Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder.
The bladder is a hollow organ designed to store urine. Urine is produced by the kidneys and travels down the ureters to the bladder. Urine is removed from the bladder through the urethra (urethra). The walls of the bladder are formed by a special type of muscle; the inside of the organ cavity is lined with mucous membrane.
Most often, inflammation in cystitis affects only the mucous membrane, but in some cases, the muscle tissue of the walls of the bladder can also be involved in the inflammatory process.
Causes of cystitis
Inflammation can be caused by various reasons. For example, toxic and allergic cystitis are distinguished. However, in most cases, cystitis is caused by an infection.
An infection in the bladder can occur in the following ways:
- ascending
route - along the urethra. This is the most common route of infection. In this case, cystitis develops as a complication of urethritis; - descending
route - from the kidney through the ureter (with an inflammatory process in the kidney, for example, chronic pyelonephritis); - lymphogenous
- with the flow of lymph from the pelvic organs (in women - with inflammation of the appendages, endometritis, etc.); - hematogenous
- with blood flow. It is rare, but this way the infection can get from distant foci of inflammation; - in a direct
way - when ulcers break through from the tissues surrounding the bladder into the bladder. Infection can be introduced during surgical or instrumental intervention, as well as during the installation of a catheter.
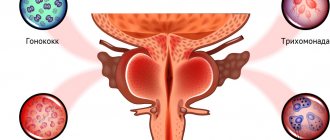
The causative agent of cystitis is most often Escherichia coli (from 80 to 95% of cases of acute uncomplicated cystitis). This bacterium is normally found in the rectum; if it enters the urethra, it can lead to inflammation. Other bacteria (enterococci, enterobacteria, staphylococci, etc.) can also be the causative agent of cystitis. Another group of pathogens consists of sexually transmitted infections (STIs): chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasma, ureaplasma, fungi of the genus Candida (the causative agent of thrush), herpes.
Cystitis is considered a “female” disease, since it mainly affects women. Cystitis in men is rare and, as a rule, is a complication of chronic prostatitis that does not require separate treatment: when inflammation of the prostate gland is relieved, the signs of cystitis also go away.
The fact that women often suffer from cystitis is explained by the structure of the female body. The urethra in women is short and wide; it is located relatively close to the anus. It is easier for E. coli to enter it than into the urethra in men, and it is easier for it to travel up it into the bladder. As a rule, the inflammatory process in the bladder is preceded by inflammation of the vagina (vaginitis) or a disturbance of the vaginal microflora (bacterial vaginosis).
An infection can also get into the urethra during sexual intercourse. In this case, signs of cystitis usually appear within the next 12 hours.
Factors contributing to the development of cystitis
The likelihood of cystitis increases if:
- injuries to the mucous membrane of the bladder;
- congestion in the pelvis (circulatory disorders);
- decreased immunity;
- hypothermia;
- overwork, stress;
- hormonal changes (during pregnancy);
- incomplete emptying of the bladder. Stagnation of urine promotes the proliferation of pathogenic microbes.
Causes and risk factors for developing cystitis
Cystitis is divided into bacterial and non-infectious. In most cases, inflammation of the bladder is caused by bacteria entering the urethra, most often Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally live in the gastrointestinal tract, and when they enter the bladder, they begin to exhibit their pathogenic properties.
Non-infectious factors can also cause inflammation in the bladder.
- Interstitial cystitis (painful bladder syndrome). The cause of this chronic inflammation remains unclear.
- Cystitis caused by taking medications, in particular chemotherapy.
- Post-radiation cystitis that occurs after radiation therapy to the pelvic area.
- Cystitis that occurs against the background of concomitant pathologies such as diabetes mellitus, urolithiasis, prostatitis.
Symptoms of cystitis
Symptoms characteristic of cystitis can also be observed in other diseases, so only a doctor can make a final diagnosis.
The main symptoms of cystitis are:
Frequent urination
Increased urination with cystitis is usually accompanied by pain in the bladder area and a burning sensation in the urethra.
More about the symptom
Feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder
Cystitis typically involves a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. There is a frequent and strong urge to urinate due to the release of small volumes of urine.
Hematuria
There may be blood in the urine. Urine becomes cloudy.
Temperature increase
In acute cystitis, an increase in temperature to 37-37.5°C may be observed.
