Ursofalk
Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones
The recommended dose is 10 mg of ursodeoxycholic acid per 1 kg of body weight per day, which corresponds to:
| Body mass | Measuring cup | Compliant (ml) |
| 5 - 7 kg | 1/4 | 1,25 |
| 8 - 12 kg | 1/2 | 2,50 |
| 13 – 18 kg | 3/4 | 3,75 |
| 19-25 kg | 1 | 5,00 |
| 26 – 35 kg | 11/2 | 7,50 |
| 36 – 50 kg | 2 | 10,00 |
| 51 -65 kg | 21/2 | 12,50 |
| 66 – 80 kg | 3 | 15,00 |
| 81 – 100 kg | 4 | 20,00 |
| Over 100 kg | 5 | 25,00 |
The drug must be taken daily in the evening, before bedtime.
Duration of treatment is 6-12 months. To prevent recurrent cholelithiasis, it is recommended to take the drug for several months after the stones have dissolved.
Treatment of biliary reflux gastritis
1 measuring cup of Ursofalk daily in the evening before bed.
The course of treatment is from 10-14 days to 6 months, if necessary - up to 2 years.
Treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis
The daily dose depends on body weight and ranges from 2 to 7 measuring cups (approximately 14 mg ± 2 mg ursodeoxycholic acid per 1 kg of body weight). The following mode of application is recommended:
| Body weight (kg) | Measuring cups Ursofalk suspension for oral administration 250 mg/5ml | |||
| First 3 months of treatment | Subsequently | |||
| Morning | During the day | Evening | Evening (1 time per day) | |
| 8-11 | — | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/2 |
| 12-15 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 3/4 |
| 16-19 | 1/2 | — | 1/2 | 1 |
| 20-23 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 11/4 |
| 24-27 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 11/2 |
| 28-31 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1 | 13/4 |
| 32-39 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1 | 2 |
| 40-47 | 1/2 | 1 | 1 | 2 1/2 |
| 48-62 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 63-80 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| 81-95 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| 96-115 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| More than 115 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
Symptomatic treatment of chronic hepatitis of various origins -
daily dose 10-15 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. Duration of treatment is 6-12 months or more.
Primary sclerosing cholangitis -
daily dose 12-15 mg/kg; if necessary, the dose can be increased to 20 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. The duration of therapy ranges from 6 months to several years (see section: “Special instructions”).
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) -
daily dose 20 mg/kg/day in 2-3 divided doses, with a further increase to 30 mg/kg/day if necessary.
Body weight more than 10 kg: dosage 20-25 mg ursodeoxycholic acid/kg/day.
Measuring device: measuring cup
| Body weight (kg) | Daily dose of ursodeoxycholic acid (mg/kg body weight) | Number of measuring cups of Ursofalk suspension 250 mg/5 ml | |
| Morning | Evening | ||
| 11-12 | 21-23 | 1/2 | 1/2 |
| 13-15 | 21-24 | 1/2 | 3/4 |
| 16-18 | 21-23 | 3/4 | 3/4 |
| 19-21 | 21-23 | 3/4 | 3/4 |
| 22-23 | 22-23 | 1 | 1 |
| 24-26 | 22-23 | 1 | 1 1/4 |
| 27-29 | 22-23 | 1 1/4 | 1 1/4 |
| 30-32 | 21-23 | 1 1/4 | 1 1/2 |
| 33-35 | 21-23 | 1 1/2 | 1 1/2 |
| 36-38 | 21-23 | 1 1/2 | 1 3/4 |
| 39-41 | 21-22 | 1 3/4 | 1 3/4 |
| 42-47 | 20-22 | 1 3/4 | 2 |
| 48-56 | 20-23 | 21/4 | 21/4 |
| 57-68 | 20-24 | 23/4 | 23/4 |
| 69-81 | 20-24 | 31/4 | 31/4 |
| 82-100 | 20-24 | 4 | 4 |
| > 100 | 41/2 | 41/2 | |
* Conversion table:
| Oral suspension | Rsodeoxycholic acid | |
| 1 measuring cup | 5 ml | 250 mg |
| 3/4 measuring cup | 3.75 ml | 187.5 mg |
| ½ measuring cup | 2.5 ml | 125 mg |
| 1/4 measuring cup | 1.25 ml | 62.5 mg |
Children weighing up to 10 kg get sick very rarely. In this case, a commercially available disposable syringe should be used.
Single doses for children weighing up to 10 kg should be measured using a syringe as the measuring cup provided is not designed for volumes less than 1.25 ml. Use a disposable 2 ml syringe in 0.1 ml increments. Please note: disposable syringes are not included in the drug package, but can be purchased at your local pharmacy.
