Urologist
Belkin
Andrey Ivanovich
20 years of experience
Urologist of the first category, member of the European Association of Urology
Make an appointment
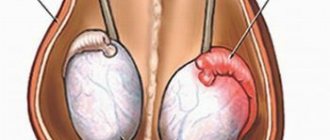
Varicocele is a change in the veins in the spermatic cord, which causes a violation of the outflow of the veins from the testicle. Signs include pulling and bursting pain, heaviness or discomfort in the scrotum, and noticeable dilatation of the veins. In this case, the danger of varicocele lies in the possible rupture of varicose vessels, leading to hemorrhage in the scrotal area. If varicocele progresses in men, the testicles decrease in size, spermatogenesis fails and menopause or infertility occurs.
Varicocele in men does not pose a threat to the patient’s life and does not cause much concern. The main danger lies in the development of early menopause or infertility. Clinical trials have shown that the presence of pathology leads to impaired spermatogenesis in half of the cases. About 20% of men suffer from varicocele. However, the data varies greatly across age groups. Varicicol is more common in adolescents than in conscripts. In this case, the course of the disease is mainly characterized by the absence of manifestations.
Symptoms
The severity of varicicol symptoms is related to the degree of dilation of the veins. The initial stages have no signs of pathological development. Varicose veins can only be detected during a preventive examination.
Varitsikole 2 degrees are characterized by complaints of pain in the scrotum. At the same time, the severity of pain varies. Symptoms of varicicole at this stage:
- discomfort while walking;
- sharp almost neuralgic pain;
- burning in the scrotum area;
- sexual dysfunction;
- increased sweating;
- asymmetrical position of the testicles and sagging of half of the scrotum;
- visible dilatation of veins.
Grade 3 varicicole is characterized by a lack of connection between physical activity and the occurrence of pain. The pain syndrome becomes constant and intense. Externally, countless clusters of veins and the brightness of the asymmetrical appearance of the scrotum are noted.
Are you experiencing symptoms of varicicole?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Varicocele
Diagnosis of varicocele is mandatory if the partner is not pregnant for more than six months or if the quality of sperm is impaired.
If you suspect a varicocele, it is important to exclude other diseases that give similar symptoms. Considering the fact that dilation of the veins of the spermatic cord may be a consequence of tumors of the retroperitoneum and pelvis, additional examination may be required.
Which doctors should I contact?
Varicocele is detected during preventive examinations. When the first symptoms appear, you should contact, but in the future you need to consult an andrologist.
Treatment of varicocele
Stage 1 varicocele does not require treatment. It is enough to eliminate the cause of congestion in the pelvis (chronic constipation, avoidance of heavy physical activity, etc.). If there is discomfort in the scrotum, pain in the testicle caused by varicocele, cold (an ice pack) applied to the affected area and the prescription of vasoconstrictor medications usually help.
Agents that dilate blood vessels and heat, on the contrary, are contraindicated due to the fact that they only worsen the patient's condition. Conservative treatment methods include:
- restriction of physical activity;
- exclusion of active sports, horse riding;
- wearing a suspensor (a bandage used to immobilize the scrotal organs).
Surgery is indicated in later stages of the disease, when pain symptoms are present, there is hemorrhage in the scrotum, a decrease in testicular volume, in case of infertility and a pronounced cosmetic defect.
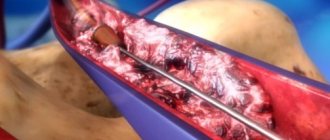
Today, methods of surgical treatment of varicocele can be divided into three groups: vein excision, testicular lift, and blockage of veins from the inside (embolization). Surgical treatment of varicocele can be performed using open retroperitoneal access (Ivanisevich or Palomo operation), inguinal and subinguinal method (Marmara operation), as well as laparoscopic access.
The most common is the Ivanisevich operation: ligation of the testicular vein at or just above the internal inguinal ring. This is the simplest but least effective surgical technique. Can be performed under local anesthesia. Disadvantages: large skin incision (4-5 cm), high trauma, cosmetic defect, frequent development of complications.
Microsurgery according to Marmar is recognized as the gold standard, as its effectiveness and safety reach 98%. It is performed through a small (3 cm) incision in the groin area; after the operation, the scar is practically invisible. Performed under local anesthesia. Such an intervention is carried out in the presence of an operating microscope. With high precision, all veins of the pampiniform plexus are sequentially ligated and intersected (in this section of the spermatic cord there are, as a rule, from 3 to 6). In this case, the abdominal cavity is not opened, there is no trauma to the lymphatic vessels of the spermatic cord, which significantly reduces the risk of complications and allows you to resume physical and sexual activity in a short time. The use of optical systems minimizes the risk of ligation of arterial vessels and, accordingly, the risk of testicular necrosis. However, the intervention is considered technically challenging.
