Compound
The active substance is human insulin (rDNA).
1 ml of injection suspension contains 100 IU of human biosynthetic insulin (recombinant DNA obtained from Saccharomyces cerevisiae).
One IU (international unit) is equal to 0.035 mg of anhydrous human insulin.
One multi-dose disposable pen contains 3 ml of injection suspension, which is equivalent to 300 IU.
"Protafan® NM FlexPen®" is a suspension of isophane (NPH) insulin.
Excipients: zinc chloride; glycerol; metacresol; phenol; sodium hydrogen phosphate, dihydrate; sodium hydroxide (for pH correction); diluted hydrochloric acid (for pH correction); protamine sulfate; water for injections.
Protaphane HM Penfill
Release form, composition and packaging
The suspension for subcutaneous administration is white; when standing, it separates, forming a white precipitate and a colorless or almost colorless supernatant; When stirring, the sediment should resuspend. 1 ml insulin isophane (human genetically engineered) 100 IU*. Excipients: zinc chloride, glycerol, metacresol, phenol, sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate, protamine sulfate, hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide solution (to maintain pH level), water for injection. * 1 IU corresponds to 35 mcg of anhydrous human insulin.
Clinical and pharmacological group: Human insulin of medium duration of action.
pharmachologic effect
Protafan NM Penfill is a suspension of biosynthetic human isophane insulin with medium duration of action. The onset of action is 1.5 hours after subcutaneous administration. The maximum effect develops between 4 hours and 12 hours. Duration of action is 24 hours. The action profile of insulin is approximate: it depends on the dose of the drug and reflects individual characteristics.
Pharmacokinetics
Insulin absorption and, as a consequence, the onset of the hypoglycemic effect depends on the injection site (abdomen, thigh, buttocks), injection volume, insulin concentration and some other factors. In the blood, the half-life of insulin is several minutes.
Thus, the action profile of insulin depends mainly on the rate of its absorption. This process is influenced by many factors, resulting in significant individual differences. When switching from an insulin concentration of 40 U/ml to 100 U/ml, small changes in insulin absorption due to the lower volume are compensated by its higher concentration.
Indications
- insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type I);
- non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type II): stage of resistance to oral hypoglycemic agents, partial resistance to these drugs (with combination therapy), intercurrent diseases, operations, pregnancy.
Dosage regimen
The dose of the drug is determined by the doctor individually in each specific case. The drug is used only for subcutaneous injections. After injection, the needle should remain under the skin for several seconds to ensure complete administration of the dose. For insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type I), the drug is used as basal insulin in combination with a fast-acting insulin preparation.
For non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (type II), the drug can be used both as monotherapy and in combination with fast-acting insulins.
When transferring a patient from highly purified pork or human insulin to Protafan NM Penfill, the dose of the drug remains the same.
When transferring from beef or mixed insulin to Protafan NM Penfill, the dose should be reduced by 10%, except in cases where the initial dose is less than 0.6 U/kg body weight. At a daily dose exceeding 0.6 U/kg, insulin must be administered in the form of 2 or more injections in different places.
Rules for using the Penfill cartridge and administering the drug Before use, you must make sure that there is no damage to the Penfill cartridge. The Penfill cartridge should not be used if there is any visible damage or if the visible part of the rubber piston is wider than the white strip. Before inserting the Penfill cartridge into the pen, it should be rocked up and down. The movement should be made in such a way that the glass ball in the cartridge moves from one end to the other. This manipulation should be repeated at least 10 times until the liquid becomes cloudy white and homogeneous. If the Penfill cartridge is already inserted into the syringe pen, the mixing procedure should be repeated before each subsequent injection.
After injection, the needle should remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds. The syringe pen button must be kept pressed until the needle is completely removed from under the skin. After each injection, the needle should be removed immediately. The Penfill cartridge is intended for individual use only. When the cartridge is inserted into the NovoPen 3, NovoPen 3 Demi or Innovo syringe pen, a colored stripe should be visible through the window of the cartridge holder.
