Advantages of the Tick-E-Vac vaccine
- The vaccine stimulates the development of cellular and humoral immunity to the tick-borne encephalitis virus after completion of a vaccination course of two injections in at least 90% of those vaccinated.
- The vaccine protects against all currently known subtypes of tick-borne encephalitis, as well as against the Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus.
- The vaccine is used for emergency prevention of tick-borne encephalitis in case of suspected tick bite.
- The drug does not contain formaldehyde, antibiotics or preservatives.
- The high quality of the vaccine makes it indispensable when it is necessary to carry out routine and emergency vaccination of children and elderly people who have a reduced immune status.
Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis “Tick-E-Vac” (one-time)
The Tick-E-Vac vaccine is a purified, concentrated suspension of formalin-inactivated tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBE) strain “Sofin”, obtained by reproduction in a primary culture of chicken embryo cells sorbed on aluminum hydroxide.
Immunological properties - The vaccine stimulates the production of cellular and humoral immunity to the tick-borne encephalitis virus. After two injections of the drug (vaccination course), virus-neutralizing antibodies are detected in at least 90 vaccinated people.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Clinical studies of the safety of the Klesh-E-Vac vaccine for pregnant and lactating women have not been conducted.
Vaccination of pregnant women can only be carried out after carefully determining the risk of their possible infection with the TBE virus.
Vaccination of breastfeeding women can be carried out 2 weeks after birth.
Preventive vaccination
1.1. Routine vaccination
The primary course of vaccination consists of two intramuscular injections of 1 dose each with an interval of 1-7 months.
One vaccination dose is:
- Adults 16 years and older - 0.5 ml;
- Children from 1 to 16 years old - 0.25 ml.
Vaccinations can be carried out throughout the year, including during the epidemic season. Visiting a TBE site during the epidemic season is allowed no earlier than 2 weeks after the second vaccination.
The most optimal interval between the first and second vaccinations is 5-7 months (autumn - spring).
1.2. Emergency vaccination
For epidemic indications, emergency vaccination may be carried out. In this case, the vaccine is administered twice with an interval of 2 weeks to the following persons:
- Adults 16 years and older - 0.5 ml;
- Children from 1 to 16 years old - 0.25 ml.
Visiting the TBE outbreak during the epidemic season is allowed no earlier than 2 weeks after the second vaccination.
The first revaccination with both regimens is carried out once 1 year after completion of the primary course of vaccination with a dose of 0.5 ml for persons aged 16 years and older and a dose of 0.25 ml for children from 1 year to 16 years.
Subsequent distant revaccinations are carried out once every three years at an age-specific dosage.
General vaccination scheme
| Type of vaccination | First vaccination | Second vaccination | Subsequent (revaccination) |
| Routine vaccination | Selected date | 1-7 months after the first vaccination | After the second - every 3 years |
| Emergency vaccination | Selected date | 2 weeks after the first vaccination | |
| Dose for adults 16 years and older | 0.5 ml | 0.5 ml | 0.5 ml |
| Dose for children from 1 year to 16 years | 0.25 ml | 0.25 ml | 0.25 ml |
2. Vaccination of donors
The course of vaccination is two intramuscular injections of 0.5 ml with an interval of 5-7 months or three injections of 0.5 ml with an interval of 3-5 weeks between vaccinations. The first scheme provides the best immunization effect. Revaccination - a single dose of 0.5 ml every 6-12 months. The first blood draw from donors should be carried out 14-30 days after the vaccination course.
Side effects
After administration of the vaccine, local and general reactions may develop in some cases.
For adults 16 years and older
Local reactions
- Redness, swelling, pain at the injection site;
- Development of infiltration;
- Slight enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Local reactions may appear within 2 days after vaccination. The duration of local reactions does not exceed 3 days.
General reactions
- General malaise, headache, nausea, fever (often up to 37.5 C (weak reaction)) (occasionally - from 37.5 C to 38.5 C (average reaction)) (rarely - over 38.5 C ( strong reaction)).