Endovascular testicular vein embolization is a low-traumatic intervention performed by vascular surgeons. It is performed under local anesthesia. The doctor makes a small incision in the thigh to gain access to the femoral vein. Through a catheter installed under X-ray control in the testicular vein, a special plug (embolus) or sclerosing agent is inserted to stop blood flow through the vessel.
Advantages of embolization:
- low trauma, virtually no blood loss;
- minimal risk of hydrocele (hydroxycele), since the procedure takes place in a vein and does not affect other blood and lymphatic vessels;
- fast rehabilitation.
Flaws:
- radiation exposure - the operation is performed under x-ray control;
- sometimes the doctor is unable to get into the testicular vein due to the anatomical features of the patient’s venous system;
- a relatively high risk (up to 11%) of developing hematomas, bleeding and perforations.
With laparoscopic venectomy, access to the testicular vein is carried out through small punctures of the anterior abdominal wall and only under general anesthesia.
The doctor inserts an endoscope with surgical instruments inside, which crosses the testicular vein. Surgery with laparoscopic access provides the possibility of simultaneous ligation and excision of testicular vessels on both sides in the presence of bilateral varicocele. Laparoscopic surgery is performed through three punctures. The vein is isolated and ligated from the abdominal cavity. The advantage of laparoscopy is that it is less traumatic. However, with this treatment there remains a relatively high risk of relapse and complications. After surgery, infertility resulting from the development of varicocele is cured in most cases.
Complications
The occurrence of varicocele at a young age can lead to testicular hypotrophy or atrophy and infertility. A connection between varicocele and decreased production of the male hormone testosterone, early ejaculation and impaired potency has been described. Men with this pathology are at risk of losing potency in adulthood and old age.
Sometimes varicocele leads to testicular hypotrophy (reduction in size by more than 10%), up to complete atrophy. This happens due to impaired blood circulation.
With timely treatment, blood supply to the testicle is restored. In most cases, the volume of the organ is also restored.
Stagnation of venous blood in the pelvic veins disrupts the blood supply to the organs; the testes reduce the production of sperm and testosterone. A decrease in testosterone levels leads not only to a decrease in libido and potency, but also to a deterioration in general condition. Metabolic processes slow down, the man begins to gain weight. The amount of adipose tissue increases, which in turn accelerates the decline in testosterone. In addition, varicocele provokes the development of adenoma and prostate cancer.
Due to the rupture of dilated venous vessels or their inflammation, causing severe pain, such serious and rare complications as hemorrhages in the scrotum occur.
After surgery for varicocele, the following complications are possible:
- lymphostasis – impaired lymph outflow;
- purulent discharge at the incision site;
- pain syndrome;
- hydrocele (dropsy of the testicle) is an accumulation of fluid in the tissues of the male gonads.
After therapy, varicocele recurrence is possible.
Depending on the chosen surgical treatment method, the frequency of relapses in children varies from 1 to 20%; in adults, varicocele recurs 2 times less often. In this regard, many doctors recommend performing operations after the end of puberty. Prevention of varicocele
There are no effective methods for preventing varicocele, since this disease is often determined by hereditary factors. Elimination of congestion in the pelvic organs, which involves normalizing stool, eliminating prolonged and severe physical stress, avoiding alcohol abuse, regular sex life, etc. for this category of patients are mandatory.
Experts strongly recommend that all young men aged 19-20 years (at the end of puberty) undergo examination by a urologist/andrologist. If no clinical signs of varicocele are detected, in principle, there is no need to worry about this in the future.
Sources:
- Great Medical Encyclopedia (BME), edited by Petrovsky B.V., 3rd edition, volume 4.
- Akhvlediani N.D., Chernushenko A.S., Reva I.A., Pushkar D.Yu. Subclinical varicocele: criteria for diagnosis, role in the development of male infertility, modern approach to treatment // – Obstetrics and Gynecology. – 2020; 11. – pp. 71-76.
- Kogan M.I., Afoko A., Tampuori D. Varicocele: a controversial problem // – Urology and Nephrology. – 2009; 67(6). – pp. 67-71.
