Etiology of the disease
Treatment of leukoplakia is preceded by taking an anamnesis. Depending on the type of pathology and possible causes of the disease, therapy will vary. Doctors identify the following risk factors:
- infection with human papillomavirus;
- presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- inflammatory processes in the reproductive system;
- hormonal imbalance;
- injuries during gynecological manipulations (abortion, childbirth, installation or removal of an intrauterine device);
- mucosal erosion;
- early sexual life and pregnancy.
The risk group for this pathology also includes women who have concomitant chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, immunodeficiency and others).
Medicines
Photo: kak-bog.ru
In the presence of an infectious disease of bacterial etiology, antibiotics are prescribed, the action of which is aimed at destroying pathogenic microorganisms. As a rule, broad-spectrum antibacterial agents are used, since they are effective against both gram-negative and gram-positive microflora. While taking antibacterial agents, various undesirable effects may appear, but the most common side effects are from the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, vomiting, heartburn, diarrhea). As is known, taking antibacterial agents affects the quantitative composition of the normal microflora of the intestinal tract, which is why in some cases probiotics are additionally prescribed.
In case of herpes infection, acyclovir is prescribed. The dosage of the drug and the frequency of administration are determined by the attending physician, based on the severity of the process and the severity of clinical manifestations. While taking the drug, the following side effects may occur: periodic discomfort in the epigastric region, nausea, occasionally vomiting, increased stool frequency. It is also worth noting that while taking acyclovir, it is important to monitor creatinine and urea levels, since this drug is known to have a detrimental effect on kidney function. Accordingly, people suffering from chronic kidney disease are advised to refrain from using this drug or to more carefully monitor laboratory parameters to assess kidney function.
Antifungal drugs (fluconazole, ketoconazole, itraconazole) have a fungicidal or fungistatic effect and are used for the treatment and prevention of mycoses. The most common undesirable effects that occur while taking antifungal drugs are: periodic discomfort or pain in the abdomen, heartburn, a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea, occasionally vomiting, flatulence, constipation, dry oral mucosa.
In the presence of an infectious-inflammatory disease of the reproductive system, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, diclofenac) are prescribed. The mechanism of action is to inhibit the enzyme COX (cyclooxygenase), as a result of which the synthesis of prostaglandins is disrupted. Thanks to this mechanism of action, not only an anti-inflammatory effect is achieved, but also an antipyretic and analgesic effect. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be used with caution by people with gastrointestinal diseases, since long-term use of these drugs, especially in large doses, leads to damage to the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
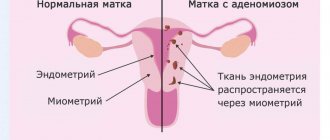
Types of leukoplakia
How to treat leukoplakia depends on its type. The disease is dangerous because pathological processes in the epithelium can become malignant and provoke oncological tumors.
Today, medicine distinguishes three categories of leukoplakia.
- Simple. The formations are located flush with the epithelium. They are usually white in color and the changes are benign.
- Proliferative. It is expressed in dense growths rising above the epithelium. There are warty and scaly forms.
- Erosive. Characterized by cracking and bleeding lesions. This form is the most dangerous because the structures contain atypical cells.
Leading specialists in the treatment of leukoplakia in the Southern Federal District
Ermolaeva Elvira Kadirovna is a well-known and recognized specialist in the North Caucasus in the treatment of leukoplakia of the vulva, vagina and cervix, diagnosis and treatment of kraurosis, lichen sclerosus, Keir's erythroplasia and other diseases of the vulva. One of the authors of the method of regenerating microinjections for the treatment of leukoplakia. Desperate people turn to her and women exhausted by suffering. Experienced gynecologist, physiotherapist-health resort specialist, ultrasound doctor.
Ermolaev Oleg Yuryevich Candidate of Medical Sciences, gynecologist-endocrinologist with 25 years of experience and successful experience in the treatment of leukoplakia, kraurosis and vulvar dysplasia Able to see relationships that elude others
About the doctors of the Clinic in detail...
| INTERNATIONAL RECOGNITION of the reputation and achievements of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in the development and implementation of effective and safe treatment methods and the quality of medical services provided is the AWARDING of the Women's Health Resort Clinic in Pyatigorsk with the SIQS International QUALITY CERTIFICATE in the field of medicine and healthcare. International Socratic Committee, Oxford, UK and Swiss Institute for Quality Standards, Zurich, SWITZERLAND. |
The resort women's health clinic is open 7 days a week and on holidays:
Monday - Friday from 8.00 to 20.00, Saturday, Sunday, holidays from 8.00 to 17.00.
