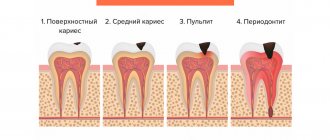
Lymphatic edema of the lower extremities is a chronic disease in which there is a violation of the circulation of lymph, the biological fluid of the body. The latter is formed in tissues, accumulates in lymphatic capillaries and from there spreads throughout the body. Violation of its flow leads to stagnation of fluid in the limbs.
The disease can affect one or both legs. Both men and women are susceptible to the disease, but, as practice shows, the fair sex suffers from it much more often. This problem does not go away on its own. If lymphostasis of the lower extremities is not treated in any way, it will turn into an irreversible form, in which thickening of the legs is observed - elephantiasis.
At the Yusupov Hospital, through the joint efforts of specialists in various fields of medicine, an original comprehensive method for treating lymphostasis of the lower extremities was developed. The essence of the method is not only that swelling is “dispelled” from the affected limb, but also through a complex effect on the lymphatic system, lymphatic outflow is activated. This allows the body to further regulate the drainage function of the lymphatic system.
Treatment of leg lymphostasis must begin immediately. This pathology can progress quite quickly, leading to serious complications, such as impaired motor activity, the appearance of skin ulcers, inflammation, and sepsis. Pathology treatment is successfully performed at the Yusupov Hospital. For the treatment of lymphostasis, doctors draw up an individual treatment plan, which allows them to obtain the best results in eliminating the disease.
Types of pathology
In accordance with the modern classification, a distinction is made between primary lymphatic edema of the legs and secondary, that is, acquired, which develops with inflammation of the extremities. The causes of congenital lymphostasis are disturbances in the structure of the lymphatic system, such as the absence of certain lymphatic vessels or their expansion. This type of illness manifests itself at an early age. Acquired lymphostasis of the legs has more diverse causes.
In the initial stages, lymphostasis of the legs leads to the formation of extensive edema. As they develop, they turn from soft and reversible into intractable and dense formations. If acquired lymphostasis of the lower extremities is not stopped at the second stage, elephantiasis will develop. It worsens the quality of life and can cause the development of related ailments.
The most dangerous is the third stage. At this stage, there are disturbances in the blood supply to the lower extremities. As a result, red areas form on the skin affected by edema, where after some time trophic ulcers appear. Lymphostasis of the third degree is often accompanied by infectious complications. In addition, the risk of developing cancer increases.
Make an appointment
Lymphedema - what is it?
The body's lymphatic system is no less complex and branched than the system of veins and arteries. It provides immune protection, participates in fluid exchange and maintaining its balance, and transports products that are absorbed from food. The lymphatic system includes nodes, trunks, ducts, vessels and capillaries.
Lymph circulation has its own characteristics. From the blood capillaries, fluid enters the tissues - this is necessary for their nutrition, and then the lymph is reabsorbed into the lymphatic capillaries. Ideally, the processes of filtration (fluid release into tissues) and lymph drainage should be balanced. If lymph flows poorly from the tissues, then edema forms.
Lymphedema is a pathology that is accompanied by swelling of soft tissues, most often the legs. Lymph contains a lot of protein, and its accumulation in tissues leads to swelling: protein molecules attract water. If you do not consult a doctor and do not carry out the necessary treatment for lymphedema, the protein will continue to accumulate, which will ultimately lead to the growth of collagen fibers, thickening of the edema and a change in the shape of the limb. Also, excess protein disrupts tissue respiration, which can lead to negative consequences for patients.
Stages
Excessive accumulation of lymph is a long-term process. It happens very slowly. In this case, lymphatic drainage and even the entire blood supply system are disrupted.
There are three stages in the development of lymphostasis:
- The first, or mild, swelling of the legs is observed in the evenings, which goes away by the morning. Swelling of the lower extremities is possible after prolonged immobility or excessive physical exertion. If the disease is at an early stage, it may disappear for a long time and reappear after several years;
- The second, or moderate, swelling does not disappear even after rest, the skin thickens and becomes tense, and pain develops. If you press your finger on the swollen area, a mark remains for a long time;
- The third, or severe, disruption of lymphatic drainage becomes irreversible, and fibrocystic changes are observed. In later stages, the pathology affects the knee joints and even the ligaments. Possible enlargement of regional lymph nodes. In especially severe cases, elephantiasis and lymphosarcoma occur. With the development of sepsis, death is possible.
