Pain in the mammary glands does not always indicate the development of any disease, but in any case it should cause concern. With breast cancer, which ranks first among all cancers in the world, chest pain is one of the main symptoms.
Ultrasound of the mammary glands with lymph nodes - 1000 rubles. Consultation with a specialized doctor based on the results of ultrasound and tests - 500 rubles. (optional).
MAKE AN APPOINTMENT, TEST OR ULTRASOUND
In the world, every 8th woman has some stage of breast cancer, and for every 100 women, one man is diagnosed with this disease. The earlier a tumor is detected, the greater the patient's chances of recovery. That is why every person should be attentive to pain in the soft tissues of the chest.
Pain in the mammary glands due to hormonal disorders
The content of the article
A woman's hormonal levels depend on the menstrual cycle. Its duration is 21-35 days, but a 28-day cycle is considered ideal. The main thing here is not the number of days, but the regularity of the duration of the cycle, because at each stage certain hormones are produced and predominated in the body, and a sharp change in hormonal status can lead to changes in the mammary glands.
Let's look at how hormonal levels change depending on the period of the cycle:
- Follicular phase . It lasts approximately 14 days. During this period, which occurs immediately after the cessation of bleeding, a hormone is produced that stimulates the formation of follicles and the maturation of the egg. The hormone estrogen is also actively produced, which is responsible for preparing the uterus for possible embryo implantation.
- Ovulation and luteal phase . The period lasts 12-16 days. The egg ruptures the follicle and comes out, moving along the fallopian tube towards the male reproductive cell. This is facilitated by the release of progesterone. In place of the follicle, a corpus luteum is formed, which, in the absence of conception, decreases and the level of hormones drops. Menstruation and bleeding occur.
Excessive estrogen production causes cysts to form because the hormone promotes an increase in the number of connective tissue cells. They line the ducts of the mammary glands, which is why cysts in the breasts of women are not uncommon. An increase in progesterone levels leads to swelling of the breast tissue and deterioration of blood supply, which also causes pain. The breasts swell, the parapapillary halos enlarge, and any pressure on the mammary gland causes noticeable pain.
If unpleasant sensations are observed 2-3 days before the onset of menstruation, then this should not cause serious concern. This condition is typical for 80% of women of childbearing age. It’s another matter when pain occurs longer or throughout the entire cycle. In this case, you should consult a doctor.
Symptoms of mastopathy
Most women consider moderate tenderness of the mammary glands before menstruation to be normal and do not consult a doctor with complaints. The mammologist is visited only by those whose breasts cause pain even when wearing a bra; they can only sleep on their backs, and if they have to travel in public transport, the slightest shock causes severe pain. A woman experiences pain when touching her breasts during sex. Only in this case do patients come to their senses and make an appointment with a mammologist.
In addition to pain, the woman feels an enlargement of the mammary glands, sometimes clear liquid is released from the nipple. The breast may feel heterogeneous to the touch, and sometimes lumps can be felt.
Pain in the mammary glands with fibrocystic mastopathy
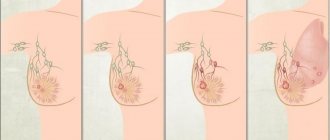
Fibrocystic mastopathy is the most common breast disease, occurring in 58% of women. Its cause is changes in the ratio of epithelial and connective tissue cells. Mastopathy can be diffuse (with a predominance of glandular, fibrous or cystic components) and nodular (lipoma, lipogranuloma, angioma).
Fibrocystic changes in the breast cause pain in the mammary glands. In advanced cases, even slight pressure on the chest is extremely unpleasant. This phenomenon is called cyclic mastodynia. It is associated exclusively with the menstrual cycle and ovarian activity.
Non-cyclical mastodynia is not associated with the menstrual cycle, but is caused by a malfunction of the body or other factors. The prerequisites for the development of non-cyclic mastodynia include:
- Initiation of hormonal contraceptives . Painful sensations are typical for the first three months of use, and then everything returns to normal.
- Pathology of the thyroid gland . The production of sex hormones is inextricably linked with thyroid hormones, and their inhibition or increased production leads to chest pain.
- Depressive and anxiety states . They lead to an imbalance in the activity of the hypothalamus, which is responsible for the production of sex hormones. Nagging pain in the mammary glands is a companion to depression. Chest pain increases already increased anxiety.
- Surgical abortion or medical termination of pregnancy. After conception, the body is rebuilt, preparing for the difficult period of gestation and childbirth. After interfering with the natural process, hormonal disruption is guaranteed, leading to problems in the reproductive system.
- Cyst in the mammary gland . This is a benign hollow neoplasm, inside of which fluid accumulates. It is believed that normally cysts can form in every woman during the cycle, but they resolve on their own without causing harm to health. If the cysts reach large sizes, they put pressure on the soft tissues, causing pain.