Side effect
Side effects associated with the effect on carbohydrate metabolism: hypoglycemic conditions (pallor, increased sweating, palpitations, sleep disorders, tremor). Allergic reactions: extremely rarely - skin rash. Other: transient refractive errors (usually at the beginning of insulin therapy).
Contraindications
- hypoglycemia;
- insulinoma;
- history of immediate allergic reactions to the administration of human insulin preparations.
Pregnancy and lactation
During pregnancy and lactation, patients' need for insulin changes, which should be taken into account to maintain adequate metabolic control. Insulin does not cross the placental barrier. When using the drug Protafan NM Penfill during lactation, there is no risk for the child.
special instructions
Patients receiving more than 100 units of insulin per day should be hospitalized when changing the drug. The transition from one insulin drug to another should be carried out under the control of blood glucose levels.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
After transferring the patient to biosynthetic human insulin, the ability to drive a car and engage in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions may temporarily deteriorate.
Overdose
Symptoms: initial symptoms of hypoglycemia are a sudden increase in sweating, palpitations, tremors, hunger, agitation, paresthesia in the mouth, pallor, headache, sleep disturbances. In severe cases of overdose - coma. Treatment: The patient can eliminate mild hypoglycemia himself by taking sugar or sugar-rich foods.
In severe cases, 1 mg of glucagon is administered intramuscularly or subcutaneously. If necessary, therapy is continued with the intravenous administration of concentrated solutions of dextrose (glucose).
Drug interactions
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is enhanced by MAO inhibitors, non-selective beta-blockers, sulfonamides, anabolic steroids, tetracyclines, clofibrate, cyclophosphamide, fenfluramine, and drugs containing ethanol.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is reduced by oral contraceptives, glucocorticoids, thyroid hormones, thiazide diuretics, heparin, lithium preparations, tricyclic antidepressants. Under the influence of reserpine and salicylates, it is possible to both weaken and enhance the action of insulin.
Pharmaceutical interactions
Ethanol and various disinfectants can reduce the biological activity of insulin.
Storage conditions and periods
Penfill cartridges should be stored in packaging, protected from sunlight at a temperature of 2° to 8°C; do not freeze. It is not recommended to store the used cartridge in the refrigerator.
Mode of application
"Protafan® NM FlexPen®" is a syringe pen filled with a long-acting insulin preparation; it can be used alone or in combination with short-acting or rapid-acting insulin.
The dosage of insulin is individual and determined by the doctor in accordance with the needs of the patient.
The individual daily insulin requirement is usually between 0.3 and 1.0 IU/kg/day. The daily need for insulin may increase in patients with insulin resistance (for example, during puberty or obesity) and decrease in patients with residual endogenous insulin production.
Introduction
The drug "Protafan® NM FlexPen®" is intended for subcutaneous injections only. Insulin suspension is never administered intravenously.
"Protafan® NM FlexPen®" is usually injected under the skin of the thigh. It can also be injected into the area of the anterior abdominal wall, buttocks or deltoid muscle of the shoulder.
With subcutaneous injections into the thigh, insulin absorption occurs more slowly and with less variability than when injected into other areas of the body.
Injection into a retracted fold of skin significantly reduces the risk of penetration into the muscle.
After the injection, the needle should remain under the skin for at least 6 seconds. This will ensure that the full dose is administered.
To reduce the risk of lipodystrophy, injection sites should always be changed, even within the same body area.
The pre-filled syringe pen “Protafan® NM FlexPen®” is intended for use with single-use “NovoFine®” or “NovoTwist®” needles up to 8 mm long.
The FlexPen® syringe pen allows you to administer a dose from 1 to 60 units in increments of 1 unit.
Detailed instructions for using these medical devices must be followed.
Protaphane® HM (Protaphane® NM)
Instructions for use for patients
You cannot use Protafan® NM:
- In insulin pumps.
