1.What is otosclerosis, its causes and predisposition to the disease
Otosclerosis
– organic focal lesion of the inner ear. Changes in the bony labyrinth cause hearing loss, usually accompanied by a feeling of tinnitus. This disease begins mainly during puberty and is less common in men than in women. Hearing loss results from the fact that the otosclerotic lesion envelops and fixes the base of the stapes in the window of the vestibule.
The otosclerotic lesion is symmetrical.
However, most often the patient first notices unilateral hearing loss, and only at the next stage of the disease development the second ear is affected. In each ear, several foci of otosclerotic changes are most often observed at once.
The course of otosclerosis is chronic. In this case, periods of noticeable increase in hearing loss can be replaced by fairly long periods of relative stability.
Causes and predisposition
To date, the etiology of otosclerosis has not been fully elucidated. The influence of a hereditary factor is noted; otosclerosis is often combined with other genetically determined diseases. A statistical association with neurological pathology and endocrine disorders has also been reported.
In addition, in some cases, patients themselves note that the onset of the disease was preceded by sound trauma (usually an intense high-pitched sound).
It is assumed that the greater incidence among women is hormonally determined. One confirmation of this is the observation that the disease is significantly worsened during pregnancy.
Often, infectious diseases of the ear serve as precursors, but most specialists consider bacteriological or viral damage not as the cause of the development of otosclerosis, but as its pathogenic background.
Organic changes in the bone labyrinth can also develop due to chronic disorders of the blood supply to the inner ear.
Typically, otosclerosis progresses quite slowly, but rapid forms are also known. Most often, rapid development with an unfavorable outcome (significant hearing loss affecting the quality of life) is observed in cases where hearing loss begins at an early age and concerns mainly sensitivity to high tones; The presence of otosclerosis in close relatives is also often noted. It has been noted that otosclerosis never leads to complete deafness; however, it is also not possible to restore hearing or completely stop its decline.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
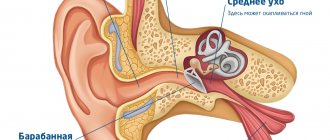
How does a normal ear work?
The ear is divided into three parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. Each part of the ear is important for hearing.
1 - Outer ear; 2 - Middle ear; 3 - Inner ear
Sound waves enter the ear canal of the outer ear, reach the eardrum, which separates the outer and middle ear, and cause it to vibrate. Three small bones in the middle ear (the malleus, incus and stapes) transmit the energy of sound vibrations from the eardrum to the fluids of the inner ear. Vibrations in this liquid stimulate the finest nerve endings (hairs). The auditory nerve then transmits these impulses to the brain, where they are analyzed and perceived as understandable sounds.
2. Classification of types of otosclerosis
The classification of otosclerosis is based on the nature of disturbances in sound conduction or sound perception.
Conductive
otosclerosis is diagnosed when, with preserved bone, only air sound conduction suffers. This form has the most favorable prognosis with surgical treatment.
Cochlear
otosclerosis is characterized by dysfunction of bone conduction. With this form of otosclerosis, communication becomes significantly more difficult, since the patient suffers from significant tinnitus and perceives any spoken speech as unintelligible. Surgical treatment is often
turns out to be only a partial solution to the problem of difficult speech perception.
Mixed
otosclerosis is diagnosed when both bone and air conduction are impaired. The prognosis here depends on the ratio of these violations. The success of surgical intervention is limited by the severity of bone conduction.
Visit our Microsurgery page
To make an accurate diagnosis, use:
- audiometry;
- tuning fork study (identifying the difference in the sensation of sound vibrations through air and directly through tissue);
- diagnostics of sensitivity threshold to ultrasound;
- radiography (detection of pathologies of the auditory bones);
- MRI. With high detail from different projections, the condition and mobility of the auditory bones are assessed, the presence of inflammation and other changes in bone or connective tissue is revealed.
3. Symptoms and diagnosis of the disease
The onset of otosclerosis is not acute or chronologically defined. Initially there is a slight hearing loss
, difficulties in understanding whispered speech, weak intermittent tinnitus. This stage can last up to several years.
Subsequent hearing loss
, already obvious and palpable, usually manifests itself as a subjective unintelligibility of low-frequency sounds and male speech, while the sensitivity of high-frequency sounds may even increase. It is noted that external noise does not affect speech intelligibility, and, for example, walking or chewing food by the patient himself can further reduce his ability to understand speech.
Noise in the ear
observed in 80% of cases of otosclerosis. The pain is episodic and appears, as a rule, during periods of exacerbation. At the same time, another decrease in hearing occurs. Activation of otosclerotic processes can be manifested by sensations of fullness inside the ear.
Significant hearing loss can form a neurotic syndrome
and lead to social maladjustment due to difficulties in communication, isolation, apathy, and sleep disturbances. Forced intense listening and unsuccessful simulation of full-fledged communication can be so painful that many patients prefer to simply avoid situations in which their participation as an active interlocutor is required.
Diagnosis of otosclerosis when contacting an otolaryngologist should be aimed not only at assessing the degree of hearing loss, but also at differentiating this disease from other ear diseases that reduce hearing (otitis media, wax plugs, neuritis, sensorineural hearing loss, etc.).
