Fibroids (fibroids) of the uterus are a benign tumor that is usually diagnosed in women between 35 and 46 years of age. Recently, there has been a trend toward “rejuvenation” of the disease, which is increasingly being found in young girls.
Until the neoplasm reaches an impressive size, beginning to put pressure on adjacent organs, fibroids can be asymptomatic. Malignancy of fibroids occurs in extremely rare cases.
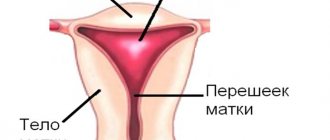
Fibroma and uterine fibroids: what is the difference between pathologies?
Uterine fibroids begin their development in muscle tissue, while the formation of fibroids is caused by the proliferation of connective tissue. In addition, uterine fibroids have their own characteristics:
- Several clinical variants of uterine fibroids are known, differing in parameters, localization and growth characteristics of tumors;
- for a long time, the condition of small tumors may remain unchanged, however, some provoking factors can accelerate the growth of fibroids: abortions, diagnostic curettages, inflammatory diseases of the uterus and appendages;
- During menopause, a benign tumor of the uterus often stops growing, decreases in size or completely disappears. However, in 10-15% of women, the tumor may increase in size during the postmenopausal period.
Impact on the pelvic organs
As the leiomyoma grows, it puts pressure on the bladder, which causes problems with urination. As a result, inflammation occurs, which can spread to the kidneys. In this case, an increase in temperature and the appearance of pathological impurities in the urine are observed. Localization of fibroid formation on the posterior uterine wall causes constipation and flatulence.
A large submucosal fibroma emerges through the uterine cervix into the vagina, which causes rupture of the neoplasm and severe bleeding. Against this background, inflammatory processes and painful sensations develop.
Causes of uterine fibroids
The reasons for the development of uterine fibroids have not been reliably established to date. However, experts note a connection between the growth of this benign tumor and the level of estrogen in the female body. In addition, the occurrence of the disease can be triggered by the following negative factors:
- hereditary predisposition to the development of tumors in the uterus
- uncontrolled long-term hormonal contraception
- violation of the hormone-producing function of the ovaries
- long-term insolation
- absence of pregnancy and childbirth in a woman over 30 years of age
- hemodynamic disturbances in the pelvis
- inflammatory processes in the uterus and its appendages
- the presence of cysts in the ovaries
- abortions and diagnostic curettages.
Treatment at home using folk remedies
Many women who have successfully recovered from uterine fibroids indicate that folk remedies helped them with this. The most effective and popular methods include:
- A decoction for douching from pomegranate peels. Pour a tablespoon of raw material with a whole glass of boiling water. Boil in a water bath for 15 minutes, then strain and cool. Douche in the evening and in the morning with a decoction at room temperature.
- Herbal decoction. It is necessary to mix celandine with mint, string, yarrow and St. John's wort in equal parts. Pour a glass of boiling water over the prepared mixture. Strain after 15 minutes. Drink half a glass three times a day for two months. Take a three-month break.
- Local herbal baths. Combine 6 tablespoons of oak bark, 4 tablespoons of oregano and marshmallow root in the amount of one spoon and pour boiling water over the mixture. Leave to cool completely, then mix with two tablespoons of Kalanchoe juice. Use for baths and douching.
Uterine fibroids: symptoms and signs
Small tumors do not manifest themselves for a long time. However, as they grow, characteristic signs of uterine fibroids appear. Typically, a benign uterine tumor is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- bleeding not related to the menstrual cycle
- painful sensations during menstruation
- prolongation of the period of menstrual flow
- frequent urination when the enlarged uterus compresses the bladder
- constipation due to compression of the intestines by the enlarged uterus
- a feeling of heaviness and pressure in the lower abdomen
- painful sensations during intimacy
- causeless growth of the abdomen
- pain in the lumbar region
- infertility
- neurological and mental disorders.
The severity of symptoms of uterine fibroids depends on the size, location of the neoplasm, and the intensity of its growth. In the early stages, a woman’s menstrual cycle may be disrupted, which should be the first “alarm bell” and a reason to consult a gynecologist.
More than 50% of women with uterine fibroids experience an increase in the volume of menstrual flow. This disorder causes the development of anemia, pathologies of the cardiovascular system, and blood coagulation disorders.
Pain due to uterine fibroids varies in nature - from pulling and aching to cramping.
With intraligamentary localization of the tumor, the ureters are compressed, as a result of which women experience urinary incontinence and other pathologies of the urinary process. When the intestines are compressed by a tumor, constipation may occur.
Due to abnormal changes in the liver in women suffering from fibroids, the hormonal balance is disrupted, and, consequently, the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates and proteins. In addition, there is a violation of thermoregulation, which leads to daily fluctuations in the patient’s temperature.
Complications
Complications and consequences of the disease include:
- postoperative infections;
- bleeding;
- the formation of adhesions localized in the pelvis;
- the appearance of synechiae in the uterus.
Danger
Transformation of the disease into a malignant formation is possible only in 15%. The disease can lead to premature birth, prevent pregnancy, and late dangerous miscarriages. The pathology in its advanced form is fraught with anemia against the background of severe bleeding.
Uterine fibroid: diagnosis
Often, a doctor discovers uterine fibroids by chance during a gynecological examination regarding other complaints of the patient. The presence of a benign tumor can initially be suspected by an increase in the size of the uterus.
