Diseases of the genitourinary system are most often caused by an inflammatory process. Increased urination, change in urine stream, retention, this is a signal that you urgently need to see a doctor. The inflammatory process in the kidneys develops complications. After tonsillitis, scarlet fever and many other diseases and inflammatory processes in the body, kidney function is disrupted. Pain, pain and burning, fever are the main symptoms of diseases of the genitourinary system.
In addition to pain, a person thinks every day that he will not be able to have children. This means that it is necessary to quickly cure these diseases, which put an end to procreation. These diseases affect your quality of life, think about it! It’s better not to wait, but to go to the doctor. The main thing is not to self-medicate; only a specialist can make a diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment. Diamed clinics have been successfully treating such diseases for a long time. We employ experienced urologists with extensive practical experience in treating diseases of the genitourinary system.
Many methods are used to treat the urinary system. The speed of recovery depends on the cause of the disease. Compliance with the regime and diet is of great importance. The main thing is that you need to undergo complete treatment so that the disease does not have time to become chronic.
When treating a bladder problem, you need to drink a lot of fluids, take diuretics, and sometimes the doctor prescribes antibiotics.
Main diseases of the genitourinary system:
- Cystitis is a common disease in which the mucous membrane becomes inflamed.
- Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra affected by various bacteria and viruses.
- Prostatitis is an acute disease that causes deterioration in functioning, including deterioration of erection.
- Pyelonephritis is a disease that costs a lot.
- Disease - urinary tract chladymiosis, cadidiasis.
- Urolithiasis is a disease that forms kidney stones.
- Orchitis is inflammation of testicular tissue.
- Epidymitis is an inflammatory process of the testicular appendage.
- Balanoposthitis is inflammation of the skin and glans penis.
What diseases are there?
The most commonly diagnosed diseases are cystitis and urethritis. These are diseases of an infectious nature that arise due to the penetration of harmful organisms into the bladder through the urethra or intestines.
In second place are pyelonephritis and urolithiasis. Pyelonephritis, an inflammatory disease of the kidneys, often occurs as a complication of untreated cystitis, but can also occur as an independent pathology. Urolithiasis is the process of formation of stones and crystals in the kidneys, ureters and bladder.
In third place are benign (cysts, diverticula) and malignant neoplasms (cancer). Most often develop in certain groups of people:
- Smokers;
- Those who frequently come into contact with aniline dyes;
- Persons with congenital anomalies and chronic diseases of the pelvic organs (genitals, urinary organs).
There are also other diseases - leukoplakia, urinary incontinence, polyps in the bladder, hernia and sclerosis of the bladder. These diseases are caused by disturbances in the functioning of organs - the kidneys, bladder and ureters - and their untreated pathologies.
Courses of diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women
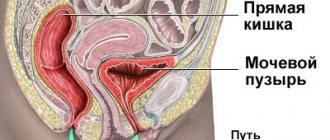
The structure of the bladder is the same in both sexes. In men, the prostate is adjacent to the lower outer part, and the seminal flows are on the sides. In men, damage to the lower parts and urinary tract often occurs. This is due to the long urethra. The man feels pain, burning, difficulty urinating, pain in the perineum.
In women, the back of the bladder borders the uterus and vagina. The length of the urethra in men is more than 15 cm, and in women 3 cm. Because of this difference, women suffer from such diseases more often than men.
Factors for bladder disease:
- Irritated mucous membrane of the bladder due to cystitis, which did not manifest itself with obvious symptoms and became chronic.
- Stagnation and retention of urine most often occurs when the urinary tract is compressed.
- Blood in the urine - a similar symptom may be associated with a tumor or kidney stones.
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages and various spices.
- Violations of personal and sexual hygiene rules.
The only correct way to treat such diseases is to prescribe competent antibacterial therapy.
Doctors at Diamed clinics take care of every patient. If you have any painful or troubling urinary tract symptoms, don’t hesitate to contact us. #infections #signs #urology diseases of the genitourinary system
Symptoms
Most urinary organ diseases have similar symptoms, which makes self-diagnosis difficult:
- Pain in the lower abdomen (pulling, cutting, aching);
- Frequent urge to urinate (including at night);
- Pain during urge and urination;
- Feeling of fullness in the bladder;
- Sensation of a foreign body in the urethra;
- Change in urine color;
- Impurities in the urine (including blood);
- Temperature rises to 37–38 C.
In some cases, the disease can be asymptomatic in a latent form. This is a reason to undergo preventive medical examinations at least once a year and take tests to detect hidden infections.
