Compatibility with other vaccines
Vaccination against mumps can be carried out simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccinations included in the National Vaccination Calendar (vaccinations against measles, rubella, polio, hepatitis B, whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, influenza, Haemophilus influenzae) provided they are administered in different areas body or no earlier than 1 month after the previous vaccination. After the administration of human immunoglobulin preparations, vaccinations against mumps are carried out no earlier than 2 months later. After administration of the Mumps vaccine, immunoglobulin preparations can be administered no earlier than 2 weeks later. If it is necessary to use immunoglobulin earlier than this period, vaccination against mumps should be repeated.
Principles and purposes of vaccination
Vaccination is included in the mandatory calendar of preventive vaccinations due to the risk of complications during mumps. An insufficiently high level of vaccination coverage with the mumps vaccine (less than 80%) can lead to undesirable epidemiological changes - a shift in the incidence of mumps to older age groups of the population. By the end of 2013, mumps vaccine had been introduced nationally in 120 countries.
Prevention consists of vaccinating children with a live mumps vaccine in accordance with the vaccination schedule.
Contraindications
Only a doctor can decide whether Mumps is suitable for vaccination
The Mumps vaccine is contraindicated if there is a history of an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine, as well as in cases where the patient:
- Anaphylactic reactions or severe forms of allergic reactions to aminoglycosides (gentamicin sulfate), chicken and/or quail eggs have previously been observed.
- There are primary immunodeficiency states, malignant blood diseases and neoplasms.
- A previous severe reaction (temperature rise above 40 C, hyperemia and/or swelling more than 8 cm in diameter at the site of vaccine administration) or a complication to a previous administration of mumps or mumps-measles vaccines has been observed.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
- Acute diseases or exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Why get the mumps-measles vaccine?
Complicated forms of mumps are quite dangerous because they can lead to the development of inflammatory processes:
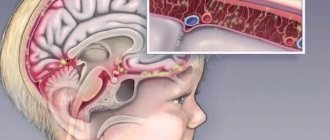
- membranes of the brain and spinal cord - meningitis;
- membranes and substance of the brain and spinal cord - meningoencephalitis;
- pancreas;
- testicles in men - orchitis;
- mammary glands - mastitis;
- kidney - nephritis.
Infection with the virus can lead to testicular atrophy in boys, infertility, the development of diabetes mellitus, deafness and dysfunction of the central nervous system. Modern medicine does not have specific methods for treating this disease. The best option is a live mumps-measles vaccine, which provides protection not only against mumps, but also against measles.
The latter is an infectious disease of viral etiology with a very high level of contagiousness - about 90%. It is deservedly considered the most contagious disease in the world. When in contact with a sick person, only one person out of ten avoids infection. Measles is very dangerous for adults. It is severe and can lead to the development of meningitis, meningoencephalitis, and keratitis. Just like mumps, no specific treatment has been created for it.
Possible side effects
- Often
- Rarely, in the first two days after vaccination, local reactions occur, expressed in skin hyperemia and mild swelling at the site of vaccine administration, which go away without treatment. In the period from 5 to 42 days from the moment of vaccination, a slight increase in the parotid salivary glands may occur, which goes away on its own within 2-3 days. Restlessness, lethargy, and sleep disturbances may also occur.
- Very rarely, allergic reactions appear in the first two days. In the period after 2-4 weeks - benign serous meningitis or painful short-term swelling of the testicles.
in the period from 5 to 15 days after vaccination, a short-term slight increase in body temperature and catarrhal phenomena in the nasopharynx (mild hyperemia of the pharynx, rhinitis) occur. An increase in body temperature above 38.5 C in the post-vaccination period is an indication for the prescription of antipyretics.
Considering the possibility of developing immediate allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, urticaria) in particularly sensitive individuals, vaccinated persons must be provided with medical supervision for 30 minutes.
Come get vaccinated at MiracleChildren. A full range of vaccines for children and adults, family vaccinations - at a special price!
How to prepare your child for vaccination
For successful immunization and minimizing side effects, the baby must be prepared in advance and follow some rules before and after vaccination:
- It is necessary to undergo an examination by a pediatrician and neurologist in advance. Possible reasons for delaying vaccination include: acute viral and bacterial diseases, severe anemia, high fever, etc. After eliminating the acute form of the disease, immunization is carried out according to the course;
- Before and after vaccination, it is advisable not to feed the baby until he asks;
- If inflammation develops at the injection site, immediately consult a supervising doctor;
- It is not advisable to walk for a long time after vaccination;
- Avoid hypothermia and overheating;
- Prepare in advance for a possible increase in temperature (have paracetamol or ibuprofen at home). Fever is a predicted reaction to vaccination. But it should not be too high (40° C or more);
- After the injection, do not leave the Medical Center for at least 30 minutes.
