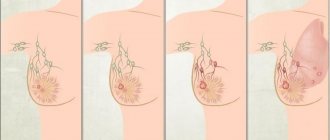
A breast cyst is a manifestation of fibrocystic disease (mastopathy), accompanied by hardening of gland tissue, dilation of the milk ducts and a disorder of hormonal metabolism.
A cyst is a cavity, usually filled with light-colored fluid. It is mainly formed from parts of the mammary gland or milk ducts. Due to excessive enlargement of the surrounding tissues, as well as the tissue of the ducts, stagnation of mammary gland secretion occurs in the dilated ducts. The volume of secretion increases over time and a breast cyst forms. This formation occurs very often, mainly in nulliparous women aged 35–55 years.
Basically, the cyst capsule includes benign cells, but there may also be malignant ones. The size of the cyst can be several millimeters and reach several centimeters. Cysts can be grouped or single.
With polycystic disease, numerous cysts of different sizes merge and form multi-chamber clusters. The cyst can cause pain as it grows and compresses the surrounding breast tissue, where nerve fibers may be located. In addition, there are fatty cysts that form when the sebaceous glands are blocked and can appear in any part of the breast. Such formations are safe, but with inflammation they can greatly increase.
Cystic formations can have an oval, round, irregular shape. A typical cyst has even and smooth internal walls, while the atypical type is characterized by growths on the walls and protruding into the cystic cavity.
What is a breast cyst
Cysts are benign, fluid-filled sacs that develop in the breast. They can be single or multiple. Cysts are usually round with regular edges and resemble a water balloon in appearance.
These types of growths are usually benign and do not require any special treatment until they become painful. In this case, there is a need for aspiration (surgical removal). Excision is also performed in that case. If the tumor increases in size.
Cysts are symptoms of nodular mastopathy. They are formed due to the expansion of one of the ducts of the mammary gland; first, a capsule is formed from the connective tissue, limiting the cavity, and then non-inflammatory fluid accumulates in the cavity. The shape of the formations can be round, oval or irregular.
The size of the cyst ranges from a few millimeters to 3-5 centimeters. The practice of mammology confirms that formations that are especially large in diameter can lead to deformation and change in the shape of the breast or to a complete replacement of its tissue itself.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Needle biopsy (without the cost of histological examination) | 2 500 |
| Ultrasound of the mammary glands | 3 000 |
| Mammography | 3 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
How to identify a cyst in the mammary gland: symptoms
Clinical signs depend on the location and size of the formation, as well as on the emotional state of the patient. The breast has a smooth, round lump that moves easily and has clear edges.
Small cysts usually do not cause discomfort. Often they can only be detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
If the cyst grows to a significant size or compresses the ducts and nerve endings, then the woman may experience the following complaints:
- aching pain in the area of education;
- breast irregularities and changes in its shape;
- the skin in this area may turn red and even blue;
- upon palpation of the chest, it is defined as a smooth round formation, painless and not welded to the surrounding tissues;
- may rarely be accompanied by nipple discharge;
- with inflammation and suppuration, many other symptoms are associated.
Pain syndrome has a relationship with cyclic changes. When
lumps in the chest, you need to visit a doctor for a comprehensive examination.
Surgical removal of cysts
When cysts grow and the pills are no longer effective, surgical intervention becomes necessary. There are several methods for removing tumors:
- Puncture - performed in cases where the cyst consists of vesicles connected to each other by connective tissue and filled with liquid inside. During the manipulation, the cyst is punctured and all the secretion is removed from it.
- Laser removal is a modern and safe, but not a cheap method. Excision of a cyst with a laser is carried out quickly and painlessly, without scarring. LED exposure destroys only atypical cells. Over the next two months, they are completely replaced by healthy glandular cells.
- Surgical intervention is necessary for large cysts or high-density neoplasms. The operation is carried out with high precision; upon completion, the tissue at the incision site is stitched together in layers. A sick leave after surgery is issued by the doctor for the entire recovery period.
