- How does it manifest?
- What causes fluid to accumulate?
- Risk factors
- Classification and types
- How to treat?
- Clinical case
- What causes ascites to develop in cancer?
- Features of the treatment of ascites in cancer patients
- Conservative therapy
- Surgery
- Diagnostic methods
- Possible complications
- Forecast
- Prevention
- Prices
Euroonco doctors specialize in working with patients with ascites. We have the following treatment features for this disease:
- We provide comprehensive treatment. During laparocentesis (a puncture of the abdominal wall to remove fluid from the abdomen), we install temporary or permanent peritoneal catheters, as well as port systems. This allows the patient not to be limited in movement.
- If this is indicated, the patient is prescribed a special diet with limited water and salt load.
- If this condition occurs against the background of cancer, chemotherapy may be performed. Thanks to this, we achieve improvement in the condition of such patients with advanced ovarian and colon cancer.
- Intracavitary chemotherapy is effective. After the fluid is removed, a chemotherapy drug is injected into the abdominal cavity. In approximately half of the cases, repeated evacuation of the fluid is not required for at least 2 months.
When a patient with cancer and ascites switches to complex therapy, laparocentesis is required 2–3 times less often than usual.
How does it manifest?
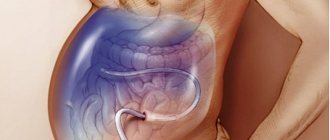
The presence of a small amount of fluid in the abdominal cavity does not manifest itself clinically. In addition, the human body normally produces and absorbs approximately 1.5 liters of fluid in the abdominal cavity per day. At the initial stage of this condition, patients have no special complaints, and fluid can only be detected during an ultrasound examination.
As the disease progresses, there is more fluid in the abdominal cavity, the person feels heaviness in the abdomen, and dull aching pain in the lower part. Subsequently, difficulty breathing, indigestion (nausea, belching, stool disorders) and urination problems occur. In the most severe forms, health deteriorates significantly, discomfort appears in the abdomen, shortness of breath occurs, early satiety occurs, an umbilical hernia forms, and swelling of the lower extremities appears.
5–10 liters of fluid, and sometimes 20 liters, can accumulate in the abdominal cavity. Because of this, internal organs are strongly compressed, intra-abdominal pressure increases, and the diaphragm is pushed into the chest cavity. This entails severe difficulty breathing. Due to the fact that resistance to blood flow increases in the abdominal organs, heart failure occurs. The consequence of long-term ascites is a violation of the drainage of the lymphatic system. Because of this, there is also a violation of lymphatic drainage in the lower extremities and, as a result, their swelling. There may also be a backflow of lymph into the internal organs. As a result, cancer cells enter healthy organs from the affected lymph nodes. This can trigger the development of metastases in the liver, stomach, pancreas and other organs. [4.8]
When there is more than one liter of fluid in the abdominal cavity, this can be noticed during a routine examination: the abdomen is enlarged or deformed, in an upright position it looks saggy, in a lying position the abdomen is flattened, the sides look swollen (the so-called “frog belly”). In thin patients, the navel often protrudes. A person may also experience hydrothorax, the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity. Typically, this condition develops in patients with congestive heart failure with long-standing ascites.
Mild or moderate ascites develops in 15 to 50 percent of patients in the early stages of cancer. Severe occurs in advanced stages in 7 to 15 percent of patients. [1]
In patients with advanced advanced cancer, exudative pleurisy is most common.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Pathogenesis
The disease provokes expansion of the cerebral ventricles for various reasons. The main provocateur is a violation of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
The process of cerebrospinal fluid circulation
The choroid plexuses produce approximately 600–700 ml of cerebrospinal fluid per day. It enters the central canal through special openings, washing the brain and then the spinal cord. Reabsorption occurs through the cerebral hemispheres through the venous sinuses.
Brain damage process
Excessive pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid provokes its leakage into the surrounding substance, which causes the development of edema. The dilated ventricles begin to compress the brain tissue.
The white matter takes the brunt of the attack, causing destruction of the myelin sheaths that transmit nerve impulses to the body.
Up to a certain point, such changes are reversible—after timely surgery, it is possible to almost completely restore neurological functions. Otherwise, atrophy of the brain substance develops, causing spastic paralysis, and the person ceases to control the functioning of the pelvic organs.
