Definition
The epigastric region (also called epigastrium or epigastrium) is not a separate organ, but a zone located between the umbilical part and the xiphoid process of the sternum. On the right and left, the epigastric zone is limited by the so-called midclavicular lines.
The epigastrium corresponds to the projection of the stomach, which goes to the abdominal wall, located in the front of the human body.
If pain occurs in this area, the doctor may suspect damage to the stomach, pancreas, liver, intestines, appendix and other organs. Therefore, discomfort in the epigastric region is a condition that can develop against the background of various disorders.
Serious and life-threatening situations
Some diseases can lead to a serious threat to human life. The most dangerous pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract are appendicitis and gastric or intestinal ulcers. Appendicitis in the absence of surgical treatment leads to rupture of the appendix and infection in the abdominal cavity.
The ulcer may be complicated by bleeding. With prolonged progression, the risk of perforation (the appearance of a through hole in the intestines or stomach) increases significantly. When perforation occurs, secondary peritonitis develops. The mortality rate for perforated ulcers, even with timely treatment, is about 7%.
Structure
The epigastric region is a zone in which several organs are located. To describe the structure of this area in simple words, we can conditionally divide the abdominal region into 3 horizontal zones: hypogastric, epigastric and mesogastric.
Epigastric region
The central zone (epigastrium) can be easily determined by visually drawing a triangle on a person’s stomach. The top is located between the ribs, and the bottom of the triangle will pass along the navel line. It is this zone that is considered the epigastric region.
The epigastric region includes the stomach, duodenum, pancreas, part of the liver and gall bladder. In addition, the epigastric zone is the accumulation of the largest number of nerve endings.
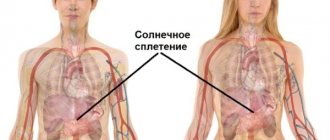
This is the solar plexus, which is located closer to the top of the triangle covering the epigastric region. Due to the fact that there are a large number of organs in this part of the peritoneum, the causes of abdominal pain can also be very different.
Colon diverticulosis
Diverticula are projections on the outside of the wall of the colon, commonly called “pockets.” The causes of colonic diverticulosis are not fully known. It is believed that the pathology may be associated with a congenital predisposition and constipation. Diverticulosis itself does not usually cause pain, but it can interfere with bowel movements, make bowel movements difficult, cause air to accumulate in the area, and cause bowel spasms, which can be painful.
Another cause associated with severe pain is inflammation of diverticulitis (diverticulosis). With inflammation, the pain is acute, severe discomfort, bloating, cramps, blood, mucus or pus in the stool may occur, and the temperature may rise. Antibiotics are usually prescribed and surgery is rarely required.
Types of diseases
One way or another, most of the internal organs are connected to the epigastric region.
Therefore, when pain occurs, various pathologies can be suspected:
- Stomach diseases. In this case, the person complains of severe pain in the peritoneum. Additionally, the patient may suffer from vomiting and nausea.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system. Pain sensations are concentrated in the solar plexus area. The pain may radiate to the right shoulder and reach the jaw.
- Acute form of pancreatitis. The pain resembles colic. A feeling of discomfort may appear in the left shoulder area. The person also experiences pain on the left side of the back.
- Diseases of the intestine (large or small). The pain is localized in the upper abdominal cavity. Patients complain of attacks of nausea and vomiting. Colic may occur. Similar symptoms are most often observed with duodenal ulcers.
- Gallbladder pathologies. The pain syndrome does not allow the patient to even sleep.
- Inflammation of the appendix. The pain is localized in the umbilical region. Gradually, the pain syndrome spreads to the entire abdominal cavity and begins to intensify. The stomach hurts especially badly when walking and when lying in a horizontal position on the right side.
- Kidney diseases. Characterized by sharp pain in the central part of the abdomen. Gradually the pain shifts to the lumbar and groin area. Patients may complain of problems urinating. Bloody impurities may be observed in the urine, and a kidney stone may pass out. Renal colic may be suspected. The pathology is characterized by sharp pain under the right rib.