To clarify the location of the tumor and the number of nodes, the woman is prescribed additional diagnostic studies:
- clinical laboratory studies and pregnancy tests
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs - to identify pathological processes in the uterus
- hysteroscopy - an instrumental examination, for which a special apparatus (hysteroscope) and an optical instrument are used. Prescribed to clarify the features of the hyperplastic process in the uterus, identify suspicious areas of the endometrium and perform a biopsy
- laparoscopy – prescribed according to indications, allows you to examine the uterine cavity using an endoscope
- Metrosalpingography is a contrast X-ray examination that allows you to assess the condition of the uterine cavity and the patency of the fallopian tubes.
Identification of the disease
As soon as the patient begins to observe such symptoms of fibroma, it is necessary to immediately consult a doctor, since the development of formation is easier to prevent than to eliminate its consequences.
During a qualified examination in a gynecological chair, a specialist can easily determine the enlargement of the uterus, the lumpy surface and its dense consistency. On an ultrasound examination, changes can be seen in the form of nodes in the organ cavity, the location of the neoplasm and its direction in relation to other organs can be determined. Differentiated as a pathology, not a cyst.
X-ray or ultrasound hysterosalpingoscopy helps determine the presence of submucosal fibroids in the endometrial cavity. If the patient complains of bleeding in the absence of scheduled menstruation, it is important to check the body for the presence of a cancerous tumor:
- perform an endometrial biopsy for histological examination of the tumor;
- use separate diagnostic curettage.
When making a final diagnosis, fibroma is distinguished from:
- ovarian cysts;
- sarcomas of the uterus.
For this purpose, additional research may be used in the form of:
- computed tomography;
- magnetic resonance therapy;
- diagnostic laparoscopy.
Uterine fibroid: treatment
When choosing treatment tactics, doctors are based on the results of the examination, taking into account the location of the fibroids, the size of the node and the need to preserve the reproductive function of the patient diagnosed with uterine fibroids. Treatment can be carried out conservatively or surgically.
Uterine fibroid: conservative treatment
Conservative therapy for uterine fibroids involves the use of hormonal drugs to help stop tumor growth. This type of treatment is indicated for the following conditions:
- small size node (less than 12 weeks of pregnancy)
- mild symptoms that do not reduce the patient’s quality of life
- the need to preserve a woman’s reproductive function
- extragenital diseases that are a contraindication to surgical treatment
- postoperative rehabilitation or preparation for myomectomy.
The positive effect of hormonal therapy is achieved if it is continued for at least six months. This or that drug is selected in accordance with the patient’s age and the characteristics of the course of the disease. Hormone therapy for uterine fibroids is carried out using the following drugs:
- estrogen-progestin drugs
- progestational drugs
- androgen drugs
- GnRH and antigonadotropic drugs.
Hormonal therapy for uterine fibroids has a number of contraindications:
- intense increase in tumor size
- presence of severe pain, frequent bleeding
- size of the uterus exceeding 12 weeks of pregnancy
- concomitant diseases of the pelvic organs
- somatic pathologies (not used in the presence of diabetes mellitus, hypercoagulation, hypertension, etc.).
In addition to hormonal therapy, nonspecific methods that affect the elements of the pathogenesis of the disease are used to treat uterine fibroids:
- vitamin therapy - taking vitamin and mineral complexes to speed up metabolic processes in the body and improve the general condition of a woman;
- diet therapy – the patient’s diet includes iron-containing and protein foods, as well as foods that help improve liver function;
- immunomodulatory therapy - to strengthen the immune system;
- antianemic therapy – for large blood losses during menstruation;
- taking sedative drugs – prescribed for vegetative-vascular pathologies;
- venotonics – normalizing the menstrual cycle;
- physiotherapeutic treatment – magnetic therapy, autotransfusion, electrophoresis, etc.
In the absence of an increase in symptoms and an increase in the size of fibroids, the woman is prescribed dynamic observation by a doctor with regular ultrasound examinations, which allows assessing the condition of the tumor.
Laparoscopic excision of fibroids
If fibroids are located subserosally and intramurally, it is more advisable to perform laparoscopic removal. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, small (3-5 mm) incisions are made on the anterior wall of the peritoneum, through which a special laparoscope is inserted, allowing tumors to be excised carefully and sparingly.
Laparoscopic removal is a one-day procedure. If there are no complications, the patient is discharged from the clinic the next day. The rehabilitation period takes up to 2 weeks, during which you need to avoid physical and psycho-emotional stress.
Factors promoting tumor formation
According to research results, the key factor in the occurrence of fibroids is an increase in estrogen with progesterone deficiency, which is associated with ovarian dysfunction. Estrogen promotes the growth of certain muscle groups of the uterus. An increase in the production of female hormones is provoked not only by inflammatory and infectious diseases of the reproductive system, abortions, contraceptives, but also by poor nutrition. Thus, foods high in refined carbohydrates, saturated fatty acids and insufficient fiber when consumed regularly increase the risk of developing tumors.
Fibroids can also appear as a result of trauma to the uterus - trauma during childbirth, curettage, diagnostic hysteroscopy, insertion of an IUD (intrauterine device). Women who are overweight are susceptible to tumor processes - fatty tissue transforms androgens into estrogens. Therefore, this disease occurs 3 times more often in patients weighing more than 70 kg. The distribution of fat mass affects the production of estrogen, so women with deposits in the upper torso and waist (apple body type) are most susceptible to fibroids. Hormonal levels are affected by hypertension, psycho-emotional stress, a sedentary lifestyle, regional factors, and incompatibility with a sexual partner.