Femoston® conti
The drug is prescribed only in the presence of symptoms that adversely affect the quality of life. All patients receiving HRT at least once a year require an assessment of the benefit-risk ratio. Therapy should be continued until the benefits of taking the drug outweigh the risk of adverse reactions. Experience with the drug in women over 65 years of age is limited.
Information about the risks associated with HRT in cases of premature menopause is limited. Due to the lower absolute risk in younger women, their benefit-risk ratio may be more favorable than in older women.
Medical examination
Before prescribing or resuming therapy with Femoston® conti, it is necessary to collect a complete medical and family history and conduct a general and gynecological examination (including the mammary glands) of the patient in order to identify possible contraindications and conditions requiring precautions.
During treatment with Femoston® conti, it is recommended to conduct periodic examinations, the frequency and nature of which are determined individually, but not less than once every 6 months. It is advisable to perform mammography for additional examination of the mammary glands. Women should be informed about those possible changes in the mammary glands that need to be reported to their doctor.
The use of estrogens may affect the results of the following laboratory tests: determination of glucose tolerance, study of thyroid and liver functions.
Endometrial hyperplasia
The risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer when patients use only estrogens depends on the dose and duration of treatment and increases from 2 to 12 times compared with patients not receiving therapy; the risk may remain elevated for 10 years after stopping therapy.
In women with a preserved uterus, HRT with estrogens alone is not recommended due to the increased risk of developing endometrial cancer.
Cyclic use of progestogen (at least 12 days of a 28-day cycle), or use of a continuous combined HRT regimen in women with a preserved uterus, may prevent the estrogen-increased risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
For the purpose of timely diagnosis, it is advisable to conduct ultrasound (US) screening and, if necessary, conduct a histological (cytological) examination.
Bloody vaginal discharge
In the first months of treatment with the drug, there may be bleeding and/or scanty spotting from the vagina. If such bleeding appears some time after the start of therapy or continues after cessation of treatment, its cause should be determined. An endometrial biopsy may be performed to rule out malignancy.
Venous thromboembolism
HRT is associated with a 1.3-3-fold risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), i.e. deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. The development of this phenomenon is most likely during the first year of HRT.
If there is a family history of thrombosis/thromboembolism in first-degree relatives aged less than 50 years, as well as a history of recurrent miscarriage, it is necessary to conduct a hemostasis study (screening reveals only some of the disorders of the blood coagulation system). If the patient is taking anticoagulants, a careful assessment of the benefit-risk ratio should be carried out when using Femoston® conti. Until a thorough assessment of the factors for the possible development of thromboembolism or the initiation of anticoagulant therapy is completed, Femoston® conti is not prescribed.
If a thrombophilic condition is detected in a family member and/or in the case of the seriousness or severity of the defect (for example, antithrombin III deficiency, protein S or C deficiency, as well as a combination of defects), Femoston® conti is contraindicated.
Since patients with diagnosed thrombophilic conditions have an increased risk of developing venous thromboembolism, the use of Femoston® conti, which increases this risk, is contraindicated.
In most cases, risk factors for developing VTE include: estrogen use, older age, major surgery, prolonged immobilization, obesity (body mass index > 30 kg/m2), pregnancy or the postpartum period, systemic lupus erythematosus and cancer. There is no consensus on the possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE.
To prevent VTE after surgery, prophylactic measures should be considered in all postoperative patients.
In case of prolonged immobilization after surgery, it is recommended to stop taking Femoston-conti 4-6 weeks before, and treatment should not be resumed until the woman’s mobility is completely restored.
If VTE develops after initiation of therapy, the drug should be discontinued and patients should be informed that they should contact their physician immediately if they experience any possible symptoms of thrombosis/thromboembolism (for example, tenderness or swelling of the lower extremities, sudden chest pain, shortness of breath).
Mammary cancer
In women receiving long-term HRT using estrogen alone or in combination with estrogen and progestogen, the incidence of breast cancer diagnosis increases, which returns to the original level within 5 years after cessation of therapy.
The increase in risk depends on the duration of HRT use. In women taking combined HRT for more than 5 years, the risk of developing breast cancer can increase up to 2 times.
Combination therapy with estrogen and progestogen
Results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (Women's Health Initiative (WHI)) and epidemiological studies have shown an increased risk of breast cancer in women taking combined estrogen and progestogen HRT. This increase becomes noticeable after approximately three years of therapy.
