Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
If staphylococcal bacteria enter the hair follicle of the skin, it can cause serious inflammation. An accumulation of pus with tissue necrosis that has captured the affected area along with the sebaceous glands and tissue is called a boil, and the disease itself is called furunculosis. Its appearance is quite painful, and its development is relatively fleeting. To avoid infection of the skin and the spread of the inflammatory process to healthy tissues, at the first signs of pathology you should seek medical help.
Causes
The inflammatory process and tissue suppuration are promoted by:
- non-compliance with personal hygiene requirements or its inadequate quality;
- constant friction of clothing on the skin;
- abrasions and injuries that provide access to the subcutaneous layer for bacteria;
- intensive work of the sebaceous and sweat glands;
- hypovitaminosis;
- metabolic disorders.
Most boils form on areas of the skin with hair follicles. They often appear on the neck, face, back of the hands, and in the lumbar region. At the initial stage, inflammation makes itself felt by the appearance of a characteristic red bump that rises above the surface of the skin. After 3-4 days, a purulent head appears. Later, the boil breaks out under the influence of an increase in the volume of purulent secretion or mechanical impact. At the site of the skin break, a core is visible - the so-called necrotic tissue. 2-3 days after the rupture, the rod, along with the remainder of the purulent contents, is rejected, and the wound begins to heal.
Are you experiencing symptoms of boils and furunculosis?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Symptoms
The boil develops gradually, going through three stages: formation of infiltrate, suppuration and rejection of the purulent core, healing. At the first stage, tingling, burning, and pulsation are felt. The area gradually turns red, becomes denser and slightly rises above the skin.
In the center of the cone-shaped inflamed area, the upper part of the purulent capsule, the pustule, is visible. On the fourth day, the abscess acquires its maximum size - from one to three cm in diameter. After “ripening,” the pustule opens (usually spontaneously or from an accidental touch), and pus comes to the surface. The capsule is separated by light pressure on adjacent areas of the skin or “pushed out” with special preparations.
If boils appear in several places or after the healing of one abscess the next one quickly forms, then it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive diagnosis to identify the cause of the disease.
Kinds
Depending on the location and development characteristics, general and local furunculosis are distinguished.
- The local type of disease occurs in a limited area of skin. Its cause is the incorrect treatment of one rash or violation of sanitary requirements in matters of skin care.
- General furunculosis covers a significant area of skin and is characterized by numerous rashes. More often it occurs against a background of weakening of the body, disturbances in the functioning of the immune system, long-term chronic diseases or during a period of remission, with anemia or disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system.
The course of furunculosis can be acute or chronic. In the first case, inflammation occurs simultaneously or with a short time interval, and the disease makes itself felt by increased body temperature, headache and a feeling of weakness. The chronic form of furunculosis develops with prolonged physical fatigue, with overheating or hypothermia of the body, as well as against a background of weakened immunity. Regardless of the type of disease, if symptoms of furunculosis appear, you should contact a dermatologist as soon as possible to clarify the causes of the boil and develop effective treatment tactics.
Factors of occurrence
The causative agent of the infection is usually a pyogenic bacterium - Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is present on the skin of any healthy person, and causes infection only if it reaches the deep layer of the skin (for example, through microtrauma). The development of boils is also promoted by:
- dirty skin;
- increased sweating;
- overweight;
- poor nutrition;
- hot humid climate;
- hormonal imbalances in the body;
- poor metabolism.
People with diabetes mellitus, skin diseases, and those prone to stress and depression are often at risk of developing furunculosis because they have a weakened immune system.
Treatment
The main method of treating furunculosis is the use of external topical agents that relieve inflammation and pain. The course is based on the sequential use of antibiotics, antiseptic and painkillers. If there is a possibility of developing an abscess, it is possible to surgically open the boil, extract its contents and treat the site of inflammation. It is possible to use UHF therapy, which demonstrates high efficiency at any stage of the disease.
Please note: it is strictly unacceptable to self-medicate, or try to open a boil yourself to extract its contents. In addition, it is important to change clothes and bedding more often, strictly observe personal hygiene rules, but limit exposure to raw water on the affected area.
When to contact a surgeon
Boils can be treated at home only for those who are not at risk (do not suffer from chronic diseases), and boils are small in size (up to 5 mm). You should not self-medicate in the following cases:
- if the appearance of a formation is accompanied by intense pain and fever;
- if the abscess has not opened within 2 weeks;
- if furunculosis has developed;
- if the abscess occurs in a small child;
- if the boil is near the nose, lips, in the ear canal;
- there was a relapse of the disease.