- Lung diseases. The pain syndrome intensifies during breathing. There is a possibility that the patient has pneumonia. In this case, in addition to pain in the epigastric region, body temperature also rises and heart rate increases. Patients experience uneven shallow breathing. There may also be problems with the diaphragm. In this case, patients experience difficulty breathing when taking a deep breath. Similar symptoms are typical for diaphragmatic hernia.
- Liver diseases. In this case, the person suffers from sharp pain of a paroxysmal nature, which is localized under the right rib.
Causes of pain in the epigastric region
Among the pathological causes of pain in the epigastrium are:
- gastritis;
- ulcer;
- gastrointestinal obstruction;
- gurgle;
- esophageal stenosis;
- pancreatitis;
- appendicitis;
- cryptosporidiosis.
Various inflammatory diseases at the initial stage may manifest themselves as mild pain. The occurrence of deep damage to the gastric or intestinal mucosa leads to increased pain. The nature of the pain can determine the severity and danger of the disease.
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammatory disease of the gastric mucosa. Pathology occurs due to poor nutrition, increased or decreased gastric acidity, or infection by a bacterium called Helicobacter Pylori. To treat gastritis, it is necessary to eliminate all possible provoking factors and adjust the diet.
Symptoms include epigastric pain after eating, heartburn, fatigue, and nausea. Gastritis is considered the most common gastrointestinal disease. If a pathology of the digestive system is suspected, gastritis is diagnosed in 8 out of 10 cases. If left untreated, the disease becomes more complicated (erosions and ulcers occur).
Stomach ulcer
A stomach ulcer is a deep inflammatory lesion of the mucous membrane. Among the causes are:
- the presence of sluggish bacterial inflammation of the mucous membrane (gastritis);
- long-term use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- alcohol abuse;
- increased stomach acidity.
An ulcer is characterized by the occurrence of severe pain in the epigastrium 1-2 hours after eating. The pathology is also accompanied by sour vomiting, after which the pain becomes less noticeable.
Symptoms
The epigastric region is a zone of the human body where organs are located, the pathologies of which lead to discomfort in the abdominal region. In addition to pain, patients also complain of quite specific symptoms. For example, a person feels full too quickly even before the stomach is full. It doesn’t matter at all what kind of food a person eats.
If, in addition to pain and a feeling of satiety, signs of bloating appear, then the person may experience attacks of nausea and vomiting. It is worth paying attention to the appearance of a burning sensation and increased body temperature.
However, the most common symptom is pain directly in the pit of the stomach. Considering that in this zone there are a large number of organs, the diseases of which can be extremely dangerous, then if any alarming symptoms appear, it is worth visiting a doctor.
It is also worth paying attention to the nature of the pain, as this can tell you what pathology the person is suffering from.
| Symptoms | What pathologies are observed? |
| Dull or aching pain that is bothersome with equal intensity. | Gastritis |
| The so-called hunger pains that appear if a person goes to bed on an empty stomach. Symptoms may only appear at night. | Duodenal or stomach ulcer |
| Pain appears or intensifies mainly after eating. | Gastritis, stomach cancer |
| The pain is of a girdling type, and severe discomfort can radiate to the rib area and back.
| Pancreatitis |
| A dangerous syndrome in which a person may lose consciousness. Without an ambulance, there is a high probability of death. The syndrome is characterized by severe pain. The abdominal muscles become very tense, the pulse slows down, and the skin becomes pale. | Ulcer perforation |
| First there are severe abdominal pains. Then they suddenly go away, but the person’s skin turns very pale. There may be blood in the stool. Nausea and vomiting with blood are also observed. | Bleeding from an ulcer |
| The pain is localized on the right side of the ribs. The temperature rises and signs of jaundice appear. | Calculous cholecystitis |
| Malignant pathologies may not manifest themselves in any way. Some patients note weakness, a slight increase in body temperature, and sweating. Performance decreases. | Neoplasms |
It is also worth considering other features of diseases of the epigstral region.
It is important to consider at what time the pain syndrome appears and under what conditions.
For example, if the pain:
- If they last no more than 5 minutes and go away on their own, this indicates movement of the stomach muscles, or rather, they begin to tense very much.
