The solar plexus in humans is a collection of nerve endings that are located inside the abdominal cavity around the main arteries that feed the tissues of the internal organs. In medical terminology, this part of the human body is also found under the definition of “celiac or nerve plexus.”
The solar plexus in humans is a multiple number of nerve endings and nodal connections that are interconnected with the internal organs of the peritoneum. Concentrates a collection of nerve cells of several types.
The celiac plexus is located below the diaphragm, and its nerve endings, nodal connections and branches take part in the nervation of the smooth muscles of the blood vessels of the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, diaphragm, as well as the kidneys and adrenal cortex.
The nerve plexus originates near the superior and celiac arteries (mesenteric) and extends to the upper intestine. This part of the body is the most vulnerable place.
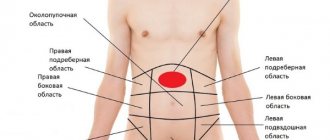
The location of the solar plexus in humans
A fall or other mechanical injury that causes injury to the nerve plexus can lead to prolonged and excruciating pain. In medical practice, there are periodically cases where a blow delivered to a given part of the body causes death.
Functions
Due to the fact that the plexus is an important center of the peripheral nervous system with localization in the abdominal cavity, its main functions are related to regulating the activity of tissues of internal organs.
The purpose of the celiac plexus is as follows:
- timely contraction and relaxation of the smooth muscles of the walls of large blood vessels that supply nutrition to the internal organs of the abdominal cavity;
- acts as an indicator of a pathological process developing in the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract, spleen, pancreas, kidneys and adrenal glands (development of the inflammatory process, ulcerative formations, benign and cancerous tumors, provoke acute or aching pain in various parts of the nerve plexus);
- with the help of peripheral nerve processes and endings localized in the solar plexus area, information about the state of the internal organs is collected, which in the form of neural impulses enters the centers of the brain;
- takes part in the reflex contraction of the muscles of the stomach and intestines during digestion and assimilation of consumed food;
- regulates local blood circulation in large main vessels located in the upper part of the peritoneum (mesenteric and celiac arteries).
Damage or compression effects on the branches of the nerve plexus can lead to temporary dysfunction of internal organs, as well as cause the development of painful shock.
Why else can the solar plexus hurt?
Let's look at less common causes of pain under the solar plexus:
- Intestines. When the duodenum or small intestine is inflamed, pain appears just below the solar plexus. If the pain is low, then perhaps the pathological process affects part of the large intestine.
- Wearing tight things. More often than not, women suffer from this when they choose narrow clothes. In this case, pain below the solar plexus will be associated with wearing certain clothes.
- Irritation of the nerve plexuses. Nerve plexuses are localized in the celiac region, irritation of which can be accompanied by pain. The provoking factor will be hard work or injury.
- Injuries. This nuisance awaits fans of ball games or people who are fond of contact sports. When practicing martial arts or boxing, men's solar plexus hurts due to frequent blows to this area.
Pain in the solar plexus can occur for various reasons. But if pain occurs frequently or painful discomfort does not go away for a long time, you should visit a doctor.
Structure
The solar plexus in humans is located just below the diaphragm.
This part of the body consists of the following structural elements:
- right-sided and left-sided celiac nodes;
- splanchnic nerve endings of small and large types;
- superior unpaired ganglion of the nerve plexuses (mesenteric);
The celiac plexus nodes contain multi-processed nerve endings that form branches with sensory synapses. Nerve endings extend from the above nodes in the form of multiple branches. Outwardly, they resemble the rays of the sun's disk. This is where the name of this organ of the peripheral nervous system comes from.
Video
An anatomy video tutorial will help you determine exactly where the solar plexus is located.
Solar plexus
Types of diseases
The solar plexus is located below the diaphragm in humans, and its nerve endings are interconnected with the tissues of the internal organs. Attacks of acute or aching pain in the solar plexus are felt if a person suffers from the following diseases.