To measure the required dose using a syringe:
1. Shake the bottle before opening it.
2. Pour a small amount of suspension into the measuring cup that is included in the package with the drug.
3. Fill the syringe with a slightly larger volume of the drug than required.
4. Tap the syringe with your fingers to remove air bubbles from the collected suspension.
5. Make sure that the required volume of suspension is in the syringe; if necessary, add or release excess volume.
6. Carefully pour the contents of the syringe directly into the child's mouth.
Do not insert the syringe into the vial. Not
pour unused suspension from the syringe or measuring cup back into the vial.
Body weight up to 10 kg: dosage 20 mg ursodeoxycholic acid/kg/day. Measuring device: disposable syringe
| Body weight (kg) | Ursofalk suspension dose 250 mg/5 ml (ml) | ||
| Morning | Evening | ||
| 4 | 0,8 | 0,8 | |
| 4,5 | 0,9 | 0,9 | |
| 5 | 1,0 | 1,0 | |
| 5,5 | 1,1 | 1,1 | |
| 6 | 1,2 | 1,2 | |
| 6,5 | 1,3 | 1,3 | |
| 7 | 1,4 | 1,4 | |
| 7,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 | |
| 8 | 1,6 | 1,6 | |
| 8,5 | 1,7 | 1,7 | |
| 9 | 1,8 | 1,8 | |
| 9,5 | 1,9 | 1,9 | |
| 10 | 2,0 | 2,0 | |
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis -
the average daily dose is 10-15 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. The duration of therapy ranges from 6-12 months or more.
Alcoholic liver disease -
the average daily dose is 10-15 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. The duration of therapy ranges from 6-12 months or more.
Biliary dyskinesia -
the average daily dose is 10 mg/kg in 2 divided doses for 2 weeks to 2 months. If necessary, it is recommended to repeat the course of treatment.
Ursofalk suspension orally 250mg/5ml 250ml
Compound
Active ingredient: Excipients: benzoic acid - 7.5 mg, xylitol - 1600 mg, glycerol - 500 mg, microcrystalline cellulose - 100 mg, propylene glycol - 50 mg, sodium citrate - 25 mg, sodium cyclamate - 25 mg, anhydrous citric acid - 12.5 mg, sodium chloride - 3 mg, lemon flavor (Givaudan PHL-134488) - 1.5 mg, purified water - 2875.5 mg.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, ursodeoxycholic acid is rapidly absorbed in the jejunum and proximal ileum by passive diffusion, and in the distal ileum by active transport.
Approximately 60-80% of the dose taken is absorbed. After absorption, ursodeoxycholic acid is almost completely conjugated in the liver with glycine and taurine and excreted in the bile. During the first passage through the liver, up to 60% is metabolized. Depending on the daily dose, the type of disease and the condition of the liver, more or less amount of ursodeoxycholic acid accumulates in the bile. At the same time, there is a relative decrease in the content of other, more lipophilic bile acids. Under the influence of intestinal bacteria, ursodeoxycholic acid is partially degraded to form 7-keto-lithocholic and lithocholic acid. Lithocholic acid is hepatotoxic; in some animal species it causes damage to the liver parenchyma. In the human body it is absorbed only in small quantities. During the process of metabolism, it is sulfated in the liver, due to which it is neutralized even before it is excreted into bile and excreted from the body with feces. The half-life of ursodeoxycholic acid is 3.5 to 5.8 days.
Indications for use
- dissolution of cholesterol gallstones;
- biliary reflux gastritis;
- primary biliary cirrhosis of the liver in the absence of signs of decompensation (symptomatic treatment);
- chronic hepatitis of various origins;
- primary sclerosing cholangitis, cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis);
- non-alcoholic steatohepatitis;
- alcoholic liver disease;
- biliary dyskinesia.
Contraindications
- X-ray positive (high calcium content) gallstones;
- non-functioning gallbladder;
- acute inflammatory diseases of the gallbladder, bile ducts and intestines;
- liver cirrhosis in the stage of decompensation;
- severe dysfunction of the kidneys, liver, pancreas;
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Pediatric population
Unsuccessfully performed portoenterostomy or cases of failure to restore normal bile flow in children with biliary atresia.
