In healthy people, urination does not cause discomfort or discomfort. But in the presence of pathologies, the process is accompanied by pain, pain and burning.
Unpleasant sensations when emptying the bladder occur due to a violation of the integrity of the walls of the urethra, which leads to exposure of nerve endings.
The pain can be sharp or dull, cutting or aching, burning or tingling. They can bother you when you need to go to the toilet, at the beginning or end of urination, throughout the entire process.
Cystitis and sex
If you had prolonged or too intense sexual contact, then after it you may experience a frequent urge to urinate and pain during it; these symptoms do not always indicate an infection. They often arise due to the fact that the bladder, and in particular the neck and urethra, become “irritated” due to mechanical stress.
If these symptoms do not subside within 24 hours, then you should collect a urine test, an average sample, and contact a specialized doctor for cystitis (urogynecologist, gynecologist, urologist) as a matter of urgency.
Cystitis at any age
An acute attack of cystitis after sexual intercourse can occur at any age. Decades ago, when women maintained their virginity until marriage, cystitis that occurred after sexual intercourse was called the “honeymoon disease.”
At the present time, the fact is that no matter what your age, if the contact took place after a long break, the meeting was too active or sex happened with a new partner, you are not immune from the development of acute cystitis.
Causes of cystitis after sex
The main cause of inflammation of the bladder after sexual intercourse is a bacterial infection - the entry of pathogenic microorganisms into the female bladder.
Inflammation of the urinary tract after sexual intercourse can occur for several reasons, mainly anomalies of physiological development. In some women, the external opening of the urethra is located close to the opening of the vagina and bacteria easily enter the bladder.
Another cause of cystitis may be poor personal hygiene, both by women and men. Dirt and bacteria from the hands or genitals can enter the urinary system and cause inflammation.
In addition, the cause of the disease may be a combination of anal and vaginal sex in one sexual act. Among the bacteria that cause cystitis is E. coli, which, when it enters the urinary system, causes extremely unpleasant consequences. Up to 90% of cystitis is caused by the bacterium Escherichia coli, and movement during sex helps move this bacterium into the urethra and bladder.
Cystitis after sex can also develop due to sexually transmitted diseases, microflora disturbances in the vagina, and as a result, with inflammatory phenomena in the pelvic organs.
Any damage to the mucous membrane of the urethra during sexual activity gives rise to excessive proliferation of pathogenic microflora and the development of inflammatory processes. This is especially true if a woman has not had sex for a long time, sexual intercourse was prolonged and/or the woman’s vagina is poorly moisturized (dry, due to the lack of a sufficient amount of “natural” mucus).
Some women also find that certain sexual positions cause irritation and cystitis. Sex from behind, for example, is especially harmful for women who are prone to cystitis.
Pain when urinating
Colpitis
Cystitis
17037 05 July
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain when urinating - causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Pain when urinating is a symptom of a number of diseases and should be the reason for a thorough examination.
Types of pain
In most cases, the cause of pain is diseases of the genitourinary system: infections, urolithiasis, inflammatory and tumor processes. Depending on the cause of the pain, its character can be sharp (piercing), cutting, pulling (aching). Pain may occur before you start urinating, when you first start urinating, or when you finish urinating. In some diseases, pain during urination may radiate to other areas (lower back, perineum, lower abdomen).
Possible reasons
One of the most common causes of pain when urinating is sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Urogenital chlamydia is an infectious disease caused by chlamydia. In men, chlamydia occurs in the form of urethritis. Sometimes the disease does not give obvious symptoms, but often there is itching in the urethra, moderate discharge and minor pain when urinating. Chlamydia may be accompanied by other STIs (most often gonorrhea).
Chlamydial infection can cause the development of prostatitis, and then the symptoms characteristic of urethritis are combined with pain in the perineum, sacrum and rectum and intensify with prolonged sitting.
