Pain in the left side can be caused by a variety of reasons. In the simplest case, this is associated with gas formation or intense training, intense walking, running. In this case, the pain stops quite quickly. But if they recur or are severe, you should immediately consult a therapist or call emergency help.
Causes of pain
On the left side of the abdomen there are a large number of organs, each of which can cause pain. There are several possible causes for the condition:
- inflammation;
- injury;
- circulatory disorders (ischemia, heart attack);
- torsion of the ligaments of an internal organ;
- suppuration;
- systemic damage;
- genetic disease;
- poisoning;
- organ dysfunction;
- spasm;
- the appearance of a neoplasm.
A doctor should find out the cause during a face-to-face appointment. He will prescribe the necessary diagnostic procedures and select the optimal treatment.
Visceral pain
The cause of visceral pain can be functional disorders and organic changes in the organ. With functional disorders, this type of pain appears due to a decrease in the pain threshold and can affect all parts of the gastrointestinal tract2. In diseases of the digestive tract, visceral pain can be triggered by stretching, lack of blood supply, or peristalsis. Usually the patient feels it in the midline of the abdomen and is not able to accurately indicate the painful point2.
- The nature of visceral pain is cramping, with periods of subsiding and increasing pain. More often it can be described as aching, much less often - stitching or burning.
- Pain in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can be caused by errors in diet, alcohol intake and exposure to factors such as running, bumpy riding, etc.
- The severity of pain can be reduced by warming or taking antispasmodics3.
Diagnostics
A doctor can guess the cause of pain through examination and palpation. The further diagnostic method is selected based on the results:
- general blood test - will indicate an infectious lesion, detect leukemia;
- general urinalysis - will help determine kidney pathology;
- Ultrasound is the fastest and easiest method for examining the abdominal organs;
- MRI - gives the most reliable results;
- colonoscopy - assessment of intestinal condition;
- radionuclide testing is relevant for some diseases of internal organs, for which other methods are not informative.
Based on the results of diagnostic measures, the patient is diagnosed. Pain treatment is selected according to the detected disease.
Read also: Pulling in the lower abdomen
Parietal pain
Another type of pain is parietal. It differs from the visceral one: it has a distinct localization in the area of the pathological process. Severe, painful and aggravated by sudden movements and coughing. It occurs due to irritation of the nerve receptors of the peritoneum, which covers the surface of the internal organs. It is projected onto the corresponding skin segments and is accompanied by tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall2, 3.
Such pain, acutely occurring and intensifying, may be a sign of a serious pathology, so you should immediately consult a doctor3.
Possible diagnoses
Pain in the left side of the lower abdomen can be caused by damage to any organ located on this side. Possible diagnoses for such a patient:
- pathology of the spleen (abscess, heart attack, rupture, inflammation);
- lymphocytic leukemia or myeloid leukemia;
- intestinal pathology (malsorption, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome, ulcerative colitis, polyps, obstruction);
- oncology;
- pathologies of the reproductive organs (salpingitis, endometriosis, torsion of the ovarian pedicle, salpingoophoritis, adnexitis, rupture of uterine ligaments);
- ectopic pregnancy;
- kidney damage (enlargement of the pelvis).
Pain in the left side can be caused by other diagnoses, but radiate (transition) to this area. Therefore, it is important to contact a medical facility in a timely manner and conduct a comprehensive examination.
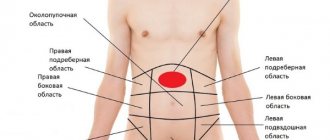
Anatomical features of the left half of the abdomen
Abdominal pain on the left can be caused by any anatomical structure located in this area. These include the digestive organs:
- stomach;
- pancreas;
- duodenum and half of the small intestine;
- part of the large intestine from the transverse colon, descending, sigmoid and rectum.
The organ of hematopoiesis and immune defense is the spleen. Organs of urination and excretion: left kidney, ureter, bladder. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the possibility of damage to:
- abdominal wall and layers of peritoneum lining the internal cavity;
- lower ribs on the left;
- vessels and nerves of the abdominal cavity.