Directions for use and doses
Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones
The recommended dose is 10 mg of ursodeoxycholic acid per 1 kg of body weight per day, which corresponds to:
| Body mass | Measuring cup | Compliant (ml) |
| 5 - 7 kg | 1/4 | 1,25 |
| 8 - 12 kg | 1/2 | 2,50 |
| 13 – 18 kg | 3/4 | 3,75 |
| 19-25 kg | 1 | 5,00 |
| 26 – 35 kg | 11/2 | 7,50 |
| 36 – 50 kg | 2 | 10,00 |
| 51 -65 kg | 21/2 | 12,50 |
| 66 – 80 kg | 3 | 15,00 |
| 81 – 100 kg | 4 | 20,00 |
| Over 100 kg | 5 | 25,00 |
The drug must be taken daily in the evening, before bedtime.
Duration of treatment is 6-12 months. To prevent recurrent cholelithiasis, it is recommended to take the drug for several months after the stones have dissolved.
Treatment of biliary reflux gastritis: 1 measuring cup of Ursofalk daily in the evening before bed.
The course of treatment is from 10-14 days to 6 months, if necessary - up to 2 years.
Treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis The daily dose depends on body weight and ranges from 2 to 7 measuring cups (approximately 14 mg ± 2 mg of ursodeoxycholic acid per 1 kg of body weight). The following mode of application is recommended:
| Body weight (kg) | Measuring cups Ursofalk suspension for oral administration 250 mg/5ml | |||
| First 3 months of treatment | Subsequently | |||
| Morning | During the day | Evening | Evening (1 time per day) | |
| 8-11 | — | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/2 |
| 12-15 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 1/4 | 3/4 |
| 16-19 | 1/2 | — | 1/2 | 1 |
| 20-23 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 11/4 |
| 24-27 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 11/2 |
| 28-31 | 1/4 | 1/2 | 1 | 13/4 |
| 32-39 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1 | 2 |
| 40-47 | 1/2 | 1 | 1 | 2 1/2 |
| 48-62 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| 63-80 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| 81-95 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| 96-115 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 |
| More than 115 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 |
Symptomatic treatment of chronic hepatitis of various origins is a daily dose of 10-15 mg/kg in 2-3 doses.
Duration of treatment is 6-12 months or more. Primary sclerosing cholangitis - daily dose 12-15 mg/kg; if necessary, the dose can be increased to 20 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. The duration of therapy ranges from 6 months to several years (see section: “Special instructions”).
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) - daily dose of 20 mg/kg/day in 2-3 doses, with a further increase to 30 mg/kg/day if necessary.
Body weight more than 10 kg: dosage 20-25 mg ursodeoxycholic acid/kg/day.
Measuring device: measuring cup
| Body mass (kg) | Daily dose of ursodeoxycholic acid (mg/kg body weight) | Number of measuring cups of Ursofalk suspension 250 mg/5 ml | |
| Morning | Evening | ||
| 11-12 | 21-23 | 1/2 | 1/2 |
| 13-15 | 21-24 | 1/2 | 3/4 |
| 16-18 | 21-23 | 3/4 | 3/4 |
| 19-21 | 21-23 | 3/4 | 3/4 |
| 22-23 | 22-23 | 1 | 1 |
| 24-26 | 22-23 | 1 | 1 1/4 |
| 27-29 | 22-23 | 1 1/4 | 1 1/4 |
| 30-32 | 21-23 | 1 1/4 | 1 1/2 |
| 33-35 | 21-23 | 1 1/2 | 1 1/2 |
| 36-38 | 21-23 | 1 1/2 | 1 3/4 |
| 39-41 | 21-22 | 1 3/4 | 1 3/4 |
| 42-47 | 20-22 | 1 3/4 | 2 |
| 48-56 | 20-23 | 21/4 | 21/4 |
| 57-68 | 20-24 | 23/4 | 23/4 |
| 69-81 | 20-24 | 31/4 | 31/4 |
| 82-100 | 20-24 | 4 | 4 |
| > 100 | 41/2 | 41/2 | |
* Conversion table:
| Oral suspension | Rsodeoxycholic acid | |
| 1 measuring cup | 5 ml | 250 mg |
| 3/4 measuring cup | 3.75 ml | 187.5 mg |
| ½ measuring cup | 2.5 ml | 125 mg |
| 1/4 measuring cup | 1.25 ml | 62.5 mg |
Children weighing up to 10 kg get sick very rarely.
In this case, a commercially available disposable syringe should be used. Single doses for children weighing up to 10 kg should be measured using a syringe as the measuring cup provided is not designed for volumes less than 1.25 ml. Use a disposable 2 ml syringe in 0.1 ml increments. Please note: disposable syringes are not included in the drug package, but can be purchased at your local pharmacy.
