Our body is made up of billions of building blocks that work together to ensure the efficient functioning of the entire body. One such block is the amino acid N-acetyl-L-tyrosine. Taking extra amounts of this amino acid may benefit the body, but there are also some factors to consider before you start taking L-tyrosine. So, should you take L-tyrosine? Let's find out!
This article will cover the following questions:
- What is L-tyrosine?
- Advantages
- Why take it
- Side effects
- Dosage
We recommend together with this drug:
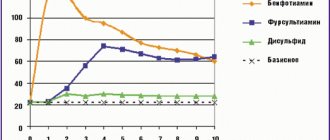
L-Tyrosine is a drug that is an amino acid; it normalizes the functionality of the thyroid gland and metabolism in the body, and also has a beneficial effect on the human nervous system. This drug activates the secretion of dopamine, adrenaline, melotonin, which are neurotransmitters and improve the transmission of nerve impulses. Tyrosine “gently” stimulates a person’s mental functionality, which suppresses “depressive reactions.”
Advantages
1. May improve your mood
Because L-tyrosine is a precursor to dopamine, the “feel-good” hormone, it has been suggested that L-tyrosine may have beneficial effects on low mood.
Research has shown that in healthy people under stressful conditions, such as exposure to extreme cold for several hours, tyrosine can prevent mood from deteriorating too much.3
However, it remains unclear whether these results can be applied to everyday life. Still, if you're stressed, L-tyrosine can help prevent catecholamine depletion, which in turn can help prevent your mood from getting too low.1
2. May improve performance in hot climates
Research has shown that the presence of increased amounts of dopamine helps improve heat tolerance when exercising in high temperatures.
In a study examining the effects of tyrosine on cyclists in 30-degree heat, it was found that those who took tyrosine were, on average, able to continue cycling 15% longer.4 However, these results were obtained from only one study, so the results generally cannot be considered convincing.2
Based on the results of these studies, it appears that taking L-tyrosine during training or competition in hot climates may improve an athlete's performance. However, you shouldn't expect any noticeable performance improvements.
3. May Improve Cognitive Functions in Stressful Situations
There is evidence that during acute stress, such as temperature extremes and sleep deprivation, L-tyrosine may prevent the depletion of anti-stress catecholamines such as dopamine.1
However, the effect will depend on the degree of stress and whether the stress is severe enough to deplete catecholamines. This may mean that L-tyrosine is not as effective in everyday situations.
L-Tyrosine: properties
Tyrosine is an amino acid and a precursor of catecholamines. Its main function: helps increase the production of neurotransmitters adrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine, melatonin, and thyroid hormones. Its main properties: - activates fat burning; — improves metabolic processes in the body; — normalizes the activity of the thyroid gland; — Tyrosine increases the speed of nerve impulses; — neutralizes alcohol toxins; - improves memory; — Tyrosine improves concentration; - improves oxygen supply to the brain; - improves brain functionality (noticeably in children).
The role of tyrosine in the body
Tyrosine is a non-essential aromatic amino acid. In the human body it is formed as a result of hydroxylation of phenylalanine.
It exists in two optically isomeric forms - L and D. Tyrosine is also known as 4-hydroxyphenylalanine. The human body is capable of producing tyrosine itself, so it is considered to be a non-essential amino acid.
The word "tyrosine" comes from Greek and is translated as "cheese". It received its name in 1846, when it was first discovered by the German chemist J. Liebig.
Rice. Justus von Liebig
In the body it is able to cross the “hemaincephalic barrier” and quite quickly penetrate into the central nervous system. At the same time, the level of adrenaline, norepinephrine and dopamine increases, and is also able to influence many processes and functions in the body.
Tyrosine also promotes the functioning of organs responsible for producing and regulating hormone levels in the body, such as melanin (the hormone that determines skin and hair color).
Positive properties of tyrosine:
- Promotes the production of dopamine;
- Improves attention and gives vigor;
- Improves mood;
- Energy.
