Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
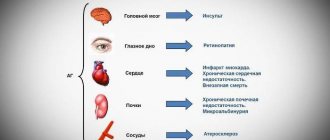
The drug has an arrhythmic effect, antianginal , lowers blood pressure by reducing the formation of cyclic AMP from adenosine triphosphate . The intracellular current of calcium ions decreases, the processes of excitation and inhibition are inhibited, heart rate decreases, and myocardial .
Due to the fact that beta2-adrenergic receptors are inhibited, the activity of alpha-adrenergic receptors . In this regard, in the first few days of using Coronal, OPSS , but after a couple of days, it returns to its normal level.
During treatment with the drug, the reninangiotensin system , the sensitivity of baroreceptors returns to normal, and, as a result, the minute volume of blood .
Due to the decrease in the heart's oxygen demand, due to improved myocardial perfusion and prolongation of diastole , the drug has a strong and lasting antianginal effect . The antiarrhythmic effect of the drug is associated with a combination of the factors listed above, as well as the ability to reduce the rate of excitation of sinus and ectopic pacemakers .
Bisoprolol is very well absorbed into the bloodstream, about 90% of the drug enters it. It reaches maximum concentration after 3 hours, about 30% of the active substance binds to blood proteins, and is metabolized mainly in the liver. Excretion is carried out through the kidneys within 10-12 hours.
Coronal 5 mg 60 pcs. film-coated tablets in Moscow
Pharmacological action: Pharmacodynamics
A selective β1-blocker, without its own sympathomimetic activity, does not have a membrane-stabilizing effect. It has only slight affinity for β2-adrenergic receptors of the smooth muscles of the bronchi and blood vessels, as well as for β2-adrenergic receptors involved in the regulation of metabolism. Therefore, bisoprolol generally does not affect airway resistance and metabolic processes in which β2-adrenergic receptors are involved.
The selective effect of bisoprolol on β1-adrenergic receptors persists beyond the therapeutic range.
Bisoprolol does not have a pronounced negative inotropic effect. Its maximum effect is achieved 3–4 hours after oral administration. Even when bisoprolol is used once a day, its therapeutic effect persists for 24 hours due to the 10-12 hour T1/2 from blood plasma. As a rule, the maximum reduction in blood pressure is achieved 2 weeks after the start of treatment.
Bisoprolol reduces the activity of the sympathoadrenal system by blocking β1-adrenergic receptors of the heart.
When administered once orally in patients with coronary artery disease without signs of CHF, bisoprolol reduces heart rate, reduces the stroke volume of the heart and, as a result, reduces the ejection fraction and myocardial oxygen demand. With long-term therapy, the initially elevated TPR decreases. A decrease in renin activity in blood plasma is considered as one of the components of the antihypertensive effect of β-blockers.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
Bisoprolol is almost completely (>90%) absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Its bioavailability due to minor metabolization during the initial passage through the liver (>10%) is about 90% after oral administration. Food intake does not affect bioavailability. Bisoprolol exhibits linear kinetics, with its plasma concentration being proportional to the dose taken in the range from 5 to 20 mg. Tmax in blood plasma is 2–3 hours.
Distribution
Bisoprolol is distributed quite widely. Vd is 3.5 l/kg. The binding to plasma proteins reaches approximately 30%.
Metabolism
Metabolized via the oxidative pathway without subsequent conjugation. All metabolites are polar (water-soluble) and are excreted by the kidneys. The main metabolites found in blood plasma and urine do not exhibit pharmacological activity. Data obtained from experiments with human liver microsomes in vitro
, show that bisoprolol is metabolized primarily by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme (about 95%), and the CYP2D6 isoenzyme plays only a minor role.
Removal
The clearance of bisoprolol is determined by the balance between excretion by the kidneys unchanged (>50%) and metabolism in the liver (>50%) to metabolites, which are also excreted by the kidneys. The total clearance is 15 l/hour. T1/2 - 10–12 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in different patient groups
There is no information on the pharmacokinetics of bisoprolol in patients with CHF and concurrent impairment of liver or kidney function.
Indications for use of Coronal
Indications for the use of Coronal tablets are arterial hypertension , coronary heart disease and angina pectoris .
Sinus tachycardia is also considered an indication for the use of Coronal ; extrasystole (ventricular and supraventricular); prolapse ; arrhythmia caused by thyrotoxicosis .
Indications for Coronal 5 mg include the prevention of myocardial infarction and minor heart rhythm disturbances.