General reactions can develop within 2 days after vaccination; their duration does not exceed 2 days.
For children from 1 year to 16 years old
Local reactions
- Redness, swelling, pain at the injection site;
- Development of infiltration;
- Slight enlargement of regional lymph nodes.
Local reactions may appear within 2 days after vaccination. The duration of local reactions does not exceed 3 days.
General reactions
- General malaise, headache, nausea;
- Increase in temperature (up to 37.5C (weak reaction) - often; from 37.5C to 38.5C (medium reaction) - often; above 38.5C (strong reaction) - rarely).
General reactions can develop within 3 days after vaccination, their duration does not exceed 3 days.
Local and general reactions often develop after the first vaccination. In isolated cases, vaccinations may be accompanied by the development of immediate allergic reactions, and therefore those vaccinated should be under medical supervision for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination sites must be provided with anti-shock therapy.
Overdose
No cases of overdose have been identified.
It is extremely rare that vaccinations can be accompanied by the development of immediate allergic reactions, and therefore those vaccinated should be under medical supervision for 30 minutes after vaccination. Vaccination sites must be provided with anti-shock therapy.
The effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Severe general reactions to the vaccine (significant increase in temperature, severe headache) are a contraindication for driving vehicles and machinery.
Interaction with other immunobiological drugs
It is allowed to vaccinate against tick-borne encephalitis simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccinations with inactivated vaccines of the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar and the Preventive Vaccination Calendar for epidemic indications (with the exception of rabies). In other cases, vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is carried out no earlier than 1 month after vaccination against another infectious disease.
special instructions
The drug cannot be administered intravenously!
Vaccinations are carried out in strict compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. The room must be equipped with anti-shock and anti-allergic therapy. Before opening the ampoule, it is necessary to carry out a visual inspection. The drug is not suitable in ampoules with damaged integrity, labeling, if foreign inclusions are detected, if there are large unbreakable conglomerates, if the expiration date has expired, if the temperature conditions of storage or transportation are violated. Immediately before injection, the vaccine in the ampoule is shaken until a homogeneous suspension is obtained. The drug is administered immediately after opening the ampoule intramuscularly into the deltoid muscle of the shoulder. Vaccinations performed are recorded in established registration forms indicating the name of the drug, date of vaccination, dose, batch number, manufacturer, reaction to vaccination.
Vaccination of children and adults with chronic diseases in the acute stage is carried out no earlier than 1 month after recovery (remission) . The vaccine is not used for children under 1 year of age.
Indications for examination
Specific prevention of tick-borne encephalitis for persons aged 16 years and older in a dose of 0.5 ml; immunization of donors in order to obtain specific immunoglobulin.
Contingents subject to specific prevention:
- Population living in territories exotic for tick-borne encephalitis;
- Persons arriving in these territories performing the following work:
- agricultural, drainage, construction, excavation and movement of soil, procurement, fishing, geological, survey, expedition, dermatosation and pest control;
- for logging, clearing and landscaping of forests, health and recreation areas for the population.
- Persons visiting areas endemic for tick-borne encephalitis for the purpose of recreation, tourism, work in summer cottages and gardens;
- Persons working with live cultures of tick-borne encephalitis.
Preparing for the examination
No special preparation is required.
Contraindications
Only a doctor can decide whether Klesch-E-Vac is suitable for vaccination
"Tick-E-Vac" is contraindicated if there is a history of an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine and in the following cases:
- Acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, chronic diseases in the acute stage - vaccinations are carried out no earlier than 1 month after recovery (remission).
- History of severe allergic reactions; bronchial asthma; autoimmune diseases.
- History of allergy to the components of the drug (aluminum, eggs).
- Severe reaction (fever above 40C; swelling at the site of vaccine administration, hyperemia more than 8 cm in diameter) or complications from the previous dose of the vaccine.
- Age up to 1 year.