The most important property is considered to be the weakening of stressful conditions, due to the production of adrenaline and norepinephrine, which helps relieve fatigue.
Functions in the body:
- Protein synthesis
- Brain work
- Stress and the nervous system
- Melanin production
- Hormones
- Helps deal with addictions
Side effects
Taking tyrosine as a supplement can lead to a number of side effects, especially for people with an overactive thyroid gland.
- Anxiety
- Digestive disorder
- Migraine
- Tachycardia
- Nervousness
How to understand that a person lacks tyrosine
The following symptoms indicate this:
- Muscle weakness
- Poor appetite
- Drowsiness
- Headache and migraine
Daily norm
In the form of a dietary supplement, up to 12 g per day. A healthy person needs 1.5 grams per day, this is enough for the body to perform its functions.
People with excess weight, poor memory, and abnormalities in the thyroid gland need tyrosine more. You can increase the daily dose of tyrosine to relieve unpleasant symptoms of PMS, also for severe mental disorders, from 600 to 2000 mg per day.
The need for tyrosine increases with:
- Frequent depression
- Bad memory
- Overweight
- Deviations from normal thyroid function
- To reduce pain during PMS
- Symptoms of Parkinson's disease
The need for tyrosine decreases with:
- High blood pressure
- At low body temperature
- In old age (from 65 years old)
- If you have Felling's disease
Table
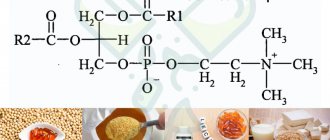
Tyrosine-rich foods
| Product name (100g) | Tyrosine content (in grams) per 100g |
| Parmesan | 2 |
| Soy products | 1.5 |
| Beef | 1.4 |
| Pork | 1.2 |
| Salmon | 1.15 |
| Chicken | 1.15 |
| Pumpkin seeds | 1.1 |
| Chicken eggs | 0.5 |
In addition to the above-mentioned products, the daily requirement of tyrosine can be obtained from different types of cheeses, such as edam, mozzarella, and hard goat’s curd. Meat products include lamb and turkey dishes. Fish products include tuna, cod, mackerel, shrimp and crab.
Tyrosine is one of the most important amino acids and an essential part of protein structure. It can be used to improve brain function, improve memory and strengthen the immune system. But improper use can lead to hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. This amino acid can be considered a remedy for sadness and depression, a substance that increases strength and physical activity. To achieve the same effects, it is not necessary to resort to pharmaceutical drugs. Nature has everything that is needed for a person to obtain amino acid reserves from natural products. This method almost never causes side effects.
Tyrosine: indications and contraindications
This drug is used in cases of: - brain dysfunction; - absent-minded attention, lack of concentration; - poor memory; — chronic fatigue syndrome; - depression; - mood swings; — drug and alcohol addiction; - vegetative-vascular dystonia; - hypotension; - Parkinson's disease; - childhood hyperactivity; - diseases of the thyroid gland; - vitiligo; - metabolic disease. Contraindications for the drug L-Tyrosine: - pregnancy; - period of breastfeeding; - allergy to the drug; - Do not combine with MAO inhibitors.
Why take it?
L-tyrosine can be used to improve attention and concentration.
This amino acid has been proven to be effective in helping the body cope with the harmful effects of stress in extreme stressful situations. Given L-tyrosine's role in dopamine production, researchers have been studying it to see if it can improve mood.
As stated above, the results showed improvements that appeared to only occur under stressful conditions, such as exposure to cold temperatures. For example, there is evidence that taking tyrosine helped prevent worsening mood among those who lived in Antarctica for a long time.5
Based on this, if your mood suffers during the cold winter months, tyrosine may be worth considering.
As a sports nutrition product, L-tyrosine may help an athlete continue training even in extreme heat.4 However, again, research results are mixed.
Because L-tyrosine is a precursor to epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine, which can help speed up metabolism, it has been suggested that it could be used for weight loss and calorie burning. Unfortunately, research to support this claim is very limited.