- Laurent O.B., Sokolshchik M.M., Gagarina S.V., Stoyko Yu.M., Golitsyn A.V. Choosing a method for surgical correction of varicocele, taking into account the characteristics of venous hemodynamics // – Urology. 2006; 5. – pp. 24-9.
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Causes of occurrence and development
The cause of varicicole lies in the disruption of the valves of the veins in the spermatic cord. When the valves cannot cope with the pressure during the outflow of blood, the veins begin to expand, forming nodes. Pressure increases during physical activity or prolonged stay in an upright position.
Factors influencing the appearance of pathology:
- deficiencies of connective tissue of venous vessels;
- disturbances in the development or changes in the functioning of the valve apparatus of regional and main veins;
- failures in the formation of the inferior vena cava during pregnancy.
One of the reasons is a feature of the anatomical structure, which leads to increased pressure in the renal vein and, as a consequence, to disruption of the valves in the veins of the testicles. The provoking factor is increased intra-abdominal pressure, which is observed against the background of constipation or excessive physical exertion, etc. The development of pathology occurs due to complications of a large process in the pelvis, retroperitoneal cavity, and kidneys. The reason for the development is the presence of obstacles to sufficient outflow of blood from the veins of the testicles and spermatic cord.
Preventive measures
An annual visit to the urologist, even in the absence of any complaints or symptoms, in combination with a healthy lifestyle, decisive and unconditional cessation of bad habits (primarily smoking) and active sports is the best set of preventive measures at any age. You should also pay attention to the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and take care to exclude fatty, fried and spicy foods from your diet. Clothing should be comfortable and not constrict the genitals. It is important to remember that hypothermia of the body is an additional provoking factor for the occurrence of varicocele or its progression.
Degrees of varicicole
There are a number of degrees of varicicol:
- 0 degree – it cannot be determined by palpation, and varicose veins can only be seen during instrumental diagnostics: Doppler or ultrasound;
- varicose veins of the 1st degree - palpation allows you to determine varicose veins in a vertical position;
- 2nd degree – palpation allows you to feel varicose veins in any position of the body: standing and lying down;
- Grade 3 varicose veins – the visibility of varicose veins with the naked eye.
Valsalva maneuver
Sometimes, at rest, reflux with varicocele is not at all expressed; in such cases, additional tests are required, such as a test with straining and holding the breath or a Valsalva maneuver.
The Valsalva maneuver for varicocele is performed as follows: the patient takes a deep breath and begins to strain the abdomen. At this moment, in the Color Doppler mode, the doctor normally sees only the pulsation of the testicular artery and the artery of the ejaculatory duct. With a varicocele, a network of bending tubular structures in blue and red colors is visualized in the Color Doppler mode - these are varicose veins or varicoceles. Coloring of the veins for more than 1 second indicates malfunction or so-called reflux. This condition is expressed in the penetration of blood through incompetent valves and dilated varicose nodes into the testicle and contributes to the malnutrition of the testicle.
Complications
The most important complication of varicose veins in the spermatic cord is infertility. It occurs against the background of impaired thermoregulation of the testicles, which leads to the cessation of sperm production.
Other dangerous consequences of varicicole are:
- heart valve malfunction;
- phimosis or flat feet.
When to see a doctor
Often varicose veins are one of the signs of the presence of malignant tumors. That is why it is not recommended to postpone visiting a doctor for a preventive examination when symptoms of the disease appear.
The slightest signs of pathology of the veins of the spermatic cord should be a reason for an unscheduled visit to the doctor. It is recommended to visit a urologist or phlebologist for varicicol.
JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) employs doctors from 66 specialties, trained at the highest level. You can make an appointment and choose a doctor on the website, by phone or from the administrators at the clinic at the address: Moscow, 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya Lane, 10, in the immediate vicinity are the Novoslobodskaya, Belorusskaya, Chekhovskaya, Tverskaya metro stations.
Stages of development of testicular varicose veins
Varicocele begins with a mild form and gradually progresses. At the same time, the pathology does not always reach its climax; varicose veins can stop developing, remaining undetected.
The disease occurs in 4 stages:
- Symptoms of varicocele are hidden.
The veins of the testicle are not visible or palpable. Dilatation of the veins is detected on ultrasound of the scrotum. That is why preventive ultrasound examination is recommended for all young men at the age of 17-18 years. - The veins are palpated in a horizontal position.
In the supine position no changes are noticeable. - Veins can be palpated in any position.