In infants, under the influence of such excess pressure, there is a rupture of adhesions inside the subarachnoid space, which opens the way for the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid and self-healing. In advanced situations, brain tissue ruptures. Timely treatment can prevent the development of neurological disorders.
What causes fluid to accumulate?
Pathological accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity occurs in certain diseases in which the regulation of water-salt metabolism and normal circulation are disrupted. The reason may be:
- Oncological diseases: secondary peritoneal carcinomatosis, lymphoma and leukemia, metastases in the hepatic portal area, primary mesothelioma.
- Diseases of the liver and its vessels: liver cancer, portal hypertension, liver cirrhosis, veno-occlusive disease, Budd-Chiari disease.
- Peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) of various origins: pancreatic, fungal, parasitic, tuberculous.
- Congestive heart failure, constrictive pericarditis.
- Other diseases: ovarian tumors and cysts (Meigs syndrome), pancreatic cyst, Whipple's disease, sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, myxedema.
Euroonco treats ascites of various origins. But since our main work is related to the treatment of malignant neoplasms, a significant part of our patients are cancer patients. [4,5]
Risk factors
Among the risk factors for the development of ascites, pathologies that can lead to liver cirrhosis are of greatest importance. First of all, these are viral hepatitis B and C, alcoholic hepatitis. Other most common risk factors:
- congestive heart failure;
- renal failure;
- obesity;
- diabetes mellitus type II;
- increased levels of “bad” cholesterol in the blood. [eleven]
Classification and types
Classically, depending on the level of protein in ascitic fluid, ascites is divided into exudative (25 g/l or more) and transudative (<25 g/l). This allows us to indirectly judge the reasons. Currently, a more accurate indicator is used - the serum albumin-ascitic albumin gradient (SAAG):
- When SAAG is more than 1.1, the cause of ascites is usually pathologies such as cirrhosis, congestive heart failure, and Budd-Chiari disease. They are associated with increased pressure in the portal vein.
- If SAAG is less than 1.1, it can be assumed that the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen is caused by pancreatitis or cancer.
According to the clinical course, the following types of ascites are distinguished:
- Depending on the severity of the current:
- 1st degree. There are no clinical manifestations; the diagnosis is established by ultrasound (determining the level of free fluid in the abdominal cavity).
- 3rd degree. Significant visual enlargement of the abdomen.
2nd degree. Slight visual enlargement of the abdomen.
- Resistant to diuretics: treatment with diuretics in combination with a diet in which sodium chloride intake is limited to less than 2 g per day is ineffective (no effect after 1 week of therapy).
Uncontrolled by diuretics: It is impossible to use diuretics because they cause significant side effects. [6,7]
Treatment of hydrocele (hydrocele) and lymphocele without surgery. Duration of observation.
Hydrocele in children under 1 year of age requires observation by a pediatric urologist-andrologist. If fluid accumulates and tension appears in the membranes of the testicle, punctures are performed to remove hydrocele. Sometimes repeated punctures are required.
Communicating hydrops with a narrow peritoneal process is usually observed up to 2 years.
Observation is also required for traumatic dropsy, which occurs as a result of a bruise without compromising the integrity of the testicle. As a rule, 3 months are enough to assess the dynamics of the process and, if there is no improvement, prescribe surgical treatment. The same applies to hydrocele formed after inflammation.
The most difficult is the management of patients with lymphocele that forms after surgical treatment of an inguinal hernia and varicocele. In this case, prematurely performed surgery has little chance of success. For 6-12 months, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the testicle according to ultrasound and duplex examination of the scrotal organs in order to assess the dynamics of the process and the effectiveness of the therapy.
How to treat?
There are several main methods for treating ascites in patients with cancer:
- conservative therapy (aldosterone antagonists, diuretics) - aimed at normalizing water-salt metabolism and reducing the formation of fluid in the abdominal cavity;
- laparocentesis - puncture of the abdominal wall under ultrasound control; used not only for removing fluid, but also for installing drainage, which will serve for long-term removal of fluid;
- palliative surgical operations - peritoneovenous shunt, omentohepatophrenopexy, deperitonization of the abdominal walls and others. [1.9]
Traditional methods of treating ascites caused by cancer do not have proven effectiveness and safety, therefore they are not used at Euroonko.