- A lactocele is a cyst of the mammary gland, but it is not fluid that accumulates inside the cavity, but breast milk. In nursing mothers, the lactocele resolves on its own, but in case of severe growth, this is already a serious pathology in which surgical excision is performed under local anesthesia.
- Breast fibroids are a benign neoplasm in the glandular tissue of the mammary gland. It occurs due to an increase in the amount of estrogen, which, in turn, leads to hormonal imbalance and the occurrence of tumors. Stress is especially dangerous for women as it triggers hormonal imbalance.
Causes of mastopathy
The main cause of mastopathy is a hormonal disorder, namely excessive production of estrogen, which promotes tissue proliferation, and a lack of progesterone, which regulates the proliferation process. The second reason may be an excessive amount of the hormone prolactin, which is responsible for milk production during breastfeeding.
Therefore, before prescribing treatment, you should establish the cause: take hormone tests.
Those women who have the following diseases are at risk:
- Ovarian tumors
- Myomas
- Endometriosis
- Inflammation of the pelvic organs
- Thyroid diseases
- Obesity
- Adrenal gland dysfunction
- Diabetes
- Diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract
Hormonal imbalance and, as a result, mastopathy can be caused by the following reasons:
- Chest injuries
- Tight, uncomfortable underwear
- Stress
- Irregular sex or lack thereof
- Abortion
- Refusal of breastfeeding (BF)
- GW less than 6 months and more than one and a half years
- Iodine deficiency
- Alcohol abuse
- Smoking
Inflammatory and purulent processes in the mammary glands
A common cause of pain in the breast tissue is an inflammatory process caused by various factors.
Pain in the mammary glands with lactostasis
Lactostasis is stagnation of milk, leading to severe inflammation in one or more lobes of the breast in a nursing mother. The essence of the disease: milk for some reason does not pass through the ducts to the nipple, and, stagnating, begins to ferment. A milk plug forms, which causes severe pain and a significant increase in temperature. In the lobules of the chest you can feel a lump that swells and turns red.
The cause of lactostasis is illiterate expression of milk, improper attachment to the breast, refusal to wear underwear or wearing low-quality underwear.
Mastitis
If lactostasis is not treated, a more serious disease develops - mastitis (inflammation of the entire mammary gland with a predominance of pathogenic microflora). Purulent-inflammatory processes in the mammary glands are accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39 degrees, redness and thickening of the breast, dilation and protrusion of veins.
Mastitis not caused by lactation (breastfeeding) also occurs. Its symptom is also pain in the mammary glands. This condition is typical of adolescents and occurs even in infants, but its cause is infections or hormonal imbalances.
If the temperature rise lasts more than a day, you should immediately contact a gynecologist or therapist. After a visual examination, an ultrasound of the mammary glands is performed, which shows the area of inflammation. The doctor prescribes ointments for the woman (Traumel S, Vishnevsky ointment) and physiotherapeutic procedures, in particular:
- Ultrasonic massage . It is based on the penetration of ultrasonic waves with an intensity of 0.2-0.4 W into the glandular tissue of the breast. A delicate massage occurs, stimulating the resorption of seals. Women feel much better after the 2nd session, and complete recovery occurs after the fifth day of daily 5-minute procedures.
- Pulsed magnetic therapy . The impact is carried out on both sides of the affected areas of the chest.
- Centimeter and decimeter wave therapy . It works on the same principle, the course is 8-10 procedures.
For mastitis, additional antibiotics are prescribed. They are selected depending on the type and sensitivity of the pathogen. For example, to destroy pathogenic microflora, the doctor may prescribe Ospamox, Amoxiclav, Cefazolin, etc.
Mastitis also occurs in men. The reason may be a hormonal imbalance with a predominance of the female hormone estrogen, a large amount of beer consumption, and the use of anabolic steroids by athletes.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Minor pain in the mammary glands, caused by hormonal reasons and the approach of the menstrual cycle, is not dangerous. To reduce discomfort, it is recommended to choose a larger bra with good breast support, which will not compress the breast tissue and aggravate symptoms. In case of severe swelling, 3-4 days before menstruation, it is necessary to limit the consumption of spicy and salty foods.