Dysfunction of the genitourinary system is accompanied by frequent and painful urge to urinate, partial urinary retention and sexual dysfunction.
In women, urogenital chlamydia is often asymptomatic; only in the acute form are pain, burning and increased urge to urinate (urethrocystitis).
Gonorrheal urethritis is accompanied by more severe symptoms. Women experience heavy discharge, and urination is accompanied by burning and itching in the vagina. If left untreated, gonococci spread through the genitourinary tract and reach the fallopian tubes, causing pain in the lower abdomen, fever, frequent painful urination and menstrual irregularities. The first sign of gonorrhea in men is itching and a burning sensation in the area of the external opening of the urethra. Scanty grayish sticky discharge appears from the urethra. Urination is painful, accompanied by a burning sensation throughout the urethra.
A group of STIs that are accompanied by pain when urinating includes trichomoniasis. The causative agents of the disease - Trichomonas - live in the prostate gland and seminal vesicles in men, and in the vagina in women. In women with trichomoniasis, the vagina (colpitis) and cervix (cervicitis) become inflamed.
and paraurethral glands. In men - the urethra (urethritis) and the prostate gland (prostatitis).
Other infectious lesions of the genitourinary tract in women include fungal diseases (candidiasis, or thrush). Opportunistic microorganisms also multiply in the vagina, causing pain when urinating and during sexual intercourse.
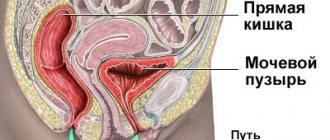
In women, severe pain when urinating occurs due to inflammation of the bladder (cystitis). The cause of infectious cystitis can be Escherichia coli, and less commonly, staphylococci.
The short and wide urethra allows infection to easily penetrate from the vagina and periurethral area into the bladder.
Escherichia coli penetrates the bladder through the urethra and attaches to its epithelium with the help of villi. The disease develops very quickly and is accompanied by nagging pain in the lower abdomen and an increase in the frequency of urination day and night. Emptying the bladder is accompanied by pain and spasms, especially at the end of urination. Characterized by a false urge to urinate, which becomes debilitating. In acute cystitis, blood may appear in the urine.
If in women the most common cause of pain when urinating is cystitis, then in men this symptom appears when the prostate gland is inflamed - prostatitis. The disease can occur as a result of ingestion of the herpes simplex virus, gonococci, trichomonas or fungi.
However, when the process is chronic, the causative agent of the disease is often not detected.
Pain with prostatitis, as a rule, radiates to the sacrum, perineum, especially to the scrotum. Their intensity can vary from barely noticeable aching pain to pronounced pain. Pain may increase with defecation, ejaculation and urination after sexual intercourse. Associated symptoms include frequent urge to urinate, especially at night, difficulty passing urine, and increased pain with prolonged sitting.
Non-infectious causes of pain during urination include urolithiasis. If there are stones in the bladder, pain occurs in the lower abdomen, which can radiate to the perineum and genitals. It may get worse with movement and urination. During the passage of urine, urination may be interrupted when the bladder is not completely emptied. A stone fragment, passing through the urethra, injures the walls of the urethra, which is accompanied by piercing pain and the appearance of blood in the urine.
Possible causes of pain when urinating include neoplasms of the bladder, prostate and urethra (polyps). If the tumor is located at the bottom of the bladder, it can partially block the urethra, causing pain and difficulty passing urine. A similar situation occurs with prostate tumors. With bladder cancer, pain can not only accompany the passage of urine, but also be permanent, localized in the suprapubic region and irradiating (returning) to the perineum, sacrum, and lumbar region.
Diagnostics and examinations
Any pain that occurs during urination or is localized in the genital area requires consulting a doctor.
Primary information about the cause of the disease can be obtained by passing a general clinical urine test.
The first signs of cystitis after sex
Cystitis after sex has several differences from acute cystitis. First of all, symptoms of the disease occur either in the first few hours or 1-2 days after intimacy.