All the vaccines we use comply with WHO standards, which guarantees their effectiveness, safety and reduced risk of side effects.
multidisciplinary medical center
VACTRIVIR Combined vaccine against measles, rubella and mumps, cultured live. International nonproprietary or generic name.
Vaccine for the prevention of measles, rubella and mumps.
Dosage form.
Lyophilisate for preparing a solution for subcutaneous administration.
Compound.
One vaccination dose (0.5 ml) contains: Active ingredients: - measles virus - at least 1,000 (3.0 lg) tissue cytopathogenic doses (TCC50); — rubella virus – at least 1000 (3.0 lg) TCD50; — mumps virus – at least 20,000 (4.3 lg) TCC50. Excipients: - aqueous solution of LS-18* - 0.12 ml; - gelatin solution 10% - 0.03 ml; — gentamicin sulfate** – no more than 0.5 mcg. Note. * Composition of an aqueous solution of LS-18: sucrose – 250 mg, lactose – 50 mg, sodium glutamic acid – 37.5 mg, glycine – 25 mg, L-proline – 25 mg, Hanks dry mixture with phenol red – 7.15 mg, water for injections up to 1 ml. **Technological impurity.
Description.
Lyophilisate is a homogeneous porous mass from yellowish to pinkish in color, hygroscopic. The reconstituted drug is a transparent pink liquid.
Characteristic.
The drug is a lyophilized mixture of liquid semi-finished products of measles, rubella and mumps vaccines. To produce the vaccine, attenuated strains of the measles virus Leningrad-16 (L-16) and mumps virus Leningrad-3 (L-3), cultured on a primary cell culture of quail embryos, and an attenuated strain of rubella virus RA 27/3, cultured on diploid cells, are used. human MRC-5.
Pharmacotherapeutic group.
MIBP vaccine.
ATX Code:
J07BD52
Immunological properties.
The vaccine stimulates the production of antibodies to measles, rubella and mumps viruses in seronegative vaccinated individuals, reaching maximum values 3-4 weeks (to measles and rubella viruses) and 6-7 weeks (to mumps virus) after vaccination.
Indications for use.
Prevention of measles, rubella and mumps in persons from the age of 12 months. In accordance with the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar, children are vaccinated twice at the age of 12 months and 6 years.
Contraindications:
- anaphylactic reactions or severe forms of allergic reactions to aminoglycosides (gentamicin sulfate, etc.), chicken and/or quail eggs;
- hypersensitivity to any of the components of the vaccine;
- primary and acquired immunodeficiency conditions;
- malignant blood diseases and neoplasms;
- severe reaction (temperature rise above 40 °C, hyperemia and/or swelling more than 8 cm in diameter at the site of vaccine administration) or complication of previous administration of vaccines for the prevention of measles, mumps, rubella;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- acute infectious or non-infectious diseases, exacerbation of chronic diseases - vaccinations are carried out 2-4 weeks after recovery or remission. For mild ARVI and acute intestinal diseases, vaccinations are carried out after the temperature has normalized;
- immunosuppressive and radiation therapy - vaccination is possible 12 months after the end of treatment.
Note. HIV infection is not a contraindication to vaccination.
Carefully.
Considering the possibility of developing immediate allergic reactions (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, urticaria) in particularly sensitive individuals, vaccinated persons must be provided with medical supervision for 30 minutes. Vaccination sites must be provided with anti-shock therapy.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Use is contraindicated. Pregnancy should not be allowed to occur within 1 month after vaccination.
Method of administration and dose.
Immediately before use, the vaccine is diluted with a solvent (water for injection) at the rate of 0.5 ml of solvent per one vaccination dose of the vaccine. The vaccine should completely dissolve within 3 minutes. The dissolved vaccine looks like a transparent pink liquid. The vaccine or solvent in ampoules with damaged integrity, labeling, changes in their physical properties (color, transparency, etc.), expired or improperly stored are not suitable for use. The opening of ampoules and the vaccination procedure are carried out in strict compliance with the rules of asepsis and antiseptics. Ampoules with the vaccine and solvent at the incision site are treated with 70% ethyl alcohol and broken off, while preventing alcohol from getting into the ampoule. To dilute the vaccine, select the entire required volume of solvent and transfer it to an ampoule with dry vaccine. After dissolution, the vaccine is drawn with another needle into a sterile syringe, which is then used for vaccination. The vaccine is administered subcutaneously in a volume of 0.5 ml under the shoulder blade or in the shoulder area (at the border between the lower and middle third of the shoulder from the outside), having previously treated the skin at the site of vaccine administration with 70% ethyl alcohol. The dissolved vaccine is used immediately and cannot be stored. The vaccination performed is registered in the established registration forms, indicating the name of the drug, date of vaccination, dose, manufacturer, batch number, expiration date, reaction to the vaccine.
Side effect.