- They last for more than 10 minutes, and there is no relationship with whether the person has eaten or not. Similar symptoms are observed in situations of panic or stress. It is not recommended to eat a lot of food in this situation. It is better to drink mint or other soothing tea.
- They appear immediately after eating and some time after food enters the esophagus. These symptoms are characterized by a decrease in sugar levels. Some people in this situation think that they are feeling hungry, but in fact the person needs to drink water.
- They are regular in nature, and discomfort mainly appears during the daytime, which can also suggest stress due to sleep disturbances. At the same time, patients complain that they cannot fully restore strength after work.
- Appear after eating fatty, hot, spicy foods. A similar reaction is observed when there are problems with the pancreas. A person suffers from heartburn and belching.
- Occurs 6-7 hours after eating. In this case, the pain syndrome gradually increases. Similar symptoms are typical for peptic ulcers and gastritis. It is necessary to conduct an examination of the stomach as soon as possible.
The epigastric region includes a variety of organs, so it is simply impossible to independently determine this or that pathology. This means that it is not enough to collect an anamnesis; you need to perform a set of tests and conduct the necessary research. Otherwise, there is a risk of serious exacerbation.
Causes of diseases
If we talk about the reasons that can provoke pain in the epigastric region, then it all depends on the specific organ. For example, if the cause of pain is lung disease, then pain in the epigastric region is explained by the fact that the epigastric zone passes directly under the lungs. Therefore, discomfort may appear with bronchitis, tuberculosis, pneumonia.
Only a doctor can help you find out exactly why discomfort and pain appeared in the epigastric region. First of all, it is necessary to visit a local therapist, who will refer the patient to the necessary specialists. Most often, people with pain in the abdominal area are referred to see a gastroenterologist. Additionally, consultation with a surgeon and cardiologist may be required.
Diagnostics
The epigastric region is a zone of the human body, pain syndromes in which may indicate pathologies of a very different nature. First of all, the therapist collects anamnesis.
It is imperative to inform your doctor about all chronic diseases in your relatives. For example, if there are people in the family with malignant tumors, then first of all the doctor will check the patient for the presence of tumors.
After this, the doctor conducts a finger examination. He palpates and alternately presses on different areas of the patient’s abdominal region. If the patient indicates pain in any place, the specialist may suggest one or another disease.
For example, if you press on the xiphoid process and the patient experiences pain, this most likely indicates cholecystitis. If the cause of pain is appendicitis, then the person experiences the greatest pain when pressing on the right iliac region.
Next, you need to donate blood and urine for tests, and conduct kidney tests. Such diagnostic measures will help to understand whether the patient is suffering from inflammatory processes.
It is also important to perform additional diagnostic measures:
- Determine the amount of pancreatic enzymes in the blood. Thanks to this study, pancreatitis can be ruled out.
- Ultrasound of the pancreas. Ultrasound examination allows you to determine exactly where the inflammation is localized.
- Ultrasound of the gallbladder. It is performed to identify stones that are necessary for the subsequent diagnosis of calculous cholecystitis. Also, an ultrasound examination will detect thickening of the walls, which is characteristic of the acalculous form of cholecystitis.
- Ultrasound of the liver. This test allows you to determine whether the organ is enlarged. Ultrasound examination can also detect cysts, helminthic infestations, inflammatory processes, bile stagnation and other pathological processes.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. Performed to detect possible tumors.
- X-ray of the abdominal cavity. The study is performed to determine whether there is an accumulation of free gas under the diaphragm dome. If it is present, then a perforated ulcer is diagnosed.
- FDGS. Used to diagnose gastritis, ulcers, tumors.
Additional research worth highlighting:
- ESR. This is a test that allows you to determine the rate and reaction of erythrocyte sedimentation. This is an inexpensive diagnostic procedure, thanks to which the presence and nature of inflammation is clarified.
- Endoscopy. Allows you to assess the condition of the stomach and esophagus. This testing also makes it possible to perform a biopsy. It allows you to confirm or deny the presence of a peptic ulcer or tumor.