What types of cysts are there in the mammary glands?
Depending on the number of cysts, a single formation (single cyst) and multiple formations (polycystic mammary glands) are distinguished. Also, depending on the number of cavities, the cyst can be single-chamber or multi-chamber. If the capsule of the cyst has growths from the inside, then they speak of an atypical cyst.
There are two types of cysts based on size:
- Microcysts
. Quite small formations that cannot be detected by palpation. They can be visualized using ultrasound and mammography. - Macrokists
. Determined by palpation. The size varies from 2.5 to 5 cm. Large formations compress the nerve endings in the chest, causing discomfort and pain.
Depending on the type of breast cyst, there are:
- Simple
. They consist of a single (solitary) formation, which is an elastic neoplasm of a round shape. The nodes most often contain a fibrous component. - Complex
. The formation consists of simple cysts fused together. May contain fibrous tissue growths. These also include atypical cysts.
Types of neoplasms
Breast cysts can be atypical, fibrous, fatty, solitary, multi-chamber, ductal, developing against the background of diffuse mastopathy - let's look at their features and symptoms.
Atypical
They grow inside the cavity due to their lack of walls, form in an enlarged duct, can become inflamed, and are prone to relapses. There may be papillomomatous neoplasms in the cavity, both benign and malignant.
Fibrous
Their distinctive feature is the proliferation of connective (fibrous) tissue, leading to the formation of cavities that accumulate fluid. Over time, this fluid comes out of the nipples. These neoplasms create the background for the occurrence of cancer.
Fatty
The reason for its appearance is blockage of the sebaceous gland in the skin and overflow with secretion (milk). A benign formation has smooth walls and appears during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Solitary
They may contain liquid of different colors and are benign. They form only in one breast and resemble a dense capsule.
Multi-chamber
Small breast cysts that eventually merge into one.
Ductal
They appear after 50 years and are benign in nature, but in medicine they are considered a precancerous condition.
Against the background of diffuse mastopathy
Diffuse mastopathy is characterized by a change in the structure of the breast tissue, in which the correct ratio of connective tissue and epithelial structures is disrupted. With diffuse changes in tissues, connective tissue structures grow unevenly, forming cords and nodules. This leads to the fact that the structure of the breast lobules and its ducts is disrupted, and very small cysts appear. Under certain conditions, this form of the disease can develop into nodular mastopathy, which is a risk factor for cancer.
Reasons for development
In most cases, a cyst develops under the influence of hormonal changes in the body, for example, during pregnancy or prolonged fasting.
The neoplasm appears against the background of the following factors:
- metabolic disorders in the body (diabetes mellitus, etc.);
- psycho-emotional shocks (stress, depression, etc.);
- long absence of sexual intercourse;
- birth of a child at the age of 30-35 years;
- diseases of the female reproductive system (adnexitis, endometritis, etc.);
- breast injuries and wearing uncomfortable underwear;
- inflammatory processes in the breast (mastitis, etc.).
If a woman has already been diagnosed with cysts, for example in the paranasal sinuses, gallbladder, this is not a predisposing factor for the development of cysts in the breast. This is due to various reasons for the appearance of neoplasms.
Kinds
There are the following types of breast cysts:
- Shape: oval, round, irregular;
- By size – small, medium and large;
- By quantity – single or multiple;
- By the number of cameras - single-chamber or multi-chamber;
- Based on the presence of signs of inflammation - cysts with or without inflammation.
Typical cysts have smooth internal walls, while atypical cysts have growths on the walls. There is an atypical, fibrous, ductal, solitary, multilocular cyst of the mammary glands. If a complex breast cyst contains pinpoint tissue inclusions, doctors conduct in-depth diagnostics.
Atypical breast cyst
An atypical breast cyst is an accumulation of fluid in the cavity, which was formed when the gland duct expanded. It is round or oval in shape, can be of different sizes, and has a fibrous capsule. An atypical cyst is a benign neoplasm with growths that protrude into the cavity.