| Type of disease | Clinical manifestations of pathology |
| Gastritis | Inflammatory damage to the gastric mucosa, which is expressed in the manifestation of nagging pain in the central part of the solar plexus. Depending on the factors that caused the pain, discomfort may increase or decrease. |
| Stomach ulcer | Severe pathology of the digestive organ, characterized by damage to the mucous and epithelial layer of the stomach walls. The disease is accompanied by acute pain in the center of the nerve plexus. Depending on the location of the ulcer, the discomfort may shift slightly to the right or left. |
| Cholelithiasis | This is a disease of the digestive system, which occurs due to the formation of foreign stones in the gallbladder. In the presence of this disease, a person experiences sharp and cutting pain on the right side of the solar plexus. Pathological symptoms intensify as the stone moves toward the bile ducts, or when its position changes. |
| Pancreatitis | A dangerous disease of the endocrine system, which is characterized by inflammation of the pancreas tissue, occurring in acute or chronic form. The development of the disease provokes acute cramping pain on the left side of the solar plexus. Depending on the stage of the disease and the extent of damage to the organ, the pain syndrome can be shooting and pulsating in nature. It is believed that this type of disease can cause the most severe and burning pain from the solar plexus. |
| Gastroduodenitis | This is a pathological condition of the intestinal mucosa, which is associated with its chronic or acute inflammation. The presence of this disease causes nagging pain at the bottom of the solar plexus. The unpleasant symptoms feel localized in the middle of the abdominal cavity with a slight shift to the left side. |
| Inflammation of the duodenal mucosa | The mucous membrane of this organ of the digestive system can be affected by an acute inflammatory process or ulcerative formations. In this case, the nerve plexus may experience acute or chronic pain in the central segment of the abdominal cavity. Pathological symptoms become even more intense after eating sour, pickled, salty, fried and rough foods. |
Nerve endings, nodal connections and multiple branches of the solar plexus can be destroyed by infectious, viral microorganisms, as well as mechanical injuries. In this case, neuralgia or nerve contusion develops, the functions of the internal organs, the tissues of which are connected to the damaged celiac plexus node, are disrupted.
Pathological processes in the stomach
Gastritis. The pain can be mild and quite tolerable, most often it is aching or pulling. If the source of inflammation is located at the bottom of the stomach, discomfort appears almost immediately after eating just below the sternum. Painful sensations can also be felt on an empty stomach if the affected area is located near the duodenum.
Peptic ulcer disease is distinguished from gastritis by stabbing and sharp pain, often occurring at night. The integrity of the tissues lining the inside of the stomach wall is compromised. Gastric juice gradually eats them away, resulting in the formation of an affected area - an ulcer.
If there are tumors in the stomach, they make themselves felt with pulling and pressing pain. Such manifestations bother a person for a long time, periodically subsiding and appearing again. Therefore, you should always pay attention to the diagnosis of stomach cancer in order to identify the problem in time.
Symptoms
The solar plexus is located in the upper abdomen in humans.
The main signs of a painful state of the organ are expressed in the following sensations:
- sharp, pulling, aching, spasmodic, throbbing or cutting pain, which is concentrated in the center, in the upper region, on the right or left of the abdominal cavity;
- severe lack of air and spasm of the lower respiratory tract (similar symptoms appear when falling from a great height or hitting the nerve plexus);
- complete or partial loss of appetite, aversion to food (this sign of a painful condition of the celiac plexus is associated with stomach dysfunction or a decrease in intestinal peristaltic activity);
- heartburn and acute pain in the stomach;
- increased gas production, intestinal bloating and involuntary removal of gases (this symptom may also be accompanied by cutting pain in the left hypochondrium, which indicates a disruption of the pancreas tissue and the possible development of chronic pancreatitis);
- disturbance of local blood circulation in the tissues of internal organs, which is caused by dysfunction of the muscles of large arterial vessels, innervation of which is carried out using the nerves of the celiac plexus;
- shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, feeling of chest compression;
- a decrease in the functional activity of one or several internal organs at once if damage has occurred to the processes of the nerve plexus connected to their tissues;
- nausea and vomiting (in most cases, this sign of the disease is accompanied by attacks of cramping or acute pain from the stomach);
- constant rumbling in the stomach, slow digestion of food, insufficiency of the pancreas and deficiency of digestive enzymes.
Symptoms of a painful condition of the nerve plexus are similar to the manifestations of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder and pancreas. This is due to the fact that disturbances in the functioning of the nerve endings of the celiac plexus lead to pathologies of the stomach, large and small intestines, as well as other abdominal organs.
Excessive exercise
Pain in the solar plexus area can occur during excessive physical activity. It is acute, usually stabbing or burning in nature. The sensations are quite intense, they force a person to stop and rest.
