Instructions for use TAVANIC
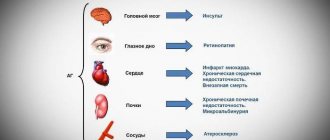
When prescribing the drug to elderly patients, it should be borne in mind that patients in this group often have impaired renal function.
In patients with previous brain damage (including stroke or severe brain injury), the use of Tavanic may provoke seizures.
In severe pneumonia caused by pneumococcus, the use of Tavanic may not be effective enough.
Hospital-acquired infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa may require combination therapy.
Severe allergic reactions may sometimes be preceded by milder skin manifestations. However, these reactions can develop after the first dose - a few minutes or hours after using the drug.
To avoid the development of photosensitivity, patients should avoid exposure to the sun or UV exposure (for example, exposure to the sun at high altitudes or visiting a solarium).
If pseudomembranous colitis is suspected, Tavanik should be discontinued immediately and appropriate treatment should be initiated. In such cases, drugs that inhibit intestinal motility should not be used.
In elderly patients, when using the drug Tavanic, the likelihood of developing tendinitis increases. The use of corticosteroids appears to increase the risk of tendon rupture. If tendonitis is suspected, Tavanik should be immediately discontinued and appropriate treatment should be initiated, ensuring a state of rest in the affected area.
Tavanic should be taken at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking sucralfate, magnesium- or aluminum-containing antacids, as well as iron salts.
With the simultaneous use of vitamin K antagonists, control of the blood coagulation system is necessary.
Tavanic should be prescribed with caution simultaneously with probenecid and cimetidine, which block tubular secretion. This applies primarily to patients with impaired renal function.
During treatment you should avoid drinking alcohol.
Experience with other quinolones suggests that they can cause exacerbation of porphyria. A similar effect cannot be excluded when using the drug Tavanic.
When using fluoroquinolones in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, hemolysis of erythrocytes is possible. Considering this, treatment with Tavanik in this category of patients should be carried out with extreme caution.
The recommended duration of administration should be strictly adhered to, which should be at least 60 minutes for 100 ml of infusion solution. Experience with the use of levofloxacin shows that increased heart rate and a transient drop in blood pressure may occur during infusion. In rare cases, vascular collapse may occur. If a significant drop in blood pressure is observed during the infusion, the administration is stopped immediately.
Elderly patients with normal renal function do not require dosage adjustment.
Use in pediatrics
Tavanic is contraindicated for the treatment of children and adolescents due to the likelihood of damage to articular cartilage.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Tavanic can cause dizziness or stiffness, drowsiness, visual disturbances, and also reduce the ability to concentrate and the speed of psychomotor reactions. This should be taken into account if it is necessary to use the drug in persons whose activities involve driving a car, servicing machines and mechanisms, or performing work in an unstable position.
Features of the composition and action of Tavanik
The medicine is produced in tablets and solutions for droppers. The composition of the tablet form is presented:
- levofloxacin;
- crospovidone;
- MCC;
- sodium stearyl furamate;
- hypromellose;
- macrogol 800;
- food additive E 171 and E 172;
- talcum powder
100 ml of Tavanika solution contains levofloxacin, sodium chloride and hydroxide, water, concentrated chlorous acid.
The instructions indicate that the antibiotic affects the production of protein in foreign substances, which provokes the death of pathogenic organisms. Tavanik does not apply:
- with Staphylococcus aureus;
- certain strains of pneumococcus;
- gonococcus, enterococcus;
- Salmonella, Shigella, Pseudomonas.
After administration, the active components penetrate almost all internal organs within 2 hours. Residues are excreted by the kidneys after 6-8 hours; in case of renal pathologies, indicators may change.
Dosages and methods of taking Tavanik
The frequency of use, dose and duration of therapeutic procedures depend on the current disease and its complexity, and the general condition of the body.
Tavanik tablets are taken orally, they can be divided and crushed:
- sinusitis, bronchitis, prostatitis, damage to the urinary tract - from 0.25 to 0.5 g daily, therapy lasts 3-14 days, for prostatitis - lasts 28 days;
- infectious lesion of the dermis, hypodermis - from 0.25 to 0.5 g up to 2 doses per day, for 7-14 days;
- damage to the abdominal part or septicemia - 500 mg of the drug up to 14 procedures per day.