- Dilated veins are greatly enlarged and visible
. If severely disturbed, they may even hang down. Pain appears.
Spermagenesis is disrupted gradually, which leads to infertility. The brighter the signs, the more reasons to suspect a male factor in infertility.
Diagnostics
An angiosurgeon or phlebologist can easily identify varicicole. Diagnosis determines the relationship between symptoms and treatment for varicicole. Primary diagnosis consists of collecting anamnesis - interviewing the patient about the nature and presence of complaints, their dependence on physical activity or injuries received.
At certain stages of the disease, physical examination reveals visible varicose nodes, and palpation gives an idea of plexuses in the bunch. A sign of pathology is laxity of the affected testicle. Palpation must be carried out standing and lying down under pressure and in a calm state, which makes it possible to clarify the localization of the diagnosis.
Instrumental diagnostic methods:
- with varicicol, ultrasound is done for the abdominal cavity, including the kidneys;
- MRI and CT to exclude thrombosis;
- after adulthood, a spermogram is performed - pathology shows asthenozoospermia or oligospermia, a decrease in activity or quantity, respectively.
Additional diagnostic methods:
- Ultrasound of the scrotum,
- dopplerography,
- thermography and thermometry,
- rheography.
To construct a treatment regimen for varicicolitis in men, retrograde venography of the kidneys and testicles, transscrotal testicular phlebography and antegrade venography are performed.
The multidisciplinary medical clinic (academician Roitberg’s clinic) offers modern, accurate and fast research methods.
Advantages of Marmara microsurgery:
- A small cosmetic incision in the groin area, in the hair growth area (the scar is almost invisible)
- The greatest efficiency of the operation is achieved through the use of operating binoculars and microsurgical instruments
- Lowest percentage of relapses and complications (less than 5 percent)
- Can be performed on an outpatient basis, without hospitalization
- Short and easy postoperative and recovery period
I am aware of my responsibility for preserving the main thing that my patient trusts me, and I will do everything to justify the trust!
Treatment
Treatment of varicicol secondary form comes down to the fight against the original disease.
The initial stages of the pathology of the primary form of varicicolitis can be treated without surgery. It comes down to the following tips:
- eliminating congestion in the pelvis;
- wearing a jockstrap gives positive results in adulthood.
Stages 2 and 3 of pathology require surgical intervention. Indications for surgery for varicicol:
- asthenozoospermia or oligospermia;
- delayed testicular growth during puberty;
- aesthetic defect.
Types of operations for varicicol: testicular lift, vein excision, embolization or removal of varicicol. Vein excision occurs at the entrance to the inguinal canal, directly in the inguinal canal, or at the exit from it.
Today, the most popular methods of treating varicose veins are microsurgery and laparoscopy for ligation of varicose veins. These methods have a lower percentage of complications and relapses, as well as a simplified rehabilitation procedure.
Treatment at the Innovative Vascular Center
The Innovative Vascular Center uses endovascular technology to eliminate varicoceles. We perform retrograde venography of the testicular vein and embolize this dilated vein with special coils and sclerosants. This operation for varicocele does not require incisions or hospitalization for treatment, but reliably eliminates venous hypertension in the left testicle.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important for the outcome of these patients. The need for timely intervention is indicated by the fact that among patients operated on before the age of 21, the risk of infertility is minimal, and before the age of 30, the probability of childlessness increases 4 times! The earlier surgery is performed for varicocele in men, the greater the likelihood of avoiding complications. This is all the more important because modern technologies are highly effective and completely painless and have low prices.
Prevention
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it, so it is necessary to carry out preventive measures.
Measures aimed at reducing the risk of developing pathological dilation of veins in the scrotum:
- healthy eating has a beneficial effect on the intestines;
- taking vitamins;
- use contraception during sexual intercourse;
- reasonable physical activity;
- Regular visits to the doctor from adolescence.
Reasonable adherence to preventive measures not only minimizes the risk of developing the disease and its relapse, but also contributes to the choice of an effective and less invasive treatment method.
Postoperative period
During the first month after surgery, it is recommended to limit physical activity. It is also considered advisable to wear thick panties or swimming trunks for 2-3 weeks.
Subsequently, the patient should be regularly observed by an andrologist for at least 1 year.
At the discretion of the doctor, courses of antioxidant therapy, venoprotectors, and hyperbaric oxygenation can be used.
After the operation, strict observance of clinical follow-up is necessary.