Congestion in the ears, shooting pain in the ear canal, decreased hearing acuity may indicate a wide range of pathologies: from cerumen to infection.
The human ear is a complex organ responsible for the perception of sound. The complex anatomy of the ear allows it to detect sound vibrations over a wide range of frequencies. But it is the complex structure of the organ that leads to an increased risk of injury, infection, and congenital anomalies that cause an unpleasant symptom - ear pain. Later, other signs of the disease appear: from tissue swelling to partial deafness.
Why do my ears hurt?
Ear pain occurs for various external and internal reasons:
- ear injury. An accidental blow can damage the cartilage and external auditory canal. Sometimes pain occurs when there is strong pressure on the ear: for example, when wearing a tight hat or headphones;
- entry of a foreign object into the external auditory canal. Most often, this problem occurs in young children;
- damage to the lining of the external auditory canal. A careless attempt to remove accumulated wax from the ears can damage the thin skin of the external auditory canal. The scratch becomes inflamed and swollen, an unpleasant aching pain appears;
- ingress of water while swimming. One of the most common causes faced by both children and adults. To avoid getting water when immersed in water, it is recommended to use earplugs;
- exposure to loud noise. WHO estimates that about 1.1 billion people are at risk of hearing damage in entertainment settings due to music or noise that is too loud. This exposure is usually accompanied by minor ear pain. No less dangerous is constant exposure to noise pollution (for example, in some industries), which leads to the development of hearing loss, but is not accompanied by pain;
- accumulation of large amounts of earwax. A cerumen plug forms, which presses on the walls of the ear canal, causing pain.
Symptoms of ear diseases:
- painful sensations in the ear;
- deterioration or loss of hearing;
- feeling of ear fullness;
- pathological discharge from the ear;
- dizziness, balance disorder;
- noise in ears.
First aid
If an adult’s ear hurts, then at home you need to relieve the acute pain yourself. Regardless of the intensity of the pain, the patient must insert a cotton pad soaked in boric alcohol. The following tactics are:
- Take painkillers if the pain is unbearable. Paracetamol or ibuprofen will do.
- Topical corticosteroids are used in the nose to relieve swelling of the mucous membranes and normalize ventilation of the ear canals. The condition improves after 10-20 minutes.
- If the pain does not go away, you can put ear drops in each ear, regardless of which ear hurts. The product is first warmed up in the palms.
It is necessary to avoid drafts, not to go outside unless absolutely necessary, and to avoid contact with water when washing your hair. Important to remember! You cannot make compresses, instill ear drops with an antibacterial effect, or warm up the area of inflammation if there is any discharge from the ear.
Why does it shoot in my ear?
Acute shooting pain in the ear can be a symptom of infection; severe and severe pain is caused by diseases such as:
- mastoiditis – inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone, accompanied by the accumulation of pus;
- Otitis externa is an inflammation of the outer part of the ear, which includes the pinna, external auditory canal and eardrum;
- Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle section. Usually develops as a complication of other ENT infections: for example, tonsillitis or laryngitis;
- Labyrinthitis is an irritation of the inner ear caused by viruses or bacteria. In addition to severe pain, the patient may complain of dizziness and loss of balance.
Any pain in the ear indicates pathological processes occurring in it. Chronic infections and untreated injuries cause hearing loss. To get rid of pain and prevent the development of hearing loss, it is recommended to make an appointment with an otolaryngologist.
How to test your hearing? Types of diagnostics
In modern clinics, a hearing tester may offer several diagnostic procedures to determine the cause of ear pain. Let's look at the main ones.
Otoendoscopy of hearing. This type of examination is increasingly used in ENT practice. The examination is carried out using an innovative device. A device is placed in the auricle - a small diameter tube with a tip in the form of a mini video camera and a light bulb. The camera films the internal tissues of the ear, this image is displayed on a computer screen, the doctor can enlarge it, thus examining the hearing organs from the inside in detail. This method allows you to diagnose almost any pathology of the hearing organ and make the most accurate diagnosis.
The advantages of this procedure are that it is painless and has no serious contraindications. The only reason why otoendoscopy cannot be performed is if there is a serious injury to the ear accompanied by swelling and bleeding. More information about how the procedure is carried out and whether preliminary preparation is needed for it can be found in the article on the website: Otoendoscopy.