Kidney pathologies require a reduction in standard dosages.
The solution in droppers is administered slowly over 60 minutes. The duration of therapy does not exceed 2 weeks; if it is necessary to increase the treatment period, the patient is transferred to tablets.
Analogs
If adverse reactions to treatment or signs of intolerance to Tavanik occur, it is replaced with a more suitable medication. The list of analogues is presented:
- Zolevoy, Leflokad, Levobact;
- Glevo, Levobax, Levocin;
- Levoxa, Lebel, Levomak;
- Levotor, Levoximed, Levostad;
- Levoflox, Levocel, Levofloxacin;
- Levoflocin, Leflock, Loxof;
- Tigeron, Lexid, Floxium.
Changes in the therapeutic regimen can only be made by the attending physician. Independent selection of analogues is prohibited; an incorrectly selected antibiotic can cause serious harm to health.
Reviews
According to doctors, the drug has all the characteristics declared by the manufacturer. If the recommendations from the instructions are followed exactly, the antibiotic is easily tolerated and does not provoke the development of side effects. During therapy, patients should increase the amount of fermented milk products consumed, drink a lot and comply with the requirements for maintaining a sleep-wake schedule.
There are different reviews about Tavanika on the forums; some patients refused treatment procedures due to the risk of developing non-standard responses of the body. People who have undergone a therapeutic course emphasize its effectiveness against many infectious diseases. Following the doctor's recommendations on dosages and duration of treatment allows the body to easily tolerate the antibiotic. Some patients experienced slight dizziness and headaches while taking Tavanic.
Clinical diagnosis of pneumonia
Usually the onset of the disease is acute, less often gradual, sometimes the development of pneumonia is preceded by an episode of acute respiratory viral infection or tracheobronchitis. Clinical diagnosis of pneumonia is usually [5] based on such signs as fever to febrile and subfebrile levels, cough (usually with sputum production). Some patients experience chills, chest pain, and shortness of breath. With lobar pneumonia, signs of consolidation of the lung tissue are revealed - shortening of the percussion sound, bronchial breathing, increased vocal tremors. The phenomenon of crepitus is characteristic, although local fine-bubble rales are most often detected on auscultation.
Severe pneumonia is characterized by the following clinical signs [3–5]: • bilateral, multilobar localization or abscess formation; • rapid progression of the process (increase in the infiltration zone by 50% or more within 48 hours of observation); • severe respiratory failure; • severe vascular insufficiency requiring the use of pressor amines; • leukopenia less than 4 or hyperleukocytosis more than 20 × 1000/μl with the number of immature neutrophils more than 10%; • oliguria or manifestations of acute renal failure.
In severe cases of pneumonia, life-threatening manifestations such as infectious-toxic shock, distress syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, and multiple organ failure are often diagnosed. Severe pneumonia is diagnosed in the presence of 2–3 or more of the listed signs.
Elderly and senile individuals may not have the classic manifestations of pneumonia, but may experience fever, hypothermia, confusion, shortness of breath (or a combination of these symptoms).
When examining the patient, you should carefully record dangerous symptoms: shortness of breath, hypotension, oliguria, severe bradycardia/tachycardia, confusion. Of the possible complications, pleurisy is the most common, and abscess formation is less common. However, we should not forget about more rare and severe complications: meningitis, brain abscess, arthritis, pericarditis, endocarditis, peritonitis, pleural empyema.
Pneumonia of mycoplasma nature is characterized by signs of pharyngo-laryngo-tracheobronchitis at the onset of the disease, myalgia, profuse sweating (even with low subfebrility), an obsessive dry “whooping cough” cough of an unusually low timbre (manifestations of tracheobronchial dyskinesia). The same features (except for myalgia and profuse sweating) are common with chlamydial pneumonia.
Contraindications and indications for treatment with Tavanik
The instructions recommend prescribing tablets for therapy:
- bronchitis and exacerbations of the chronic form of the disease;
- urinary tract infections - ordinary and complicated;
- pneumonia, sinusitis, septicemia;
- bacterial or chronic prostatitis;
- complex forms of tuberculosis;
- infectious lesions of the dermis, abdominal cavity or soft tissues.