The incidence of diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women of different ages has increased sharply in recent years.
This is due to a sharp deterioration in the quality of life and health of people, especially residents of megacities.
Such “companions” of the life of a modern person as poor ecology, nervous overstrain, improper combination of rest and work, unbalanced diet, bad habits - all this leads to the appearance of many diseases.
Unfortunately, under certain unfavorable conditions, urological diseases occur even more often than diseases of other human systems and organs.
The human genitourinary system, both men and women, is more susceptible to the influence of various negative factors than other internal organs.
Only Clinic provides assistance to men and women in the fight against diseases of the genitourinary system at different stages of their development.
Urologists at the Only Clinic will provide quick and effective assistance in the treatment of diseases of the bladder and other organs of the genitourinary system.
Diseases of the genitourinary system of men and women. Symptoms and causes
The urinary system in men and women includes the bladder, ureters, urethra and kidneys.
The urinary system of men and women is closely related to the human reproductive system.
Every day the body processes a large volume of fluid. The human urinary system is constantly under enormous stress. A huge volume of fluid regularly passes through the genitourinary system of men and women. The body regulates its composition around the clock, removes excess, and gets rid of toxins.
Inflammatory processes – including specific and nonspecific; congenital anomalies; Damage after injury is the main cause of the most common diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women.
Cystitis.
Cystitis is a disease of the mucous membrane of the genital organs of men and women. The appearance and development of cystitis can be triggered by harmful bacteria that enter the human body through the genitals. Stagnation of urine also contributes to the development of cystitis.
Cystitis can have chronic or acute forms.
The acute form of cystitis is expressed in periodic exacerbations of the disease. The chronic form haunts the patient constantly.
Both the chronic form and the acute form are pain, increased urge to urinate, discomfort, and increased body temperature.
Urinary incontinence.
Urinary incontinence is a disease of a person's inability to control the process of urination.
Urinary incontinence is more often diagnosed in women. Urinary incontinence appears as a consequence of weakening of the pelvic muscles, as well as weakness of the bladder sphincter. Also, the causes of urinary incontinence in women can be difficult childbirth, excess weight, gynecological operations, and changes in hormonal levels. Treatment of urinary incontinence can be carried out using non-surgical, non-drug methods (exercises, training, physical therapy). Urinary incontinence can be treated with medication or surgery (surgery or laser therapy).
Tumors.
Tumors in the bladder area usually appear in people over 40 years of age.
Tumor-like formations of the organs of the genitourinary system of men and women are the result of exposure to aggressive environmental factors on the human body, the influence of long-term chronic diseases or external harmful influences associated, for example, with the type of activity.
Alarming signs that some kind of disease is developing in the body are bloody impurities in the urine, difficulty urinating, and pain radiating to other organs, often to the kidneys or rectum.
A patient who consults a urologist with the above symptoms of diseases is first examined for oncology.
After excluding the malignant nature of the neoplasm, urologists at the Only Clinic conduct thorough examinations, collection of tests, ultrasound, if necessary, MRI or CT.
After the diagnosis is established, treatment is prescribed.
Correct diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women.
To correctly prescribe a method for treating diseases of the genitourinary system in men and women, it is necessary to thoroughly study the condition of the patient’s body. To do this, at the Only Clinic the patient is prescribed a comprehensive examination of the body.
Initially, the urologist examines the abdominal wall, bladder, kidneys, inguinal lymph nodes, and palpates the pelvic organs.
The doctor also collects anamnesis and listens to complaints.
Then, based on the data obtained, the urologist prescribes instrumental and laboratory examinations of the patient.
Typically, a urologist prescribes biochemical tests of blood and urine; biopsies and a number of other studies can be performed, such as uroflowmetry (determination of sphincter contractions); cystoscopy – endoscopic examination of the urethra and urethra; PCR; immunofluorescence reaction (RIF).
Additionally, a urologist may prescribe radiography, ultrasound (US), computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Dear patients! Highly recommend!!!
It is a mistake to believe that any genitourinary infection can be treated quickly and that a short course of antibiotics is enough to get rid of the problem.
The asymptomatic course of the disease can cause it to become chronic, and short-term treatment in this case becomes impossible.
A person who cares about his health should undergo urological examinations twice a year, even if there is no suspicion of organ inflammation.
For women, visiting a gynecologist with the same frequency is additionally recommended. This will make it possible to detect any disease at the stage of its sluggish process.