The first symptoms are a frequent urge to urinate, which is accompanied by pain, burning, stinging, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, urine changes color and smell, and becomes cloudy. Body temperature may rise to subfebrile levels, pain or discomfort may appear in the lower abdomen and lumbar region. Some symptoms may be less severe or not appear at all.
Make an appointment
Make an appointment with a gynecologist by calling 8(812)952-99-95 or filling out the online form - the administrator will contact you to confirm your appointment
guarantees complete confidentiality
Complications
Bacteria, viruses and fungi can cause an acute infection that quickly spreads to nearby organs. So, in the case of urethritis and cystitis, an ascending infection affecting the kidney tissue is possible. The negative consequences of such a disease can threaten the patient's life.
Dangerous complications of diseases that cause dysuria:
- Purulent lesion of renal tissue.
- Severe renal failure due to chronic infection.
- Pregnancy disorders in women.
- Penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the bloodstream with the development of sepsis.
Thus, burning when urinating is not a harmless symptom. Diseases of the genitourinary system that cause dysuria can lead to serious complications. Urological examination allows for timely therapeutic or surgical treatment.
Complications and consequences of postcoital cystitis
Cystitis after sex is dangerous due to its complications, like any other inflammation.
If you ignore the first signs, the disease may develop into a more severe form that is more difficult to treat. Infection from the bladder can spread higher and provoke inflammatory kidney disease - pyelonephritis. In addition, if cystitis after sex occurs every time, a woman will eventually lose the desire to have sexual intercourse due to the fear of getting cystitis again, and this in turn leads to uncertainty, stress, disagreements between partners, etc.
Recently, self-medication has become widespread, and women who already know their problem can take a course of antibiotics immediately after sexual intercourse, but regular use of such drugs can cause other, more serious problems (in particular, uncontrolled use leads to drug resistance, i.e. e. antibiotics become powerless in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms).
In addition, antibiotic treatment is contraindicated during pregnancy, and cystitis in this situation can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, and cessation of fetal development. All experts agree that cystitis requires professional and complete treatment, otherwise not only physical problems are possible, but also psychological ones, both on the part of the woman and the family as a whole.
In response to inflammation, an admixture of blood may appear in the urine - hemorrhagic cystitis, and frequent episodes of inflammation lead to a chronic process with the involvement of deeper layers of the bladder wall in the inflammatory process, partial or complete destruction of the GAG layer (glycosaminoglycan layer) - a protective or barrier layer , which prevents the adhesion of bacteria to the bladder mucosa.
Risk factors
In addition to certain diseases that affect the process of urine excretion, urologists take into account the significance of various forms of predisposition to dysuria. These may be individual characteristics of a person, diseases of distant organs and other signs.
Possible risk factors:
- Taking certain medications. Thus, the use of chemotherapy often leads to dysuria.
- Gender. Women have a shorter and wider urethra, which increases the risk of genitourinary infections.
- Age. Discomfort in the urethral area is typical for older people.
- Recent diagnostic or therapeutic interventions in the urethral or bladder area. This may involve taking a smear, urography, or another procedure.
- Improper use of personal hygiene products. Penetration of soap into the urethra leads to irritation of the mucous membrane of the organ.
- Allergies to personal care products, synthetic materials and other items.
- Congenital anatomical defects of the excretory system.
Before making a diagnosis, you need to make sure that the pain is not associated with the above factors.
Tests for diagnosing cystitis
If a urogynecologist diagnoses “postcoital cystitis” (or cystitis after sex), to confirm it, not only anamnesis and examination of the patient is required, but also additional examination.
First of all, analyzes are carried out:
- general blood test (the basis for diagnosing most diseases),
- general urinalysis (study of the chemical and physical properties of urine, which may indicate pathological processes in the body),
- urine culture - bacteriological examination (detects infection in the urinary tract and its sensitivity to antibiotics),
- vaginal smear (allows you to identify pathogenic bacteria and identify the inflammatory process).