ACCURATE determination and treatment of leukoplakia in Pyatigorsk by appointment no later than 3 days in advance by multi-channel telephone 8 (800) 500-52-74 (free call within Russia), or +7 (for foreign calls).
| about treatment in Pyatigorsk can be found at REGISTER ONLINE for leukoplakia treatment here. REGISTER online for leukoplakia treatment here. SIGN UP for treatment by phone or here. |
Sign up for treatment
The doctors of our PROFILE women's clinic have gained EXTENSIVE EXPERIENCE in treating leukoplakia of the female genital organs with resort factors and medicines from natural raw materials.
We accept women from all cities of Russia, near and far abroad.
The spa clinic for women's health facilitates the accommodation and accommodation of women, women with children and couples during examination and treatment.
ACCOMMODATION in Pyatigorsk is NOT INCLUDED IN THE PRICE of the treatment course and is paid separately.
About living conditions and transfer from Mineralnye Vody airport and Pyatigorsk railway station in detail in the article “Accommodation”.
If you need to book accommodation, please coordinate your arrival date no later than 7 days in advance.
We are at your complete disposal if you have any doubts or wishes.
Clinical manifestations
Treatment of leukoplakia of the vagina or uterus is prescribed depending on the manifestations and symptoms. Women with this pathology may complain of the following types of discomfort:
- insufficiency of vaginal secretion;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- pain during urination;
- cracks on the labia;
- spots on the mucous membrane;
- warts;
- erosion;
- genital discharge;
- scales.
Often the lesions do not cause discomfort, remaining unnoticed by the patient. This is why regular visits to the gynecologist are necessary. You can find a doctor you can trust at the Dr.AkNer clinic. We employ the best specialists with extensive experience in the treatment of women's diseases.
Symptoms
Photo: mirbodrosti.com
In most cases, cervical leukoplakia is detected during a routine examination of a woman. Much less often, this disease manifests itself with certain symptoms, which are the reason for a woman’s visit to a medical facility.
About 30% of women who have cervical leukoplakia complain of some discomfort in the vaginal area; pain is usually absent. In addition, pathological discharge from the genital tract - leucorrhoea - may appear. The presence of contact bleeding (minor discharge of blood from the genital tract after sexual intercourse) is extremely rare. In the presence of hormonal disorders in a woman’s body, which can also cause the appearance of cervical leukoplakia, a disturbance in the menstrual cycle is noted.
When the pathological process spreads to the vulva, complaints of severe itching appear, which leads to scratching.
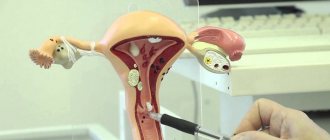
Diagnostic measures
Treatment methods for cervical leukoplakia are chosen by the doctor depending on the severity and type of disorder. To clarify the diagnosis, the following tests and studies are performed:
- colposcopy (examination of the cervix using an optical device);
- scraping cytology;
- PCR test for HPV;
- histological examination of a tissue sample;
- tests for sexually transmitted diseases;
- Schiller test to identify atypical cells.
The doctor receives the first information about the disease during a standard examination. Whitish growths are found on the epithelium, which make it possible to identify leukoplakia.
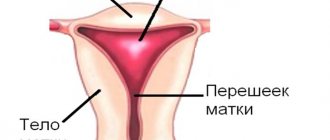
Leukoplakia of the cervix - symptoms and treatment
Conservative treatment
Drug treatment for leukoplakia includes:
- etiotropic anti-inflammatory therapy;
- correction of vaginal microbiocenosis, hormonal and immune disorders [22];
- treatment of HPV with immunomodulators is justified only in conjunction with surgical intervention [23].
If a young nulliparous woman is diagnosed with cervical leukoplakia, but there is no HPV, then you can not have surgery yet, but you must monitor the patient’s condition [24].