With “late” edema, moderate damage to one limb is first observed. Over time, the disease spreads to the second limb. In most cases, swelling in one leg is much more noticeable than in the other.
Forecast of lymphostasis and prevention of lymphedema
Refusal of therapy and bringing the disease to a serious condition threatens with serious consequences: chronic disruption of lymph flow, fibrous tissue changes, elephantiasis, sepsis, lymphosarcoma. Lymphostasis can become so severe that the affected limb loses its shape and ceases to function normally.
At the stage of elephantiasis, the following pathologies often develop:
- contracture (limited limb movement);
- limb deformity;
- osteoarthritis (dystrophic changes in joints);
- trophic ulcers (edematous, non-healing wounds associated with necrosis, affecting the skin and deep-lying tissues).
When diagnosing lymphostasis, it is necessary to begin treatment of the disease as early as possible. Moreover, even after successful treatment, a person must undergo regular courses of maintenance therapy throughout his life.
Symptoms
Lymphostasis of the lower extremities is accompanied by:
- pain;
- constant swelling;
- changes in the appearance of the skin;
- immediate appearance of edema after drinking liquid;
- skin itching;
- general weakness;
- rapid fatigue.
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the development of fibroedema (irreversible edema) and elephantiasis (overgrowth of fibrous tissue), leading to disability, is possible.
Causes of heavy legs
There are several reasons for swelling and heaviness in the legs.
It can be:
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- excess weight, which puts more strain on the heart and puts pressure on the legs;
- monotonous or sedentary work leading to venous stagnation;
- gender predisposition: women suffer from varicose veins more often. This occurs during pregnancy, hormonal imbalance or due to constant walking in high-heeled shoes.
Causes of pathology
The causes of lymphostasis of the lower extremities are associated with damage to the lymph nodes and blood vessels. Most often, this pathology develops after surgical intervention during excision of a malignant tumor. Lymphostasis may appear several weeks after surgery or occur after a longer period of time. Lymphostasis of the legs has the following causes:
- lower limb injuries;
- neoplasms compressing lymph vessels;
- heart failure;
- damage to lymphatic vessels in the legs during operations;
- kidney diseases;
- reduced amount of proteins in the body;
- immobility of legs;
- infection of the lymph nodes by parasites.
To prevent the disease, the doctor may prescribe doing gymnastics and wearing compression garments or a bandage. A thigh bandage for lymphostasis is also used to treat an already developed disease. Treatment of lymphostasis must begin immediately. Otherwise, it will be quite difficult to eliminate it without unpleasant consequences.
Prevention
- It is advisable to engage in the prevention of lymphedema before the first symptoms are detected. What should you pay attention to?
- Limit the amount of salt you consume as much as possible, increase the amount of fruits and vegetables in your diet.
- Quit cigarettes and alcohol.
- Use moisturizing lotions for the skin, dry the body thoroughly after bathing, and avoid sudden changes in temperature.
- Moderate physical activity will help keep your body toned and reduce the possibility of swelling.
- After operations or with constant swelling, you need to wear special compression stockings and tights, which your doctor will help you choose.
Diagnostics
When the first symptom of lymphostasis of the lower extremities (swelling) appears, you should contact:
- vascular surgeon;
- phlebologist;
- lymphologist.
At the Yusupov Hospital, patient diagnosis begins with an examination and analysis of the patient’s general clinical data. In order to clarify the nature of the course of the disease, the state of the drainage function, and the cause of edema, in some cases it is necessary to use special research methods, such as:
- lymphoscintigraphy;
- dopplerography;
- CT and MR tomography;
- lymphangiography.
The Yusupov Hospital uses an individual approach, which takes into account all the features of the medical history and condition of the human body. This allows us to create the most effective therapy that normalizes the lymph flow of the lower extremities.
Make an appointment
Drug therapy
Drugs for the treatment of lymphostasis of the lower extremities are prescribed only by the attending physician. Drug treatment is part of general therapy and cannot be used as the only method of eliminating lymphostasis. The following drugs are used to treat pathology:
- phlebotropic agents: eliminate swelling, increase the tone of vascular walls, stabilize blood flow;
- diuretics (diuretics): remove excess fluid from the body;
- antibacterial drugs: prescribed in case of infection;
- anticoagulants: actively fight the formation of blood clots;
- painkillers: used when severe pain develops;
- external use (ointment for lymphostasis of the lower extremities): used to treat ulcers and erysipelas.