— If you are allergic (hypersensitivity) to human insulin or any of the components included in the drug Protafan® NM.
- If you experience hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
— If the protective cap is missing or not firmly attached. Each bottle has a protective plastic cap. If the protective cap on a new bottle is damaged, return the bottle to the pharmacy.
— If the storage conditions of the drug were violated or it was frozen.
— If the insulin does not turn uniformly white and cloudy after stirring.
Before using Protafan® NM:
— Check the label to make sure you are using the right type of insulin.
— Remove the protective cap.
How to use Protafan® NM
The drug Protafan® NM is intended for subcutaneous administration. Never give insulin intravenously or intramuscularly
.
Always rotate injection sites within the anatomical area to reduce the risk of lumps and ulcerations at the injection site. The best places for injections are: the buttocks, front of the thigh or shoulder.
How to administer Protafan® NM if only Protafan® NM is administered or if it is necessary to mix Protafan® NM with short-acting insulin:
- Make sure you use an insulin syringe that has a scale that allows you to measure the dose in action units.
— Fill the syringe with air in an amount corresponding to the required dose of insulin.
— Follow the instructions your doctor or nurse gives you.
— Immediately before taking the dose, roll the bottle between your palms until the insulin becomes uniformly white and cloudy. Resuspension is facilitated if the preparation is at room temperature.
— Inject insulin under the skin. Use the injection technique recommended by your doctor or nurse.
— Hold the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds to ensure that the entire dose of insulin is injected.
Protafan® NM suspension for subcutaneous administration in FlexPen® syringe pens
Instructions for use for patients
Read these instructions carefully before using Protafan® NM in the FlexPen® syringe pen.
The FlexPen® is a pre-filled insulin pen with a pump. You can select a dose from 1 to 60 units in 1 unit increments. The FlexPen® syringe pen is designed for use with NovoFine or NovoTwist® disposable needles up to 8 mm in length. As a precaution, always carry a spare insulin injection system with you in case your FlexPen® syringe pen with Protafan® NM is lost or damaged.
FlexPen® syringe pen with Protafan® NM
See fig. 1 and fig. 2.
Storage and care
The FlexPen® syringe pen is designed for effective and safe use and requires careful handling. In the event of a fall or strong mechanical impact, the syringe pen may be damaged and insulin may leak.
The outside of the FlexPen® syringe pen can be cleaned with a cotton swab. Do not wash, immerse or lubricate the pen as it may this may damage the mechanism. FlexPen® syringe pens must not be refilled.
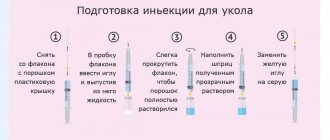
Preparing the FlexPen® syringe pen with Protafan® HM for use
Check the label to make sure that the FlexPen® pen with Protafan® NM contains the required type of insulin.
Mix the insulin before the first injection using the new FlexPen® pen.
A
To facilitate mixing, allow the preparation to warm to room temperature. Remove the cap from the pen (see Figure A).
IN
Raise and lower the pen up and down 20 times as shown (see Figure B) so that the glass ball moves from one end of the cartridge to the other. Repeat these steps until the contents of the cartridge become uniformly white and cloudy.
Before each subsequent injection
Stir the contents by lifting the pen up and down at least 10 times until the contents of the cartridge are uniformly white and cloudy.
After mixing, inject immediately.
- Always ensure there are at least 12 units of insulin left in the cartridge to ensure even mixing. If there are less than 12 units left, use a new FlexPen® syringe pen with Protafan® HM.
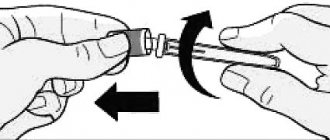
Attaching a needle
WITH
Remove the protective sticker from the disposable needle.
Carefully and tightly screw the needle onto the FlexPen® syringe pen (see Fig. C).
D
Remove the outer needle cap but do not throw it away (see Figure D).