Tympanometry. this diagnosis in Moscow This is another modern procedure that allows you to identify pathologies of the middle ear. An apparatus is inserted into the auricle, which changes the pressure in the ear in a certain sequence. This change in pressure causes vibrations in the eardrum, which are recorded by the device. The resulting “picture” is called a tympanogram. It can be used to determine whether the eardrum has ruptured, whether there is fluid or pus in the ear, and a number of other pathologies that are important for the accuracy of the diagnosis. This procedure is indispensable for diagnosing otitis, injury to the eardrum, and inflammation of the auditory tube. get tympanometry done in Moscow in a few minutes at Lev Rudin’s clinic. The procedure is painless and has no serious contraindications.
Hearing audiogram. Ear pain usually causes hearing loss. will help determine the nature of pathological disorders . Audiometry in this case will be the most effective procedure. This type of diagnosis is carried out as follows: the patient is wearing headphones, through which multi-frequency sound signals are sent to the hearing organ. The strength of the incoming signals is recorded, resulting in a graphic image showing the patient’s hearing range. Only a hearing audiogram can determine this indicator . The price in Moscow depends on the clinic where the diagnostics will be carried out. The pricing policy of the Lev Rudin Clinic can be found on the official website in the services section: prices.
You can learn in detail about hearing problems and methods of diagnosing them in a special section: examination and treatment of the ear.
What to do if your ears hurt when you have a cold?
Aching pain in the ears can occur due to a cold. Due to the close proximity of the ENT organs, the infection spreads to neighboring areas: for example, a sore throat is often accompanied by a runny nose, and rhinitis leads to painful pressure in one or both ears. Why is this happening?
When you have a runny nose, your paranasal sinuses become inflamed and swollen. This interferes with the normal removal of fluid, mucus accumulates, and bacteria begin to actively multiply in it. Gradually, irritation affects the Eustachian tube, sensations of unpleasant itching and pressure on the ears appear, and pain occurs. To avoid this, during a cold it is necessary to use vasoconstrictor nasal drops: they restore normal ventilation in the sinuses and reduce the risk of inflammation of the Eustachian tube.
If you consult a doctor in time and follow the prescribed treatment, ear pain due to a cold will quickly go away. But if you have already recovered, and the discomfort in your hearing organs has not gone away, there is a risk of developing complications. In this case, you need to make an appointment with an ENT specialist as soon as possible.
Ear pain in a healthy person
Unpleasant sensations in the organ of hearing can occur in a completely healthy person, and there are many reasons for this (we will look at some in more detail):
- sensitivity to strong wind and cold (Due to a long stay in the wind, a hematoma may form in the ear - it will go away on its own in a few days. No additional measures need to be taken in this situation.);
- water getting into the ear;
- presence of sulfur plug;
- mechanical injuries (if, in addition to pain, bleeding from the ear begins, consult a doctor immediately);
- acoustic injuries (occur due to exposure to loud sounds on the organ of hearing, for example, at a rock concert, in a noisy industry, or during prolonged use of headphones. As a rule, the pain goes away when moving away from the source of noise. If, due to the nature of the work, it is impossible to eliminate the source of noise, You definitely need to use special earplugs.);
- barotrauma (manifested by changes in atmospheric pressure; most often occur during air travel or diving. When your ears are blocked on an airplane, you need to yawn more often, swallow, or simply chew something to eliminate the condition of “stuffiness”);
- foreign body.
What is otitis media and how does it manifest?
Ear pain is often caused by otitis media, an infectious inflammation of the hearing aid. Otolaryngologists distinguish three forms of the disease:
- otitis externa A disease of the outer ear in which a purulent boil forms in the ear canal. If the inflammation is not treated, it spreads to the eardrum, which causes not only pain, but also hearing impairment;
- Otitis media Develops when an infection enters the middle ear. Causes shooting pain and a feeling of pressure. The patient's temperature rises, pus or ichor may be discharged from the ear;
- internal otitis or labyrinthitis. Otitis media can spread to the inner ear and cause labyrinthitis. Symptoms of otitis media include severe headaches, loss of balance, and dizziness.
Otitis can be acute and chronic. In the acute stage, the disease is manifested by high fever (38.5℃), weakness, lethargy and apathy. Chronic otitis media leads to a gradual decrease in hearing; the pain may not be severe, but constant.
First aid for ear pain
Regardless of what caused the pain in the ear, to get rid of it you need to contact a specialist. Only a doctor can accurately determine the type of disease and prescribe comprehensive treatment. But what to do if ear pain takes you by surprise, for example, at night? For these cases, there are general recommendations that allow, if not completely relieve the pain syndrome, then at least partially reduce its manifestation.