Such pain, which develops as a result of improper exercise and hard work, does not indicate any pathology. It’s enough just to rest, and for the future draw up a proper training program, without overworking yourself.
If excessive physical activity is repeated constantly, and is always accompanied by pain in the solar plexus area, then this can lead to a more serious condition - neuritis.
Causes of organ diseases
Nerve plexus pathologies can be caused by concomitant diseases of internal organs, or acquired as a result of the negative influence of negative factors.
The following causes of solar plexus diseases are identified:
- severe bacterial and viral infections that can penetrate the human nervous system, affecting its cells (such microorganisms include spirochete pallidum, meningococcus, herpes virus);
- alcohol abuse, smoking, taking drugs (synthetic drugs have a particularly destructive effect);
- mechanical injuries to the nodes and processes of nerve endings, which were received as a result of a fall from a great height, missed blows to the upper part of the abdominal cavity (the latter cause of the painful state of the organ is quite common among athletes who engage in strength sports and martial arts);
- lifting heavy objects, which led to tearing or stretching of the muscle fibers of the abdominal cavity, preserving the physiologically correct location of the internal organs and nerve plexuses;
- complications of surgical interventions that were performed on the tissues of internal organs, and arise as a result of postoperative inflammation, bacterial infection, and the development of adhesions;
- gastric ulcer, which is in the acute stage, the development of which is characterized by an increasing inflammatory process, pain and internal bleeding;
Peptic ulcer is the most common gastrointestinal disease - the last stage of pancreatitis, when the pancreatic tissue undergoes a process of necrosis and disintegrates
- hereditary diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system associated with inflammation or premature cell death (polyneuritis, neuritis).
The causes of the disease must be determined based on the results of a diagnostic examination. Symptomatic therapy without identifying the pathological factors causing the disease will lead to relapse of the disease and a repeat course of treatment.
Neuritis
Neuritis is an inflammatory process occurring in nerve fibers. This deviation is characterized by specific pain in the solar plexus area. The causes of the pathology are very diverse, ranging from an unhealthy lifestyle to previous intestinal pathologies and surgical interventions.
Solar plexus neuritis is characterized by:
- severe, sharp, drilling paroxysmal pain in the solar plexus area;
- feeling of heat, fullness and heaviness in the abdomen;
- an increase in pain intensity during physical activity.
The location of pain in solar plexus neuritis is the space between the navel and the sternum. In this case, you need to contact a neurologist for diagnostics.
Diagnostics
To determine the pathological state of the nerve endings, processes and nodes of the celiac plexus, differential diagnosis is carried out. This is necessary for timely determination of possible damage to peripheral nerves, as well as to exclude the factor of concomitant diseases of internal organs.
The examination process includes the following diagnostic measures:
- an initial examination by a general practitioner and a neurologist in order to promptly suspect pathologies of internal organs that may affect the functioning of the celiac plexus, as well as identify nerve pathologies;
- Ultrasound of internal organs that are in close proximity to the nodes and branches of the nerve plexus (stomach, gallbladder, pancreas);
- X-ray diagnostics of the abdominal cavity to detect foci of potential inflammation, foreign tumors that can cause compression and disrupt the functioning of peripheral nerves;
- palpation of the abdominal surface (performed by a specialized neurologist, surgeon or therapist);
- venous blood for biochemical analysis;
- capillary blood from the ring finger to determine its clinical parameters;
- morning urine, which is given on an empty stomach during the period from 07-00 to 10-00, and then examined in a laboratory for biochemical indicators.
If necessary, MRI diagnostics may be required to determine the health status of all abdominal organs, as well as brain centers.
The above types of examinations are carried out in a public hospital or in private medical centers. The most effective diagnostic method is abdominal MRI. The average cost of a comprehensive examination in a privately owned medical institution is 8,000-10,000 rubles.
When to see a doctor
The solar plexus is located inside the abdominal cavity in humans, and next to the nerve processes are the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, pancreas, and arterial vessels. A visit to a doctor should take place in the first 1-2 days after a person feels prolonged pain in the middle, on the left or on the right side of the abdomen.
Especially if the pain syndrome is acute, spasmodic or cutting in nature. First, you need to make an appointment with a therapist, and if a nerve plexus disease is confirmed, the specialist will refer the patient to a neurologist.
Characteristics of pain syndrome
The characteristics of pain depend on the type of pathological process, its duration, prevalence and cause of the disease. When making a diagnosis, specialists determine several characteristics:
By severity: strong, moderate or weak.
