Date of publication: 04/06/2017
until January 31
We are giving away 1000 rubles for all services for a visit in January More details All promotions
Blood or arterial pressure is the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels. It is determined by the volume of blood that the heart pushes out per unit time, and the strength of the vascular response resistance. Pressure creates conditions that allow blood to reach organs and supply them with oxygen and the nutrients it transports. It is believed that a person’s blood pressure is normal when the heart copes with its pumping function and the blood vessels remain elastic and strong.
from May 14 to 24 as part of the Year of the Heart at the City Hospital No. 1
them. G.I. Drobyshev hosts an informational and practical campaign
“Learn to control your blood pressure.”
One of the most common health complaints and one of the most “favorite” diseases among older people is increased blood pressure. This pathology can explain any changes in well-being, bad mood and other troubles. Blood pressure can rise and fall several times during one day, and a person’s normal blood pressure is a purely individual concept.
What is blood pressure and what indicators are considered normal?
Blood pressure is a general concept that determines the force with which blood presses on the walls of blood vessels; it would be more correct to call it blood pressure, because pressure matters not only in the arteries, but also in the veins and capillaries. But it is only possible to measure pressure in large vessels located on the surface of the body—in the arteries—without the help of special instruments.
Blood pressure - blood pressure - depends on the speed and force with which a person’s heart contracts, how much blood it can pump in one minute, on the properties of the blood itself and the resistance of the walls of blood vessels.
Factors influencing blood pressure:
- the ability of the heart to contract with sufficient force and ensure normal release of blood through the vessels;
- from the rheological properties of the blood - the “thicker” the blood, the more difficult it is to move through the vessels; diseases such as diabetes mellitus, increased coagulability, greatly impede the flow of blood and can lead to problems with blood pressure; with thick blood, some doctors prescribe treatment with leeches;
- elasticity of the walls of blood vessels - blood vessels wear out over time and cannot withstand increased load - this becomes the cause of the development of hypertension in older people,
- atherosclerotic changes - reduce the elasticity of the walls;
- sharp narrowing or dilation of blood vessels - as a result of nervous shocks or hormonal changes, a sharp narrowing or dilation of blood vessels is possible - for example, with fear, anger or other strong emotions;
- diseases of the endocrine glands.
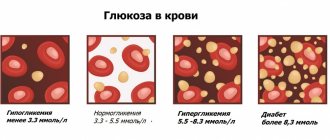
Normal blood pressure is determined by a combination of a large number of parameters, and for each age, gender and for an individual person, its indicators can vary greatly. Medical standards are taken as average values from healthy people of a certain age. It has long been proven that blood pressure of 120/80 cannot and should not be considered the ideal norm for people of different ages.
To find out what normal blood pressure a person should have at different age periods, you can use the following table.
Blood pressure indicators for an adult:
- Normal blood pressure is considered to be between 110\70 and 130\85 mm. rt. Art.
- Low normal pressure – 110\70 – 100\60;
- Low blood pressure – hypotension – below 100\60;
- Increased normal pressure – 130\85-139\89;
- High blood pressure - hypertension - more than 140\90 mm. rt. Art.
Indicators of normal blood pressure for different age periods:
- 16 – 20 years – 100\70 – 120\80 mm. rt. Art.
- 20 – 40 years – 120\70-130\80;
- 40 -60 – up to 140\90;
- over 60 years old – up to 150\90 mm. rt. Art.
From the table above, it is clear that the older a person is, the higher the normal blood pressure indicators; this is due to age-related changes in blood vessels, in the heart muscle and in other organs. High blood pressure, like low blood pressure, can cause various health problems, but in order to determine whether changes in blood pressure are to blame for poor health, you need to measure it regularly and keep a special diary. For this, several trips to the clinic or visits to the doctor are not enough; only daily regular blood pressure measurements can give correct results.
Measurement.
The correct diagnosis and prescription of treatment largely depends on the correct measurement of blood pressure, because the doctor, when prescribing medicine or prescribing treatment, is largely guided by the measurement numbers.