You can use special ear drops that have an analgesic effect.
If there is no fever, a warming salt compress can help relieve pain. Warm salt should be wrapped in a piece of cloth and applied to the ear area. If the disease has just begun to manifest itself, such manipulation will help alleviate the condition.
Attention! It is contraindicated to heat the ear if purulent discharge is observed. This can provoke the development and proliferation of harmful microorganisms and worsen the condition.
Warming up is also dangerous if ear pain is caused by caries. This can cause swelling and spread of infection. For toothache that radiates discomfort into the ear, you can rinse with an iodine-saline solution. But you should understand that this is temporary help. Only a dentist can solve the problem.
Ear otitis - how to treat?
Treatment of otitis depends on the form and stage of the disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to contact an ENT specialist. The doctor will develop a treatment regimen taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Typically treatment for otitis media is as follows:
- taking antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs. Medicines fight the pathogen, relieve swelling and inflammation;
- Antipyretics are prescribed for high temperatures. Also, if necessary, the otolaryngologist can prescribe a course of antibiotics;
- removal of pus from the outer ear. To do this, cotton swabs (turundas) moistened with alcohol or other disinfectant are immersed in the ear canal. They collect pus and disinfect surrounding tissues.
After recovery, the ENT specialist may prescribe physiotherapy to restore local immunity (for example, UHF, drug electrophoresis). Untreated otitis media can lead to a ruptured eardrum. Therefore, if ear pain occurs, it is important not to self-medicate, but to seek medical help.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
To reduce otalgia, ear drops with local anesthetics or oral tablets with analgesics are used before visiting a doctor. Medicines can be used if the pain does not occur due to injury. The pathological process that affects the ear quickly involves the bones of the skull and the brain, so self-medication is unacceptable. A qualified ENT doctor should provide assistance to patients with otalgia.
Conservative therapy
Treatment involves the use of local or systemic medications, or a combination of both. For otitis, ear drops containing antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic substances are used, and the ear is toileted. To improve the outflow of exudate from the tympanic cavity, vasoconstrictors are instilled into the nose. To reduce pain in the first days (before the eardrum ruptures), heated 96% alcohol is dripped into the ear.
To eliminate the consequences of taking ototoxic drugs, ATP and galantamine are prescribed, which stimulate regeneration processes. Nootropics help improve the nutrition of the auditory analyzer structures. To influence the neurological causes of otalgia, sedatives, anticholinergics, metabolic and vasoactive drugs are recommended. Severe painful paroxysms require the use of anticonvulsants.
Physiotherapy methods are effective in practical otolaryngology. To stop the inflammatory process and stimulate local immunity, microwave therapy, laser therapy, and UHF are performed. To prevent hearing disorders during the recovery period, pneumomassage of the eardrum is performed. Reflexology and amplipulse therapy help eliminate paroxysms of neuralgia of the ear node.
Surgery
The tympanic cavity is cleared of pus during myringotomy, followed by washing the ear with antibacterial solutions. In case of chronic otitis and the absence of effect from conservative measures, anthrodrainage is performed in the mastoid area. Indications for surgical treatment are external cholesteatomas, exostoses, and abscesses.
To eliminate the consequences of middle ear trauma, reconstructive surgeries are prescribed: myringoplasty, tympanoplasty, mastoidoplasty. In case of damage to the inner ear, otosurgical interventions are performed to restore the integrity of the anatomical structures. In case of severe illnesses and injuries accompanied by hearing loss, the patient requires selection of a hearing aid or cochlear implantation.
How to distinguish otitis media from cerumen plug?
Ear pain does not always indicate the development of an infection. Perhaps the painful sensations are caused by sulfur plugs. In the outer ear there are special glands that produce earwax, a secretion that protects the organ from pathogenic bacteria. When the glands malfunction, the wax becomes too dense and begins to accumulate in the ear, which leads to the formation of a plug.
For a long time, the accumulation of sulfur does not cause any discomfort, but over time the plug becomes larger and larger and can completely block the lumen of the ear canal. As a result, a person experiences a feeling of fullness in the ears.
If the plug puts pressure on the eardrum, headaches and nausea may occur. But at the same time, the plug does not lead to an increase in body temperature and purulent discharge from the ear canal (as happens with purulent otitis media). The pain with a plug is moderate, not shooting, which also makes it possible to distinguish it from an infection.