Do not self-medicate! Antibacterial drugs and their uncontrolled use lead to complex consequences.
Risk factors
No person is immune from diseases of the urinary system, but there are a number of risk factors that increase the likelihood of an infectious or oncological disease. These include:
- Urogenital infections;
- Unprotected sexual intercourse;
- Insufficient genital hygiene;
- Pregnancy;
- Smoking;
- Excessive consumption of salt and red meat;
- Uncontrolled use of medications and dietary supplements;
- Diabetes;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Obesity.
The above does not mean a 100% probability of developing diseases, but if you find yourself at risk, you should pay attention to your health and not ignore the symptoms. Talk to your doctor about ways to improve your quality of life and reduce your risks.
Pregnant women should definitely see a gynecologist in a timely manner and report any suspicious symptoms. In 7% of cases during pregnancy, pyelonephritis develops when infected with a bladder infection.
Diagnosis of diseases
Diagnosis of bladder diseases begins with a survey and examination by a doctor. The patient needs to be told in detail about the symptoms, circumstances of occurrence and stages of development of the disease, medications taken, and treatment performed. If you have the results of past examinations on hand, you need to take them with you to your appointment.
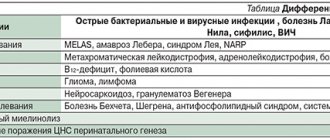
To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations [6]:
- three-glass sample. With its help, you can identify the source of blood and pus in the urine. The patient urinates successively in 3 containers during one urination. If the bladder turns out to be a source of blood, then it will appear in the last (3rd) portion of urine, if the source of pus is the source, the urine will be cloudy in all three glasses [6].
- laboratory: general urine analysis, cytological, biochemical examination of urine, according to Nechiporenko, general clinical and biochemical blood analysis, determination of tumor markers in blood and urine;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI and CT;
- X-ray diagnostics with contrast (excretory cystography);
- urethrocystoscopy - the doctor examines the bladder using a cystoscope and can immediately pinch off a piece of suspiciously altered mucosa for histological examination.
Prevention
Doctors have several recommendations that will help avoid the development of diseases of the urinary system:
- Do not overcool the urinary organs - dress according to the weather and do not wear short jackets and thin pants in cold weather, do not sit in the cold and do not spend a lot of time in cold water.
- Drink enough fluids throughout the day.
- Avoid unprotected sex with an untrusted partner.
- Maintain good hygiene - take a shower every day, wear clean underwear made from natural materials, change feminine hygiene products on time during menstruation.
- Do not abuse alcohol, tea and coffee, fatty, smoked and pickled foods.
- Stop smoking. Smoking increases the risk of developing cancer of the urinary system by 4 times.
- Treat diseases on time. Even mild cystitis can become chronic and, once in the kidneys, cause the development of pyelonephritis, a more severe and dangerous disease.
- Monitor the course of your chronic diseases and undergo regular medical examinations.
Description of the disease
Pathology develops as a result of the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the body or a rapid increase in the population of opportunistic microorganisms already living in it. They either directly penetrate the renal structures or are transported by the blood stream from the primary infectious focus. A violent inflammatory process develops, affecting almost the entire pyelocaliceal system and interstitial tissues.
Most often, acute pyelonephritis is diagnosed in women due to anatomical features - a short and wide urethra. It is often detected in children, because their immune system has not yet fully formed and cannot adequately withstand the attack of infectious pathogens.
How to treat diseases of the urinary system?
It is often impossible to independently diagnose and treat in the event of the development of urological diseases. Symptoms of different diseases can be similar, and out of ignorance a person can misclassify the symptoms and begin the wrong treatment, thereby aggravating the course of the disease.
The best solution is to consult a urologist when the first unpleasant symptoms appear. The urologist will diagnose, prescribe treatment or refer you to a doctor of another profile - a gynecologist, nephrologist or dermatovenerologist - depending on the detected pathology.
There is no need to be afraid of the urologist. This is a doctor like any other. The examination and test procedure can be unpleasant, but it is better to endure a couple of minutes than to then treat complications for several months.
Take care of yourself!
Which doctor should I contact if symptoms appear?
Several specialists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of the genitourinary system. Among them, special attention deserves:
- urologist;
- nephrologist;
- andrologist;
- gynecologist.
Consultation with these specialists helps to accurately differentiate diseases, prescribe adequate treatment and a diagnostic plan. If you are in doubt about which specialist to visit first, you can always consult a therapist. Based on your complaints, this doctor will coordinate your further actions and prescribe the first necessary tests.