If you come to our clinic with ascites due to cancer, we recommend getting a second opinion regarding the treatment of the underlying disease from our clinical oncologists and chemotherapists.
Diseases and circumstances that are often accompanied by the occurrence of hydrocele
- Cryptorchidism (undescended testicle)
- Hypospadias
- False hermaphroditism
- Epispadias and exstrophy
- Ventriculo-peritoneal shunt
- Prematurity
- Low birth weight
- Liver diseases with ascites
- Defects of the anterior abdominal wall
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Burdened heredity
- Cystic fibrosis
- Inflammatory diseases of the scrotum leading to the development of reactive hydrocele
- Testicular torsion
- Injury
- Infection
- Previous operations affecting the lymphatic system of the testicle
Clinical case
A 59-year-old woman, Sh., was diagnosed with stage IV ovarian cancer (adenocarcinoma), ascites, and chronic pain syndrome 2 b according to the ShVO. The patient noticed an increase in the abdomen up to 120 cm in circumference, difficulty breathing, and weight loss. Specific treatment at the place of residence was denied. According to the patient, she was “sent home to die.” Read more…
A 59-year-old woman, Sh., was diagnosed with stage IV ovarian cancer (adenocarcinoma), ascites, and chronic pain syndrome 2 b according to the ShVO.
The patient noticed an increase in the abdomen up to 120 cm in circumference, difficulty breathing, and weight loss. Specific treatment at the place of residence was denied. According to the patient, she was “sent home to die.” Patient Sh. was urgently hospitalized in the specialized department of Euroonko, after active symptomatic therapy aimed at normalizing blood counts and restoring water and electrolyte balance, a peritoneal port was installed. Resolution of ascites was carried out under the control of plasma protein levels. The use of peritoneal ports allows for the removal of ascitic fluid in fractional doses, which ultimately eliminates the occurrence of serious complications in the form of hemorrhagic syndrome associated with hemodilution and coagulopathy as a result of massive entry of ascitic contents into the venous bed.
After stabilization of the general condition, against the background of nutritional support, antiemetic and antisecretory therapy, patient Sh. received specific chemotherapy treatment with good effect. Upon resolution of ascites in the presence of a peritoneal port, intra-abdominal chemotherapy became possible.
Six months after the described hospitalization, the patient returned to her usual lifestyle and continues to receive systemic treatment on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a team of Euroonco specialists. The response to treatment is regarded as positive in the absence of ascites and a total reduction in the size of the lesions by more than 70%. Combined treatment in the format of systemic and local (intra-abdominal) therapy with implantation of a port system is the optimal treatment regimen for this group of patients. In the practice of Euroonco doctors, such cases occur on a regular basis. Hide
What causes ascites to develop in cancer?
The most common cancers that cause fluid accumulation are:
- ovarian cancer (in 25–30 percent of patients),
- mammary cancer,
- uterine cancer,
- stomach cancer,
- colon cancer. [2]
The accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity during cancer occurs due to the fact that the peritoneum (the membrane lining the inside of the abdominal wall and covering the organs located in it) is affected. Tumor cells settle on its parietal and visceral layers, resulting in disruption of lymphatic drainage. This causes deterioration in fluid absorption. Typically caused by tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and ascites in ovarian cancer.
When a tumor or metastases forms in the liver, the reason for the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is different: the venous system of the liver is compressed and the natural venous outflow from the intestine is disrupted. This condition develops quickly and usually lasts longer and is more severe. 15 percent of cancer cases occur in this particular form.
Abdominal lymphoma causes ascites through blockage and effusion (leakage) of lymph from the intra-abdominal lymph ducts. [2.6]
When is surgery performed for hydrocele?
- Operations for communicating hydrocele of the testicle are most often performed in children aged 2 years.
- From 1 to 2 years, operations for communicating hydrops are performed if:
- combined dropsy and inguinal hernia
- when the volume of the scrotum clearly changes with changes in body position
- dropsy increases, causing discomfort
- infection joins
- Surgeries for post-traumatic dropsy – 3-6 months after injury.