Coronal
Combinations not recommended
Slow calcium channel blockers (SCBCs) of the verapamil group and, to a lesser extent, the diltiazem group, when used simultaneously with bisoprolol, can have a negative effect on AV conduction and myocardial contractility. Intravenous administration of verapamil to patients receiving beta-blocker treatment can lead to a significant decrease in blood pressure and AV blockade.
Centrally acting antihypertensive drugs (for example, clonidine, methyldopa, moxonidine, rilmenidine), when used together with bisoprolol, can reduce heart rate and cardiac output, and also cause vasodilation due to a decrease in central sympathetic tone. Abrupt withdrawal of beta-blockers may increase the risk of developing the syndrome of “rebound” rise in blood pressure).
Combinations requiring special caution
Dihydropyridine BMCCs, such as nifedipine, felodipine, amlodipine, when used simultaneously with bisoprolol, may increase the risk of a sharp decrease in blood pressure. In patients with chronic heart failure, the risk of further deterioration in the pumping function of the ventricles of the heart cannot be excluded.
The use of class I antiarrhythmic drugs (for example, quinidine, disopyramide, lidocaine, phenytoin, flecainide, propafenone) during treatment with bisoprolol may adversely affect AV conduction and reduce myocardial contractility.
Concomitant use of class III antiarrhythmic drugs (eg, amiodarone) and bisoprolol is associated with an increased risk of developing AV conduction disorders.
Concomitant use of bisoprolol and parasympathomimetic drugs (for example, pilocarpine, choline alfoscerate) may increase the risk of developing AV conduction disorders and bradycardia.
Topical beta-blockers (for example, eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma) may enhance the systemic effects of bisoprolol (lowering blood pressure and heart rate). The hypoglycemic effect of insulin and hypoglycemic agents may be enhanced when used together with bisoprolol. Blockade of beta-adrenergic receptors can mask the symptoms of developing hypoglycemia (tachycardia, increased blood pressure) in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Phenytoin, when administered intravenously, and drugs for inhalation anesthesia increase the severity of the cardiodepressive effect and the likelihood of a significant decrease in blood pressure (see section “Special Instructions”).
The use of cardiac glycosides together with bisoprolol helps reduce heart rate and increases the risk of developing bradycardia and/or AV block.
The antihypertensive effect of bisoprolol is weakened by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (sodium ion retention and blockade of prostaglandin synthesis by the kidneys), glucocorticosteroids and estrogens (sodium ion retention).
Bisoprolol in combination with beta-sympathomimetic agents (isoprenaline and dobutamine) may weaken the therapeutic effect of both drugs. Sympathomimetics that activate beta and alpha adrenergic receptors, in combination with bisoprolol, can cause an increase in blood pressure. Such interactions are more likely when using non-selective beta-blockers.
The simultaneous use of bisoprolol with antihypertensive drugs, as well as with other drugs that can lower blood pressure (for example, tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenothiazines) increases the risk of an excessive decrease in blood pressure.
The simultaneous use of bisoprolol with MAO inhibitors is contraindicated (with the exception of MAO type B inhibitors), due to a significant increase in the antihypertensive effect; the break in treatment between taking MAO inhibitors and bisoprolol should be at least 14 days.
The likelihood of disturbances in cardiac automatism, conduction and contractility of the myocardium increases (mutually) against the background of combination therapy with quinidine drugs (mefloquine, chloroquine) and bisoprolol.
Tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants, antipsychotics (neuroleptics, including sultopride), ethanol, sedative and hypnotic drugs that inhibit the activity of the central nervous system, in combination with bisoprolol, can provoke heart rhythm disturbances, bradycardia and a decrease in blood pressure.
There is a decrease in the antihypertensive effect of bisoprolol with the use of adrenaline and norepinephrine.
When used simultaneously with baclofen or amifostine, an increase in antihypertensive effect is observed.
Contraindications
Prescription and use of the drug is contraindicated in
- allergies to the active substance or other components;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- bronchial asthma;
- cardiogenic or other type of shock ;
- acute heart failure;
- sinoarterial blockade;
- severe bradycardia ;
- a decrease in blood pressure below 100 mm. Hg;
- myocardial infarction;
- AV block , especially second and third degree;
- with Raynaud's disease .
The drug is not prescribed to children or nursing women.
The medicine cannot be combined with MAO inhibitors, floctafenine, or sultopride .
CORONAL
special instructions
The use of the drug CORONAL in children under 18 years of age is contraindicated, since the effectiveness and safety have not been established.
Monitoring of patients taking CORONAL should include measuring heart rate and blood pressure (at the beginning of treatment - daily, then once every 3-4 months), conducting an electrocardiogram, determining the concentration of glucose in the blood in patients with diabetes mellitus (once every 4 months). -5 months). In elderly patients, it is recommended to monitor renal function (once every 4-5 months).