Prevention methods
You can reduce the risk of infection with staphylococcal bacteria and the development of furunculosis if:
- keep your body clean, take a shower regularly;
- carefully treat injuries and cuts;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- exercise regularly;
- diversify your diet, focusing on foods high in vitamins.
In addition, it is important to promptly treat emerging diseases of internal organs, as well as dress according to the season, avoiding overheating or hypothermia of the body.
Price
Allergology-immunology
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with an allergist-immunologist, primary | 3 500 ₽ |
Advantages
- The latest, constantly updated equipment
- Interest-free installments for all services
- Online consultations with an ENT doctor
- Visit of an ENT doctor to your home
- Friendly and qualified staff
- 24/7 ENT assistance
Furunculosis is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding subcutaneous fat. Formed on the hairy parts of the skin. The causative agent of the infection is usually Staphylococcus aureus.
Furunculosis is more common in people with weakened immune systems, adolescents and adults. Furunculosis is rare in children and the elderly. The disease affects men more than women. Unsanitary living conditions increase the risk of infection.
Boils may disappear without any treatment. Sometimes they burst on their own and heal without a trace within 2 days to 3 weeks. However, after healing, they can lead to a complication of furunculosis such as scars. If the abscess is accompanied by fever, pain and other symptoms that affect well-being, the person should seek medical help.
Three or more episodes within 12 months are defined as recurrent furunculosis. In this case, you should also consult a doctor, even if the boils tend to heal on their own.
Treatment of furunculosis at JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg)
Qualified therapists and dermatologists of JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) in the Central Administrative District of Moscow are ready to receive and examine patients with suspected furunculosis. To confirm the diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo a comprehensive examination in your own laboratory center. Treatment is prescribed on an individual basis, and its progress and results are strictly monitored by specialists. Each client is guaranteed tactful and attentive treatment, confidentiality of personal information, as well as comfort and safety during diagnostic and treatment procedures.
How to open a boil yourself?
Dermatologists categorically do not recommend trying to cope with inflammation on your own, wanting to squeeze out the purulent contents and the core of the boil at home. This is dangerous due to secondary infection, the spread of the inflammatory process to healthy tissue, the formation of new areas of inflammation and blood poisoning. The decision to open a boil is made only by a surgeon at a specialized medical institution, and only he has the right to carry out such manipulations.
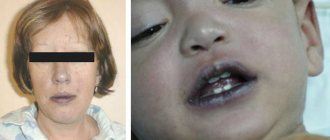
What does a boil look like?
A boil is a visible lump or red bump with a purulent head on the surface of the skin. When you touch its surface, you feel relatively severe pain, the skin around it is noticeably inflamed, and its temperature is increased. The most common places of development are the back of the head, the back of the hands, the lower back, and the face. The rash can be single or massive; its symptoms do not depend on the number of points of inflammation.
Why do boils appear?
This question can be answered accurately only after a thorough diagnosis of the boil. Among the most likely causes are infection of the hair follicle of the skin with staphylococcus bacteria against the background of vitamin deficiency, violation of personal hygiene rules, wearing too tight clothes, poor-quality antiseptic treatment of abrasions and skin injuries. The disease can also be caused by intense work of the sebaceous and sweat glands, the secretion of which is a favorable environment for bacteria.
Stages of development
At the very beginning of development, a boil can easily be confused with an ordinary pimple. However, within 3-4 days the inflammation grows, covering the surrounding tissues. Upon palpation, you can feel the tension and density of these tissues.
After a few more days, a sac with a purulent formation forms in the center of the boil, a necrotic core appears and the tissue softens.
Over time, the boil, unable to withstand a large amount of pus, opens and the pus, rejecting the necrotic core, flows out. After which the swelling gradually subsides and redness passes, and a small scar forms in the center of the former boil.
The most dangerous boils are those that arise near the lips, ears and nose. You should not try to squeeze out boils yourself, even if they have arisen in other locations. This can lead to the spread of infection, which will entail serious complications leading to the development of regional lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, and thrombophlebitis.
Let's talk in more detail about what contributes to the occurrence of this disease?
We have already mentioned that the immediate cause of a boil is an infection, namely staphylococcal.
We can also include damage to the skin - abrasions, cuts, scratches, scratches, abrasions - which contribute to the penetration of infection. We will also include lack of personal hygiene here.
Decreased immune status of the body due to hypothermia, or associated with vitamin deficiency, stress, diets, chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity, gastrointestinal diseases), taking certain medications, hormonal disorders.