Otoscopy, audiometry, radiography and CT scan of the skull, acoustic impedance measurement, and assessment of the functioning of the vestibular apparatus are performed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Postoperative period
After the operation, the patient must lie on his back or on the side opposite the operated ear for 3 days. If modern titanium prostheses are used, this period can be shortened. Excessive strain, heavy lifting and strenuous exercise should be avoided for 3 weeks after surgery. Typically, within a week after surgery, patients notice improvement in hearing. The patient should not travel by plane for 2-3 weeks after surgery. It is necessary to avoid getting water into the ear canal for 1 month after surgery. Swimming is possible 1 month after surgery, but diving is not advisable. Any action associated with changes in air pressure (flying, climbing to high altitudes, diving) can lead to barotrauma of the cochlea and hearing loss.
Three weeks after surgery, you will be able to drive a car and fly an airplane.
4. Treatment of the disease
Conservative treatment
otosclerosis is ineffective. It can only be aimed at stabilizing the level of hearing loss. If factors and conditions are known against which chronic otosclerosis worsens with further hearing loss, therapy can be aimed at controlling the general condition and reducing reactivity. This is, for example, special pregnancy management, neurological, endocrinological or immune therapy.
Surgical treatment methods show the greatest effectiveness:
- mobilization of the stapes;
- fenestration of the labyrinth;
- Stapedoplasty.
The first operation is usually performed on the ear with the worst hearing. If the results are positive, the second ear will be operated on no sooner than six months later. Surgical treatment stops the development of hearing loss and sometimes even improves hearing for several years. However, over time, hearing begins to decline again. If all available treatment methods are ineffective, hearing aids or the use of hearing aids are indicated, and, of course, one should not refuse such a solution for aesthetic reasons or because of popular prejudices (“The device reduces hearing even faster”). The priority in such situations is to ensure and maintain an acceptable quality of life, level of social adaptation and ability to work.
Registration for surgery
Operation at the expense of the budget
Surgical treatment of otosclerosis in accordance with Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1610 of December 7, 2019 (link) is included in Section II (the list of types of high-tech medical care not included in the basic compulsory medical insurance program, the financial support of which is provided through subsidies from the budget of the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund to federal government institutions ). Stapedoplasty surgery for otosclerosis can be performed free of charge for the patient by completing a package of documents with the ENT doctor at the place of residence (extract from medical records and referral for hospitalization) and then the health authority of the patient’s region of residence. OHC places a package of documents in the electronic subsystem for monitoring the implementation of the state task for the provision of high-tech medical care at the expense of the federal budget on the waiting list. The waiting time for VMP depends on the volumes allocated to the institution for the year by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation and the number of patients on the waiting list. Today, waiting times range from 1.5-2 years. Apply for a referral at the expense of the budget
VHI operation
In addition, surgical treatment of otosclerosis in our institute can be carried out at the expense of voluntary health insurance (VHI), non-cash payment by an organization, or at the expense of citizens’ personal funds.
When performing surgical intervention at the expense of VHI, the voluntary health insurance program must include elective surgery. When coordinating surgical treatment - stapedoplasty - with a medical insurance organization, it is necessary to take into account that the operation involves replacing the patient’s fixed auditory ossicle (stapes) with an auditory ossicle prosthesis, which is often not included in the insurance program. Sign up for VHI
Paid surgery to improve hearing
The cost of surgical treatment of otosclerosis at our institute, which includes surgery under local anesthesia with the installation of a titanium K-piston prosthesis, an 8-day hospital stay with treatment, and a tone threshold audiogram before discharge, averages 135,000-155,000 rubles. The cost depends on the category of the ward in which the patient is accommodated (cost of stay in the ward).
Considering the existing waiting list for surgery on average for 1-2 months for nonresident patients, in order to optimize preoperative examination and subsequent surgical treatment (reducing the number of visits to St. Petersburg), it is possible to pre-register for surgery on the website of our institute (Registration).
In this case, the patient, in agreement with him, is pre-recorded on the operating list for a certain date (if you wish to be placed in a superior ward, you must also agree on its availability for your dates). 1 day before the expected date of surgery, the patient arrives at the institute for an in-person consultation, and if the indications for surgery are confirmed and there are no contraindications to surgery due to concomitant diseases, he is admitted to the clinic. At your place of residence, you will need to take tests in advance (list of tests).
Read also
Chronic laryngitis
Understanding Chronic Laryngitis Chronic laryngitis occurs when the larynx and its vocal cords become inflamed, swollen and irritated due to prolonged exposure to external factors.
This is quite... Read more
Vasomotor rhinitis
The concept of vasomotor rhinitis Vasomotor rhinitis is an inflammatory process in the nasal cavity. Irritants or allergens can cause this inflammation. Sometimes there are cases when there is no specific reason...
More details
Tubootitis
What is tubootitis Tubootitis is an inflammation, also called eustachitis, salpingotitis or tubotympanitis, which occurs in the area of the Eustachian tube, causing a decrease in the lumen of the ear canal. How…
More details
Sore throat
A sore throat is a pain, scratching, or irritation in the throat that gets worse when you swallow. The most common cause of this disease is viruses, namely colds (ARVI) or...
More details
Hoarseness of voice
What is Hoarseness Hoarseness is an abnormal change in voice that is a common symptom that often occurs in combination with a dry or scratchy throat. If your voice is hoarse...
More details