- MRI and CT. Allows you to accurately determine the source of pain. Computer research is considered one of the most effective.
- ECG. This study is performed if pain in the epigastric region is not caused by gastrointestinal diseases. Similar testing is also used in diagnosing heart attacks. This study is mandatory only for patients over 45 years of age. For younger patients, ECG is recommended as a preventive measure.
If we talk about the cost of diagnostics, then the cheapest option is to go to the district clinic, where the tests will be carried out free of charge according to the health insurance policy.
However, some testing will have to wait. For example, there is usually a fairly long queue for computer examinations. If you need to complete all diagnostic tests faster, you can contact a private medical center. However, in this case, the cost of the entire set of studies may exceed 10,000 rubles.
Diagnosis of pain in the epigastric region
Epigastric pain is a non-unique symptom, the presence of which makes it impossible to make a diagnosis. An in-depth examination is required using the following methods:
- gastroscopy (FGDS) of the stomach and intestines;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- Ultrasound or CT scan of the abdominal cavity;
- analysis of stool and urine.
With the help of FGDS, it is possible to carefully examine the stomach and duodenum using an endoscope. A blood test gives a general idea of the condition of the body. If gastritis or peptic ulcer is detected, a breath test is additionally prescribed to determine the presence of Helicobacter bacteria.
To make an accurate diagnosis, it is important to use instrumental, hardware and laboratory diagnostic methods. If a person is admitted to the hospital with acute pain, differential diagnosis is used. First of all, the most dangerous pathologies are excluded.
Recommended video:
When to see a doctor
It is important to consider that abdominal discomfort can be caused by a variety of circumstances. For example, internal bleeding could occur. Therefore, any alarming symptoms should not be ignored, especially if we are talking about acute, girdling pain.
However, even indigestion can cause unpleasant consequences, so if you feel heaviness and bloating, heartburn, or feel full too quickly while eating, you should definitely visit a doctor.
Indigestion and flatulence can be signs indicating developing gastrointestinal pathologies, infections, and inflammatory processes. Therefore, if you have pain in the epigastric region, you need to visit a gastroenterologist, oncologist, traumatologist and surgeon.
Prevention
To prevent diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and other internal organs, you need to support the immune system and monitor your weight.
You should also follow the following recommendations:
- Stick to moderate physical activity. It is equally important to keep your body in good shape. To do this, you don’t need to go to the gym, just do exercises and exercise periodically. It is better to refrain from strength exercises, as they put a lot of stress on the cardiovascular system.
- Periodically undergo general examinations and visit a therapist to assess your health.
- Treat pathologies and colds in a timely manner.
- Do not eat a lot of fried, smoked, spicy foods.
- Spend more time outdoors.
Treatment methods
When symptoms appear in the epigastric region, it is important to make the correct diagnosis. Further treatment will depend on what specific pathology caused the discomfort.
Medications
If we talk about drugs that are aimed directly at relieving a person of pain and other symptoms in the epigastrium, then most often doctors prescribe:
- Mesalazine. The drug allows you to get rid of pain due to gastrointestinal diseases. The product is sold in the form of tablets that must be taken without chewing. The dosage and duration of treatment with the drug are prescribed depending on the specific diagnosis. For example, with ulcerative colitis in the acute stage, adults are usually recommended to take 4 g of the drug per day. The reception must be divided into several stages. For children, the dosage is selected at the rate of 20 mg per 1 kg of weight. The doctor can also develop maintenance therapy. The cost of the drug is about 600 rubles.
- Prednisol. This drug is necessary to stop inflammatory processes occurring in the stomach or outside the intestines. The duration of use and dosage of the product is determined only by a doctor. The fact is that the drug can be administered intravenously or intramuscularly. There are drip and jet methods of administration. The amount of active substance depends on the stage of the pathology. The product costs about 35 rubles.