Estrogen-only therapy
According to the WHI study, there was no increased risk of breast cancer in women with a previous hysterectomy who received estrogen-only HRT.
Most observational studies showed a small increase in the risk of breast cancer, although this risk was markedly lower in women taking combined estrogen and progestogen therapy.
The increase in risk becomes noticeable after several years of using HRT drugs, and after stopping therapy it returns to the original level within several (maximum five) years.
While taking HRT medications, there may be an increase in the density of breast tissue during mammography, which can make it difficult to diagnose breast cancer.
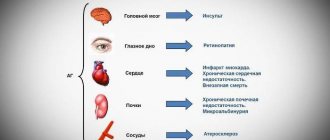
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is much less common than breast cancer. Epidemiological data obtained from a large meta-analysis suggest a small increase in the risk of developing ovarian cancer for women receiving HRT as estrogen monotherapy or combination therapy with estrogens and progestogens.
These studies (increased risk) become more apparent when therapy lasts more than five years, and after discontinuation, the risk gradually decreases over time. Findings from a number of other studies, including the WHI, indicate that combined HRT is associated with a similar or slightly lower risk of ovarian cancer.
Risk of ischemic stroke
Combination therapy with estrogen and progestogen or therapy with estrogen alone is associated with a 1.5-fold increase in the relative risk of ischemic stroke. The risk of hemorrhagic stroke does not increase when receiving HRT.
The relative risk does not depend on age, time of menopause, or duration of therapy. However, the baseline risk is highly dependent on age, so the overall risk of stroke in women taking HRT will increase with age.
Coronary heart disease (CHD)
Randomized controlled clinical trials provided no evidence of a protective effect of HRT against myocardial infarction in women with or without CAD who received combined estrogen and progestogen HRT or estrogen monotherapy.
Combination therapy with estrogen and progestogen
The relative risk of coronary heart disease during the use of combined estrogen and progestogen HRT is slightly increased. Because the absolute risk of CAD is highly dependent on age, the number of additional cases of CAD due to combined HRT use in healthy premenopausal women is very small, but increases with age. The risk is slightly higher in women over 60 years of age.
Estrogen-only therapy
Based on data from randomized controlled trials, there was no increased risk of coronary artery disease in women with a previous hysterectomy who received estrogen monotherapy.
Other states
Estrogens can cause fluid retention, which may adversely affect patients with impaired renal or cardiac function. This group of patients should be under medical supervision. Patients with hypertriglyceridemia while taking HRT medications should also be under medical supervision, because There are reports of very rare cases of significant increases in the concentration of triglycerides in the blood plasma, which contributes to the development of pancreatitis.
Estrogens increase the concentration of thyroxine-binding globulin, which leads to an overall increase in the concentration of circulating thyroid hormones, as measured by determination of plasma protein-bound iodine, thyroxine (T4) concentration - chromatographic or radioimmunoassay, or triiodothyronine (T3) - radioimmunoassay. A labeled triiodothyronine uptake test shows elevated levels of thyroxine-binding globulin. The concentrations of free hormones T3 and T4 usually do not change. Plasma concentrations of other binding proteins (eg, transcortin and sex hormone-binding globulin) may also be increased, resulting in increased concentrations of circulating corticosteroids and sex hormones.
The concentrations of free or biologically active hormones do not change. It is possible to increase the concentration of other plasma proteins (angiotensinogen/renin system, α-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin).
The use of HRT does not improve cognitive function. There are reports of an increased risk of developing dementia in women who start using HRT (combined or estrogen-containing only) after 65 years.
Femoston® conti is not a contraceptive.
Femoston conti tablet p/o film 1mg+5mg 28 pcs
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period; diagnosed or suspected breast cancer; diagnosed or suspected estrogen-dependent malignancies (for example, endometrial cancer); diagnosed or suspected progestogen-dependent neoplasms (for example, meningioma); bleeding from the vagina of unknown etiology; untreated endometrial hyperplasia; thrombosis (arterial and venous) and thromboembolism currently or in history (including thrombosis, deep vein thrombosis; pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, ischemic or hemorrhagic cerebrovascular disorders); multiple or pronounced factors of arterial or venous thrombosis associated with congenital or acquired predisposition, for example, protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, the presence of antibodies to phospholipids (anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant), angina pectoris, prolonged immobilization, severe forms obesity (body mass index more than 30 kg/m2), diseases of the cerebral vessels or coronary arteries, transient ischemic attacks, complicated lesions of the heart valve apparatus, atrial fibrillation; acute or chronic liver diseases currently or in history (before normalization of liver function tests), including malignant liver tumors; porphyria; hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome. Taking Femoston® conti should be discontinued if contraindications are identified and/or if the following conditions occur: jaundice and/or liver dysfunction; uncontrolled arterial hypertension; migraine-like headache that first appeared during the use of drugs for HRT. Carefully
HRT is prescribed to women if they have currently or in history been diagnosed with: uterine leiomyoma, endometriosis; the presence of risk factors for the occurrence of estrogen-dependent tumors (for example, 1st degree relatives with breast cancer); arterial hypertension; benign liver tumors; diabetes mellitus, both in the presence of vascular complications and in their absence; cholelithiasis; migraine or severe headache; systemic lupus erythematosus; history of endometrial hyperplasia; epilepsy; bronchial asthma; otosclerosis.