- An atypical cyst is formed for the following reasons:
- Long period of existence of cystic formation;
- Often recurrent breast cysts:
- Inflammatory processes that occur in the cyst;
- The presence of papillomatous formations in the cystic cavity.
If the cavity of an atypical cyst is small, it does not pose a problem for the patient and does not reveal its presence for a long time. After the cavity enlarges, the first signs of pathology appear - nagging pain in the mammary glands, which intensifies during menstruation.
Fibrous cyst of the breast
Fibrous cyst of the mammary gland occupies a central place in mammology and is a background disease in the development of breast cancer. There are non-proliferative and proliferative forms of fibrous cyst. Fibrous cysts of the mammary glands develop under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Weakened immunity;
- Disorders of internal organs (liver, thyroid gland).
The disease manifests itself with characteristic symptoms:
- Increased pain on the eve of menstruation;
- The presence of cluster-shaped nodular seals in the mammary gland;
- Discharge of fluid from the nipples.
A fibrous cyst with dense mammary contents is predominantly expelled by papillomas.
Solitary cyst of the mammary gland
A solitary cyst of the mammary gland is a benign dysplasia that does not degenerate into a malignant tumor. The neoplasm has a round shape and elastic consistency. It is a cavity filled with liquid of various colors and surrounded by a capsule. Brown fluid in a breast cyst may be evidence of atypia or vascular microtrauma.
The following reasons for the development of a solitary cyst are distinguished:
- Burdened heredity;
- Neuroendocrine disorders;
- Multiple abortions;
- Age after 35 years;
- Overweight;
- Late birth.
The cause of the disease can be stress, nervous strain, early puberty, complete refusal of breastfeeding, mastitis and trauma to the mammary gland.
A solitary cyst is manifested by pulling, pressing or aching pain in the mammary gland, which intensifies in the second phase of the menstrual cycle. The pain may radiate to the shoulder blade, neck or shoulder. At the end of menstruation, the pain stops.
Ductal cysts of the mammary glands develop at any age, but are most often detected after 48 years. This disease is diagnosed in 1% of cases among all breast tumors. Ductal cysts are small growths inside the breast. This is a benign tumor that is a precancerous condition. The risk of developing a malignant breast tumor against this background is high.
Ductal cysts develop under the influence of the following provoking factors:
- Hormonal disorders;
- Ovarian dysfunction;
- Abortion;
- Inflammation of the uterine appendages;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine diseases.
Clinically, this pathology is manifested by discharge from the nipples of a clear, brown, bloody or greenish fluid. A ductal cyst can be palpated if it is present in the area of the milk ducts. It is palpated as a dense, painless formation. The disease is most often discovered by chance, during a routine examination.
Multilocular breast cyst
A multi-chamber cyst develops with an unhealthy lifestyle, alcohol abuse, nicotine and drug use, and poor diet. The cause of the disease may be poor nutrition, metabolic disorders, stress, anxiety, and hormonal imbalances.
A multi-chamber cyst of the mammary glands is a dangerous disease that can develop into a malignant tumor. When felt, cysts resemble soft balloons, but sometimes they are hard. May be round, oval or irregular in shape.
Complications of breast cysts
Common problems associated with breast cysts include inflammation and suppuration. If treatment measures are not taken in time, this can lead to the development of cavities filled with pus. Both a small cyst and a large formation can fester.
Most often, complications develop when a woman wears tight underwear or has intense breast massage.
NB!
The danger of such breast cysts is the possibility of their transformation into cancer. This happens in 1-3% of cases. A cyst, large or small, should be under the supervision of a specialist. To find out about its presence, it is enough to undergo routine examinations on time, and when confirming the diagnosis, follow the recommendations of your doctor.
Rules for disease prevention
- Annual visit to a mammologist, regular mammography or ultrasound of the mammary glands.
- Regular self-examination.
- Taking care of the mammary gland.
- Take COCs only as prescribed and under the supervision of a physician.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Selecting and wearing the right bra.