Other reasons
Not in all cases, discomfort during urine output is associated with infection. Structural diseases can also cause dysuria.
Additional reasons:
- Urolithiasis is the formation of stones in the urinary tract. Stones not only make it difficult to pass urine, but also damage the mucous membranes, resulting in pain.
- Oncology. The growth of a malignant or benign tumor in the urinary tract can cause severe pain. This can be a relatively harmless disease, such as urethral polyps, or an aggressive variant of oncology with a poor prognosis.
- Abnormal narrowing of the lumen of the urethra (urethral stricture). In the presence of such a disease, urination becomes not only painful, but also very difficult.
- Formation of stones in the kidney tissue (renal stones). Small stones spread with urine into the underlying parts of the excretory system.
It is advisable to conclude that dysuria can occur in a large number of urological disorders, so it is impossible to clarify the cause of the symptom without further examination of the patient.
Instrumental diagnosis of cystitis
Instrumental diagnostics, as the name suggests, is carried out using instruments. Cystitis after sex can be confirmed in the following ways:
- Kidney ultrasound
- Ultrasound of the bladder
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs
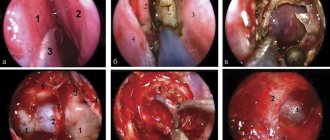
- Cystoscopy of the bladder in women
Ultrasound examination to detect signs of inflammation in the bladder and kidneys, uterus and its appendages.
Cystoscopy is an examination of the urinary tract using a special optical system to determine the volume and depth of damage to the bladder mucosa. (more details...)
Diagnostics
The disease that causes pain when urinating can be diagnosed through a comprehensive examination.
During the first examination of the patient, the doctor seeks to clarify the localization of sensations and the ability of pain to radiate to other areas: the perineum, lower back, lower abdomen. The nature of the pain is also taken into account: cutting, aching or piercing. It matters at what point the discomfort occurs: pain after urination, during or when the first urine appears, etc. Other symptoms must be taken into account during the examination: itching, redness of tissue, vaginal discharge, etc. It is necessary to be extremely frank with the attending physician, so that he can obtain reliable information about the disease.
Such an examination can be carried out by a general practitioner, who will recommend contacting one (or more) specialized specialists after determining the patient’s medical history and receiving the results of a general blood test and a general urinalysis,
This doctor can be a urologist, gynecologist, venereologist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, immunologist, dermatologist, nutritionist, oncologist, traumatologist, neurologist.
Taking into account the collected medical history and visual examination of the patient, the doctor may prescribe a number of laboratory and instrumental studies:
- Enzyme immunoassay of blood, amniotic fluid, cerebrospinal fluid. This analysis refers to indirect methods for identifying the pathogen.
- PCR diagnostics of blood, urine, hair, urogenital smear, sputum, epithelium is the most reliable method of direct detection of infectious diseases, but from the moment the material is taken for analysis until the result is obtained, it takes from 2 to 10 days.
- Analysis of a smear for flora from the cervical canal.
- Urinalysis according to Nechiporenko.
- Cystoscopy is an examination of the bladder using a device equipped with a video camera.
- Urine culture for sterility.
- Ultrasound of the pelvis.
- X-ray or magnetic resonance imaging of the lumbosacral spine.
Differential diagnosis of cystitis
Differential diagnosis consists of excluding diseases that are characterized by similar symptoms.
For example, if there are signs of cystitis (painful and frequent urination, changes in urine composition, etc.) and high fever, then this condition may be caused by inflammation of the renal pelvis, not the bladder, and the presence of blood or pus in the urine may be caused by the presence of stones in the urinary tract.
If cystitis after sex bothers you for a long time and is difficult to treat, you should undergo a full examination; perhaps the reasons lie in the presence of other diseases - for example, an active viral infection, sexually transmitted diseases, etc.