Why the ear hurts: causes and diagnosis
Pain in the ear can be sharp and “shooting” or, conversely, muffled. Sometimes it hurts only on one side, and sometimes unpleasant sensations appear simultaneously in the left and right ears. Ear pain can occur not only with otitis media: in fact, it has many causes with similar symptoms, so a doctor must make a diagnosis.
If you have any discomfort in your ears, you can seek help from the MedEx Personal Medicine Clinic. A therapist will help you find the cause of your pain and create a treatment plan that will be effective in your case and fit into your lifestyle.
Diseases of the hearing organs that cause pain
The main reason why severe pain in the ears can occur is diseases of the hearing organs, injuries and other pathological conditions.
Acute pain can be felt by:
- Otitis externa is the mildest form of otitis, when the inflammation does not affect the eardrum and is localized in the external auditory canal. This type of otitis media develops when an infection is caused due to negligence (for example, when cleaning the ears).
- Otitis media, in which the middle ear and eardrum become inflamed. Most often, otitis occurs against the background of tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections, sinusitis and other diseases of the ENT organs, because bacteria from the nasopharynx can penetrate into the ear. In addition, fairly mild otitis externa can take on the form of otitis media if left untreated or without medical supervision.
- Labyrinthitis, or internal otitis, is a dangerous complication that can occur with untreated otitis media. The infection affects the inner ear and vestibular system, so in addition to pain, severe dizziness and nausea occur.
- A possible cause of ear pain in a child, and sometimes in an adult, is a foreign object lodged in the ear canal. You cannot remove such an object yourself, because you can damage the eardrum and injure the ear canal. In this case, you need to urgently consult a doctor.
- The presence of a plug of earwax in the ear canal is a painful and unpleasant phenomenon in which the accumulated wax presses on the eardrum. Trying to remove the plug yourself is not recommended: a doctor will do it much faster and safer. To prevent the formation of plugs, it is better to abandon cotton swabs, because if you try to clean the ear canal in this way, you risk “compacting” the earwax.
- Acoustic trauma is the stretching or even rupture of the eardrum from too loud a sound. Such an injury can occur at work, at a concert and in other situations.
- Barotrauma is damage to the hearing organs due to a sudden change in pressure, for example, during a flight. Additional signs of serious barotrauma, in addition to sharp pain, are ringing in the ears and dizziness. Some blood may leak from the ear canal.
- Mechanical damage to the ear - if you hit yourself or failed to clean the ear canal.
Other causes of ear pain
Sometimes the pain radiates to the ear, but its real source is located elsewhere and is not associated with the hearing organs.
This can happen, for example:
- For neuralgia of the trigeminal, facial or nasopharyngeal nerve;
- With sinusitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, the sinuses or tonsils become inflamed, and the pain radiates to the ears;
- For arthritis or injury to the jaw joint;
- With advanced caries or pulpitis of the outer teeth above or below, as well as with inflammation of the gums; referred toothache intensifies if the diseased tooth comes into contact with hot or cold food or if you deliberately press on it.
These conditions can be dangerous and also require consultation with a doctor, as do problems directly with the hearing organs.
However, sometimes the cause of congestion and pain in the ear can be quite harmless - for example, if water got into the ear canal while swimming. In this case, try actively chewing food or sucking on a lollipop: when swallowing and moving your jaw, the pressure in the ear canal returns to normal.
Associated symptoms
Sometimes ear pain in an adult or child is complicated by other unpleasant symptoms - be sure to tell the doctor about them at your appointment, this will help you quickly find the cause of the pain and begin treatment.
Diseases of the hearing organs can manifest themselves, in addition to acute pain:
- Feeling of ear fullness and partial dullness of hearing;
- Noise or buzzing in the ears;
- Discharge from the ear canal (wax or pus may be released depending on the type of disease);
- Itching in the ear, if we are talking about an infection of the external auditory canal;
- General malaise and weakness, as with colds and flu;
- Dizziness and nausea;
- Sensitivity and soreness in the area around the ears.
It is also important to inform your doctor about the nature of the pain: the sore ear may throb, shoot, or ache. Tell the specialist how the pain feels, how long ago it started – all this is important for making a diagnosis.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
Any discomfort in the ears may be a reason to contact a therapist - this is the case when it is better to play it safe and start treatment as early as possible, if necessary. There are also special “alarming” signals that are important to pay attention to in time.