special instructions
The drug is prescribed only in the presence of symptoms that adversely affect the quality of life.
All patients receiving HRT are required to assess the benefit/risk ratio at least once a year. Therapy should be continued until the benefits of taking the drug outweigh the risk of side effects.
Experience with the drug in women over 65 years of age is limited.
Information about the risks associated with HRT in cases of premature menopause is limited.
Due to the lower absolute risk in younger women, their benefit/risk ratio may favor HRT compared with older women.
Medical examination
Before prescribing or resuming therapy with Femoston® conti, it is necessary to collect a complete medical and family history and conduct a general and gynecological examination (including the mammary glands) of the patient in order to identify possible contraindications and conditions requiring precautions. During treatment with Femoston® conti, it is recommended to conduct periodic examinations, the frequency and nature of which are determined individually, but not less than once every 6 months. It is advisable to perform mammography for additional examination of the mammary glands. Women should be informed about those possible changes in the mammary glands that need to be reported to their doctor.
The use of estrogens may affect the results of the following laboratory tests: determination of glucose tolerance, study of thyroid and liver functions.
Endometrial hyperplasia
The risk of developing endometrial hyperplasia and cancer when patients use only estrogens depends on the dose and duration of treatment and increases from 2 to 12 times compared with patients not receiving therapy; the risk may remain elevated for 10 years after stopping therapy.
In women with a preserved uterus, HRT with estrogens alone is not recommended due to the increased risk of developing endometrial cancer. Cyclic use of progestogen (at least 12 days of a 28-day cycle), or use of a continuous combined HRT regimen in women with a preserved uterus, may prevent the estrogen-increased risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
In women, the use of combined HRT for 5 years did not lead to an increased risk of developing endometrial cancer.
For the purpose of timely diagnosis, it is advisable to conduct ultrasound (US) screening and, if necessary, conduct a histological (cytological) examination.
Bloody vaginal discharge
In the first months of treatment with the drug, breakthrough bleeding and/or scanty spotting from the vagina may occur. If such bleeding appears some time after the start of therapy or continues after cessation of treatment, its cause should be determined. An endometrial biopsy may be performed to rule out malignancy.
Venous thromboembolism
HRT is associated with a 1.3-3-fold risk of developing venous thromboembolism (VTE), i.e. deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism. The development of this phenomenon is most likely during the first year of HRT.
If there are thromboembolic complications in first-degree relatives at a young age, as well as with a history of recurrent miscarriage, it is necessary to conduct a hemostasis study (during screening, only some disorders of the blood coagulation system are detected).
If the patient is taking anticoagulants, it is necessary to carefully consider the prescription of Femoston® conti from the point of view of the benefit/risk ratio. Until a thorough assessment of the factors for the possible development of thromboembolism or the initiation of anticoagulant therapy is completed, Femoston® conti is not prescribed.
If a thrombophilic condition is detected in a family member and/or in case of seriousness or severity of the defect (for example, deficiency of antithrombin III, protein S or C, as well as a combination of defects), Femoston® conti is contraindicated.
Since patients with diagnosed thrombophilic conditions have an increased risk of developing venous thromboembolism, the use of Femoston® conti, which increases this risk, is contraindicated.
In most cases, risk factors for developing VTE include: estrogen use, older age, major surgery, prolonged immobilization, obesity (body mass index > 30 kg/m2), pregnancy or the postpartum period, systemic lupus erythematosus and cancer. There is no consensus on the possible role of varicose veins in the development of VTE.
To prevent VTE after surgery, prophylactic measures should be considered in all postoperative patients.