CELT clinic specialists will help you choose the appropriate treatment and maintain your health. The latest equipment, advanced techniques, professional doctors - CELT offers complete patient support, from diagnosis to recovery.
Diagnosis of breast cyst
As soon as a breast tumor is detected, the attending physician will immediately prescribe screening tests. The specialist will also ask about the duration of the pain and perform a physical examination.
Mammography
A screening x-ray method that is widely used to examine patients aged 40 years and older. The diagnostic procedure is based on the ability of adipose tissue to transmit x-rays to varying degrees. By obtaining different images on a mammogram, the doctor can visualize the problem to make a diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment.
Ultrasonography
An ultrasound is performed to find out whether the cyst is filled with fluid or is a solid growth. Depending on the type of non-cancerous growth, a biopsy may be performed to rule out cancer.
Fine needle aspiration is by far the most preferred test for cyst confirmation. During this procedure, a needle is inserted into the cyst cavity, the fluid is aspirated under local anesthesia and sent to the laboratory for analysis.
This study completely confirms the diagnosis. If the clear fluid is aspirated and the lump disappears, no treatment or further testing is required.
What you need to tell at an appointment with an oncologist-mammologist
At the appointment, the specialist makes a first assessment of the patient’s condition, based on the collected anamnesis and medical history. It is for this reason that you need to inform your doctor about your symptoms and their relationship with the menstrual cycle.
At the appointment, the mammologist should tell you about the presence of:
- symptoms that caused you to visit the clinic;
- the stresses, experiences and changes that have occurred in life;
- drug and vitamin therapy, use of dietary supplements.
You should prepare in advance a list of questions that will be asked to the specialist. First of all, you should ask about the risk of malignant degeneration and the examinations that need to be completed. It is also recommended to clarify the principle of treatment and inquire about the availability of additional individual recommendations.
Vacuum breast biopsy
Vacuum biopsy of the breast is performed for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, depending on the nature of the tumor. If there is a risk of developing malignant tumors or cysts, the procedure is performed to take tissue samples from the breast.
Vacuum biopsy is less traumatic than traditional surgery. The procedure can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the patient’s condition and the nature of the formation in the female breast.
The procedure is carried out as follows:
- The patient sits on the couch, the mammary gland is treated with an antiseptic solution;
- Under ultrasound guidance, a puncture is made using a special biopsy needle in the area of the mammary gland where the cystic formation is located;
- With the help of a vacuum, the necessary tissues are suctioned, and a special blade excises them from the mammary gland.
This method is not used in the presence of a malignant neoplasm confirmed before surgery.
Treatment of breast cyst
If the cyst is very small and only visible on x-rays, no treatment is required. In this case, a wait-and-see approach is recommended. This is especially true if the woman has not reached menopause. The most preferred treatment for breast cysts is aspiration.
If the cyst is quite large and needle aspiration does not resolve it, surgical excision is recommended. Cysts are quite common and tend to recur frequently and may require further intervention.
Drug therapy
Regulating your menstrual cycle can help reduce relapses. This can be done with the help of hormones, but the treatment must be under the strict supervision of a gynecologist, as there are many side effects and complications associated with the use of hormonal medications.
Hormonal therapy is carried out using oral contraceptives (birth control pills). Aimed at restoring menstrual cycles and reducing the likelihood of relapse. Hormones are prescribed only in the presence of severe symptoms, which is associated with the risk of adverse reactions.
Iodine preparations and sedatives are also prescribed. For severe pain, your doctor may recommend taking diuretics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic intervention is necessary when medications do not give the desired result. The doctor prescribes procedures that increase the effectiveness of medications.
Physiotherapy has an analgesic, absorbable and anti-inflammatory effect. A good result is observed after electrophoresis and magnetic therapy.
Surgical intervention
The decision about surgery is made by the doctor, who is based on the patient’s well-being. Painless small cysts (up to 1 cm) are left for dynamic observation. But for most women, neoplasms themselves cause psychological discomfort. In this case, the issue of removing the tumor is also resolved.