In our country, leukoplakia is usually subjected to destruction—the destruction of pathological tissue. This is justified, since over time leukoplakia can transform, the patient can become infected with HPV and tissue degeneration will occur, which will require new biopsies and unnecessary visits to the doctor.
Surgery
The most commonly used treatment methods for cervical leukoplakia are:
- radio wave surgery;
- laser therapy (high-intensity CO2 laser radiation);
- diathermocoagulation (as undesirable, due to the large number of potential complications, but a possible method of treatment).
Preparation for surgery includes:
- gynecological smear, examination for sexually transmitted infections and bacteriological culture from the cervical canal if there is inflammation;
- HPV test using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with genotyping;
- cytological examination;
- colposcopy;
- Ultrasound to detect cervical masses of unknown origin;
- hormonal examination if appropriate disorders are suspected;
- point biopsy with adequate colposcopy;
- excisional biopsy (the tissue being examined is removed entirely) in case of inadequate colposcopy - due to severe inflammation that distorts the picture, severe bleeding, severe cicatricial changes when the atypically changed epithelium extends deep into the cervical canal;
- diagnostic curettage of the epithelium of the cervical canal to exclude precancerous changes and malignant transformation of the endocervix [27].
If cervical leukoplakia is combined with inflammation of the vulva and vagina, then it must be eliminated before surgery [28].
How are gynecological operations performed?
Manipulations are performed in the first half of the menstrual cycle (4-7 days from the start of menstruation). To more accurately determine the pathological tissue, the procedure is controlled by colposcopy, and the cervix is treated with Lugol's solution. Complete healing and the patient’s return to normal life (the possibility of sexual activity, the use of vaginal tampons, visiting the pool, etc.) is often expected 28-40 days after the procedure. Correction of hormonal disorders and adequate hormone therapy, according to some data, can speed up the healing time of postoperative wounds and reduce the frequency of recurrence of benign diseases of the cervix.[10]
When leukoplakia is combined with deformation and hypertrophy of the cervix, it is advisable to perform reconstructive plastic surgery (cervical plastic surgery) to restore the anatomy of the cervical canal.[14][15]
Modern foreign researchers regard leukoplakia as a benign physiological process and in most situations recommend preventive monitoring.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is the destruction of a pathological focus using low temperature. It is carried out by contact method, most often once. The duration of the procedure depends on the nature and extent of the pathological process. On average, at a temperature of minus 90 °C, 10 minutes is enough [26].
The advantages of this method include painlessness and the ability to perform it on an outpatient basis. The effectiveness of this treatment ranges from 54 to 96%. Disadvantage of the method: repeated cases of leukoplakia, especially in patients with menstrual irregularities [19].
Chemical coagulation
Leukoplakia was treated with chemical coagulants, for example Solkovagin, in the 90s of the twentieth century. The effectiveness of treatment of simple cervical leukoplakia in young nulliparous women was about 70%. Now this method is not used.
Antibiotic therapy
Before surgery, it is necessary to eliminate the concomitant inflammatory process in the cervix. The choice of antibacterial drugs depends on what pathogenic microorganisms are identified during the tests [29][30][31][32]. After surgery, antibiotics are not required, since surgery is performed only if there are no infectious processes.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy after cervical surgery, including leukoplakia, is not performed.
Traditional methods of treatment
You should not use products that affect tissue metabolism: sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil, aloe ointment, etc. These drugs can promote tissue proliferation and the occurrence of cervical dysplasia [23].
Pregnancy and leukoplakia
During pregnancy, treatment of cervical leukoplakia, both without atypia (keratosis or hyperkeratosis) and with atypia (dysplasia), is not carried out. For changes in the cervix, including grades II and III cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN II–III), prenatal observation is indicated: cytological examination and colposcopy once every 3 months [16]. Control cytological examination and colposcopy are carried out no earlier than 6 weeks after birth [17].
If cervical leukoplakia is detected in pregnant women, it is necessary to treat urogenital infection, bacterial vaginosis and restore vaginal microbiocenosis.
If HPV infection is detected, interferon therapy is used, for example the drug Viferon (gel, rectal suppositories) after the 14th week of pregnancy. Repeated courses are carried out at 22–24 and 32–34 weeks of pregnancy [16]. Leukoplakia does not affect the course of pregnancy and gestation.