- Lymphocele that occurs after surgery for an inguinal hernia or varicocele is operated on 6 to 18 months after the appearance of fluid in the membranes of the testicle.
Features of the treatment of ascites in cancer patients
In hospitals that do not specialize in the treatment of cancer, the approach to patients with ascites may be ineffective due to the characteristics of this condition. For example, the main treatment may be the use of diuretics, aldosterone antagonists, and dietary changes to limit water and salt load. The effectiveness of this approach for reducing portal hypertension is relative; in cancer patients, fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity is caused by peritoneal carcinomatosis. Therefore, conservative therapy cannot be the main treatment method in such patients.
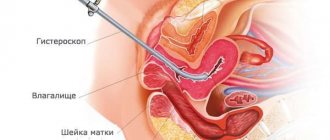
Typically, fluid is removed from the abdomen using laparocentesis (abdominal paracentesis). This is a surgical procedure that is performed by a surgeon and an anesthesiologist-resuscitator. [3.10]
Causes of fluid accumulation in the ovaries
Typically, hydrocele occurs on only one testicle; in rare cases, mainly due to trauma, two are affected.
Congenital dropsy is formed during the period of intrauterine formation of the child, when the process of development of the testicle takes place, which descends into the scrotum through the inguinal canal. After which the gap between the peritoneum and the appendix closes:
- if this does not happen, fluid accumulates in the tissues of the scrotum, which flows from the peritoneum along the vaginal process, called communicating;
- if the process of closing the valve has passed, and there is water around the testicle that does not pass into other cavities - isolated.
In case of congenital dropsy of the ovarian membranes, the operation is not performed immediately, since the fluid can resolve. Therefore, up to 18 months, the child is examined monthly by a doctor, establishing the dynamics of the development of the disease.
Acquired hydrocele occurs in adolescents and adult men when the outflow of lymph from the testicle is impaired, which is formed in the process of:
- early surgical intervention, for example, removal of an inguinal hernia;
- damage or compression of lymphatic vessels (trauma, tumor);
- inflammatory processes during the development of infections, including colds.
According to the nature of the disease, hydrocele is divided into acute and chronic forms.
Conservative therapy
Conservative therapy is used in the treatment of small and moderate ascites. In other words, if there are no tiring and debilitating symptoms: pain, rapid breathing (tachypnea), etc. Up to 65% of patients have an improvement in their condition when treated with diuretics - this way you can remove up to 1 liter of fluid per day. [5]
In the later stages of cancer, reducing salt and water intake can reduce quality of life. Therefore, at Euroonko such diet correction is rarely prescribed.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Prevention methods
It is necessary to take measures to prevent inflammation of the scrotum. Parents should regularly examine their child's genitals and contact a doctor immediately if they notice any swelling. Those children who have a congenital disease should be regularly monitored by a pediatric urologist.
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12378019 Han CH, Kang SH. Epididymal anomalies associated with patent processus vaginalis in hydrocele and cryptorchidism // J Korean Med Sci. 2002 Oct;17(5):660-2.
- A.V. Grinev, S.I. Nikolaev, V.E. Serdyutsky, D. S. Efremenkov. New technologies in the treatment of hydrocele in adults and children // Bulletin of the Smolensk State Medical Academy, 2003, No. 5.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
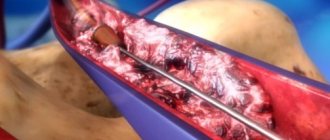
Surgery
Ascites in cancer must be treated surgically when it:
- Refractory, that is, not amenable to conservative treatment.
- Large, that is, if it is necessary to remove up to 6–10 liters of fluid at a time (this difficult procedure is carried out for strict medical reasons).
- Giant. In this case, a combined operation is needed, which includes removing a large volume of fluid (up to 5–7 liters) on the first day and removing the remaining volume at a rate of no more than 1 liter per day for 7–10 days.
In the classic version, laparocentesis is performed on an empty bladder, the patient sits down, and the seriously ill person is placed on his side. [4]
It is dangerous to perform laparocentesis without observing the rules of asepsis and antisepsis. Therefore, the release of fluid is carried out only in a specialized medical institution with a license to perform surgical interventions and with a hospital. If the patient is in serious condition, it is difficult for him to move, an ambulance team is called for him.