Tavanic in solution is indicated for patients with pneumonia, tuberculosis, bacteremia, and genitourinary infections.
The drug is contraindicated in case of individual intolerance to the component composition, epilepsy. The medicine is not prescribed to pregnant and lactating women, minor patients, or persons undergoing fluoroquinolone therapy.
Adverse reactions
During therapeutic procedures, a non-standard response to the drug may occur. Tavanik is capable of provoking:
- dyspeptic disorders, discomfort in the epigastric and abdominal areas;
- drop in blood pressure, sinus tachycardia;
- decreased visual acuity, extraneous noise in the ears;
- dermatological rash, obsessive itching, redness;
- joint pain, anorexia, drop in blood glucose levels;
- exacerbation or development of fungal infection;
- breathing problems, changes in sleep patterns, unreasonable anxiety;
- confused consciousness.
When injecting the solution, redness and an inflammatory process may form at the needle entry point. Rarely, fever associated with phlebitis is observed.
Evidence-based criteria for diagnosis
Evidence is provided by X-ray examination [5], in which the detected pathology may be characteristic of certain pathogens. Infiltrative changes can be lobar and multilobar, which is typical for bacterial pneumonia (including pneumococcal, legionella, caused by anaerobes, fungi) and mycobacteriosis, including pulmonary tuberculosis. Diffuse bilateral infiltration is typical for pathogens such as influenza virus, pneumococcus, staphylococcus, legionella. Focal and multifocal infiltration can be homogeneous (pneumococcus, legionella) or inhomogeneous (staphylococcus, viruses, mycoplasma). The combination of infiltrative and interstitial changes is typical for pneumonia of a viral, mycoplasma and pneumocystis nature. Interstitial changes can be miliary (mycobacterium tuberculosis, salmonella, fungi) or reticular (viruses, pneumocystis, mycoplasma, chlamydia). The combination of infiltrative or interstitial changes against the background of lymphadenopathy is quite typical for pulmonary tuberculosis and pneumonia caused by fungi, mycoplasma, chlamydia, measles and varicella viruses. Finally, with pneumonia, radiographic changes may be absent. This happens at the very beginning of the disease, with dehydration, severe neutropenia, as well as with pneumocystis etiology of the disease.
X-ray of the lungs reveals complications such as abscess formation, exudative pleurisy. Computed tomography of the lungs is justified only for differential diagnosis, if a regular X-ray is not very informative, as well as for a more accurate assessment of possible complications. Computed tomography makes it possible to detect early infiltrative and interstitial changes in cases where standard radiography is not yet demonstrative. Cavities, lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion and multifocal changes are clearly identified.
When studying the leukocyte formula, leukocytosis of more than 10 × 1000/μl, a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left (more than 10% of band neutrophils), and toxic granularity of neutrophils are typical. With the so-called In atypical pneumonias (mycoplasma and chlamydial), the leukocyte formula is often unchanged; moderate leukocytosis without neutrophilia is usually observed.
To identify the causative agent, bacteriological examination of sputum is traditionally carried out. Quantitative assessment of microflora is considered necessary, since concentrations of more than 1 million microbial bodies in 1 ml of sputum are diagnostically significant. The most convincing data are from sputum cultures obtained before the start of treatment, as long as the results of bacteriological examination are not distorted by previous ABT.
Determining the sensitivity of microflora isolated from sputum (blood, pleural fluid) to antibiotics can be a good help for the clinician, especially in cases where the initial therapy was ineffective. For the etiological deciphering of chlamydial, mycoplasma, and legionella pneumonia, serotyping is usually used. Specific antibodies to these pathogens are determined using the indirect immunofluorescence reaction (IRIF) or more modern methods - the ELISA test (IgM and IgG antibodies to mycoplasma and chlamydia) and determination of antigen in urine (legionella).
It should be noted that the current classification of pneumonia has led doctors to simplified diagnoses such as “community-acquired pneumonia”, “domestic pneumonia”, etc. It should be borne in mind that such diagnoses do not correspond to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, according to which statistical records are kept. The requirement of Roszdravnadzor for statistical encryption of pneumonia based on etiological principles is legitimate.