The patient should be taught how to calculate the heart rate and instructed about the need for medical consultation if the heart rate is less than 50 beats/min.
Before starting treatment, it is recommended to conduct a study of external respiratory function in patients with a burdened bronchopulmonary history.
In approximately 20% of patients with angina, beta blockers are ineffective. The main causes are severe coronary atherosclerosis with a low ischemic threshold (heart rate less than 100 beats/min) and increased left ventricular end-diastolic volume, impairing subendocardial blood flow.
In smokers, the effectiveness of beta-blockers is lower.
Patients using contact lenses should take into account that during treatment the production of tear fluid may decrease.
When used in patients with pheochrocytoma, there is a risk of developing paradoxical arterial hypertension (if effective alpha-blockade is not previously achieved).
In thyrotoxicosis, bisoprolol may mask certain clinical signs of thyrotoxicosis (for example, tachycardia). Abrupt withdrawal in patients with thyrotoxicosis is contraindicated because it can increase symptoms.
In diabetes mellitus, it can mask tachycardia caused by hypoglycemia. Unlike non-selective beta-blockers, it practically does not enhance insulin-induced hypoglycemia and does not delay the restoration of blood glucose concentrations to normal levels.
When taking clonidine simultaneously, it can be discontinued only a few days after discontinuation of the drug CORONAL.
It is possible that the severity of the hypersensitivity reaction may increase and there will be no effect from usual doses of epinephrine against the background of a burdened allergic history. If planned surgical treatment is necessary, the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the start of general anesthesia. If the patient took the drug before surgery, he should select a drug for general anesthesia with minimal negative inotropic effect.
Reciprocal activation of the vagus nerve can be eliminated by intravenous atropine (1-2 mg).
Medicines that reduce the supply of catecholamines (including reserpine) can enhance the effect of beta-blockers, so patients taking such combinations of drugs should be under constant medical supervision to detect a pronounced decrease in blood pressure or bradycardia.
Patients with bronchospastic diseases can be prescribed cardioselective beta-blockers in case of intolerance and/or ineffectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs. An overdose is dangerous due to the development of bronchospasm.
If increasing bradycardia (less than 50 beats/min), a pronounced decrease in blood pressure (systolic blood pressure below 100 mmHg), or AV blockade occurs in elderly patients, it is necessary to reduce the dose or stop treatment.
It is recommended to discontinue therapy if depression develops.
The drug should be discontinued before testing the levels of catecholamines, normetanephrine and vanillinmandelic acid in the blood and urine; antinuclear antibody titers.
Features of the action of the drug when first taken or when discontinued
Treatment should not be abruptly interrupted due to the risk of developing withdrawal syndrome (severe arrhythmias and myocardial infarction). Cancellation is carried out gradually, reducing the dose over 2 weeks or more (reduce the dose by 25% in 3-4 days).
Side effects of Coronal
The most common side effects:
- dry mouth, diarrhea, nausea, constipation;
- asthenia, drowsiness, depression , headache;
- bradycardia , vasospasm , decreased blood pressure ;
- allergic reactions on the skin, hyperemia ;
- arthralgia , pain and cramps in the calf muscles.
Cases of agranulocytosis , potency disorders , thrombocytopenia , and withdrawal syndrome have been reported.
Instructions for use, Coronal tablets (Method and dosage)
The tablets are taken in the morning, 20 minutes before breakfast, whole, without chewing or splitting.
According to the instructions for use of Coronal 5 mg, the starting daily dose is from 2.5 to 5 mg. Then, according to indications, the dosage can be increased to 10 mg. The maximum amount of bisoprolol taken per day is 20 mg.
For patients with severe liver and kidney dysfunction, the daily dosage should not exceed 10 mg.
Coronal, 100 pcs., 10 mg, film-coated tablets
When prescribing Coronal, heart rate and blood pressure should be regularly monitored (at the beginning of treatment - daily, then - once every 3-4 months), an ECG should be performed, and blood glucose levels should be determined in patients with diabetes (once every 4-5 months). In elderly patients, it is recommended to monitor renal function (once every 4-5 months).
The patient should be trained in the method of calculating heart rate and instructed about the need for medical consultation if the heart rate is less than 50 beats/min.
Before starting treatment, it is recommended to conduct a study of external respiratory function in patients with a burdened bronchopulmonary history.
It should be taken into account that in approximately 20% of patients with angina, beta-blockers are ineffective due to severe coronary atherosclerosis with a low ischemic threshold (heart rate less than 100 beats/min) and increased end-diastolic volume of the left ventricle, which impairs subendocardial blood flow.