First, local anesthesia is performed, then, under ultrasound guidance, a puncture is made with a trocar (an instrument in the form of a thin tube with a sharp end) along the midline of the abdomen or along the line connecting the navel to the iliac crest. Usually no more than 5–6 liters of liquid are removed at a time. To prevent blood pressure from dropping sharply and vascular collapse, the fluid is released slowly.
In accordance with the classical technique, the patient needs to lie for several hours on the side free from the puncture. If at this time a small amount of liquid continues to be released, then a reservoir is applied, which is removed after a day or two.
If it is necessary to remove a large amount of liquid, then a loss of protein and salts occurs, which becomes the cause of protein deficiency. To prevent such a complication, the patient is given albumin. With repeated puncture, another complication may arise - fusion of the omentum (part of the peritoneum) or intestine with the anterior wall of the abdomen. Because of this, intestinal function deteriorates significantly, and during subsequent punctures serious complications can develop. [4,6]
With the modern approach to laparocentesis, fluid drainage occurs primarily through a permanent peritoneal catheter. At the same time, the deficit in circulating blood volume is replaced by plasma expanders (from the English plasma expander - increasing plasma volume). Typically, 10–20% albumin solutions are used for this. In some cases, aminosteril, polyglucin, rheopolyglucin (dextran-40), hemacell and new starch-based preparations (refortan, stabizol, HAES-steril) can be used instead of albumin. This alternative only helps to compensate for fluid deficiency in the blood, but these drugs do not affect protein deficiency.
Some patients with ascites undergo omentohepatophrenopexy. This is a laparoscopic operation in which the omentum is sutured to areas of the surface of the liver and diaphragm. Due to the fact that contact occurs between the omentum and the liver, conditions appear for the absorption of ascitic fluid by nearby tissues. If the patient has peritoneal carcinomatosis, surgery is performed to a limited extent. Typically, in such patients, omentohepatophrenopexy becomes part of palliative treatment. [6,7]
Postoperative recommendations
In most cases, the surgical process is carried out successfully, the patient quickly returns to normal life with strict adherence to the surgeon’s recommendations.
First of all, you need to temporarily change fashionable tight trousers to loose ones that do not squeeze or pinch the groin area.
It is mandatory to wear a special support bandage – a suspensor – for three weeks after surgery. The garter minimizes tension in the scrotum.
It is not recommended to play sports in the first two months; you need to rest more often.
You can take water procedures two hours after the operation, but you should not overheat or overcool. You need to give up baths, saunas, autumn or winter fishing for three months.
Additionally, after the operation, the doctor prescribes painkillers and possibly physical procedures. You must come to your appointment regularly throughout the year. The surgeon or urologist will prescribe pharmaceuticals based on the patient’s general condition and complaints.
Sexual relations can be resumed 5-6 weeks after surgery.
Diagnostic methods
If more than 500 ml of fluid has accumulated in the abdomen, the doctor may identify symptoms during an examination. Ultrasound is used to confirm the diagnosis. Sometimes ascites is discovered accidentally during an ultrasound or computed tomography scan of the abdomen, which is performed for another reason.
Euroonco operates a comprehensive gastrointestinal screening program, which helps assess the condition of the digestive system. It, in particular, includes an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity with determination of the level of free fluid. This helps diagnose ascites at an early stage.
It is important not only to identify fluid in the abdominal cavity, but also to understand the reasons for its accumulation - this helps to assess the prognosis and prescribe effective treatment. In most cases, the examination includes the following laboratory tests:
- Biochemical blood test - complete biochemical panel. It helps assess the condition and function of the liver, kidneys, and electrolyte levels.
- Blood clotting study.
- Study of ascitic fluid obtained during laparocentesis. For analysis you need a little of it - usually 20 cm³, less than a tablespoon. It examines the level of red and white blood cells, total protein, albumin, amylase, glucose, and examines for pathogenic microorganisms. A cytological examination is performed to help identify cancer cells. [6]
Symptoms
With local dropsy, symptoms depend on the location of the swelling. With severe swelling of the eyelids, the field of vision narrows. Swelling of the feet does not allow wearing usual shoes. Dropsy of the brain leads to disturbances of consciousness, and hydrocele manifests itself as nagging pain in the testicle. Neurological edema is accompanied by dysfunction of the limbs and pain due to compression of the nerve endings.