E
Remove and discard the inner needle cap (see Figure E).
- Always use a new needle for each injection to prevent infection.
- Be careful not to bend or damage the needle before use.
— To avoid accidental needle sticks, never put the inner cap back on the needle.
Checking insulin delivery
When using a pen syringe, a small amount of air may accumulate in the cartridge before each injection. To prevent the entry of air bubbles and ensure that the correct dose of the drug is administered.
F
Dial up 2 units of the drug by turning the dose selector (see Fig. F).
G
Holding the FlexPen® pen with the needle pointing up, lightly tap the cartridge several times with your fingertip to force air bubbles to the top of the cartridge (see Figure G).
N
While holding the pen with the needle facing up, press the trigger button all the way. The Dota selector will return to zero.
A drop of insulin should appear at the end of the needle. If this does not happen, replace the needle and repeat the procedure, but no more than 6 times.
If a drop of insulin does not appear, the pen is faulty and cannot be used (see Figure H).
Setting the dose
Make sure the dose selector is set to position "0".
I
Turn the dose selector to set the number of units required for injection. The dose can be adjusted by rotating the dose selector in any direction until the correct dose is set opposite the dose indicator. To avoid releasing your insulin dose, be careful when turning the dose selector to avoid accidentally pressing the trigger button.
It is not possible to set a dose greater than the number of units remaining in the cartridge (see Figure I).
— You cannot use the insulin balance scale to measure your insulin dose.
Insulin administration
Insert the needle under the skin. Use the injection technique recommended by your doctor.
J
To inject, press the trigger button all the way until a “0” appears next to the dose indicator. Be careful: when administering the drug, you should only press the start button.
Turning the dose selector will not deliver the drug (see Figure J).
TO
While removing the needle from under the skin, keep the trigger button pressed fully. After injection, leave the needle under the skin for at least 6 seconds. This will ensure that the full dose of insulin is delivered (see Figure K).
L
Guide the needle into the outer needle cap without touching the cap. When the needle is fully inserted, put on the cap and unscrew the needle.
Discard the needle carefully and cap the pen (see Figure L).
— Remove the needle after each injection and never store the FlexPen® pen with the needle attached. Otherwise, liquid may leak out of the pen, which may result in incorrect dosage.
— Caregivers should handle used needles with extreme care to avoid accidental sticking.
— Throw away the used FlexPen® syringe pen with the needle disconnected.
— The FlexPen® syringe pen with the drug Protafan® NM and needles are intended for individual use only, they cannot be transferred to other persons.
Features of application
Pregnant
Since insulin does not cross the placental barrier, there are no restrictions on treating diabetes with insulin during pregnancy.
There are also no restrictions on treatment with Protafan® NM FlexPen® during breastfeeding, since treatment of the mother does not create any risk for the child. However, it may be necessary to adjust the dose and diet for the mother.
Children
Biosynthetic human insulin preparations are effective and safe drugs for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents of different age groups. The daily need for insulin in children and adolescents depends on the stage of the disease, body weight, age, diet, physical activity, the degree of insulin resistance and the dynamics of glycemic levels.
Drivers
The patient's reaction and ability to concentrate may be impaired by hypoglycemia. This may become a risk factor in situations where these abilities are of particular importance (for example, when driving a car or working with other mechanisms).
Patients should be advised to take measures to prevent hypoglycemia before driving. This is especially important for patients who have weakened or absent warning symptoms of hypoglycemia or who have frequent episodes of hypoglycemia. In such circumstances, the advisability of driving in general should be weighed.