Signs of cystitis that are not confirmed by the presence of bacteria in the urine may be associated with a fairly common female disease - cystalgia. The disease occurs exclusively among the female population, characterized by frequent and painful urination and pain in the lower abdomen. Cystalgia has not been fully studied, but, according to some data, it is associated with hormonal disorders and circulatory disorders due to pathological processes in the pelvic organs.
When making a diagnosis, the urogynecologist relies on the patient’s complaints and the results of the examination.
General symptoms
Women often complain of unpleasant sensations during urination (deurination): cutting pain, burning and tingling in the groin, a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, accompanied by frequent urge to go to the toilet, the appearance of blood and pus in the urine, etc. All these manifestations may be characteristic of a number of diseases of the genitourinary system of a non-infectious or infectious nature.
Girls experience such symptoms as pain and pain when urinating 10 times more often than men. This can be explained by the fact that anatomically the urethra in women is shorter and is located much closer to the natural sources of infection (vagina, anus) than in men, therefore it becomes infected more easily and quickly.
Treatment of cystitis after sex
Treatment is both symptomatic and etiotropic in nature (i.e., eliminating the cause of the disease).
For example, the presence of inflammation in the vagina is eliminated with the help of local antifungal and antibacterial drugs. If a sexually transmitted disease is detected, a specialist requires treatment of both partners. If there are anatomical features of the urinary system, the urogynecologist may recommend surgical treatment - urethral transfer, i.e. transposition of the urethra (higher above the vagina), if necessary, the surgeon excises the remains of the hymen, which “stretch” the urethra.
After surgery, recovery takes 7-15 days; in 85% of cases, the operation allows you to forget forever what cystitis after sex is.
Treatment
Pain when urinating is only an individual symptom, so the root cause of the disorder should be treated after a thorough diagnosis. Depending on the identified pathology, the patient may require surgical or therapeutic treatment. Sometimes examinations do not allow us to determine the cause of the unpleasant sensation - in this case, the doctor will advise the patient to use safer hygiene products and give up bad habits.
Possible treatments for the causes of dysuria:
- The use of antibacterial drugs to destroy pathogenic bacteria. In case of chronic infection, it is recommended to test the sensitivity of microflora to certain medications.
- Antifungal and anti-inflammatory agents.
- Symptomatic therapy with painkillers and antispasmodics.
- Surgical and therapeutic interventions aimed at extracting stones, removing tumors and restoring patency of the urinary tract.
Thus, dysuria can be eliminated by treating the underlying cause of the symptom. In addition to the use of medications, patients are advised to give up alcohol, cigarettes, coffee and too spicy foods.
Medications
The main treatment for postcoital cystitis is primarily aimed at blocking the spread of infection. Antibacterial therapy helps with this.
The main treatment of cystitis is supplemented with medications that help reduce the unpleasant manifestations of the disease and normalize the functioning of the urinary system - painkillers, herbal medicines, immunostimulants, vitamin complexes.
In the treatment of inflammatory processes in the bladder, the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs through the urethra into the bladder (instillation) is often used.
Cystitis after sex with proper treatment and following all the doctor’s recommendations goes away within a week, but immunostimulating drugs, herbal medicines and vitamins should be taken longer (2-3 weeks).
With this disease, it is extremely important to complete the full course of therapy, otherwise cystitis will become chronic, and treatment of chronic pathology will be much more difficult.
Traditional treatment
Traditional medicine is used to remove inflammatory processes in the bladder, and this is only possible after prior consultation with a specialist. One of the most common methods in folk medicine is to use a heating pad or hot bottle. Yes, there really is relief, but! only for a while, because the cause has not been eliminated, and the bacteria in the bladder has not disappeared.
It is worth remembering that cystitis after sex requires an integrated approach and should include the use of antibiotics, antispasmodics, uroseptics and other medications.
It is important to follow a home regime, diet and drink plenty of fluids. So cold, the use of cold drinks, caffeine, and spicy foods aggravate the symptoms of the disease.