Removal is necessary for recurrent formations and in the presence of discharge from the nipple. Surgical intervention is not necessary if the cyst contains bloody fluid or the tumor tends to grow.
Cyst removal is carried out in various ways:
- Puncture and removal of contents
. This operation to remove a formation in the mammary gland is quite safe, but often causes relapses, because its walls remain and the process is repeated after some time. It is performed using fine needle aspiration under the control of an ultrasound probe. - Laparoscopy
. Allows you to remove the formation and maintain an aesthetically attractive breast without rough postoperative scars. - Sectoral resection and mastectomy
. Removal of part or all of the mammary gland is rarely performed, in advanced cases, with its gigantic size or abscesses that cannot be treated conservatively.
Many online sources offer recipes for treating cysts with medicinal herbs and infusions that contain phytoestrogens and affect hormonal balance. Such therapy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. Otherwise, the patient's condition will only worsen.
Over-the-counter pain relievers and NSAIDs (such as ibuprofen) can be used to reduce pain and discomfort due to breast cysts.
Non-drug treatment of cysts
Physiotherapy
A breast cyst can be treated with physical therapy, but such a program should be approached with great caution. The main condition is the absence of malignant neoplasms, pain and swelling.
For treatment, two methods can be used:
- Electrophoresis - used in low doses and under the strict supervision of the attending physician. During the procedures, medications are applied to the skin, which, under the influence of weak electrical impulses, are absorbed into the parenchyma of the gland. In 10-15 sessions, swelling and inflammation are relieved, immunity is increased, and with full conservative therapy, cysts resolve.
- Radon baths - before using these procedures, a woman should definitely visit a doctor; if there is a risk of tumor formation, treatment is excluded. In other cases, such physiotherapy will be beneficial - it will relieve pastiness, activate blood flow, and create conditions for the resorption of compactions.
Other physical procedures are strictly prohibited. If necessary, they can be replaced with therapeutic exercises.
Exercise therapy
If the disease is in remission, physical therapy can be included in the program. Exercises should be light and not overload a weakened body.
There are two types of exercises you can do at home:
- Wall push-ups are done measuredly and accurately, with a straight back and straight legs. It is optimal to do 2-3 approaches 5-8 times.
- Raising arms fastened into a lock - perform with moderate effort for 1-3 minutes.
These exercises are aimed at training the pectoral muscles and activating blood circulation.
Prevention
Proper prevention implies timely detection and treatment of diseases of the female genital organs, digestive and nervous systems, and metabolic and endocrine disorders. It is recommended to take measures to prevent the development of metabolic syndrome (limit fatty and sweet foods, increase physical activity). It is necessary to exclude abortions and extend breastfeeding to at least 6 months.
The following measures can help prevent breast lumps:
- Wearing a bra that provides good breast support.
- Conducting a self-examination.
- Regular examinations by a mammologist - once a year.
Reducing caffeine intake is important in reducing cyst symptoms. Salt restriction has also been shown to be effective in relieving symptoms of the disease.
Question answer
Question: Can a cyst in the mammary gland resolve on its own/disappear?
In very rare cases, the cyst goes away on its own, so you should not let the disease take its course. Even small formations do not resolve on their own, but they can be treated conservatively. If the cyst reaches 1.5 cm, a puncture is made to take out the contents and introduce air into the cavity.
Any traditional methods of treatment (herbs, compresses), in the hope that the formation will resolve itself, are unacceptable. Only an experienced mammologist can prescribe effective treatment, carefully monitoring the dynamics of cysts. It is unacceptable to carry out drug therapy without confirming the diagnosis. Experimenting with health in the hope that the lump will resolve on its own is unacceptable.
Question: Can a cyst in the mammary gland hurt?
The causes of severe discomfort are often not in the cyst itself, but in swelling or plethora, which are characteristic of hormonal changes. If pain occurs in the projection of the cyst, then this indicates inflammation or tension. A puncture will bring relief.