Causes of boils in children
Most often, inflammation develops due to tissue damage by Staphylococcus aureus, less often the causative agent is other groups of staphylococci or streptococci. All of them are on the skin almost constantly, but in a normal state of immunity they cannot cause disease. The pathological process starts when exposed to certain unfavorable factors:
- wounds, scratches on the skin;
- skin diseases (eczema, atopic dermatitis);
- decreased immunity due to acute respiratory viral infections, operations, injuries, exacerbation of chronic diseases);
- congenital immunodeficiency conditions;
- diabetes mellitus and metabolic disorders (often cause the constant appearance of boils in a child);
- chronic infections: tuberculosis, pyelonephritis, sinusitis, etc.
Is a boil dangerous? Possible complications
In most cases, with timely treatment, boils do not pose a serious danger. But when trying to independently squeeze out a purulent-necrotic rod, inadequate local therapy, or the addition of a secondary infection, dangerous complications can develop.
Local complications include purulent lesions of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: furunculosis, carbuncles, abscesses and phlegmon. Damage to adjacent blood vessels and lymph nodes in the form of phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, and lymphadenitis is also possible.
The greatest danger is represented by boils located in the area of the nasolabial triangle and higher on the face and ear canal, since there is a high risk of spread of purulent masses and pathogenic bacteria into the cranial cavity through blood vessels. This can lead to damage to the meninges (meningitis, arachnoiditis) and directly to the brain tissue (encephalitis, brain abscesses). In rare cases, a boil can cause purulent masses and bacteria to enter the systemic circulation with the development of sepsis.
Important! A burst boil that is not treated properly poses a particular danger to the patient and others. An ruptured boil can cause infection of other follicles with the formation of furunculosis, as well as an entry point for secondary infections. In addition, the released purulent masses can become a source of infection for other people who come into contact with it directly or indirectly (through household items).
Furuncle in the ear
A boil in the ear receives therapeutic treatment with minor differences. The opening and rejection of necrotic masses may be accompanied by their flow into the middle ear, which is very unfavorable and dangerous for the hearing organ, therefore the use of dry heat, which can also contribute to the occurrence of sepsis, is not recommended. It is recommended that the patient sleep on the affected side to prevent swelling. Be sure to contact an otolaryngologist. The specialist manages the patient conservatively throughout the entire period and only if necessary can perform minor surgery. Under no circumstances should you attempt to clean your ears at this time, squeeze out the boil, or carry out any other activities. The vascular network on the head is very well developed, so in this location it is necessary to approach treatment methods very carefully so as not to cause life-threatening complications. In addition to the local reaction, severe headache, loss of appetite, fever, and irritability often occur. When such a clinic develops, symptomatic additional treatment is prescribed: antipyretic, anti-inflammatory, analgesics.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of “boil” is usually established on the basis of characteristic clinical changes. However, in order to monitor the patient’s general condition, early detection and prevention of complications, the following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods can be used:
- General blood and urine tests (CBC, UAM).
- Biochemical blood test with determination of glucose levels.
- Blood test for HIV using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
- Determination of hepatitis B and C virus markers by ELISA.
- Bacterial culture of a sample of purulent masses to identify the pathogen and its sensitivity to main antibiotics.
For recurrent and multiple boils, fluorography or radiography of the chest organs, ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and kidneys, etc. can be additionally performed.
Differential diagnosis of a boil is carried out with other dermatological and infectious diseases, which may be accompanied by similar symptoms, including:
- Hidradenitis suppurativa,
- Erythema nodosum,
- Anthrax,
- Lupus,
- Actinomycosis.
Is stye contagious?
It is not dangerous for others, but only if basic hygiene rules are followed. The risk of infection usually occurs in young children. Due to their age, they do not yet understand the importance of hygiene and therefore often suffer from bacterial infections. Infection is also possible when the patient uses cosmetics. But in general, isolation of an adult or child suffering from hordeolum is not required.
The causative agents of the disease are found in pus located in the barley sac. There are no bacteria on the surface. But there is usually little pus inside, so even a burst stye is not dangerous. In 80% of cases, the abscess breaks out at night when the patient is sleeping. If purulent masses end up anywhere, it is on a person’s face, his pillow, or bed linen. The infection does not spread further.
Sources
- Shallcross, Laura J et al. “Incidence and recurrence of boils and abscesses within the first year: a cohort study in UK primary care.” The British journal of general practice: the journal of the Royal College of General Practitioners vol. 65.639 (2015).
- Clinical protocol for diagnosis and treatment of “skin abscess, boil and carbuncle of other localizations” Expert Council of the Republican State Enterprise at the Republican Center for Healthcare Development of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan dated December 12, 2014 protocol No. 9.
- Boils and carbuncles. Mayo Clinic.
- Federal clinical guidelines for the management of patients with pyoderma. Russian Society of Dermatovenereologists and Cosmetologists, 2015.