We do not consider here the pelvic organs, which lie in the lowest part. Their role in the examination of women and men for pain cannot be reduced to identify, for example, the source of inflammation or the original tumor.
Treatment
Treatment for a condition where the left side of the lower abdomen hurts depends on the diagnosis. Several groups of drugs can be used:
- painkillers - to relieve symptoms;
- antibiotics - for inflammation and suppuration;
- enzymes - for gastrointestinal pathologies;
- hormones - for endometriosis;
- sedatives - for irritable bowel syndrome;
- carminatives - for flatulence;
- chemotherapy - for oncology and leukemia.
If the pain is caused by kidney damage, special preparations and herbal teas may be prescribed. And in case of ectopic pregnancy, injuries and ruptures of organs, as well as in the absence of the ability to cure the patient with conservative methods, surgical intervention is performed.
Pain in the left side is a reason to consult a doctor in any case. But if they are of high intensity or began after a possible injury, this must be done urgently. Delay can threaten the patient with serious complications, including death.
Read also: Pulling in the lower abdomen during pregnancy
Dear patients! Remember that only a qualified doctor can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-(4822)-33-00-33
Be healthy and happy!
Mechanism of formation of abdominal pain
The feeling of pain serves as a protective reaction for the body. It indicates damage and requires help. According to the mechanism, pain impulses can be formed by:
- spastic contraction or hyperextension of hollow organs (intestines, stomach, bladder and ureter);
- an ulcerative process that violates the integrity of the submucosal and muscular layer (there are no pain receptors in the mucous membrane itself);
- stretching or rupture of the capsule of parenchymal organs (spleen, kidney);
- damage to nerve branches and plexuses (due to rib fractures, inflammatory processes, tumor disintegration).
Spastic pain is difficult for patients to tolerate
The classification of pain includes the following types:
- organ - caused by damage to one or more organs by inflammation, ischemia (reduced blood flow through the arteries), infectious process, pain in the left side of the abdomen migrates, does not have an epicenter and precise localization;
- parietal - connected to the abdominal wall, clearly localized at the site of the lesion;
- neurogenic - caused by damage to nerve fibers, distortion of the impulse to the brain, the organs themselves lying in the abdominal area may not be damaged;
- reflected - projected onto a zone that is connected by the location of the nerve ganglia of the spinal cord.
Pathology of the abdominal organs is caused by a mixed mechanism. One violation leads to a chain reaction. Knowledge of the combined negative process allows you to select the optimal treatment to counteract and reduce pain.
Characteristics of pain in diseases of the urinary organs
Urinary diseases occur in cases of pathology of the kidneys, bladder, and ureter. The localization we are studying includes local pain in the ureter caused by its stretching and radiating pain from the left kidney.
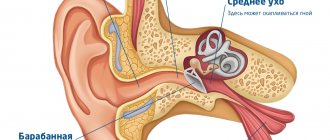
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of internal structures (pelvis, calyces) caused by infection. It begins suddenly with high fever, vomiting, chills, pain in the lower back on the left, radiating to the left side of the abdomen. Impaired urination, pain, and urinary retention occur. Pulsating pain is an unfavorable sign indicating the formation of an abscess in the kidney.
In the chronic course, exacerbations are milder, but with the same symptoms. As a result, scars appear in place of the inflamed tissue, the kidney becomes deformed and loses function. Kidney failure occurs when the second healthy kidney stops working hard to compensate for the diseased organ. The disease is treated by urologists with antibacterial agents, diuretics, and, if necessary, by opening the suppuration or resection of part of the kidney.
Urolithiasis disease
Often accompanied by inflammation of the urinary tract and metabolic disorders. It is caused by the loss of crystalline sediment in the urine, its settling in the pelvis and gluing into stones. The most common compositions are phosphates, oxalates, and urates.
The stone causes a disruption in the process of urine outflow, so stagnation and distension form in the higher-lying sections. The movement of a stone along the ureter explains why the lower abdomen hurts. Clinically, after intense shaking or running, the patient experiences an attack of renal colic.
The pain is very intense in nature, cutting. Localized in the lower back or to the left of the navel. Acute urinary retention occurs. The duration of the attack is up to several hours. For emergency care, painkillers and antispasmodics are administered. Frequent recurrence of attacks is an indication for surgical removal of the stone.