Question: Can a cyst in the mammary gland burst?
In medical practice, cases of spontaneous opening and disappearance of a tumor in the breast have been described. But this is extremely rare.
Question: Can a breast cyst become inflamed?
If treatment measures are not taken in time, suppuration will develop. This condition is accompanied by severe pain and fever. In this case, treatment is carried out by external drainage (opening) under general or local anesthesia.
Question: Can a breast cyst be malignant?
Only macrocysts can transform into a malignant cyst tumor. It all depends on the morphological properties of the neoplasm. The risk of malignancy ranges from 1 to 30%.
There are three degrees of histological severity of proliferation:
- I – absent, so the likelihood of degeneration into cancer is minimal.
- II – epithelial proliferation is present, but without the risk of atypia of cellular structures. The risk of malignant transformation is moderate.
- III – the proliferative process occurs in conjunction with cell atypia. The risk of malignant transformation is high.
Proliferating forms of breast cysts occur in 0.3-1.4% of cases. They are classified as precancerous conditions. With pronounced proliferation of the epithelium, the risk increases to 25-30%.
Question: Can a breast cyst get bigger?
Non-tumor neoplasms become larger before menstruation. During this period, there is also an increase in pain.
Question: Can a breast cyst shrink?
A decrease in cyst size is observed after menstruation every month.
Diagnostic methods
Mammologists at the Yusupov Hospital examine patients suspected of having a breast cyst according to the following algorithm:
- Clinical examination;
- X-ray mammography;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the mammary glands.
During examination, the doctor may see deformation of the breast if there is a large cyst. During palpation, a soft elastic formation with a smooth surface is determined, the walls of which are not fused with the surrounding tissues. The skin is not changed, peripheral lymph nodes are not enlarged.
Radiologists at the Yusupov Hospital perform mammograms in primary and secondary projections using expert-class digital devices, which provide high-quality images and provide minimal radiation exposure to the patient. In diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component, on radiographs against the background of a motley heterogeneous pattern, which is caused by the alternation of adipose tissue, connective tissue and glandular tissue, round, oval compactions or impressions from nearby cysts are visible. The sizes of cysts range from 0.3 to 6-8 cm. Their contours are clear, even, with a rim of clearing. If the cysts have several chambers, the contours are polycyclic and sharp.
On ultrasound, breast cysts have a picture of an anechoic, homogeneous liquid formation of a round or ovoid shape, with no reflection from the internal contents, lateral acoustic shadows and dorsal (towards the back) signal enhancement. When performing elastography, the cyst has triple mapping, layered blue, green, red palette.
If a mammogram or ultrasound reveals a cyst, doctors perform a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. This is a minor surgical procedure designed to obtain cellular material or part of the tissue of a pathological formation in the mammary gland for subsequent cytological or histological examination. Puncture of the mammary gland can be carried out for therapeutic purposes to remove the contents of the cyst or introduce a drug directly into the cystic cavity. After treatment, the breast cyst may resolve.
Trephine biopsy of the mammary gland is an innovative method that allows you to obtain samples of breast cyst tissue for further cytological and histological examination. The procedure is performed in cases where it is impossible to assess changes in breast tissue using mammography and ultrasound.
Trepanobiopsy of the breast is in most cases performed under local anesthesia. If there are contraindications, anesthesia is used. The patient lies on her back or side. Trepanobiopsy of the breast is performed using an automatic needle on a spring. A thin needle is placed in a special container and then inserted into the area where the cyst is located. She cuts off the tissue sample and stores it in a container. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes, then the patient remains lying on the couch for 5-10 minutes to avoid bleeding. If after a trephine biopsy there is swelling at the sampling site, redness, pain, or fever, the doctor will prescribe painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
conclusions
A breast cyst can be one or more fluid-filled cavities in the breast tissue. The contents may be pus or blood plasma. For a long time, the cyst may not give any symptoms, perhaps only a slight burning sensation and soreness in the mammary gland, which intensifies before the onset of menstruation.