Nausea
In severe cases of acute cystitis, attacks of nausea and vomiting are possible.
More about the symptom
Diagnosis and treatment
With unpleasant symptoms, a man is recommended to consult a urologist. Often patients try to ignore the problem and are ashamed to go to the doctor with such complaints, but this is the wrong approach. Advanced cystitis and prostate diseases, which became its root cause, eventually become severe and significantly worsen the quality of life, including intimate relationships.
At the appointment, the doctor will collect complaints and conduct a standard physical examination. To clarify the diagnosis, the specialist will prescribe an ultrasound of the prostate gland, scrotum and penis, CT scan of the pelvic organs, clinical and bacteriological urine tests. You will also need to take a smear test for sexually transmitted infections.
For bacterial cystitis, which accounts for the lion's share of all forms of inflammation, antibiotics are indicated. For men, medications are prescribed that can penetrate the prostate gland to simultaneously affect both sites of infection. The doctor can supplement the treatment regimen with uroseptics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Methods for diagnosing cystitis
Diagnosis of cystitis is carried out using laboratory and instrumental studies.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory diagnosis of cystitis includes a general blood test and clinical urine test. In some cases, a urine test according to Nechiporenko may be required. In order to identify the causative agent of the disease, a cultural study (bacteriological culture of urine) can be carried out.
Ultrasound of the bladder
Ultrasound of the bladder is the simplest and most informative study. It allows you to assess the degree of damage to the bladder wall, the extent of the process, and detect stones and tumor processes that may accompany cystitis.
More information about the diagnostic method
Cystoscopy
In cases of frequently recurring cystitis, cystoscopy may be performed.
More information about the diagnostic method
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
How to treat bladder inflammation
- During an exacerbation, bed rest is prescribed with a diet (spicy, fried and canned foods are excluded from the diet).
- Increased fluid intake.
- Uroseptics to relieve inflammation and spasms of the bladder mucosa (nolicin, palin, norbactin, furadonin).
- Antibiotics depending on the type of pathogen (ampicillin, oxacillin, cefazolin). Prescribed intramuscularly, the course of treatment is 10 days.
- Painkillers.
- Diuretic herbs in the form of decoctions and infusions.
- In some cases, when there is suspicion of the development of a tumor process, a cystoscopy is performed and material is taken for a biopsy.
- According to indications, instillations with protargol are prescribed.
Treatment is prescribed individually based on the results of the examination.
Treatment methods for cystitis
Treatment of cystitis should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor.
Self-medication cannot guarantee the desired result: as a rule, only the acute condition is relieved, the disease becomes chronic, and with any provocation (minor hypothermia, stress or infectious disease), the symptoms of cystitis return again. And untreated cystitis can lead to a serious complication – pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidney tissue). Treatment of cystitis, as a rule, includes a course of antibacterial therapy, a special regimen for the patient and a diet excluding fried, spicy and spicy foods. In some cases, physiotherapy is performed, and medications are instilled directly into the bladder.
Specialist consultation
If you experience symptoms of cystitis, you can contact JSC “Family Doctor”. Family Doctor urologists have extensive experience in treating both acute and chronic cystitis. The qualifications of doctors and modern technological equipment of clinics allow effective treatment of cystitis during periods that require a special approach, for example during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
An integrated approach to the treatment of cystitis involves not only eliminating the source of inflammation in the bladder, but also eliminating the source of infection, which may be located in the vagina, tonsils, and intestines. Therefore, you should not be surprised if, when complaining of cystitis, you are referred for a consultation to a gynecologist, ENT specialist, or gastroenterologist; Consultation with an immunologist may also be required.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Why choose treatment at the Urology Clinic named after. Fronshteina R.M.
- It is a leading institution in the field of urology.
- Service by medical staff is provided at the level of European quality.
- The clinic's staff includes world-renowned specialists.
- All services provided by the clinic are strictly confidential.
- When conducting examinations and treating patients, the latest laser and electronic technology is used.
- Treatment methods are focused on reducing trauma during endoscopic procedures.
- The use of an ultrasonic scalpel reduces the risk of blood loss during operations.
You can come to the clinic for a consultation from different regions and cities of Russia.
Bladder inflammation can be cured. It is imperative to take chemical medications, which must be prescribed by a doctor, and not self-medicate.