What organs are located in the lower left corner of the abdomen?
Organs of different systems are located on the left lower abdomen. Digestion includes: the small intestine - loops of the jejunum, part of the descending colon and the sigmoid - large intestine. To the organs of the genitourinary system: the left half of the uterus, the left appendage with the ovary and fallopian tube in women, the ureter and part of the bladder.
We must not forget that pain on the left side of the lower abdomen can cause disturbances in the bone skeleton of the pelvis, hip joint, lymph nodes, nerve bundles and vessels, irradiation downward in diseases of the spleen and left kidney.
Pathologies of the kidneys and ureters
Urolithiasis causes pain.
The kidney is a paired organ. Therefore, problems with the urinary system can be bilateral or unilateral.
In case of pathology of one of the kidneys, the symptoms may be hidden or not clearly expressed.
Therefore, pyelonephritis develops rapidly, since 2 kidneys are involved, and, for example, a stone in one of them does not manifest itself for a long time. Causes of pain:
- Urolithiasis and its manifestation renal colic. It occurs when stones or sand begin to move from the kidney down the ureter, scratching its walls. Pain syndrome occurs. It can be cramping - if there is a stone or constant strong along the ureter to the urethra - if there is sand.
- Hydroureteronephrosis is overstretching of the renal pelvis. The cause is a narrowing of the urinary tract due to various reasons. Urine accumulates in the kidney, the tissues experience pressure, and pain occurs.
We care about your health
Diseases of the large intestine do not always manifest themselves clearly and clearly. More often than not, the initial phase is accompanied by vague symptoms that people do not attach importance to. This may be a burning sensation, discomfort in the intestines, and periodic mucus discharge. The specificity of the intestines is that for a long time it may not give such signs that would indicate the need to visit a proctologist. Even when a person begins to be bothered by pain, bloating, discharge from the anus and other symptoms, he does not rush to see a doctor. At first, the patient persistently tries self-medication and those remedies that modern advertising intrusively offers. Meanwhile, the symptoms change, become more noticeable, painful and often aggressive.
Sometimes the symptoms may not indirectly indicate intestinal diseases; the symptoms may be specific:
- sudden weight loss;
- weakness in the body;
- disturbances in metabolic and hormonal processes;
- hair loss.
These signs accompany the most severe intestinal lesions: cancer, malignant tumors, polyposis. The intestine is the only organ that simultaneously belongs to two important systems of the body: the immune and gastrointestinal tract. For a full life and health, it is important to be able to recognize those symptoms and signs that indicate a pathological process in the large intestine:
- constipation;
- pain of varying intensity in the abdomen;
- bleeding during bowel movements;
- discharge of clear or purulent mucus;
- anemia;
- flatulence;
- intestinal obstruction;
- stool disorder;
- tenesmus;
- incontinence.
Intestinal constipation With constipation, difficulties with defecation are observed, up to the complete exclusion of stool for several days. Constipation can be constant and persistent and not respond to the effects of laxatives. An upset bowel movement can be replaced by constipation - this is a common picture with irritable bowel syndrome, dysbacteriosis, and functional disorders. The intensity of pain depends on the type of constipation: atonic and spastic. In the first case, the pain is aching, often not aggressive. With spastic constipation, there may be persistent pain in the groin area. The presence of frequent constipation indicates the possibility of fecal impaction or intestinal obstruction. The conditions are extremely dangerous in nature and can threaten life.
Abdominal pain Pain in the abdomen and groin often accompanies organic and functional disorders in the large intestine. Thus, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, the pain is in the nature of spastic contractions. Such pain often radiates to the lumbar region and radiates along the outside of the legs. It is difficult to determine the locality, since the pain “spreads” across the lower abdomen, often involving the perineum in the process.
Constant pain is a sign of a progressive inflammatory process. Such pains are aching, pulling, persistent. Manifested in IBS, various colitis, diverticulosis. The nature of the pain indicates the likelihood of developing peritonitis or a purulent lesion.