In most vaccinated people, the vaccination process is asymptomatic. After administration of the vaccine, adverse reactions of varying severity may occur. The incidence of adverse reactions is presented in accordance with the recommendations of the World Health Organization and includes the following categories: very often (≥1/10); often (≥1/100 and <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000 to <1/100), rare (≥1/10000 and <1/1000), very rare (<1/10000, including isolated cases ). General disorders and disorders at the injection site Often: - in the first 48 hours - local reaction, expressed in skin hyperemia, which goes away without treatment after 1-3 days. - during the first 18 days after vaccination - a short-term increase in body temperature no higher than 38.5 ° C, catarrhal symptoms in the nasopharynx (mild hyperemia of the pharynx, rhinitis). With mass use of the vaccine, an increase in body temperature above 38.5 °C should not occur in more than 2 percent of vaccinated people. An increase in body temperature above 38.5 °C in the post-vaccination period is an indication for the prescription of antipyretics. Uncommon: - during the first 18 days after vaccination - malaise lasting 1-3 days. Rarely: - in the first 48 hours - a local reaction, expressed in mild swelling at the site of vaccine administration, which goes away without treatment after 1-3 days. Disorders of the genital organs and breast Very rarely: - painful short-term swelling of the testicles. Violations of the organ of vision Uncommon: - from 5 to 18 days - conjunctivitis, lasting 1-3 days. Mental disorders Rare: - anxiety, lethargy, sleep disturbance. Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Uncommon: - cough. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract Rarely: - from 5 to 42 days - short-term slight increase in the parotid salivary glands, lasting 2-3 days. Very rare: - abdominal pain, abdominal syndrome. Nervous system disorders Very rare: - after 6-10 days - convulsive reactions that occur after vaccination against a background of high temperature; - development of encephalitis, each case of which requires differential diagnosis; - transient polyneuropathy. Immune system disorders Very rare: - in the first 24-48 hours - allergic reactions that occur in persons with altered reactivity. Disorders of the blood and lymphatic system Rarely: - lymphadenopathy (enlargement of mainly the occipital and posterior cervical lymph nodes). Very rare: - thrombocytopenic purpura. Infectious and parasitic diseases Very rare: - after 2-4 weeks - benign serous meningitis, each case of which requires differential diagnosis. Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Rare: - arthralgia that occurs between 10 and 15 days after vaccination; - transient arthritis that occurs 10-15 days after vaccination. Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues Uncommon: - from 5 to 18 days - rash lasting 1-3 days. If side effects occur that are not described in the instructions, the patient should inform the doctor about them.
Overdose.
No cases of overdose have been reported.
Interaction with other drugs.
Vaccination can be carried out simultaneously (on the same day) with other vaccinations of the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar (against polio, hepatitis B, whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus) or no earlier than 1 month after the previous vaccination. In this case, the drugs are administered with separate syringes into different parts of the body. Other vaccines are administered at intervals of at least 1 month. After the administration of blood products (immunoglobulins, plasma, etc.), the vaccine against measles, rubella and mumps should be used no earlier than 3 months later. After immunization with the measles, rubella and mumps vaccine, blood products can be administered no earlier than 2 weeks later. If it is necessary to use them earlier than this period, vaccination should be repeated after 3 months. If a tuberculin test is necessary, it should be performed 4-6 weeks after vaccination.
Special instructions.
Vaccination is not recommended during periods of increased incidence of serous meningitis. Vaccination of women of childbearing age is carried out in the absence of pregnancy and only if the woman agrees to be protected from conception within 1 month after vaccination. Accidental vaccination of a pregnant woman is not an indication for termination of pregnancy. Immunocompromised individuals who are not contraindicated for vaccination, like immunocompetent patients, may not develop an adequate immune response, resulting in the possibility of contracting measles, mumps and/or rubella, despite proper vaccination. Persons who are immunocompromised should be closely monitored for signs of measles, mumps and rubella. Persons temporarily exempt from vaccination should be monitored and vaccinated after contraindications are lifted. In order to identify contraindications, the doctor (paramedic) on the day of vaccination conducts a survey and examination of the vaccinated person with mandatory thermometry.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery.
No information available.
Release form.
Lyophilisate for preparing a solution for subcutaneous administration. 1 dose per ampoule. The pack contains 10 ampoules with instructions for use and an insert with the stacker number.
Storage conditions.
At temperatures from 2 to 8 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Transportation conditions.
In accordance with SP 3.3.2.3332-16 at temperatures from 2 to 8 °C.
Best before date.
2 years. A drug that has expired cannot be used.
Vacation conditions.
For medical and preventive institutions.
. Russia, 115088, Moscow, st. Dubrovskaya 1st, dvld. 15
Production address: Russia, 115088, Moscow, st. Dubrovskaya 1st, dvld. 15.
Marketing authorization holder/organization receiving consumer complaints.
JSC NPO Microgen. Russia, 115088, Moscow, st. Dubrovskaya 1st, dvld. 15.