The main cause of breast cysts is hormonal imbalances in the ratio of estrogen and progesterone. The cyst can become inflamed and inflamed, which is a dangerous and extremely unpleasant complication. Also, some types of tumors can develop into cancer. To exclude such an outcome, you should consult a doctor in time.
Sign up at the Medscan clinic to see a mammologist with extensive practical experience. The medical center is equipped with modern equipment, which allows you to make an accurate diagnosis in the shortest possible time.
Symptoms and complications
Small breast cysts are often discovered accidentally during an ultrasound examination. Large cystic formations can be palpated by a woman during self-examination. A breast cyst is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Painful sensations, a feeling of discomfort, burning and tingling in the chest shortly before menstruation;
- Chest pain during menstruation, which goes away at the end of menstruation;
- Discharge of various types from the nipple;
- The presence of a round or oval formation of soft elastic consistency with a smooth surface, which is not fused with the surrounding tissues.
Can cysts in the mammary glands resolve? Small cystic formations can undergo reverse development if you follow a diet, a healthy lifestyle and systematic use of medications. We should not forget that some cysts have a tendency to become malignant. For this reason, if a cystic formation is detected, you should not self-medicate or use “traditional medicine”. If you detect a lump in the mammary gland, contact the Yusupov Hospital.
Breast cysts are dangerous due to the following complications:
- Inflammation;
- Suppuration;
- Breast deformation;
- Degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
Inflammation of the cyst occurs in the event of excessive heat exposure to the breast, weakened immunity, injury to the mammary gland, or infection caused by sore throat, flu, and caries entering the breast tissue. Symptoms of inflammation of the cyst are expressed in increased body temperature, fever, chest pain, redness of the skin over the formation. With inadequate anti-inflammatory therapy or severe immunodeficiency, the cyst suppurates. Body temperature rises to 41-41°C, regional lymph nodes enlarge, and “softening” appears in the center of the cyst. During puncture, pus is visible in the syringe.
Large cysts can deform the mammary gland, which causes psychological discomfort in a woman. When it degenerates into a malignant neoplasm, the cyst becomes dense, the skin above it takes on the appearance of a “lemon peel”, and the nipple is retracted into the breast. It may ooze blood or brown fluid. In order to prevent this formidable complication, you do not need to wait until the breast cyst “resolves” on its own. At the first symptoms of the disease, make an appointment with mammologists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Literature
- Mumladze R.B., Dzukaeva N.T. New possibilities for treating patients with mammary gland cysts [Electronic resource] // Journal “Annals of Surgery”, 2015.
- Odintsov V.A., Dzidzaeva I.I., Bakhovadinova Sh.B. Modern ideas about risk factors for fibrocystic breast disease [Electronic resource] // Journal “Modern problems of science of education” - No. 5, 2022.
- Travina M.L., Popov A.G., Popov S.A. Cystic changes in the structure of the mammary gland in different age periods [Electronic resource] // Journal “Women’s Health” No. 1, 2022.
Treatment
Treatment of breast cysts is based on eliminating the hormonal imbalance that causes the development of the disease. A small cyst in the mammary gland does not require surgery. Conservative treatment consists of performing a fine-needle puncture under ultrasound guidance, pumping out the liquid contained in the capsule and administering substances that promote obliteration of the tumor. After treatment, the patient is regularly monitored by a mammologist. Conservative treatment methods are effective only in the presence of single-chamber cysts without signs of malignancy and intraductal papillomas.
If, after aspiration of the cyst and administration of ozone, relapses still occur, but no atypical cells are detected in the punctate, such formation is removed using vacuum aspiration.
If indicated, surgeons perform sectoral resection of the mammary gland. During surgery, the ducts of the mammary gland may be destroyed. This further negatively affects breastfeeding. Mammologists prefer endoscopic cyst removal. After the operation, the breast tissue is minimally injured, small, almost invisible incisions remain, and postoperative wounds heal quickly. To make an appointment with a mammologist, call the contact center of the Yusupov Hospital.