To measure the required dose using a syringe:
1. Shake the bottle before opening it.
2. Pour a small amount of suspension into the measuring cup that is included in the package with the drug.
3. Fill the syringe with a slightly larger volume of the drug than required.
4. Tap the syringe with your fingers to remove air bubbles from the collected suspension.
5. Make sure that the required volume of suspension is in the syringe; if necessary, add or release excess volume.
6. Carefully pour the contents of the syringe directly into the child's mouth.
Do not insert the syringe into the vial. Do not pour unused suspension from the syringe or measuring cup back into the vial.
Body weight up to 10 kg: dosage 20 mg ursodeoxycholic acid/kg/day. Measuring device: disposable syringe
| Body mass (kg) | Ursofalk suspension dose 250 mg/5 ml (ml) | |
| Morning | Evening | |
| 4 | 0,8 | 0,8 |
| 4,5 | 0,9 | 0,9 |
| 5 | 1,0 | 1,0 |
| 5,5 | 1,1 | 1,1 |
| 6 | 1,2 | 1,2 |
| 6,5 | 1,3 | 1,3 |
| 7 | 1,4 | 1,4 |
| 7,5 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 8 | 1,6 | 1,6 |
| 8,5 | 1,7 | 1,7 |
| 9 | 1,8 | 1,8 |
| 9,5 | 1,9 | 1,9 |
| 10 | 2,0 | 2,0 |
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - average daily dose of 10-15 mg/kg in 2-3 doses.
The duration of therapy ranges from 6-12 months or more. Alcoholic liver disease - average daily dose of 10-15 mg/kg in 2-3 doses. The duration of therapy ranges from 6-12 months or more.
Biliary dyskinesia - average daily dose of 10 mg/kg in 2 divided doses for 2 weeks to 2 months. If necessary, it is recommended to repeat the course of treatment.
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Best before date
4 years. After opening - 4 months. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
special instructions
Ursofalk should be taken under medical supervision.
During the first three months of treatment, liver function parameters should be monitored: transaminases, alkaline phosphatase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in the blood serum every 4 weeks and then every 3 months. Monitoring these parameters makes it possible to identify liver dysfunction in the early stages. This also applies to patients in the later stages of primary biliary cirrhosis. In addition, it can quickly determine whether a patient with primary biliary cirrhosis is responding to treatment.
When used to dissolve cholesterol gallstones:
In order to assess progress in treatment and to promptly detect signs of calcification of stones depending on the size of the stones, the gallbladder should be visualized (oral cholecystography) with examination of opacities in the standing and supine position (ultrasound) 6-10 months after the start of treatment .
If the gallbladder cannot be visualized on x-rays or in cases of calcified stones, poor contractility of the gallbladder or frequent attacks of colic, Ursofalk should not be used.
Patients taking Ursofalk to dissolve gallstones must use effective non-hormonal methods of contraception, since hormonal contraceptives can increase the formation of gallstones (see sections “Interaction with other drugs” and “Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding”).
When treating patients in the late stages of primary biliary cirrhosis: Cases of decompensation of liver cirrhosis have been reported extremely rarely. After cessation of therapy, a partial reverse development of the manifestations of decompensation was noted.
In patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, in rare cases, at the beginning of treatment, clinical symptoms may increase, for example, itching may increase. In this case, the dose of the drug must be reduced and then gradually increased again, as described in the “Method of administration and dosage” section.
When used in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis:
Long-term therapy with high doses of ursodeoxycholic acid (28-30 mg/kg/day) in patients with this pathology can cause serious side effects.
In patients with diarrhea, the dosage of the drug should be reduced. If diarrhea persists, treatment should be discontinued.
One measuring cup (equivalent to 5 ml) of Ursofalk oral suspension 250 mg/5 ml contains 0.50 mmol (11.39 mg) sodium. Patients monitoring their sodium intake should take this fact into account.
Description
Hepatoprotective agent.
Dosage form
Suspension for oral administration is white, homogeneous, containing small air bubbles, with a lemon aroma.
Pharmacodynamics
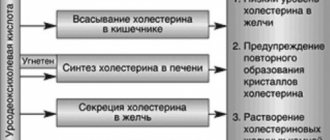
Hepatoprotective agent, has a choleretic effect. Reduces cholesterol synthesis in the liver, its absorption in the intestines and concentration in bile, increases the solubility of cholesterol in the biliary system, stimulates the formation and secretion of bile. Reduces the lithogenicity of bile, increases the content of bile acids; causes increased gastric and pancreatic secretion, enhances lipase activity, and has a hypoglycemic effect. Causes partial or complete dissolution of cholesterol stones when administered enterally, reduces the saturation of bile with cholesterol, which promotes the mobilization of cholesterol from gallstones. It has an immunomodulatory effect, affects immunological reactions in the liver: it reduces the expression of certain antigens on the hepatocyte membrane, affects the number of T-lymphocytes, the formation of interleukin-2, and reduces the number of eosinophils.