Tyrosine: reviews
Sergey L., 28 years old, Moscow “I have been suffering from vitiligo for three years. The doctors couldn’t do anything, they say it’s due to nervousness. I was advised Tyrosine with Phenylalanine. By the end of the second month, the spots on the skin began to disappear. In 6 months I got rid of this problem, now I drink Tyrosine once every 3-4 months for prevention...” Ulyana P., 34 years old, Penza “With the help of Tyrosine, I got rid of chronic fatigue syndrome. In the morning I woke up hard, came to work and felt like I was “boiled”, constant drowsiness and the impression that all the energy had been “sucked” out of you. Mom bought me a jar of Tyrosine and I started drinking three capsules a day. After a week of taking it, I felt a surge of energy, after another week I stopped falling asleep at work and worked normally until the end of the day, and by the end of the first month of taking Tyrosine, I was as energetic as a bunny, I sleep 7 hours and that’s enough for me...” Diana G. , 28 years old, St. Petersburg “Once every six months (in autumn and at the end of winter) I definitely drink a jar of Tyrosine (2 capsules a day), for me it’s like a prevention against depression and low vitality...” Vasily L., 42 years old, Norilsk “My father has Parkinson’s disease. They said that this was incurable and that I would have to live with it until the end... I read a bunch of literature on this issue, talked with doctors and decided to give my father Tyrosine, DMAE and Phosphatidylserine. We have been using it for six months and after the last examination the doctors transferred his disease from stage 3 to stage 1. The symptoms have noticeably decreased. We continue therapy..."
Links[edit | edit code]
- Chinevere TD, Sawyer RD, Creer AR, Conlee RK, Parcell AC. Effects of Ltyrosine and carbohydrate ingestion on endurance exercise performance. Journal of Applied Physiology. 2002; 93: 1590-1597.
- Watson P, Hasegawa H, Roelands B, Piacentini MF, Looverie R, Meeusen R. Acute dopamine/noradrenaline reuptake inhibition enhances human exercise performance in warn but not temperate conditions. Journal of Physiology. 2005; 565(3): 873-883.
- Tumility L, Davison G, Beckmann M, Thatcher R. Oral tyrosine supplementation improves exercise capacity in the heat. European Journal of Applied Physiology. 2011; 111:2941-2950
- Wurtman, R. J., and Lewis M. C. Exercise, plasma composition and neurotransmission. In: Advances in Nutrition and Top Sport, edited by Brouns F.. Basel: Karger, 1991, vol. 32, p. 94-109.
- Romanowski, W, and Grabiec S. The role of serotonin in the mechanism of central fatigue. Acta Physiol Pol 25: 127-134, 1974.
- Banderet, L. E., and Lieberman H. R. Treatment with tyrosine, a neurotransmitter precursor, reduces environmental stress in humans. Brain Res Bull 22: 759-762, 1989.
- https://www.nieuws.leidenuniv.nl/nieuws-2014/droeg-fruit-bij-aan-het-succes-van-apple.html
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00426-014-0610-4
Analogs
L-tyrosine has a number of analogues, for example:
- Vita - Tyrosine. Contains amino acid, iodine and potassium iodide. Used to normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland, as well as for obesity or decreased performance. Available in the form of capsules, which need to be taken 1 piece at a time. in a day. The drug is intended for adults.
- Aminoven. Contains a number of amino acids and phenylalanine (tyrosine precursor). The drug is used for nutritional deficiencies caused by the patient's serious condition and metabolic disorders. The supplement is produced in the form of a solution for intravenous infusion. Available in concentrations of 5, 10 and 15%, not for use in children under 2 years of age.
- Aminoped. Contains essential amino acids, as well as tyrosine in the form of an acetyl compound. Used for disorders of protein metabolism, intravenous nutrition or through a tube, as well as decreased cognitive function, prematurity, menopause, and mental disorders. Available in the form of a solution for infusion in a concentration of 5 or 10%.
Attention! Replacement of tyrosine with analogues should be agreed upon with an endocrinologist.