By nature: cutting, stabbing, sharp, dull, pulsating, burning.
By duration: acute (less than 6 weeks), subacute (6–12 weeks), chronic (more than 12 weeks).
By localization: in the middle of the epigastrium, in its upper part, lower, left or right.
Prevention
To avoid the painful state of the celiac plexus and prevent the development of pathologies of internal organs, the tissues of which are associated with the branches of nerve endings, it is recommended to follow the following rules of prevention:
- do not lift heavy objects;
- strengthen the muscles of the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity (pump up the press, do pull-ups on the horizontal bar, uneven bars);
- stop using alcoholic beverages, tobacco products and drugs;
- do not overeat, do not abuse fatty, pickled, sour, salty, spicy foods;
- avoid psycho-emotional stress and stressful situations that can disrupt the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous systems;
- when engaging in strength sports, use a bandage that holds the abdominal organs in an anatomically correct position, as well as special protection for the core.
Leading an active lifestyle, walking in the fresh air, and playing sports aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles minimize the risk of nerve plexus pathologies.
Treatment methods
Treatment of celiac plexus diseases is symptomatic and depends on the exact causes that provoked the disease. In medical practice, antibiotics, injections of B vitamins, and physiotherapeutic programs are used.
Medications
Antibacterial medications are used only if bacterial damage to the nerve branches and tissues of internal organs located in close proximity to the celiac plexus is diagnosed.
In this case, the following drugs can be used:
Oxacillin is an antibacterial drug of the penicillin series, which is prescribed 0.25-1 g by intramuscular or intravenous administration every 6 hours (the average duration of therapy is from 7 to 10 days, and the price of the medication is 180 rubles);- Ampicillin is a broad-spectrum antibacterial agent, administered into the body in the form of intramuscular injections of 250-500 mg 4 times a day (therapy period is 7-14 days, and the cost of the medicine is 21 rubles per 1 bottle for preparing injections);
- Vitamin 12 – is introduced into the body in the form of intramuscular injections with a single dosage of 400-500 mcg for 2 weeks (the cost of the drug is 45 rubles for 1 ampoule);
- Amoxicillin is an antibacterial drug that is available in capsule form, and its daily dosage is 750 mg - 3 g, which is divided into 3 doses (the recommended duration of treatment is at least 10 days, and the price of the medication is 190 rubles).
The prescription of antibacterial drugs should be carried out only by the attending physician on the basis of laboratory tests and determination of the strain of the bacterial pathogen.
Traditional methods
Treatment of a painful condition of the solar plexus using traditional medicine is not effective and is not practiced, as it can lead to aggravation of the pathology.
Other methods
In combination with treatment with medications, the following physiotherapeutic methods are used aimed at restoring the functions of the nerve plexus:
- massage of the anterior abdominal wall;
- drinking still mineral water (200 ml daily);
- heating using electrophoresis;
- applications with mud with a high content of hydrogen sulfide;
- mineral baths.
Some of the above procedures can be performed independently at home, and some of them require visiting a physiotherapy office or special medical centers.
Possible complications
Lack of treatment for diseases that cause pathological conditions of the solar plexus can lead to the development of the following complications:
- inflammation of nerve endings;
- loss of sensation in a part of the body in the abdominal area;
- intercostal neuralgia;
- digestive dysfunction;
- stomach cramps and uncontrollable bouts of vomiting;
- periodic shortness of breath and lack of air.
The solar plexus is a complex organ that in humans consists of a collection of nerve endings, nodes and processes. All of them are connected to the internal organs and muscles of the main blood vessels.
The nerve endings are located in the upper segment of the abdominal cavity and are responsible for the innervation of the tissues of the stomach, large and small intestines, duodenum, pancreas, gall bladder, superior and celiac mesenteric arteries. Damage to the nerve plexus causes temporary dysfunction of these organs and also causes unbearable pain.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Pain radiating to the back
With inflammation of the solar plexus nodes, the disease progresses and is prone to periodic relapses. Moreover, the pain has different characteristics each time. It can encircle, radiating to the back. Sometimes the pain first affects the upper chest, depriving sleep and rest; then suddenly an attack occurs in the lower abdomen. The pathology center is difficult to find, but all disorders affect the digestive tract. The causes of the disease are emotional and physical overload, hypothermia, and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.