The type of medication, dosage and duration of use are determined strictly by the attending physician. You should not use medications for lymphostasis without consulting a specialist.
Diagnostics. Identifying the causes of lymphostasis of the upper extremities
If the pathology affects the upper extremities, the organs of the thoracic cavity are examined; if the lower extremities are affected, the organs of the abdominal cavity and pelvis are examined.
To clarify in more detail the place where the lymphatic block developed, the following is carried out:
- lymphography;
- lymphoscintiography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging;
- bacteriological examination (practised for erysipelas of the lower leg with lymphostasis and other infectious complications).
It is necessary to find out whether the swelling is due to lymphostasis or venous diseases. In the latter case, these are the following pathologies:
- thrombosis (blockage) of deep veins;
- PTPS – postthrombophlebitis syndrome;
- varicose veins of the lower extremities
Surgery
Surgical treatment is prescribed when conservative treatment is ineffective and complications such as fibrosis and limb deformities are present.
Phlebologists at the Yusupov Hospital microsurgically create a lymphovenous anastomosis - an outflow path for lymph between a vein and a lymphatic vessel. Pathologically changed limbs are reduced in size using liposuction - aspiration of excess adipose tissue. Advanced forms of the disease are treated by excision of pathological tissue. Excess fluid is removed by tunneling the limb with a special drainage.
Frequently asked questions about Lymphostasis
What is lymphostasis?
Lymphostasis is a disease that occurs due to impaired lymph outflow and causes swelling.
What is lymphostasis of the mammary gland?
Lymphostasis of the mammary gland is a disease in which swelling of the mammary gland occurs, caused by a violation of the outflow of lymph. The disease can be caused by a bruise, burn, certain infections, or the consequences of a mastectomy.
What is lymphostasis of the extremities?
Lymphostasis of the extremities is lymphatic swelling caused by impaired lymph circulation. As a result, the limbs increase in volume, the usual contours disappear, and tissue pain appears.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is one of the key components of the treatment of lymphostasis. Lymphostasis of the lower extremities after endoprosthetics also responds well to physiotherapeutic methods. The main physical procedures for the treatment of lymphostasis are:
- hardware pneumatic compression. The patient is placed in a special chamber in which variable air compression is carried out in the direction of the lymph flow;
- laser therapy. During the procedure, a low-intensity laser is used, which helps restore the functioning of the lymphatic system;
- hydrotherapy. Water procedures are very effective for lymphostasis: hydrogen sulfide baths, contrast showers, underwater massage;
- magnetic therapy – lymphatic drainage using a low frequency magnetic field;
- thermotherapy. Used to reduce pressure on blood vessels. During the procedure, cryomassage of the legs is performed using cold.
Gymnastics
Exercise is also an integral part of the treatment of lymphedema. Gymnastics can be classified as a method of physiotherapy. Exercises are prescribed by the attending physician depending on the patient’s condition. Lymphostasis of the calf muscle, thigh and ankle responds well to treatment with gymnastics. It can also be performed to prevent congestion in the lower extremities.
Physical exercise not only helps improve blood and lymph flow, but also has a positive effect on the entire body:
- improve the functioning of the nervous system;
- normalize breathing and heart function;
- strengthen the muscles of the body, increase their tone.
To treat lymphostasis, exercises such as “bicycle”, “figure eight”, raising and lowering the legs, and turning the legs can be used. A more detailed complex is prescribed by a specialist on an individual basis. Patients are also prescribed to wear compression textiles: underwear, bandages, which stimulate fluid circulation in the extremities.
Make an appointment
Benefits of pressotherapy
Pressotherapy is a hardware lymphatic drainage massage that improves metabolic processes in a selected area of the body. A very effective way to combat lymphostasis.
Let's consider the benefits of pressotherapy:
- One session replaces 20 manual massages.
- Has a deep effect.
- Improves blood and lymph flow.
- Promotes the removal of intercellular fluid.
- It's painless.
- It has a pleasant relaxing effect.
- It also helps remove cellulite and tighten the skin.
Diet
Depending on the cause of leg lymphostasis, the doctor prepares a diet. The basic nutritional rules for patients with lymphostasis are:
- avoiding alcohol and caffeinated drinks;
- exclusion of products containing dyes, artificial fillers and flavor enhancers;
- reducing salt intake;
- exclusion of products with excess animal fat content;
- preference is given to foods rich in proteins and fiber;
- maintaining water balance;
- fractional meals: small portions, but often.