Today there are different ways to measure pressure:
- The simplest and oldest - using a cuff and a tonometer - here it is of great importance to correctly apply the cuff, the ability to use a tonometer and listen to heart sounds. This measurement requires special training and skills, but when used correctly, it gives fairly accurate and reliable results.
- Electrotonometer - the operating principle is the same, but the results are visible on a special display. This makes it easier to measure your blood pressure yourself and provides more accurate results. But such blood pressure monitors often break down and may show incorrect numbers.
Regardless of the method used to measure blood pressure, several general rules must be followed:
- before the measurement, half an hour before the start, avoid physical activity, nervous tension, smoking, eating, and so on,
- relax, sit comfortably when measuring,
- the posture should be comfortable, the back should be straight, there must be support, the hand should rest freely at the level of the patient’s chest,
- you cannot talk or move during the measurement,
- The measurement should be carried out on both hands and it is advisable to carry out a series of measurements with an interval of 5-10 minutes.
If, after correctly measuring blood pressure, the readings are very different from the norm, you need to repeat the measurements within a few days and, if confirmed, consult a doctor.
High blood pressure.
Considered one of the most dangerous diseases of mankind, hypertension affects about 25% of people worldwide, and this figure continues to increase. Hypertension is an increase in blood pressure above 140/90 mmHg. rt. Art. Causes of hypertension can be:
- overweight,
- genetic predisposition,
- diseases of internal organs,
- lack of physical activity,
- smoking and drinking alcohol,
- excessive consumption of table salt,
- nervous tension,
- other factors.
With hypertension, the patient suffers from headaches (and here pills for headaches will not help), shortness of breath, heart pain, increased fatigue, insomnia, poor health and other symptoms. In addition, the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, brain damage, pathology of the urinary system and eye diseases increases.
Treatment of hypertension is a very complex and time-consuming process, where the outcome of the disease depends on compliance with the doctor’s recommendations. It is important to find the cause of the increase in pressure and act on it. At the same time providing symptomatic treatment. In each specific case, medications, doses and their combinations must be selected individually by the attending physician.
Without timely treatment or uncontrolled use of medications, hypertension can not only seriously damage health, but also cause a life-threatening condition such as hypertensive crisis.
Hypertensive crisis.
Hypertensive crisis is a life-threatening condition caused by a sharp increase in blood pressure and damage to the nervous system and target organs. Blood pressure figures during a hypertensive crisis can vary greatly in different patients - some people normally tolerate 200\150 mm. rt. st, and for some people feel bad already at 150\85 mm. rt. Art. The nature of the lesions in GC depends on which organs previously had the pathology - if the heart hurts, myocardial infarction may occur, if you suffer from headaches, then a stroke, and so on.
The causes of GC may be:
- psycho-emotional stress,
- exercise stress,
- meteorological changes,
- drinking alcohol,
- rich foods high in salt,
- incorrectly selected antihypertensive drugs,
- diseases of the endocrine system and internal organs.
With the development of GC, the patient’s well-being sharply worsens, a feeling of fear and anxiety arises, nausea, vomiting, darkness before the eyes, swelling and flushing of the face, chills, tremors of the limbs, fainting, and even coma may appear.
If such symptoms appear, you need to lay the patient on any flat surface with the head of the bed raised and immediately call an ambulance. Before her arrival, try to provide the patient with peace, an influx of fresh air, and get rid of restrictive clothing. If the patient has had hypertension for a long time, then, most likely, he is taking some kind of antihypertensive drug, in this case, before the doctor arrives, you can give the patient the usual dosage.
Hypotension, low blood pressure.
For many people, especially those suffering from hypertension, it seems that lowering blood pressure cannot be a problem, but in fact this is not the case. Constantly low blood pressure can cause no less inconvenience and health problems than hypertension.