To prevent pain in the mammary gland associated with the development of lactation mastitis, it is important to observe the rules of personal hygiene after each feeding and to prevent stagnation of milk. It is advisable to use special nursing underwear made from natural materials. Prolonged pain accompanied by general malaise indicates the presence of a pathological cause. You should definitely consult a doctor and find out why the symptom occurred.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics depend on the etiological factor of pain in the mammary gland. Preferably, etiotropic and pathogenetic treatments are prescribed to eliminate the causes of pain and promote rapid recovery. Medicines are combined with physiotherapeutic interventions (electrophoresis, compresses), which are used only after excluding tumor pathology. Most often, pain treatment regimens include:
- Analgesics
. The drugs are indicated for severe pain in the mammary glands, which disrupts sleep, appetite, and causes asthenic symptoms. In typical cases, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which effectively reduce the level of inflammatory mediators and reduce swelling. - Antibiotics
. For bacterial infections, broad-spectrum drugs are needed that act on typical infectious causes of mastitis. Medicines are selected taking into account the results of bacterial cultures and antibiotic sensitivity tests, course therapy lasts at least 7 days. - Hormones
. If sharp pain in the mammary glands is caused by hormonal causes in the premenstrual period, estrogen preparations are recommended. The funds are also needed in the treatment of benign breast formations and mastopathy. - Infusion solutions
. Tumor and inflammatory causes are accompanied by severe intoxication, which is eliminated by intravenous infusions of colloid and crystalloid solutions in combination with loop diuretics. - Cytostatics
. Combinations of 2-3 chemotherapy drugs are prescribed for malignant neoplasms of the nipple and gland. Medicines are taken in courses; for better effect they are supplemented with local radiation exposure. - General strengthening
. In case of chronic pain in the mammary glands, the body is depleted, so ascorbic acid and B vitamins are used. For severe asthenia, anabolic steroid drugs are indicated.
Surgery
Breast cancer is an absolute indication for surgery. In rare cases, at the initial stage of the process, sectoral breast resection is performed. In most situations, a radical mastectomy with removal of regional lymph nodes is necessary. Sometimes, with unstable hormonal levels and a high risk of malignancy, a benign tumor is removed.
To reduce pain in the mammary gland during purulent inflammation, opening and drainage of mastitis is indicated, which involves making a skin incision at the site of fluctuation and washing the cavity with an antiseptic solution, followed by installation of drainage. In the case of gangrenous mastitis, removal of the entire mammary gland is required, followed by plastic surgery. Large hematomas formed after chest injuries are opened to prevent suppuration.
Pain in the mammary glands not associated with breast disease
Tietze syndrome. Tietze syndrome is a rare inflammation of the costal cartilage at the junction with the sternum. From 1 to 4 ribs are affected, the syndrome is masked as pain in the armpits or breast area. The cause of the disease is rib injuries, heavy physical activity, and exhausting training. The only way to make an accurate diagnosis is to undergo an X-ray or CT scan, which can help see these types of changes. A general and biochemical blood test, effective in diagnosing other pathologies, does not reveal pathologies in Tietze syndrome.
Wearing the wrong underwear. A woman's breasts change as they gain or lose weight. For every 5 kilograms gained, 100 grams of weight falls on the chest. If a woman has gained 10 or 20 kg (and after giving birth, it is quite possible that she has gained 25-30 kg), then instead of the usual bra size 80B, she needs to switch to 95D. In winter, the weight gains up to 5 kg, and a summer bra is no longer suitable. Wearing tight underwear leads to chest pain and discomfort.
With age, breasts also undergo changes. If glandular tissue predominates in youth, then with the onset of menopause it is replaced by adipose tissue, and the breasts stretch. In this case, a minimizer comes to the rescue. This is special underwear that evenly distributes the load on the shoulders and spine, giving the breasts a beautiful shape.
Methods for examining the mammary glands for pain
If you are worried about pain in the mammary glands, you should immediately go to a doctor - a gynecologist, an endocrinologist, and if you suspect cancer - to an oncologist. Modern methods for diagnosing breast diseases will help identify the true cause of pain.
- Ultrasound examination . Ultrasound of the mammary glands is the primary method with which to begin the examination. This is the only painless and safe method for detecting pathologies in the breast. At the same time, ultrasound of the mammary glands is very informative. High frequency acoustic waves are also used in cases where radiography is contraindicated. Examination is especially effective at a young age, when the breasts are still quite dense in structure. Ultrasound is inexpensive, and a huge advantage of the technique is that the doctor immediately examines the lymph nodes.
- Mammography. This is an x-ray with a low dose of radiation. Detects lumps, benign and malignant tumors.
- Fluorography . A regular image will also show various neoplasms in the mammary glands, but this method is rarely used.
- CT scan . With its help, a slice at different angles of inclination is displayed on the computer screen. Reveals the exact nature of the neoplasm.
- IHC . This is a method similar to a biopsy, in which tissue is removed and examined for the presence of oncogenic markers.
- Radiothermometry . This method is based on the temperature difference reflected by healthy and affected tissue areas. Helps detect cancer in the early stages.
- MRI . This is a breast scan with the resulting image displayed on the screen. Diagnoses cancer at the earliest stages.