- Metronidazole. This drug has a destructive effect on microorganisms that infect the human body. The drug is also able to prevent the development of inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract. For adult patients and children over 12 years of age, it is recommended to take 1.5 mg per kg of weight every 6 hours. Patients under 12 years of age should reduce the dosage and take the drug 3 times a day. However, the dosage may differ from the method of administration. For example, with the intravenous method, the initial dose should be about 15 mg per kg of patient weight. Gradually, the dosage and frequency of taking the drug is reduced. Metronidazole costs about 30 rubles.
Traditional methods
The epigastric region is an area in which inflammatory and other processes can develop. Treatment should be tailored to the specific diagnosis.
If the doctor approves of the use of traditional medicine, then there are several remedies that will help relieve pain:
- For gastritis with low acidity, it is recommended to brew watch leaves every day and drink them 4 times a day, a third of a glass.
- To prepare a general tonic, you can make a mixture of 2 parts flaxseeds and chamomile. You also need to add 1 part of licorice root and the same amount of lemon balm. After this, 1 tbsp. l. the resulting mixture must be filled with 1 tbsp. boiling water and heat on the stove for 5 minutes. The resulting product should be left for 2 hours (preferably in a thermos) and drunk 0.5 tbsp. every 3 hours. This remedy will help relieve stomach pain.
- For severe pain or stomach colic, it is recommended to make an infusion of chamomile herb. To prepare it, you need to pour 1 tbsp. l. dry mixture 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 20-30 minutes. This medicine should be taken 0.5 tbsp. 4-5 times a day. This infusion will help not only get rid of pain. Chamomile is also an excellent antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent. However, if symptoms persist, you should visit a doctor.
- Blueberries have a positive effect. You can also make a medicinal infusion from it. To do this you need to pour 1 tsp. fresh berries 1 tbsp. boiling water and infuse the medicinal composition for 3 hours. After this, add a small amount of sugar or honey to the liquid and drink 50 ml 6 times a day.
- If you experience aching pain in the stomach, it is recommended to prepare a remedy based on motherwort. The juice of this plant should be drunk 1 tsp. on an empty stomach before meals.
Other methods
If pain occurs in the epigastric region, a gentle diet can also help. This is especially necessary if the patient is taking medications. The exact menu is developed by the doctor.
But, there are some general recommendations:
- Eating should be even. You can’t eat a lot at night and fast during the day.
- You need to eat food in small portions. In this case, there should be more meals. The same amount of time should pass between them.
- Don't eat too cold or hot food. The same goes for drinks, and should be consumed warm.
- It is strictly forbidden to drink alcohol or smoke.
- You need to give up fried foods. You should not consume flour products, carbonated drinks, or fast food.
What medications can be used
Specific medications can be prescribed only after determining the type and nature of the disease. Among the classes of drugs that are most often used in the treatment of gastrointestinal pathologies are:
- gastroprotectors (accelerate the recovery of the affected gastric mucosa);
- antibiotics (prescribed when a bacterial infection is detected);
- food enzymes (prescribed for indigestion and inflammation of the pancreas);
- painkillers (used for severe discomfort at the initial stage of treatment);
- enterosorbents (used for intoxication and various poisonings);
- proton pump inhibitors (used for high acidity).
The dosage and duration of use of the drug is determined by the doctor. Before making a diagnosis, it is prohibited to use painkillers and antispasmodics, as this may complicate the diagnosis.
Possible complications
Any of the pathologies described in the article is dangerous due to its advanced stage. Therefore, it is important to carry out treatment in a timely manner. For example, if the patient’s condition progresses to an epigastric hernia, then tissue strangulation may occur.
Organs are at risk of ischemia and subsequent necrosis. The patient may develop peritonitis or even septic shock. These conditions are extremely dangerous and can be fatal.
Based on this, the epigastric region requires increased attention. If pain of a different nature occurs in this area, it is worth conducting a comprehensive examination. In case of timely detection of a particular pathology, the chance of restoring the normal functioning of the patient’s body increases.
Lower left quadrant
The organs in this quarter are the left kidney, part of the large and small intestine, and in women, the left ovary and fallopian tube.
Abdominal pain in this quarter can be a symptom of colitis, colonic diverticulosis or kidney stones, and in women can also be a sign of ovarian or pelvic inflammation.