- Pregnancy.
- Chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys.
- Chronic heart failure, cerebrovascular accident, diabetes mellitus, thyrotoxicosis, malignant neoplasms, blood diseases.
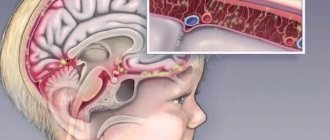
Vaccination scheme against tick-borne encephalitis
There is a standard or accelerated scheme. Whatever option the doctor advises, the result will be stable immunity to infection. It is produced 14 days after the second injection and is secured by the third vaccination. Vaccination is carried out starting from 1 year of life.
Routine vaccination:
- First vaccination: it is optimal to start in the fall (November - December)
- Second vaccination: after 1 – 7 months
- Third vaccination: after 12 months
Revaccination is done every 3 years.
The Miracle Doctor clinic makes it possible to get vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis before the start of the season, if the patient did not have time to take care of it in advance. This happens, for example, when changing jobs, business trips, unplanned trips. Emergency vaccination:
- First vaccination: March-April
- Second vaccination: after 14 days
- Third vaccination: after 12 months
Revaccination is done every 3 years
Tick-e-vac vaccine 0.25ml/dose 1 pc. intramuscular suspension
pharmachologic effect
It is a formalin-inactivated encephalitis virus. The vaccine forms immunity to the tick-borne encephalitis virus.
Composition and release form Tick-e-vac vaccine 0.25 ml/dose 1 pc. intramuscular suspension
Suspension - 0.25 ml:
- Active substance: tick-borne encephalitis virus antigen (inactivated, titer not less than 1:128) 1 dose.
- Excipients: human albumin (solution for infusion* 10% or 20%) 0.125 mg, sucrose 15 mg, aluminum hydroxide 0.2 mg; buffer system salts: sodium chloride 1.9 mg, trometamol 0.03 mg.
*Solutions for albumin infusions contain (in addition to albumin) sodium caprylate and sodium chloride.
0.25 ml (1 dose for children from 1 year to 16 years) - ampoules (1) - cardboard packs.
Description of the dosage form
Suspension for intramuscular administration; homogeneous, white, without foreign inclusions.
Directions for use and doses
The dosage regimen is individual, depending on the indications for use and the age of the recipient.
Indications for use Tick-e-vac vaccine 0.25 ml/dose 1 pc. intramuscular suspension
Routine preventive immunization in areas with a high risk of infection, as well as selective vaccination of persons visiting areas of tick-borne encephalitis. Emergency assistance for suspected tick bites in regions where tick-borne encephalitis is endemic.
Contraindications
Feverish conditions (infectious and non-infectious origin), hereditary, progressive diseases of the nervous system, epilepsy with frequent seizures, food allergies (especially to eggs), bronchial asthma, collagenosis, chronic liver and kidney diseases, chronic heart failure, cerebrovascular accident, diabetes mellitus , thyrotoxicosis, malignant neoplasms, blood diseases, pregnancy.
Application Tick-e-vac vaccine 0.25 ml/dose 1 pc. intramuscular suspension during pregnancy and lactation
Contraindicated for use during pregnancy.
Use in children
Use in children under 1 year of age is recommended only if there is a real risk of infection.
special instructions
After suffering from febrile conditions, vaccinations are permissible no earlier than 1 month after recovery, and for persons who have suffered viral hepatitis and meningococcal infection, no earlier than 6 months after recovery. Vaccinations are acceptable 2 weeks after birth.
Avoid intravascular administration.
Side effects Tick-e-vac vaccine 0.25 ml/dose 1 pc. intramuscular suspension
Very rarely: fever, headache in the first 2 days.
Local reactions: short-term burning sensation at the injection site, rarely - redness, soreness, development of infiltration.
Drug interactions
Can be used simultaneously with live and inactivated vaccines. The interval between the use of immunoglobulin against tick-borne encephalitis and the vaccine should be at least 4 weeks.