In smoking patients, the effectiveness of beta-blockers is reduced.
Patients using contact lenses should take into account that during treatment the production of tear fluid may decrease.
When using Coronal in patients with pheochromocytoma, there is a risk of developing paradoxical arterial hypertension (if effective alpha-blockade is not previously achieved).
Bisoprolol may mask certain clinical signs of thyrotoxicosis (eg, tachycardia). Abrupt withdrawal of Coronal in patients with thyrotoxicosis is contraindicated, as it can increase the symptoms of the disease.
In diabetes mellitus, bisoprolol can mask tachycardia caused by hypoglycemia. Unlike non-selective beta-blockers, it practically does not enhance insulin-induced hypoglycemia and does not delay the restoration of blood glucose concentrations to normal levels.
When used simultaneously with clonidine, the latter can be discontinued only a few days after discontinuation of the drug Coronal.
It is possible that the severity of the hypersensitivity reaction may increase and there will be no effect from usual doses of epinephrine against the background of a burdened allergic history.
If planned surgical treatment is necessary, the drug should be discontinued 48 hours before the start of general anesthesia. If the patient took the drug before surgery, he should select a drug for general anesthesia with minimal negative inotropic effect.
Reciprocal activation of the vagus nerve can be eliminated by intravenous atropine (1-2 mg).
Medicines that reduce the reserves of catecholamines (including reserpine) can enhance the effect of beta-blockers, so patients taking such combinations of drugs should be under constant medical supervision to detect a pronounced decrease in blood pressure or bradycardia.
Patients with concomitant bronchospastic diseases can be prescribed cardioselective adrenergic blockers in case of intolerance and/or ineffectiveness of other antihypertensive drugs. An overdose is dangerous due to the development of bronchospasm.
If increasing bradycardia (less than 50 beats/min), a pronounced decrease in blood pressure (systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg), or AV blockade occurs in elderly patients, it is necessary to reduce the dose or stop treatment.
It is recommended to discontinue therapy if depression develops.
The drug should be discontinued before testing the content of catecholamines, normetanephrine, vanillinmandelic acid, and antinuclear antibody titers in the blood and urine.
Treatment should not be abruptly interrupted due to the risk of developing severe arrhythmias and myocardial infarction. Cancellation is carried out gradually, reducing the dose over 2 weeks or more (the dose is reduced by 25% in 3-4 days).
Use in pediatrics
The use of the drug Coronal in children and adolescents under the age of 18 is contraindicated, because efficacy and safety have not been established.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Overdose
Symptoms of overdose are: bradycardia, arrhythmia, low blood pressure, acrocyanosis, dizziness, fainting, bronchospasm .
In case of overdose, you should rinse the stomach, take enterosorbents , drugs to eliminate symptoms ( atropine, epinephrine, lidocaine, dopamine, dobutamine, glucagon, diazepam ).
Interaction
Do not take with other beta blockers .
Combine with caution with iodine-containing radiocontrast agents , phenytoin , hydrocarbon derivatives , allergen extracts for skin tests, Nifedipine , coumarins , muscle relaxants, tricyclic antidepressants, neuroleptics , sedatives , ethanol , MAO inhibitors .
When Coronal is combined with lidocaine and xanthines , the plasma concentration of the latter increases.
Diabetics should be especially careful, since under the influence of the drug, the effectiveness of insulin may change, and symptoms of hypoglycemia may not appear.
The therapeutic effect of the drug is weakened when combined with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , corticosteroids , and estrogens .
Biosprolol affects the effectiveness of cardiac clicosides , reserpine , guanfacine , methyldopa , verapamil , diltiazem , amiodarone .
Diuretics, clonidine and hydralazine in combination with medication can greatly lower blood pressure
The combination of Coronal and Sulfasalazine increases the concentration of bisoprolol in the blood plasma, and rimafmpicin reduces the half-life of the drug.
Taking Baclofen, amifostine, floctaphanine, mefloquine, chlorquinine, adrenaline, norepinephrine and Coronal is considered undesirable.
Instructions for use CORONAL
The use of the drug Coronal, especially in patients with coronary artery disease, cannot be abruptly stopped, as this can lead to an exacerbation of the disease.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with arterial hypertension or angina pectoris with concomitant heart failure.
The drug should be used with caution when:
- diabetes mellitus with sharp fluctuations in blood glucose levels, because symptoms of hypoglycemia may be masked (for example: tachycardia, palpitations, increased sweating);
- strict diet;
- desensitization;
- AV blockade of the first degree;
- Prinzmetal's angina;
- impaired peripheral circulation (intensification of complaints is possible at the beginning of therapy);
- psoriasis, incl. family history (beta blockers should be prescribed only after a careful assessment of the benefit/risk ratio).