It is recommended to make an urgent appointment with a doctor if:
- The pain in the ears is not dull, but “shooting” and quite strong;
- The first day has passed, but the pain does not get weaker and does not stop;
- Body temperature has increased - this indicates that there is inflammation in the body;
- At the same time as ear pain, you feel dizzy or have a headache;
- Swelling appeared around the ear;
- There was a feeling that fluid was rolling somewhere deep inside the ear: this is a sign of purulent inflammation;
- The pain was sharp, long-lasting, and suddenly went away instantly - such a sensation can accompany a rupture of the eardrum with purulent otitis media.
At your appointment, the doctor will explain in detail how and with what to treat a specific cause of ear pain at home, so that it is safe, effective and fits into your usual lifestyle. You may need drug therapy or consultation with a physiotherapist who provides treatment with ultrasonic waves, microcurrents and other methods using modern equipment.
Why self-medication is dangerous
Some home treatment methods may not only not help, but also seriously harm hearing diseases. For example, if there is suppuration in the ear canal, under no circumstances should you warm up the sore ear - this can lead to rupture of the eardrum and other complications.
It’s also not a good idea to prescribe ear drops yourself: you can get an allergic reaction and waste time on ineffective and inappropriate treatment. The only thing that can be done before talking to the doctor is to take an antihistamine (for allergies) and put vasoconstrictor drops into your nose. This is necessary to maintain normal pressure in the ear canal and alleviate the condition. And everything else should be prescribed by the doctor after the examination.
Is it dangerous to make compresses in your case, what medications to take - only a qualified physician with the examination results in hand can say for sure.
Another reason to definitely consult a doctor is that without proper treatment, otitis media can lead to dangerous complications, for example:
- Inflammation of the inner ear (labyrinthitis) and infection of the vestibular apparatus;
- Damage to the auditory nerve and, as a result, irreversible deafness;
- Rupture of the eardrum due to pus accumulated in the middle ear;
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes of the brain, because it is caused by the same bacteria (for example, pneumococci).
At the same time, it is difficult to distinguish otitis media from other diseases: it does not have any specific symptoms, except for a sharp shooting pain. And there can be many reasons for such pain in the left ear or on the right side.
It is very easy to make a mistake with a presumptive diagnosis and waste time, because it is impossible to examine the ear independently in front of a mirror from the inside, like the throat with a sore throat. And the pathology continues to develop every hour and can become more dangerous. Therefore, the best option is not to hesitate and immediately make an appointment with a doctor as soon as you notice pain.
Make an appointment with a doctor in Moscow for ear pain
Only a doctor can determine the causes of ear pain and prescribe proper treatment - hearing diseases cannot be left to chance. Therefore, at the first signs of discomfort in the ears, and even more so with a sharp, “shooting” pain, it is important to immediately consult a specialist.
At the MedEx Personal Medicine Clinic, diagnosis and treatment of ear pain is coordinated by a primary care physician. The doctor will examine you and listen carefully to you, comprehensively assess your health and take into account all your personal lifestyle characteristics so that the recommendations are as useful as possible.
We provide appointments every weekday without queues or stress: you just need to arrive at the clinic at the appointed time. To schedule a consultation and get help with ear pain, call us or use the online scheduling tools on the website.
Price
| Name of service | price, rub. |
| Primary appointment with a general practitioner (examination, consultation with a candidate of medical sciences) | 3500 rub. |
| Repeated appointment with a general practitioner (examination, consultation with a candidate of medical sciences) | 3000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the spleen | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the salivary glands | 1200 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pleural cavity | 1700 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the liver | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the hepatobiliary zone | 2400 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the gallbladder with determination of its contractility | 2000 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the pancreas | 1500 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs (comprehensive) | 2700 rub. |
| Ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys and adrenal glands | 3700 rub. |
| Ultrasound detection of fluid in the abdominal cavity | 1500 rub. |
All prices are inclusive of tax deduction.
Sign up
Contact our doctor
Make an appointment
Dzhgarkava Tea Gochaevna
Therapist-cardiologist
Experience: 5 years
Read more
Removing wax plug
Do not try to remove earwax yourself using a cotton swab. This way you will only push it deep into the ear canal, and it will begin to put pressure on the eardrum. Removal of wax plug is a procedure that can be performed in the otolaryngology department of the medical center. It looks like this:
- the patient is asked to tilt his head at a certain angle;
- the doctor inserts a Janet syringe (without a needle) into the ear;
- A heated solution is supplied under pressure, which washes the plug out of the ear.
The procedure is painless and effective.
How does a boil in the ear hurt?
Another cause of ear pain is the formation of a boil in the external auditory canal. It can appear when the skin is injured: for example, when cleaning wax from the ears carelessly. An infection penetrates into the scratch, inflammation begins and a purulent boil forms.
