periodontitis after dental treatment. Occurs when potent or toxic drugs (arsenic, formaldehyde, phosphate cement, etc.) enter the periodontium. It can often be a consequence of an allergy to certain medications. |
| Traumatic | Its cause is mechanical damage, including due to an incorrectly installed seal. May become infectious. |
Causes of inflammation
Periodontitis is an acquired disease; it is caused by both health problems and mechanical damage.
The most common reasons include:
- untreated pulpitis (inflammation of the internal tissues of the tooth due to an infection brought inside);
- caries;
- fillings and dentures installed poorly (not in size or not accurately).
In addition, periodontitis occurs in smokers, people with diseases (heart, digestive) and those who are susceptible to hormonal imbalances.
Age is not a barrier for the onset of periodontitis. In children, it occurs after injuries or bruises to the oral cavity. In adults, the formation of ulcers is caused, among other things, by trauma to the canals with surgical instruments and excessively large fillings that violate the integrity of the tooth.
In addition, in some cases, periodontitis is a consequence of the body’s individual reaction to certain medications or chemicals entering the tissue during treatment.
Do not heat the sore spot or use traditional medicine. The best thing is to see a doctor
Acute periodontitis
Rapid development of the disease (literally in 48 - 72 hours). The tooth may change color and become mobile; swelling of the gums and unbearable pain are often observed. It is quite difficult to detect acute periodontitis on an x-ray, since the bone in the affected area has not yet begun to deteriorate. An enlarged periodontal gap can be seen on x-rays.
Stages of periodontitis (acute)
- Stage 1. Pain, increased sensitivity.
- Stage 2. Exacerbation of periodontitis. Severe inflammatory process, the occurrence of mobility, possible appearance of fistulas and purulent discharge.
How does the acute phase of chronic periodontitis manifest?
When exacerbated, chronic periodontitis of the tooth expresses itself with the same symptoms as the acute form of the disease. That is, there is a strong, aching pain, swelling of the gums and swelling of the cheek. Typically, chronic periodontitis enters the acute phase when the immune system is weakened, the flu, ARVI, or simply severe hypothermia are present. If, during an exacerbation of the chronic form, a fistula appears in the gum area, pus will flow from the area of inflammation and the pain in the tooth will gradually subside.
But this does not mean that periodontitis has gone away on its own; the inflammatory process will continue to develop and will manifest itself again under favorable external factors, which we discussed just above. Based on the type of periodontitis, a treatment regimen is selected. The price of the service depends on the regimen chosen for treating the disease. We will tell you below about all the stages of treatment of dental periodontitis in different forms and prices for procedures. But no matter in what form periodontitis develops, its treatment always begins with diagnosis.
Diagnosis of periodontitis involves examination of the oral cavity, x-rays, and examination of patient complaints. All this together helps to accurately diagnose the form of periodontitis and prescribe adequate and effective treatment.
Chronic form of the disease
Chronic forms of periodontitis occur much more slowly and are partly asymptomatic. It often occurs with caries, under a filling or crown, so visually detecting the disease can be quite difficult. Sometimes a fistula is observed on the surface of the mucosa in chronic periodontitis. However, the disease can be easily diagnosed using x-rays. In addition, chronic periodontitis in the acute stage causes pain, as well as a feeling as if the tooth is being torn from the inside.
Signs
Clinical manifestations of periodontal inflammation depend on the form of the disease.
In the acute course, the symptoms are pronounced, often accompanied by the formation of a painful abscess on the gum, gumboil (deeply located abscess with intense swelling of the soft tissues of the gums and face), increased body temperature, etc. Acute inflammation can occur in two forms:
- Serous periodontitis occurs without the formation of a purulent cavity. Accompanied by constant aching pain that does not intensify when touching a tooth or biting food.
- Purulent periodontitis is accompanied by the formation of an abscess. Accompanied by sharp, bursting or throbbing pain, the intensity of which may vary. Flux is noticeable on the gum near the diseased tooth, and the soft tissues of the face on the affected side swell. The mobility of the tooth is increased, the pain intensifies when biting and touching the tooth.
In the chronic form, periodontitis is not as severe as acute periodontitis. There are three forms of the disease:
- Fibrous , the symptoms of which are sluggish inflammation without the formation of an abscess and fistulas. Pain with this form rarely occurs. An external sign is a change in the color of the enamel to gray, a change in its transparency. Signs of inflammation are visible only on x-rays.
- Granulomatous , the symptoms of which are periodic formation of an abscess. As it “ripens,” a duct opens on the gum, from which purulent contents pour out. Such ducts can form permanent non-healing fistulas. On x-rays, this form of periodontitis looks like a lesion with a diameter of up to 5 mm at the root apex.
- Granulating , the symptoms of which are chronic toothache, aggravated by biting hard, hot or cold food with a sore tooth. The gums near the tooth are constantly swollen and hyperemic. The opening of the fistula can open both on the oral mucosa and on the skin of the face.
Symptoms of any form of periodontitis tend to subside when the purulent cavity is cleared of its contents.
It is important to know! The main difference between periodontitis and pulpitis is the nature of the pain. With pulpitis, it is acute, painful, reminiscent of electric discharges, intensifying when the diseased tooth comes into contact with solid food particles, hot or cold air.
