Hormones are regulators of all systems and organs of the body. In women, the functional state of the endocrine glands primarily determines reproductive health. All hormones influence each other, so a failure in the production of one of them leads to the development of other hormonal disorders. Therefore, it is so important to identify and correct the disease in a timely manner. First of all, disruption of the production of sex hormones affects the menstrual cycle. Endocrine diseases often cannot be completely cured, but an adequate quality of life can be restored and normal well-being can be restored with the help of medications.
There are usually two reasons for disruption of hormone production: congenital disorders that are established in utero and appear at a certain stage of life, or acquired. The second category includes, in particular, the consequences of taking pharmaceutical hormonal drugs.
The possibility of complete restoration of the endocrine system and other body systems depends on the severity of the disorders and their causes. At the moment, for almost all hormonal diseases, there are effective treatment regimens that allow you to get rid of unpleasant symptoms - but before selecting treatment, you will have to undergo a full diagnosis and establish the cause of the disorder.
Norm and pathology
Hormonal imbalance can occur at any age. According to statistics, teenage girls and women in the premenopausal period most often experience problems. This is understandable - at these moments serious changes occur in the endocrine and reproductive systems.
Hormones are produced in the endocrine glands: pituitary gland, hypothalamus, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, ovaries, pancreas. Let's look at the main hormones that affect reproductive function:
- Estrogens are a whole group of biologically active substances that are produced in large quantities in the first phase of the menstrual cycle.
- Prolactin is responsible for breastfeeding, its concentration increases with the appearance of milk. Prolactin reduces the concentration of estrogen and slows down ovulation - thus, it protects the body from pregnancy while breastfeeding.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone - responsible for the growth of follicles in the ovaries. Produced at the beginning of the menstrual cycle.
- Luteinizing hormone - increases the rate of estrogen synthesis and is responsible for the release of a mature egg from the follicle capsule.
- Progesterone - produced during ovulation, is responsible for the formation of the corpus luteum. Its concentration increases significantly during pregnancy.
- Testosterone - despite the fact that it is a male sex hormone, it is also present in the female body. Performs an important function during pregnancy - it stimulates the enlargement of the mammary glands.
Together, these substances regulate the menstrual cycle and affect the possibility of conception. Together with them, but to a lesser extent, reproductive health is also regulated by other hormones of the endocrine system - they are in close relationship. As a rule, a disruption in the production of one hormone provokes secondary changes, and as a result, a complex hormonal imbalance occurs.
The functional state of the reproductive system directly affects the production of hormones. For example, in adulthood, when a woman’s supply of eggs runs out, a restructuring of the hormonal system occurs - the ability to bear children disappears, and menstruation disappears. During puberty, on the contrary, the body's systems prepare to perform the reproductive function.
During such periods, the line between normal and pathological is arbitrary - unpleasant symptoms may appear, which will disappear after some time. If you have doubts about your own health, it is better to consult a specialist. Between the ages of 18 and 45, hormonal levels are considered fairly stable. If unpleasant symptoms appear during this period, a visit to the doctor is definitely required.
At CELT you can consult an endocrinologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
The role of hormones in the female body
The content of the article
Hormones are special substances of a chemical nature. Their role is to transmit information about the start of a process to organs and tissues. The movement of these substances occurs through blood and other fluids. Hormones are necessary for various body functions, including metabolism, growth, immunity and sexual reproduction. There are 2 main hormones involved in the female reproductive cycle: estrogen and progesterone. There are other hormones that are critical to the functioning of the cycle, all of which are controlled by two main areas of the brain:
- the hypothalamus plays an important role in the body's basic processes - hunger signals, sleep and sexual arousal;
- The pituitary gland produces additional hormones responsible for the menstrual cycle.
The hypothalamus secretes a hormone called gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), which alerts the pituitary gland to produce additional hormones that make the genitals work. In women, these are follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Their levels increase before ovulation and signal the body to prepare for ovulation and potential pregnancy.
Causes of pathology
Globally, all causes are divided into congenital and acquired during life.
The most common causes of hormonal imbalance in women:
- Consequences of taking oral contraceptives. Controversy continues around these drugs. Most gynecologists are confident in their safety, but only if the appointment is carried out after consultation and under the supervision of a specialist. Most often, violations appear after incorrect withdrawal of pills.
- Consequences of taking emergency contraception. These drugs greatly change hormonal levels, resulting in menstrual irregularities, which do not always recover on their own.
- Uncontrolled use of drugs containing hormones without appropriate prescription. Unfortunately, some patients neglect to consult a specialist and start taking medications purchased without a prescription. The consequences are the development of hormonal disorders.
- Diseases of the endocrine system. They lead to a failure in the production of essential hormones.
- Physiological changes during puberty and adulthood. Against the background of hormonal changes, hidden pathologies often appear.
- Abortion. This is a strong stress for the body, in which physiological restructuring has begun, and it is immediately interrupted. The body does not always manage to restore the natural functioning of the endocrine glands.