For bronchial asthma or other chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, concomitant therapy with bronchodilators is indicated. In some cases, while taking the drug, patients with bronchial asthma may require higher doses of beta2-sympathomimetics due to increased airway tone.
Like other beta blockers, bisoprolol may increase sensitivity to allergens and increase anaphylactic reactions. In such cases, treatment with adrenaline does not always provide a positive therapeutic effect.
It is imperative to notify the anesthesiologist about taking beta-blockers. When using Coronal® before surgery, the dose should be gradually reduced and the drug should be stopped 48 hours before general anesthesia.
For patients with pheochromocytoma, Coronal® is prescribed only against the background of previous therapy with alpha-blockers.
Symptoms of thyrotoxicosis may be masked while taking the drug Coronal®.
The use of Coronal® during doping control can lead to positive results.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
In the study, the use of bisoprolol did not affect the ability to drive vehicles. However, due to individual reactions to taking the drug, the ability to drive a car or operate machinery may be impaired. This circumstance must be especially taken into account at the beginning of therapy and when changing the dose, as well as when taken in combination with alcohol.
Analogues of Coronal
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Biol
Metocard
Metozok
Nebilet
Nebilong
Betaxolol
Bisogamma
Aritel
Cordinorm
Vasocardin
Corvitol
Bidop
Bisoprolol
Nebivolol
Biprol
Bisoprol
Concor Cor
Lokren
Concor
Niperten
The closest analogues of Coronal are: bicard, bisocard, bisoprolol, bisoprofar, dorez, concor, cordinorm, corbis, bisostad, biprolol .
Other analogues of the drug: azoprol, metocor, atenol, atenolol, atenobene, betak, betalok, breviblock, corvitol, egilok, betacor, vasocardin, corvtol, lokren, metoprolol, metoprolol tartrate, nebivovol, nebikor, nebilong, nebitrend, tenolol .
Coronal price (where to buy)
The price of Coronal for 30 pieces of 5 mg is 121 rubles. The same amount of the drug in a dosage of 10 mg costs approximately 209 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Coronal tablets p.p.o.
10 mg 60 pcs. Zentiva a.s./Saneka Pharmaceuticals a.s. RUB 296 order - Coronal tablets p.p.o. 5 mg 100 pcs. Zentiva a.s./Saneka Pharmaceuticals a.s.
RUB 288 order
- Coronal tablets p.p.o. 5 mg 60 pcs. Zentiva a.s./Saneka Pharmaceuticals a.s.
RUB 181 order
- Coronal tablets p.p.o. 10 mg 100 pcs. Zentiva a.s./Saneka Pharmaceuticals a.s.
475 rub. order
- Coronal tablets p.p.o. 5 mg 30 pcs. Zentiva a.s./Saneka Pharmaceuticals a.s.
121 rub. order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Coronal (tab.p.pl/vol. 5mg No. 60)Saneca
166 RUR order
- Coronal (tab.p.pl/vol. 10 mg No. 60) Saneca
RUB 281 order
- Coronal (tab.p.pl/vol. 10mg No. 30)Zentiva
185 rub. order
- Coronal tablets 5 mg No. 100Zentiva
RUB 279 order
- Coronal (tab.p.pl/vol. 5 mg No. 60) Sanofi Russia JSC/Saneca
RUB 174 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Coronal 10 mg No. 60 tablets AT Saneka Pharmaceuticals, Slovak Republic/Zentiva LLC Czech Republic
88 UAH order - Coronal 5 mg No. 60 tablets AT Saneka Pharmaceuticals, Slovak Republic/Zentiva LLC Czech Republic
59 UAH order
- Coronal 5 mg N30 tablets AT Saneka Pharmaceuticals, Slovak Republic/Zentiva LLC Czech Republic
33 UAH order
- Coronal 10 mg N30 tablets AT Saneka Pharmaceuticals, Slovak Republic/Zentiva LLC Czech Republic
59 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- Coronal tablets Coronal tablets. 10 mg No. 60, Saneca Pharmaceuticals
99 UAH order
- Coronal tablets Coronal tablets. p/o 5 mg No. 30, Saneca Pharmaceuticals
38 UAH order
- Coronal tablets Coronal tablets. 5mg No. 60, Saneca Pharmaceuticals
73 UAH order
- Coronal tablets Coronal tablets. p/o 10 mg No. 30, Saneca Pharmaceuticals
63 UAH order
show more