Insulin Protafan HM penfill suspension for subcutaneous injection 100 IU/ml cartridge 3 ml No. 5
Indications
Diabetes mellitus type 1; type 2 diabetes mellitus: stage of resistance to oral hypoglycemic agents, partial resistance to these drugs (with combination therapy), intercurrent diseases; type 2 diabetes mellitus in pregnant women.
pharmachologic effect
Medium-acting human insulin produced using recombinant DNA technology. Interacts with a specific receptor on the outer cytoplasmic membrane of cells and forms an insulin-receptor complex that stimulates intracellular processes, incl. synthesis of a number of key enzymes (hexokinase, pyruvate kinase, glycogen synthetase). The decrease in blood glucose levels is due to an increase in its intracellular transport, increased absorption and assimilation by tissues, stimulation of lipogenesis, glycogenogenesis, and a decrease in the rate of glucose production by the liver.
The duration of action of insulin drugs is mainly determined by the rate of absorption, which depends on several factors (for example, dose, route and site of administration), and therefore the insulin action profile is subject to significant fluctuations, both between different people and within the same person. person.
On average, after subcutaneous administration, this insulin begins to act after 1.5 hours, the maximum effect develops between 4 hours and 12 hours, the duration of action is up to 24 hours.
Drug interactions
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin is enhanced by oral hypoglycemic drugs, MAO inhibitors, ACE inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, non-selective beta-blockers, bromocriptine, octreotide, sulfonamides, anabolic steroids, tetracyclines, clofibrate, ketoconazole, mebendazole, pyridoxine, theophylline, cyclophosphamide, fenfluramine, drugs lithium, preparations containing ethanol.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin weakens glucagon, somatropin, estrogens, oral contraceptives, GCS, iodine-containing thyroid hormones, thiazide diuretics, “loop” diuretics, heparin, tricyclic antidepressants, sympathomimimetics, Danazole, clonidine, epinephrine, and hystamin-re-re-N1-RRETRICA Ceptors, slow calcium channel blockers , diazoxide, morphine, phenytoin, nicotine.
Under the influence of reserpine and salicylates, it is possible to both weaken and enhance the action of insulin.
Reduces tolerance to ethanol.
Dosage regimen
For subcutaneous administration only. The dose of the drug is determined by the doctor individually in each specific case, based on the concentration of glucose in the blood.
On average, the daily dose ranges from 0.5 to 1 IU/kg body weight (depending on the individual characteristics of the patient and blood glucose concentration).
Contraindications for use
Increased sensitivity to insulin; hypoglycemia.
Restrictions for children
No data
Use in elderly patients
Use with caution in elderly patients. Dose adjustment is necessary.
Restrictions for elderly patients
No data
Use for liver dysfunction
Use with caution in patients with impaired liver function. Dose adjustment is necessary.
Restrictions for liver dysfunction
Use with caution
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
There are no restrictions on the treatment of diabetes mellitus with insulin during pregnancy, because insulin does not cross the placental barrier. When planning pregnancy and during it, it is necessary to intensify the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Insulin requirements usually decrease in the first trimester of pregnancy and gradually increase in the second and third trimesters.
During and immediately after childbirth, the need for insulin may decrease dramatically. Shortly after birth, insulin requirements quickly return to pre-pregnancy levels.
Restrictions when breastfeeding
Possible use
Restrictions during pregnancy
Possible use
Use for renal impairment
Use with caution in patients with impaired renal function. Dose adjustment is necessary.
Restrictions for impaired renal function
Use with caution
special instructions
During insulin therapy, constant monitoring of blood glucose concentration is necessary.
In addition to insulin overdose, the causes of hypoglycemia can be: drug replacement, skipping meals, vomiting, diarrhea, increased physical activity, diseases that reduce the need for insulin (impaired liver and kidney function, hypofunction of the adrenal cortex, pituitary gland or thyroid gland), change of injection site, as well as interactions with other drugs.
Incorrect dosing or interruptions in insulin administration, especially in patients with type 1 diabetes, can lead to hyperglycemia. Typically, the first symptoms of hyperglycemia develop gradually over several hours or days. They include the appearance of thirst, increased urination, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, redness and dryness of the skin, dry mouth, loss of appetite, and the smell of acetone in the exhaled air. If left untreated, hyperglycemia in type 1 diabetes can lead to life-threatening diabetic ketoacidosis.