Bloody discharge and bleeding Bleeding occurs in diseases of the rectum and colon. Usually, the location of the lesion is visually determined by the color of the blood: the brighter the blood, the closer to the exit the lesion is. Thus, the appearance of clear and bright scarlet blood indicates internal or external hemorrhoids. Sometimes blood loss can be significant and cause weakness and dizziness.
If the stool is homogeneous and contains uniform bloody impurities, then this is a symptom of the formation of a tumor in the upper intestines. Sometimes such masses occur with nonspecific colitis and diverticulosis. The higher the lesion is, the more uniform the blood clots in the stool will look and the darker their color.
In Crohn's disease, blood may be released in pure form or in large clots. In some cases, scarlet blood may be a sign of a disintegrating tumor in the intestine.
Discharge of mucus or pus Such discharge is either constant or appears during bowel movements. Most often this becomes a sign of the formation of a fistula in the anus. With constant mucus secretion and pain, sphincter insufficiency can be assumed. In this case, numerous erosions and cracks form, which causes itching and pain.
Such discharge is characteristic of irritable bowel syndrome, proctitis, and the formation of tumors in the sigmoid colon. Often the discharge is combined with blood and the appearance of clots.
Pain in the anus Pain can be aching and periodic, bursting in the area of the passage. This happens with deep cracks; they heal with difficulty, especially if there is constipation. Jerking and unbearable pain occurs when hemorrhoids rupture or there are multiple nodes in the intestines. Regular hemorrhoids without complications do not cause such pain; they are only felt as distension and swelling in the anus.
Anemia Anemia develops when a person has lost a lot of blood. This occurs with severe intestinal lesions, cancerous formations, and rapid tumor progression.
Bloating and flatulence Bloating is a common sign for almost any pathology in the gastrointestinal tract. The feeling of bloating and heavy gases is typical with constipation, intestinal obstruction, and fecal impaction. Often flatulence is the result of enzyme deficiency and may indicate disturbances in the functioning of other internal organs. Bloating and flatulence often accompany those who suffer from dysbiosis and eat poorly. In some cases, bloating occurs with a feeling of discomfort and heaviness in the stomach, but with excess gas, severe abdominal pain may occur.
Intestinal obstruction Intestinal obstruction can be complete or partial. More often you have to deal with partial, which is characterized by:
- bloating;
- pain;
- flatulence;
- prolonged constipation;
- the appearance of impurities and blood;
- vomit;
- loss of appetite.
More often this indicates severe damage to the large intestine of organic origin. The condition is extremely painful and dangerous to human health. As it progresses, signs of poisoning of the body and inflammation of the peritoneum appear. With partial intestinal obstruction, stool is rare, scanty, and often replaced by profuse upset. Temporary improvement occurs under the influence of taking laxatives or cleansing enemas.
Stool disorder Diarrhea accompanies milder intestinal diseases, a common sign of dysbiosis. Also, stool disorder can be combined with other symptoms, such as constipation or various discharges. This happens with exacerbation of colitis, IBS.
Tenesmus Tenesmus is a false urge to have a bowel movement. With such urges, a small amount of mucus is released, sometimes along with diarrhea. Tenesmus is usually frequent, persistent, tiring a person with its frequency. Characteristic of excited motility of the rectum, they become a consequence of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the anus.
Incontinence Incontinence of fecal masses of secreted gases manifests itself with congenital or acquired changes in the sphincter. Another reason could be dysregulation due to psychological factors.
Localization of pain under the ribs
Precise determination of the area where painful sensations are concentrated allows one to assume a particular diagnosis.
| Back pain under the ribs on the right and left | Neuralgia, vertebrogenic disorders, colitis, enterocolitis, intervertebral hernia |
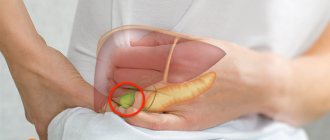
| Left hypochondrium | Pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, myocardial infarction, abscess, enlargement, spleen damage |
| Right side of the back | Gallstone disease, cholecystitis, cholangitis, cirrhosis, hepatosis, appendicitis |
| In the middle | Stomach ulcer, angina pectoris |
| Uncertain location | Pleurisy, pneumonia (pain on the side of the affected lung), stone formation in the kidneys and bladder |