Systemic dropsy is manifested by the following symptoms:
- dryness and swelling of the skin;
- fluctuations in weight during the day - typical for dropsy in pregnancy;
- a feeling of thirst due to blood thickening due to the effusion of fluid into the interstitial space;
- “pit” symptom: when pressing with a finger, a pit remains in the area of edema;
- the appearance of shortness of breath;
- fast fatiguability.
The absence of acute pain with dropsy masks the danger of the condition. Blood thickening increases the risk of thrombosis, which can lead to acute hypoxia and shock.
In pregnant women, whose internal edema appears only after retention of 3-4 liters of fluid, swelling of the placenta simultaneously occurs, due to which the umbilical cord vessels are compressed and oxygen starvation of the fetus develops.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of dropsy is not difficult and is based on clinical manifestations and medical history.
If edema is detected, additional studies are carried out to identify the cause of dropsy.
Laboratory methods used:
- general urinalysis - determines the concentrating ability of the kidneys and the integrity of the glomerular apparatus;
- special tests: according to Nechiporenko, Zimnitsky, Addis-Kakovsky - they can detect kidney damage;
- general blood test - allows you to identify inflammatory and allergic processes in the body;
- biochemical tests - determine liver function and the amount of protein in the blood plasma;
- Hormone tests are done to confirm or refute the diagnosis of a tumor of the adrenal gland, pituitary gland, as well as hypofunction of the thyroid gland.
Possible complications
If a lot of fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity, the functioning of the internal organs is disrupted, difficulties arise during breathing, as the mobility of the diaphragm is limited, and effusion forms in the pleural cavity.
With increased portal vein pressure, bacteria from the intestine can spontaneously enter the ascitic fluid and cause spontaneous bacterial peritonitis .
In rare cases, a very serious complication develops - hepatorenal syndrome . This term refers to impaired renal function with severe liver damage, up to severe renal failure. The exact mechanism of development of this condition is unknown, but it is believed to occur due to impaired renal blood flow, excessive use of diuretics and intravenous contrast agents. [4]
Causes of the disease
Acquired dropsy:
- injury;
- tumor;
- inflammation;
- complication of various diseases;
- previous infection;
- severe vascular and heart diseases;
- the result of unsuccessful surgery;
- performing peritoneal dialysis;
- testicular torsion;
- disturbances in the functioning of the lymphatic system, resulting in the formation of excess lymph that accumulates in the membranes of the testicles.
Congenital hydrocele:
- birth injury;
- pathologies during pregnancy;
- prematurity;
- developmental anomalies in infants;
- infection suffered by the expectant mother during pregnancy;
- abdominal wall defects;
- risk of miscarriage;
- location of the testicles outside the scrotum;
- hypospadias (penis malformation);
- non-fusion of the vaginal process.
Causes of isolated dropsy:
- Anomalies in the fusion of the inner membrane of the testicles. Normally, it should turn into connective tissue that cannot produce fluid. If the fusion occurs incorrectly, then the gap between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum disappears. However, the inner lining of the testicle can produce fluid, just like the peritoneum. The fluid cannot drain into the abdominal cavity and accumulates in the scrotum.
Causes of communicating hydrocele:
- An anatomical feature of the development of the scrotum, in which the canal between the abdominal cavity and the scrotum does not heal. As a result, fluid circulates into the scrotum.
Primary hydrocele appears without concomitant pathology and is the result of structural features of the body. Secondary dropsy develops due to infection, injury, disruption of the processes of reabsorption and filtration of fluid produced by the vaginal membrane. Such pathologies are usually caused by testicular torsion, tumors of the appendages and testicles, complications of influenza, ARVI, mumps, and surgery for a hernia.
The appearance of dropsy is promoted by increased intra-abdominal pressure. In early childhood, it occurs against the background of colic, constipation, and crying. In older boys - when lifting heavy objects, physical activity, severe coughing, straining during bowel movements.