- Prolonged stress is also one of the most common causes. It has been proven that stress, anxiety and depression are associated with a decrease in the production of oxytocin, which, in turn, affects the synthesis of prolactin.
Pregnancy is also considered a hormonal imbalance - but it is physiological. If the pregnancy proceeds normally from the point of view of the vital signs of the mother and child, then various unpleasant symptoms are allowed - they are not dangerous to the health of the mother and child.
Symptoms of pathology
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance may vary depending on the nature of the disorder, in particular:
- changes in the duration and regularity of the menstrual cycle;
- intermenstrual bleeding;
- hair growth disorder;
- nipple discharge;
- emotional lability;
- change in sexual activity;
- change in appetite;
- weight disorders.
The appearance of these symptoms is a reason to make an appointment with an endocrinologist.
Signs of hormonal imbalance
Manifestations of hormonal imbalance depend on the woman’s age and her overall health. Hormonal imbalances can occur due to prolonged stress, physical and mental fatigue, infectious and oncological diseases, etc. You can suspect hormonal imbalance based on the following signs:
- menstrual irregularities – irregular periods, changes in their duration and abundance;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding - heavy or spotting discharge from the genital tract outside of menstruation;
- deepening of the voice and hirsutism (excessive hair growth on the face and body) - these signs usually indicate an excess of androgen male sex hormones in your body;
- obesity - rapid weight gain is one of the most common signs of a violation of the ratio of female sex hormones. However, you may notice weight gain even while following a strict diet;
- decreased libido – if the concentration of sex hormones is impaired, it is possible that you may lose interest in sexual activity;
- deterioration of the skin condition - excessive dryness or, conversely, oily skin, as well as the appearance of acne may indicate a hormonal imbalance.
Our doctors
Mikhailova Elena Vladimirovna
Endocrinologist, diabetologist, candidate of medical sciences
47 years of experience
Make an appointment
Slovesnova Tatyana Alekseevna
Endocrinologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
Experience 49 years
Make an appointment
Kolodko Inna Mikhailovna
Doctor - endocrinologist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 27 years
Make an appointment
Pregnancy and hormone imbalance
Symptoms of hormonal imbalance during pregnancy are subtle. As a rule, the doctor notices them first. Therefore, it is important to regularly visit a gynecologist and not refuse preventive examinations.
There are manifestations that are difficult to notice immediately:
- change in endometrial thickness;
- development of fibroids;
- pathology of follicle maturation;
- disruption of hormone production: lack of progesterone and estrogen, excess testosterone.
After conception, a whole cascade of changes begins in the body. With sufficient medical control, almost all pregnancy pathologies can be corrected and do not lead to serious consequences.
Treatment of hormonal disorders
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause that caused the hormonal imbalance. To do this, when visiting a doctor, the necessary examination is carried out. Based on the results obtained, the doctor can fully draw up a complete picture of the disease and decide which active substances are causing the malfunction in the body.
The recommended treatment for hormonal disorders involves taking special medications that normalize the level of active substances produced. In case of increased hormone production, doctors prescribe inhibitory therapy, which suppresses the increased release of substances in the body. Specialists also carry out nutritional adjustments and help develop an optimal rest and work schedule.
Diagnostics
Diagnostics includes both instrumental examinations and laboratory tests. The examination begins with a visit to a therapist or a specialist - a gynecologist or endocrinologist. Often the pathology is complex, so treatment will have to be done by several doctors.
Instrumental diagnostics includes:
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and pelvic organs, as well as mammary glands. This study is carried out for any complaints with symptoms of hormonal imbalance. In most cases, ultrasound can reveal which gland the pathology is associated with.
- MRI may be required if anatomical changes are detected and further diagnostics are required.
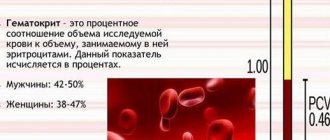
Laboratory tests include blood tests for hormones. The attending physician decides which hormones need to be determined, based on the nature of the complaints and examination data. As a rule, there are no problems with diagnostics - modern analysis methods are quite accurate.
Methods of diagnosis, treatment and prevention
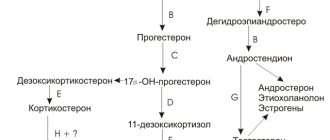
To diagnose an imbalance, laboratory tests for hormones are prescribed, which can determine the level of corticosteroids, androgens and estrogens. Additional tests may include ultrasound of internal organs and tests for infectious diseases.
The course of treatment usually includes the following activities:
- taking medications;
- hormone therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- surgical intervention;
- physiotherapy.
To prevent endocrine disorders, it is recommended to adhere to a healthy lifestyle, play sports, swim, avoid stressful situations and eat right. The diet should include foods rich in vitamins and microelements, as well as follow a sleep and rest schedule.
Any hormonal disorder can cause serious illness and malfunction of the reproductive system. To avoid this, it is important to know the typical signs of disorders and not ignore the body’s requests for help.