Treatment of lymphostasis in Moscow
The Yusupov Hospital in Moscow provides high-quality treatment for primary and secondary lymphostasis of any degree. New things in the treatment of lymphostasis of the lower extremities are actively used in their work by doctors at the Yusupov Hospital, who are constantly studying innovations in this area and developing their own unique methods.
Therapy at the Yusupov Hospital can perfectly replace the treatment of lymphostasis of the lower extremities in Russian sanatoriums. The hospital has created comfortable conditions for a day and full-time hospital stay, where the patient can undergo all procedures. The treatment plan is drawn up by the best specialists in Moscow: rehabilitation therapists, physiotherapists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors, nutritionists, etc. The treatment is under the constant supervision of specialists, therefore, if necessary, it can be adjusted or supplemented to achieve a better effect.
To make an appointment with the specialists of the rehabilitation clinic, to clarify information about the work of the center and other questions of interest, you can call the Yusupov Hospital.
Make an appointment
Lymphedema Treatment | details about the Lymphatek method
Table of contents
- 6 advantages of the Lymphatek method
- 3 stages in the treatment of Lymphedema using the Lymphatek method in one picture
- What are the general treatments for lymphedema?
- One method for all causes of lymphedema
- Why is the motility of Lymphangions needed?
- Lymphotropic therapy makes the lymphatic vessels work!
- Lymphotropic injections are not painful and safe!
- What specific medications are administered?
- How many courses of treatment are required and how long does the result last?
6 advantages of the Lymphatek method
Why choose Lymphatek for the treatment of Lymphedema:
- You entrust your problem to doctors who have been involved in scientific research in lymphology for 40 years and understand Lymphedema.
- You will find out the real cause of lymphedema. For example, primary lymphedema is often secondary.
- You will forget the massage and most likely take off your jersey.
- The basis of the method is true lymphotropic therapy using drugs. It is carried out by the authors of the method. And the treatment method itself is patented.
- You will feel the effect immediately. Our treatment hits in three directions at once: I - pericellular space; II - lymph nodes; III - motility of lymphangions.
- What about 1-2 courses of treatment that can completely eliminate swelling for 15 years?
3 stages in the treatment of Lymphedema using the Lymphatek method in one picture
First, I - clean the swelling area. Then, II - will take care of the lymph nodes, which themselves can be 99% “clogged” with infection. She could have appeared there even before lymphedema. By the way, lymphedema could form due to this infection. Finally, III - start pumping up the lymphangion muscles.
What are the general treatments for lymphedema?
There are two types of treatment methods. Hint: choose the second one.
- Symptomatic
- Pathogenetic
Symptomatic ones work only with manifestations of the disease, symptoms and complications. The manifestation of lymphedema is swelling. If you only fight swelling, then you usually use massages, bandages, salt baths, etc. There are also consequences of edema: excess tissue formation, pain, infection. Then complications are treated: from pain relief with pills to liposuction.
Pathogenetic ones affect the mechanism of diseases, that is, what causes edema: when the function of the lymphatic system suffers. This is where the Lymphatek method works. Transplanted lymph nodes can also help here. But it has to work together. If the motor function of the Lymphangion has weakened, the new Lymph Node will not start it - first you need the Lymphatek method.
One method for all causes of lymphedema
The Lymphatek method is pathogenetic. It is aimed at launching the motility of lymphangions and is sometimes supplemented by the treatment of complications and concomitant pathologies and is based on three pillars:
- Clinical study of the causes of lymphedema, the state of the lymphatic system, concomitant pathology (which intensifies lymphedema or, conversely, is caused by lymphedema) and planning the stages of treatment (yes, one day we will recommend surgical intervention).
- Intravenous administration of drugs to correct concomitant pathologies and cleanse the pericellular space.
- Lymphotropic injection administration of drugs to restore contractile motility of lymphangions, treat infections, lymph nodes.
The initial appointment for lymphedema is often done by two doctors.
Conclusion: the pathogenetic method of treatment can be supplemented with a symptomatic one. A symptomatic treatment method without a pathogenetic one is more like palliative care. This is what patients complain about: “there is no treatment method, you will have to live with this all your life,” it is with this sentiment that they come to us, having visited every office in the clinic.
Why is the motility of Lymphangions needed?