Pediatric population
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis)
According to clinical reports, there is many years of experience (up to 10 years or more) in treating pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis-associated hepatobiliary disease (CFAHD) with ursodeoxycholic acid. There is evidence that ursodeoxycholic acid therapy can reduce bile duct proliferation, slow the development of lesions detected by histological examination, and even promote the reversal of changes in the hepatobiliary system if therapy is started in the early stages of CFAHD. To optimize treatment efficacy, ursodeoxycholic acid therapy should be initiated as soon as possible after the diagnosis of CFAHD.
Side effects
The assessment of adverse events is based on the following classification:
- Very common (≥ 1/10)
- Frequent (≥ 1/100 - < 1/10)
- Uncommon (≥ 1/1000 - < 1/100)
- Rare (≥ 1/10000-< 1/1000)
- Very rare (< 1/10000).
Gastrointestinal disorders:
In clinical studies, loose stools or diarrhea were common during treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid.
During the treatment of primary biliary cirrhosis, acute pain in the right upper abdomen was very rarely observed.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract:
In very rare cases, calcification of gallstones may occur during treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid.
When treating advanced stages of primary biliary cirrhosis, decompensation of liver cirrhosis was observed in very rare cases, which disappears after discontinuation of the drug.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
In very rare cases, urticaria may occur.
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse, or you notice other side effects not listed in the instructions, please inform your doctor.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
According to animal studies, ursodeoxycholic acid has no effect on fertility.
There are no data on the effects of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment on fertility in humans. There are limited or no data on the use of ursodeoxycholic acid in pregnant women. Animal studies have shown reproductive toxicity in early pregnancy. Ursofalk should not be used during pregnancy, unless clearly necessary. The use of the drug by women of childbearing potential is only possible if they use reliable methods of contraception. It is recommended to use non-hormonal contraceptives or oral contraceptives with low estrogen content. However, patients taking Ursofalk to dissolve gallstones should use effective non-hormonal contraceptives, as hormonal oral contraceptives may increase the formation of gallstones. The possibility of pregnancy should be excluded before starting treatment.
Based on several documented case reports, the level of ursodeoxycholic acid in breast milk in women is very low and therefore adverse reactions are not expected in breastfed infants.
Interaction
Cholestyramine, colestipol and antacids containing aluminum hydroxide or smectite (aluminum oxide) reduce the absorption of ursodeoxycholic acid in the intestine and thus reduce its absorption and effectiveness.
If the use of drugs containing at least one of these substances is still necessary, they should be taken at least 2 hours before taking Ursofalk. Ursodeoxycholic acid may interfere with the absorption of cyclosporine from the intestine. Therefore, in patients taking cyclosporine, the physician should check the concentration of cyclosporine in the blood and adjust the dose of cyclosporine if necessary.
In some cases, Ursofalk may reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin.
In a clinical study in healthy volunteers, co-administration of ursodeoxycholic acid (500 mg/day) and rosuvastatin (20 mg/day) resulted in a slight increase in plasma rosuvastatin levels. The clinical significance of this interaction, including with other statins, is unknown.
In healthy volunteers, ursodeoxycholic acid has been shown to reduce peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of the slow calcium channel blocker nitrendipine. In case of concomitant use of nitrendipine and ursodeoxycholic acid, careful monitoring is recommended. The dose of nitrendipine may need to be increased. There are also reports of interactions with dapsone, which led to a decrease in the therapeutic effect of the latter. These observations, along with data from in vitro experiments, suggest that ursodeoxycholic acid is capable of inducing enzymes of the cytochrome P450 3A system. However, in a designed interaction study with budesonide, which is a known substrate of cytochrome P450 3A, no induction was noted. Estrogen hormones and blood cholesterol-lowering drugs such as clofibrate increase cholesterol secretion in the liver and therefore may stimulate the formation of gallstones, which counteracts the effect of ursodeoxycholic acid, which is used to dissolve gallstones.
Overdose
In case of overdose, diarrhea is possible. As a rule, other symptoms of overdose are unlikely, since as the dose increases, the absorption of ursodeoxycholic acid decreases and, accordingly, more of it is excreted in the feces. There is no need to use specific measures in case of overdose. Treatment of the consequences of diarrhea is symptomatic, aimed at replenishing fluid volume and restoring electrolyte balance.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Ursodeoxycholic acid does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and machines, or the effect is minimal.