Types of chronic periodontitis
| Type of periodontitis | Description |
| Chronic fibrous periodontitis | Characterized by the proliferation of fibrous tissue. Such periodontitis can be detected on x-rays due to the widened periodontal gap. This form is easier to treat than others. |
| Chronic granulating periodontitis | Rapidly destroys the bone under the apical part of the root. This type of periodontitis in the acute stage is characterized by swelling of the mucous membrane, purulent discharge (periodontitis with fistula). The tooth is often mobile. On a radiograph, granulating periodontitis often resembles a candle flame. |
| Chronic granulomatous periodontitis | On an x-ray, the area under the root tip looks like a large, round spot. This is nothing more than a granuloma. Periodontitis of this type is characterized by the appearance of purulent formations - granulomas or cysts, and in especially severe cases the diameter of the cyst can exceed 3 centimeters. |
Treatment methods
Treatment algorithms for periodontitis vary depending on what form of the disease is acute or chronic.
Stages of treatment of acute periodontitis
- Expansion of the root canal.
- Removal of affected tissue.
- Antiseptic treatment.
- Application of a periodontal bandage.
- Antibiotic therapy.
- Inspection of the canals after 3 days and installation of a temporary filling.
- Control X-ray after 2 months and installation of a permanent filling.
Treatment of chronic periodontitis
- Emphasis on canal drainage.
- Endodontic treatment of root canals.
- Impregnation methods (treatment of canals with a solution of silver salts).
- Tooth extraction if therapy is ineffective.
Disease prevention – at the very end
- Maintaining a hygienic regime: brushing your teeth twice during the day, using mouthwash and floss.
- Balanced diet: minimum carbohydrates and maximum fresh vegetables and fruits.
- Regular self-massage of the gums using your finger.
- Scheduled consultation with a dentist once every 6 months.
Treatment
Acute treatment involves getting rid of severe pain that causes discomfort. The procedure begins with cleaning the root canals from the remaining pulp, which allows the exudate to flow freely, reducing the pressure of the purulent masses inside the gums. In complicated situations, when this measure is not enough, a specialist may resort to cutting the soft tissue in the area of the root apex and installing drainage. To prevent the spread of infection released along with pus, the patient is prescribed oral antibiotics.
For apical periodontitis, the doctor performs instrumental treatment of the root canals, removing the affected areas of tissue. Then medications are administered and filling is performed.
Treatment of marginal periodontitis involves eliminating the traumatic factor that led to its appearance. Next, the gum surface is treated with antiseptics and medications that prevent the subsequent growth of bacteria.
In the chronic form, treatment is carried out according to the same algorithm as in the case of the acute form, but in addition the periodontal pocket is cleaned of accumulated pus.
At some stages, treatment may be limited to the use of drugs based on calcium oxide hydrate, penetrating into the focus of the inflammatory process through a mechanically cleaned root canal.
Prognosis for periodontitis treatment
In dentistry, periodontitis is considered a very difficult disease to treat, especially its advanced chronic forms. If in mild forms it is enough to depulpate the tooth and remove the affected tissue, then to treat severe forms it is necessary to carry out a number of more complex manipulations. In the acute form, the doctor, as a rule, opens the body of the tooth, cleans the canals and leaves them open for the release of accumulated pus. The patient is then prescribed antibiotics for periodontitis, as well as mouth rinses.
Rehabilitation for the granulating and granulomatous type takes a longer time (up to 2 - 3 months). This is due to the fact that inflammation and bone lesions are neutralized with the help of special medications based on calcium hydroxide, the effectiveness of which appears only after long-term use.
Unfortunately, conservative treatment of periodontitis is impossible if there are cysts and granulomas. Here only invasive interventions will save you, in particular, removal of the apical part of the tooth root along with the formations. Remember that complications of periodontitis take much longer to treat (and are more expensive): do not let your problems get worse and consult a doctor on time.
Treatment and prevention of periodontitis
Restoration of teeth and tissues after periodontitis occurs in several stages.
The first is accurate diagnosis. The dentist determines the form of periodontitis and prescribes a treatment regimen.
The next task is to remove the pus. To do this, you need to open the tooth (drill or remove a filling) for several days so that the pus can drain out. For severe inflammation affecting the gum, your doctor will make a small incision to open the abscess. Infected tooth tissues are also cleaned. In difficult cases, resection (removal of part) of the tooth root may be necessary.
Then disinfection is carried out. The dentist disinfects the canals, puts in medicine and performs intracanal physiotherapy.
At the final stage, the canals and tooth are filled. As a preventative measure, the patient is prescribed antibiotics.
Tips for care and prevention concern, first of all, regular and thorough oral hygiene:
- brush your teeth morning and evening. Allow at least two minutes for each procedure. Musical accompaniment will brighten up the monotony of cleaning;
- Change your toothbrush as recommended by your doctor or as stated by the manufacturer. Old brushes with frayed bristles do more harm than good;
- Use mouthwash, dental floss or chewing gum throughout the day;
- make it a rule to visit the dentist once every six months.
Self-medication will not get rid of periodontitis - it will only worsen the disease. Therefore, at the first sign of discomfort, be it an aching tooth or sore gum, seek help from a specialist.
Number of views 4,217