The pain is moderate at first, but becomes stronger as the boil grows. It often radiates to the jaw and neck, and worsens when chewing. In addition to pain, the patient may complain of itching and a feeling of fullness, as well as decreased hearing due to partial blockage of the ear canal.
Ear diseases in adults
Painful sensations can occur due to direct pathologies of the ear. These include: otitis media, eustachitis, tumors.
Otitis is an infectious inflammation of the ear, the leader among diseases of the ENT organs in terms of the number of visits to an otolaryngologist. The causes of the disease are untreated infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis), rhinitis, a deformed nasal septum, damage to the auricle, penetration of water into it or infections after self-cleaning the ear with foreign objects.
The human hearing organ consists of the outer, middle, and inner ear. Accordingly, external, middle and internal otitis are distinguished.
Otitis externa covers the ear canal. Basically, the disease develops when water penetrates into it while swimming. There is even the term “swimmer’s ear”: otitis media occurs with frequent contact with water. For treatment of ear pain caused by otitis externa, you should contact an otolaryngologist.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Otitis media: a third of all visits to an otolaryngologist are associated with this type of otitis. The main complaint of patients is shooting pain in the middle ear. The disease can occur in several forms: acute, exudative and chronic purulent.
Internal otitis (labyrinthitis) is an inflammatory disease of the inner ear. The disease is severe and occurs infrequently: usually as a complication of otitis media or a severe form of another infectious disease (for example, tuberculosis).
If you suspect inflammation, you should not self-medicate: incorrectly prescribed treatment for otitis media or an undertreated condition can cause serious complications. Only an otolaryngologist can provide effective assistance to an adult with otitis media.
Eustachitis is an inflammation of the Eustachian (auditory) tube, which connects the organ of hearing to the nasopharynx. The Eustachian tube is needed to better capture sounds and ventilate the middle ear through the nasopharynx. With the qualified help of an otolaryngologist, treatment of ear pain caused by eustachitis occurs quickly, and relief occurs in a couple of days.
Ear tumors are uncommon. CT and MRI are used to determine pathology.
Ear pain at night - what to do?
Due to the structural features of the hearing aid, ear pain intensifies when a person assumes a horizontal body position. Therefore, the pain often worsens at night during sleep. To reduce pain, you can:
- move your jaws (make chewing movements) - this allows you to equalize the pressure in the middle and inner ear and helps reduce pain;
- apply a cold compress - soak a towel in cool water and place it on the sore ear;
- Take your usual pain reliever.
Be sure to make an appointment with an ENT doctor. You cannot treat ear pain on your own, as this can aggravate the disease and lead to the development of hearing loss.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis and treatment of pathologies associated with this symptom is carried out by an ENT doctor (otorhinolaryngologist) or an audiologist (a narrower specialty in otorhinolaryngology). During the appointment, the specialist talks with the patient, examines him, conducts the necessary examination, and establishes a diagnosis.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced, highly qualified otolaryngologists. Rich clinical experience helps them make the correct diagnosis in the most difficult cases.
Ear pain - what to do at home
To cure the ear, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. This can only be done by an otolaryngologist after otoscopy and additional studies. The following remedies for self-relief of pain are unacceptable:
- warming up the ear, as inflammation intensifies and the infection worsens;
- use of ear drops. Some of them contain components that can damage the auditory nerve. Do not use any medications before consulting a doctor.
It is allowed to insert a thick turunda (cotton swab) moistened with 70% formic alcohol into the outer auditory cover. Alcohol disinfects the passage and also gently warms the surrounding tissues, which will reduce pain. Turunda should not be placed if the eardrum is damaged or if there are scratches in the external auditory canal.
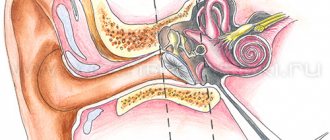
A little about the ear itself
To understand exactly what departments and problems we are talking about, you need to carefully study the structure of the ear. This is a rather complex organ, including three sections:
- Outer ear . This zone includes everything that can be seen without any additional devices. This is the concha and the visible ear canal.
- Middle ear . The invisible part, consisting of the tympanic cavity and the auditory ossicles. This section is protected by the temporal bone.
- Inner ear . The most complex section, consisting of bone canals. It ensures the conversion of incoming sounds into impulses that are transmitted to the brain and recognized there. In addition, the vestibular apparatus is located here, which is responsible for human coordination and balance.