In case of prolonged immobilization after surgery, it is recommended to stop taking Femoston® conti 4-6 weeks before, and treatment should not be resumed until the woman has completely recovered mobility.
If VTE develops after initiation of therapy, the drug should be discontinued and patients should be informed that they should contact their physician immediately if they experience any potential thromboembolic symptoms (eg, tenderness or swelling of the lower extremities, sudden pain in the chest, shortness of breath).
Mammary cancer
In women receiving long-term HRT using estrogen alone or in combination with estrogen and progestogen, the incidence of breast cancer diagnosis increases, which returns to the original level within 5 years after cessation of therapy.
The increase in risk depends on the duration of HRT use. In women taking combined HRT for more than 5 years, the risk of developing breast cancer can increase up to 2 times.
Combination therapy with estrogen and progestogen
Results from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (Women's Health Initiative (WHI)) and epidemiological studies have shown an increased risk of breast cancer in women taking combined estrogen and progestogen HRT. This increase becomes noticeable after approximately three years of therapy.
Estrogen-only therapy
According to the WHI study, there was no increased risk of breast cancer in women with a previous hysterectomy who received estrogen-only HRT.
Most observational studies showed a small increase in the risk of breast cancer, but the risk was markedly lower in women taking combined estrogen and progestogen therapy.
The increase in risk becomes noticeable after several years of using HRT drugs, and after stopping therapy it returns to the original level within several (maximum five) years.
While taking HRT medications, there may be an increase in the density of breast tissue during mammography, which can make it difficult to diagnose breast cancer.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is much less common than breast cancer. Epidemiological data obtained from a large meta-analysis suggest a small increase in the risk of developing ovarian cancer for women receiving HRT as estrogen monotherapy or combination therapy with estrogens and progestogens.
These studies (increased risk) become more apparent when therapy lasts more than five years, and after discontinuation, the risk gradually decreases over time. Findings from a number of other studies, including the WHI, indicate that combined HRT is associated with a similar or slightly lower risk of ovarian cancer.
Risk of ischemic stroke
Combination therapy with estrogen and progestogen or therapy with estrogen alone is associated with a 1.5-fold increase in the relative risk of ischemic stroke. The risk of hemorrhagic stroke does not increase when receiving HRT.
The relative risk does not depend on age, time of menopause, or duration of therapy. However, the baseline risk is highly dependent on age, so the overall risk of stroke in women taking HRT will increase with age.
Coronary heart disease (CHD)
Randomized controlled clinical trials provided no evidence of a protective effect of HRT against myocardial infarction in women with or without CAD who received combined estrogen and progestogen HRT or estrogen monotherapy.
Combination therapy with estrogen and progestogen
The relative risk of coronary heart disease during the use of combined estrogen and progestogen HRT is slightly increased. Because the absolute risk of CAD is highly dependent on age, the number of additional cases of CAD due to combined HRT use in healthy premenopausal women is very small, but increases with age. The risk is slightly higher in women over 60 years of age.
Estrogen-only therapy
Based on data from randomized controlled trials, there was no increased risk of coronary artery disease in women with a previous hysterectomy who received estrogen monotherapy.
Other states
Estrogens can cause fluid retention, which may adversely affect patients with impaired renal or cardiac function. This group of patients should be under medical supervision.
Patients with hypertriglyceridemia while taking HRT medications should also be under medical supervision, because There are reports of very rare cases of significant increases in the concentration of triglycerides in the blood plasma, which contributes to the development of pancreatitis.
Estrogens increase the concentration of thyroxine-binding globulin, which leads to an overall increase in the concentration of circulating thyroid hormones, as measured by determination of plasma protein-bound iodine, thyroxine (T4) concentration - chromatographic or radioimmunoassay, or triiodothyronine (T3) - radioimmunoassay. A labeled triiodothyronine uptake test shows elevated levels of thyroxine-binding globulin. The concentrations of free hormones T3 and T4 usually do not change.
Plasma concentrations of other binding proteins (eg, transcortin and sex hormone-binding globulin) may also be increased, resulting in increased concentrations of circulating corticosteroids and sex hormones.
The concentrations of free or biologically active hormones do not change.
It is possible to increase the concentration of other plasma proteins (angiotensinogen/renin system, α-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin).
The use of HRT does not improve cognitive function. There are reports of an increased risk of developing dementia in women who start using HRT (combined or estrogen-containing only) after 65 years.
Femoston® conti is not a contraceptive.