The causes of this pathology can be hereditary predisposition, poor nutrition and vitamin deficiency, endocrine diseases, nervous strain, general exhaustion of the body and other problems.
A person suffering from hypotension constantly feels tired, overwhelmed, has difficulty performing daily duties and is emotionally inhibited. In addition, there is a decrease in memory and brain activity, poor thermoregulation, increased sweating, headaches, drowsiness, pain in the joints and muscles, and a general feeling of poor health.
Although, unlike hypertension, hypotension does not cause serious health problems, it also requires treatment. Only a doctor can determine the cause of hypotension and prescribe treatment after a detailed examination. And without medical help, we can advise you to establish a work and rest schedule, eat well, not be nervous and give up bad habits.
Original article https://tibet-medicine.ru/sovrmed/normalnoe-davlenie-cheloveka
Age norms of blood pressure: yesterday and today
You may not know, but the European Society of Cardiology has tightened blood pressure standards. The thing is that earlier recommendations “failed” to prevent complications of vascular diseases. And damage to the brain, heart, eyes and kidneys due to hypertension continues to be a serious medical problem. So what “numbers” are recommended by leading experts? And what can “spoil” blood pressure?
What changed
According to previously existing standards, the blood pressure (BP) of a healthy person at rest should not exceed the following values:
- 120/70 – 130/80 – for people aged 20-40 years,
- 140/90 – at the age of 40-60 years,
- and 150/90 for patients over 60 years of age.
New recommendations from European experts (2018) have significantly tightened the standards, and now the blood pressure “figures” should not exceed:
- 129/80 – for people under 65 years of age
- and 139/80 for older patients.
Which, by the way, corresponds to the recommendations of American cardiologists, adopted a year earlier than European ones.
As you can see, the changes concern not only the upper (systolic), but also the lower (diastolic) pressure. This means that the diagnosis of hypertension itself and the initiation of its treatment are now authorized much earlier.
What can spoil blood pressure?
Of course, one of the most significant risk factors for hypertension is heredity and age-related changes.
Thus, cases of vascular pathologies, especially with a disabling outcome in close relatives, are a serious reason to take the vessels under constant “control”.
And with “age,” the vascular wall significantly loses its elasticity and ability to expand, because:
- firstly, the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers decreases,
- and secondly, the thickened walls of blood vessels due to pressure changes (the vasoconstrictive effect of stress hormones, cigarettes and some other factors) do not have the ability to stretch.
So we can say that vascular pathologies have a “cumulative” nature, beginning to form at a young and active age.
In addition, with age, cholesterol deposition and the formation of plaques are observed, narrowing the diameter of blood vessels and further aggravating the problem.
Blood pressure "under control"
Taking into account the above factors, it is obvious that it is better to start paying attention to blood vessels at a young age and regularly.
The presence of regular and/or prolonged stress, smoking, drinking alcohol, a sedentary lifestyle, excess weight and diseases of the kidneys, heart or adrenal glands are reasons to periodically check the degree of damage to the vascular wall. And for this, a blood test for ultrasensitive C-reactive protein is suitable.
The marker reflects vascular damage long before the formation of atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots on the damage, as well as changes on ultrasound and any clinical signs. Therefore, it can be used for the earliest detection of the degree or risk of vascular pathologies.
In addition, it is worth taking control of cholesterol and its fractions, even outside of eating “fatty” foods. After all, lipid levels have a direct relationship with:
- liver health (since this is the place of its formation),
- level of sex hormones,
- overweight,
- as well as diseases that disrupt fat metabolism (diabetes mellitus, lack of “thyroid” hormones and some others),
and cholesterol “balance” disorders can be detected at absolutely any age.
Periodic “jumps” in pressure and the development of arterial hypertension can also be provoked by:
- imbalance of salts (sodium, potassium, chlorine),
- disorders of urinary function of the kidneys
- and excess renin.
And the latter also makes hypertension resistant to standard therapy. And assessment of the renin level is used to exclude the renal nature of the “pressure”.