The dose of insulin must be adjusted in cases of thyroid dysfunction, Addison's disease, hypopituitarism, liver and kidney dysfunction, and diabetes mellitus in patients over 65 years of age.
Due to the increased risk of cardiac and cerebral complications of hypoglycemia, insulin should be used with caution in patients with severe stenosis of the coronary and cerebral arteries.
With caution in patients with proliferative retinopathy, especially those not receiving treatment with photocoagulation (laser coagulation) due to the risk of amaurosis (total blindness).
If the patient increases the intensity of physical activity or changes the usual diet, adjustment of the insulin dose may be necessary.
Concomitant diseases, especially infections and conditions accompanied by fever, increase the need for insulin.
Transferring a patient to a new type of insulin or an insulin preparation from another manufacturer must be done under the supervision of a physician.
When using insulin drugs in combination with drugs of the thiazolidinedione group in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, fluid retention in the body may occur, which increases the risk of development and progression of chronic heart failure, especially in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system and the presence of risk factors for chronic heart failure. heart failure. Patients receiving such therapy should be monitored regularly for signs of heart failure. If heart failure occurs, therapy should be carried out in accordance with current standards of care.
Side effect
Side effects due to the effect on carbohydrate metabolism:
hypoglycemic conditions (pallor of the skin, increased sweating, palpitations, tremor, hunger, agitation, paresthesia of the oral mucosa, headache, dizziness, decreased visual acuity). Severe hypoglycemia can lead to the development of hypoglycemic coma.
Allergic reactions:
skin rash, angioedema, anaphylactic shock.
Local reactions:
hyperemia, swelling and itching at the injection site, with long-term use - lipodystrophy at the injection site.
Other:
swelling, transient decrease in visual acuity (usually at the beginning of therapy).
Possible product names
- Insulin Protafan HM penfill suspension d/i 100 units/ml penfil 3.0ml N5
- PROTAFAN NM PENFILL 100 UNITS/ML 3 ML No. 5
- PROTAFAN NM PENFILL 100IU/ML 3ML N5 CART
- PROTAFAN NM PENFILL SUSP. FOR P/C INPUT. 100IU/ML CARTRIDGES 3ML No.5
- PROTAFAN NM PENFILL 100IU/ML SUSP. D/SUBCUTANEOUS ENTER 3ML CARTRIDGE X5 (R)
Overdose
Although a specific concept of overdose has not been formulated for insulin, if doses that are too high compared to the patient’s needs are used, hypoglycemia may develop in successive stages after its administration.
Mild hypoglycemia can be treated by ingesting glucose or sugary foods. Therefore, diabetic patients are advised to always have several foods containing sugar with them.
In the case of severe hypoglycemia, when the patient is unconscious, persons who have undergone appropriate instruction should immediately administer glucagon subcutaneously or intramuscularly (0.5 to 1.0 mg). A healthcare professional may give the patient glucose. Glucose should also be administered if the patient does not respond to glucagon administration within 10-15 minutes.
After the patient regains consciousness, he should take foods containing carbohydrates to prevent a relapse.
Storage conditions
Store in original packaging at 2-8°C (in the refrigerator, not too close to the freezer). Do not freeze.
To protect from light, store the pen with the cap closed.
Once opened: use within 6 weeks. Do not store in the refrigerator. Store at a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life: 2.5 years.
Product description certified by the manufacturer Novo Nordisk
.
Verified by
Likar Turumkulova Irina
Note!
Description of the drug Protafan NM Flexpen suspension. d/in. 100U/ml cart. 3ml in syringe pen No. 5 on this page is a simplified author’s version of the apteka911 website, created on the basis of the instructions for use.
Before purchasing or using the drug, you should consult your doctor and read the manufacturer's original instructions (attached to each package of the drug). Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. Only a doctor can decide to prescribe the drug, as well as determine the dose and methods of its use.