Causes of pain in men.
Pain when urinating can be caused by:
Prostatitis.
The inflammatory process in the prostate often spreads to the urinary system, which provokes pain, pain and burning during and after emptying the bladder. Pain also occurs in the perineum, scrotum, sacrum and lower back.
BPH.
A benign tumor in the prostate gland puts pressure on the organs of the urinary system, making it difficult to pass urine and causing pain.
Prostate atrophy.
With overly active sexual activity, the prostate gland is depleted, which contributes to the unhindered proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and the development of prostatitis, and, consequently, pain when going to the toilet.
Malignant neoplasms of the prostate.
Tumors can put pressure on the urethra, pinching it, which makes urination difficult and accompanied by pain.
Urogenital tuberculosis.
For a long time, the only symptoms of the disease may be pain when emptying the bladder and periodic decrease in potency.
Phimosis.
When the foreskin narrows, the genitourinary tract becomes inflamed, which causes pain during urination and erection.
Balanoposthitis.
Inflammation covers the foreskin and head of the penis, which causes painful evacuation.
Orchiepididymitis.
It combines two inflammatory diseases that occur simultaneously: orchitis (affects the testicles) and epididymitis (affects the appendages). As a result, a man may experience pain when urinating.
Vesiculitis.
With inflammation of the seminal vesicles, the main symptoms are cutting pain when emptying the bladder and the presence of blood in the urine.
Surgical treatment of cystitis
Cystitis after sex is treated mainly with therapeutic agents; surgical treatment may be required to change physiological developmental abnormalities, for example, when the urethra is located close to the vagina, which leads to trauma to the canal and the rapid spread of infection into the bladder. During the operation, the surgeon moves the opening of the urethra to the desired location. After surgical treatment there are almost no complications and the problem of cystitis after sexual intercourse for women in 85% of cases remains a thing of the past.
Physiology of urine output
Urination is necessary to remove unnecessary metabolic products and harmful chemical compounds from the body.
Urine itself is formed in the kidney tissue as a result of blood filtration: nephrons successively remove ballast substances from the blood vessels and return necessary components, such as proteins and salts, to the bloodstream. More than one hundred liters of primary urine can be formed per day, but as a result of final filtration, 800-1500 milliliters of liquid per day are removed from the body. The excretory fluid formed in the kidneys penetrates into other parts of the excretory system for accumulation and gradual removal from the body. Approximately 500 ml of urine can be deposited in the bladder, and a person begins to feel the need to urinate when a quarter of the organ’s volume is filled. The signal received from the brain relaxes the sphincter and promotes the removal of fluid from the body through the urethra. In men, part of the urethra passes through the prostate gland, so prostate pathologies can cause dysuria.
Prevention
- As a preventative measure, both partners should be sure to maintain good hygiene.
- Partners should avoid sexual positions that create pressure or friction on the urethra, as well as intense tempos.
- It is necessary to use special lubricants (lubricants) in case of natural deficiency of vaginal mucus.
- Provide timely treatment for gynecological diseases.
- Do not use spermicides or vaginal diaphragms for contraception.
- It is recommended to empty the bladder immediately after sexual intercourse, this allows you to “evacuate” most of the bacteria that have entered the bladder.
- Immediately after contact, drink at least 300 ml of liquid.
Causes of pain during urination associated with other body systems
- Tumors – benign and malignant, in the organs of the urinary system or nearby organs. Pain occurs due to mechanical compression of the ureter and bladder. Relief of the condition in this case depends on the method of treating the tumor.
- Gout is a rheumatological disease in which uric acid salts are deposited in the joints. The kidneys and urinary system are often affected. In this case, not only pain is observed, but also a burning sensation when urinating.
- Complications after diseases not related to the urinary system. These include sinusitis, all types of sore throats, flu, intestinal diseases, pathological changes in teeth and other inflammatory diseases of organs and systems.