The lymphatic vessel consists of segments - lymphangions, each of which has a muscular apparatus. The first step on the path to CURE lymphedema of any origin is to restore the independent ability of the muscular system to contract and pump lymph through the lymphatic vessel. Often it is simply weakened or does not work. This is what we want to resume.
The structure of the structural unit of the lymphatic vessel - the lymphangion (Prof. Borisov AV) and the lymphatic vessel and lymphangion under a microscope (Prof. Garyaeva NA)
These are the muscles we activate with the help of medications. Our experience shows that in most cases, restoration of lymphatic vessels is very successful. Over the past 3 months, out of 13 patients, all 13 have had a positive result! Of course, you need to contact us as early as possible.
Until you have found out the safety of this mechanism, it is a little early to think about lymph node transplantation or anastomosis, and immediately starting to bandage or massage is stupid!
Lymphotropic therapy makes the lymphatic vessels work!
This is a method of administering drugs where the lymphatic system literally “accepts” the administered drug mixture.
No, the drugs are not injected into a lymphatic vessel or into a lymph node, as you might think. This approach to administration has not justified itself since the 1980s (it is labor-intensive and traumatic), but we are fighting for the safety of lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels, right?
Treatment of lymphedema takes place in two stages: infusion therapy and lymphotropic therapy
In fact, classical lymphotropic therapy is when drugs are injected subcutaneously into the compromised (affected) region. But this is very different from a regular subcutaneous injection.
And here's the difference:
- The medicinal solution is prepared taking into account the requirements for medicinal mixtures for lymphotropic injections (concentration, pH, chemical composition, etc.)
- The injection site is carefully selected
- A drug depot is created in the tissues
- The medicine will enter the lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes without damaging them
- The subcutaneous tissue where the drug was injected remains unharmed
- Medicines affect the lymphatic system and surrounding tissues
- Medicines have almost no systemic effect on the body
Be careful: if someone offers you lymphotropic therapy, start simple. As we have already said, belonging to a scientific school is important.
First ask: from whom did this person learn lymphology as a science (and not as individual physical procedures)? And then don’t be lazy and contact the teacher and ask this teacher to confirm that the student can be trusted. The fact is that many tried to start lymphotropic therapy, but did not follow the methodology and suffered complications.
Lymphotropic injections are not painful and safe!
Yes, it doesn't hurt at all. And without complications. And that's why:
- All injections are performed with a small needle (insulin)
- Medicinal mixtures contain an anesthetic or contain drugs that do not irritate tissues
- In case of increased sensitivity, the injection site can be additionally treated with an anesthetic if desired.
- Injections are performed through a syringe pump (infusion pump) - slowly
- Medicinal mixtures are prepared specifically for lymphotropic injection
- Injections are performed strictly by a doctor, not a nurse.
What specific medications are administered?
Macro- and microelements, electrolytes, anesthetics, immunotropic drugs, antibiotics, adrenomimetics, hormonal drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs. Therapy may be accompanied by other pharmaceutical variety with concomitant pathology.
No dietary supplements or balms. Only official medicines, often original ones.
Dosages, site of administration, speed of administration, frequency of administration, combinations of drugs, sequence, dilution of drugs, indications and contraindications are determined individually in each specific case.
How many courses of treatment are required and how long does the result last?
For some, just one course of treatment consisting of 12-17 visits will help. In other situations, the preliminary treatment of erysipelas may initially take 5-7 days. In the third case, maintenance courses will be needed: first after 3 months, and then after a year. For example, our English patient Susan completed one course in 2005, and then a second in 2007. Since then I have no more lymphedema. You always need to start with the reason.
As for advanced stages and elephantiasis, it is likely that surgical intervention may be required. As we said in our webinar, we are not against any of the treatments, but rather for their logical and consistent use. None of them should be imposed as the only one. By the way, it happens that a very large edematous limb can be managed without surgery, because the edema can be large, but fibrosis of the subcutaneous tissue and sclerosis of the vessels have not yet occurred.
In future issues on the topic Lymphedema
- Photos to the studio! We analyze the results by day of treatment.
- Does the Lymphatek method work for primary lymphedema? Yes, but let's sort it out in order. There will be a video testimonial from the patient.
- Why is the Lymphatek method not used in regular hospitals? Honest answer.
- What to do with lymphedema after a mastectomy or after pelvic surgery?
- Analysis of a case of complicated lymphovenous insufficiency and video review of the patient.
PS: after almost every phrase we wanted to write: “we’ll tell you more about this.” Which is exactly what we’ll do!