Forecast
Ascites in cancer significantly worsens the prognosis. From the moment of diagnosis, only half of the patients remain alive within 1–4 months. The average life expectancy is from 20 to 58 weeks. Timely treatment in a clinic that specializes in working with such patients helps improve survival. If the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity is caused by cirrhosis of the liver, when there is no cancer, the prognosis is better, and if there is chronic heart failure, with appropriate treatment, you can live for years. [6]
Diagnosis: dropsy of the membranes
Patients who do not consider the disease serious are susceptible to complications, namely:
- internal suppuration;
- spread of inflammation to nearby organs and tissues;
- possible testicular rupture;
- infertility;
- hernia;
- sexual disorders (erectile dysfunction).
The diagnosis of hydrocele is established by a urologist after a thorough diagnosis and receipt of test results. With timely access to a medical center, namely surgical intervention, complications occur extremely rarely.
Methods of surgical treatment, operations:
- Ross;
- Lord;
- Winckelmann and Bergman.
Modern clinics perform Winkelmann surgery in 55% of cases for hydrocele. This method does not require intensive preparation, it is carried out within 40-60 minutes, the approximate price is 25-30 thousand rubles.
Prices
Euroonko has a special offer for drainage of ascites in a day hospital - 63,300 rubles.
The program includes:
- Examination and consultation with an oncologist surgeon.
- Complete blood count, biochemical blood test, ECG.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs with determination of the level of free fluid
- Conducting laparocentesis with ultrasound navigation.
- Complex drug therapy aimed at restoring water and electrolyte balance.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Pharmacotherapy of tumors. Dedicated to the memory of Mikhail Lazarevich Gershanovich // A.N. Stukov and the team of authors / Ed. A.N. Stukova, M.A. Blanca, T.Yu. Semiglazova, A.M. Belyaeva. St. Petersburg: Publishing House ANO “Oncology Issues”, 2022, 512 p.
- Willert A.B., Kolomiets L.A., Yunusova N.V., Ivanova A.A. Ascites as a subject of research in ovarian cancer. Siberian journal of oncology. 2019; 18 (1): 116–123. – doi: 10.21294/1814-4861-2019-18-1-116-123.
- Willert A. B., Kolomiets L. A., Yunusova N. V. Ascites as a tumor microenvironment in ovarian cancer: relationship between prognosis and chemoresistance. Advances in Molecular Oncology 2019;6(2):8–20.
- Yu.M. Stepanov, I.N. Kononov, T.A. Skorokhod, Ascites associated with intraperitoneal rupture of the bladder and urinary peritonitis. Clinical decline of current gastroenterology, 4 (66) • 2012.
- T.A.Baeva, D.N.Andreev, E.M.Mironova, D.T.Dicheva - Ascites: differential diagnosis and treatment. — Directory of a polyclinic doctor. No2, 2016.
- Alekseichik, S. E. Ascites. Differential diagnosis: method. recommendations / S. E. Alekseychik. – Mn.: BSMU, 2005. – 28 p.
- V.T. Ivashkin, M.V. Mayevskaya, Ch.S. Pavlov, E.A. Fedosina. Clinical recommendations of the Russian Society for the Study of the Liver and the Russian Gastroenterological Association for the treatment of complications of liver cirrhosis. Ros journal gastroenterol hepatol coloproctol 2016; 26(4).
- J. T. Tamsma, H. J. Keizer, A. E. Meinders. Pathogenesis of malignant ascites: Starling's law of capillary hemodynamics revisited. - Annals of Oncology 12: 1353-1357. 2001.
- Rony A Adam, Yehuda G Adam. — Malignant ascites: past, present, and future. - VOLUME 198, ISSUE 6, P999-1011, JUNE 01, 2004. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2004.01.035
- Michelle Meier, Frank V. Mortensen, Hans Henrik Torp Madsen. — Malignant ascites in patients with terminal cancer is effectively treated with permanent peritoneal catheter. — Acta Radiologica Open 4(7) 1–7. DOI: 10.1177/2058460115579934.
- RC Oey, HR van Buuren, RA de Man. — The diagnostic work-up in patients with ascites: current guidelines and future prospects. OCTOBER 2016, VOL. 74, NO. 8