Rehabilitation
Immediately after the procedure, the patient may experience nagging pain in the lower abdomen, but this quickly passes. The discharge is most often light mucous or watery, rarely streaked with blood.
Bloody discharge after surgery is rare. But if they appear, bother you for more than 5-10 days and/or menstruation becomes heavier and blood clots are released, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Body temperatures above 37.5 °C, severe pain in the lower abdomen and purulent discharge from the genital tract with a strong unpleasant odor should also alert you.
Within a month after surgery it is recommended:
- abstain from sexual intercourse;
- do not take a bath, you can only wash in the shower;
- do not douche or use vaginal tampons;
- avoid overheating, do not visit baths and saunas;
- do not swim in the pool or swim in natural bodies of water;
- Do not play sports or lift weights over 3 kg.
Two weeks after surgery, the doctor performs a gynecological examination to ensure that the patient is recovering. The mucous membrane completely returns to normal in 4–6 weeks.
Observation after treatment
The frequency of visiting a doctor depends on the form of the disease, the effectiveness of treatment and the presence of risk factors that may complicate recovery: smoking, HIV infection, sexually transmitted diseases, carriage of oncogenic types of HPV, etc.
The cytological method is the most optimal for monitoring after surgery; abroad, the HPV test is sometimes additionally used. If the results of the PAPP and HPV tests are positive, then colpososcopy is performed [25].
Clinical observation after treatment of leukoplakia without atypia is carried out once every six months for two years. Includes colposcopic and cytological examinations, HPV analysis [18]. If the treatment was effective, no pathologies were detected on colposcopy, there are no atypical cells in the oncocytology smear, and the HPV test is negative, then the patient can visit the doctor once a year.
After treatment of cervical leukoplakia with atypia (with CIN I–II - cervical intraepithelial neoplasia of I and II degrees), “post-treatment monitoring” is required: once every 3 months during the first year and 2 times a year thereafter [18]. If all indicators are normal, then the patient is also transferred to the usual screening regimen - once a year.
Diet
After treatment of leukoplakia, you should adhere to the principles of proper nutrition; a specific diet is not required.
Prevention of leukoplakia
The key measures for the prevention of leukoplakia are basic rules of personal hygiene and strengthening the immune system:
- regular hardening;
- sufficient physical activity;
- balanced diet;
- timely treatment of any disorders;
- regular preventive examinations;
- giving up bad habits, heavy and spicy foods that irritate the esophagus;
- careful intimate hygiene and visiting a gynecologist;
- compliance with all doctor’s recommendations during a preventive examination.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Prevention and prognosis
In most cases, the prognosis is favorable. The absence of human papillomavirus infection and dysplasia indicates a low risk of malignant tissue degeneration. Surgical intervention not only eliminates the risk of organ malignancy, but also preserves reproductive function. After treatment, the gynecologist regularly conducts examinations to eliminate the risk of relapse.
Simple medical recommendations can reduce the likelihood of leukoplakia and other diseases of the reproductive system. Prevention methods are aimed at changing lifestyle and eliminating negative external factors.
Basic methods of prevention:
- use of hormonal drugs only under the supervision of a physician;
- regular gynecological examinations;
- keeping a calendar of the menstrual cycle and contacting a doctor if disorders occur;
- refusal of alcoholic beverages and cigarettes;
- timely treatment of chronic diseases of the genital and endocrine organs;
- using a latex condom;
- sexual intercourse only with a trusted partner (HPV infection can be transmitted even when using a condom).
A consultation with a gynecologist or oncologist will help a woman learn more about the risk factors for leukoplakia and treatment methods for this disease. If necessary, the doctor immediately conducts an examination and excludes the presence of suspicious changes in the cervix.
Diagnosis of background and precancerous diseases of the cervix
During the consultation, the doctor will talk with you, look at the results of previous studies (bring with you to the appointment all the medical documents you have on hand and related to women’s health), and conduct an examination to identify changes in the condition of the mucous membrane. Video colposcopy will help the doctor see the situation in more detail. During the examination, the doctor will make smears for a Pap test and flora examination. If necessary, a biopsy will be performed for subsequent histology. Gynecological patients also undergo ultrasound with a transvaginal probe, as well as ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. You will be prescribed tests - a complete blood count, a blood test for hormones, and a urine test.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and decides in favor of one or another treatment method.