Mycoplasmosis is a group of infectious diseases caused by mycoplasmas and most often transmitted sexually.
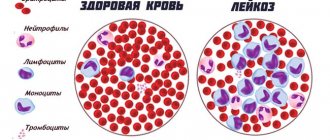
Mycoplasmas are microorganisms that occupy a middle position between bacteria and viruses. The similarity with viruses is manifested in their small size, with bacteria - in the presence of their own DNA. There are several dozen types of mycoplasmas, but only four of them can lead to disease. One of the pathogenic types of mycoplasmas is called ureaplasma, and the infection it causes, ureaplasmosis, also belongs to mycoplasmosis.
Course of the disease and symptoms
Once in the human body, mycoplasmas attach to epithelial membranes in the intestines, respiratory organs, genitourinary system, and even attach to red blood cells and sperm.
symptoms characteristic only of mycoplasmosis, and its manifestations are very similar to other infectious diseases of the genitourinary system. Often the disease is so secretive that half of the patients do not even know about it. The main noticeable symptoms of genitourinary mycoplasmosis are
- significant vaginal discharge in women;
- whitish or yellow discharge from the urethra in men;
- pain during sexual intercourse and urination.
Mycoplasmosis
Mycoplasmosis is an infectious disease that is provoked by the presence in the body of a specific microorganism called mycoplasma. Mycoplasmas in their structure are neither bacteria, nor fungi, nor viruses. They are not independent - in the sense that the life activity of mycoplasmas is possible only in the cells of the host organism. It must be said that several types of mycoplasmas are found in the human body, but only four of them can, under certain conditions, lead to disease. Mycoplasma pneumonia negatively affects the respiratory system and causes inflammatory processes in the throat, bronchi, and lungs. Mycoplasma genitalium and Mycoplasma hominis infect the genitourinary tract.
Most often, mycoplasmas attach to the membranes of epithelial tissue cells in the intestines, respiratory organs and genitourinary system. After they are fixed on the surface of the tissue, they penetrate deeper, trying to settle between the cells and enter into intermembrane interaction with them. By doing this, they, of course, disrupt the natural functioning of the cells and the entire organ as a whole. However, the exact mechanism of mycoplasmosis is still unknown. Once in the external environment, mycoplasmas quickly die as they are deprived of nutrition.
You can become infected with mycoplasmosis through unprotected sexual contact. There is also a possibility of infection from mother to fetus, in utero (this probability is low, it is estimated at 5-10%). It is possible to theoretically assume the possibility of infection through very close bodily contact, for example, if you put on underwear that an infected person recently removed. But, you must admit, such a situation is unlikely in reality. Mycoplasmosis is not transmitted through household means - through dishes, face towels - since its causative agent cannot exist in the external environment. The presence of mycoplasma in the body does not always lead to disease.
According to statistics, mycoplasmosis is most often diagnosed in people who have an active sexual life with several partners, in homosexuals. It often accompanies other sexually transmitted infections - for example, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis. Unfortunately, it is often detected during pregnancy - and it is for pregnant women that this disease poses a particular danger. The probability of a threatened miscarriage (miscarriage, frozen pregnancy) with mycoplasmosis is about 60%, the risk of premature birth increases two to three times. The probability of gestosis (a disorder of the functioning of vital organs, especially the vascular system) in the last trimester of pregnancy is about 30%. Fetal pathologies, primarily chronic hypoxia (oxygen starvation), are diagnosed in every third pregnant woman suffering from mycoplasmosis.
If a child is infected in utero, then immediately after birth he is at risk. Such children experience slow weight gain, frequent infectious and allergic diseases, and a high risk of damage to the central nervous system. The risk of congenital defects increases significantly: these can be defects of the liver, lungs, kidneys, or central nervous system. In the first days of life, such a child may develop pneumonia.
And for a woman suffering from mycoplasmosis, any outcome of pregnancy - natural birth, abortion, cesarean section - is complicated by an infectious process in the uterus (endometritis).
Symptoms
Mycoplasmosis is often asymptomatic. About half of the patients do not observe any alarming changes in the functioning of their body and find no reason to worry or see a doctor. It often happens that the infection seems to “sleep”, awakening at a moment of severe stress. If mycoplasmosis does manifest itself, then its visible symptoms may be heavy vaginal discharge, moderate pain during urination and sexual intercourse.
Diagnostics
To diagnose mycoplasmosis, the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is used. It is the most accurate and informative, and allows you to determine the presence of a pathogen in the discharge of the cervical canal. If necessary, it is possible to use determination of the presence of antibodies in blood serum to determine disease activity.
Treatment
The treatment regimen is developed individually by the doctor, taking into account the symptoms manifested, the severity of the disease, the general condition of the body, and allergic reactions. Both sexual partners must be treated, even if mycoplasmosis is diagnosed in only one of them.
The course of treatment for mycoplasmosis includes drugs aimed at combating mycoplasmas and drugs that support the body's natural resistance. To eliminate mycoplasmas, the following drugs can be used: Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Minocycline, Metacycline, Rifampicin, Ericicline, Roxithromycin, Vilprafen, Clarithromycin, Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin. Erythromycin and Rovamycin are used to treat pregnant women. The duration of treatment is 10-14 days. Recently, Wobenzym is often added to the treatment regimen as a drug that increases the body’s ability to resist genetically foreign microorganisms. And to restore the intestinal microflora and correct local immunity, preparations containing strains of representatives of the microflora of a healthy human body are recommended. This could be Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Bififor.
After completing the course of treatment, it is necessary to conduct a control study - after 10 days. A second study is recommended after three menstrual cycles. If mycoplasmas are not detected, we can talk about cure.
Spreading
Mycoplasmosis is divided into three main types: genitourinary, respiratory and perinatal. The spread of the disease occurs through sexual contact, airborne transmission and in the womb. The most common diagnosis is genitourinary mycoplasmosis, which occurs in people who are sexually active with multiple partners without using condoms .
With perinatal mycoplasmosis, infection occurs from mother to fetus during pregnancy. But the presence of a confirmed diagnosis in an expectant mother does not mean that her child will also be sick after birth.
Mycoplasmosis is not transmitted through household means - through dishes, towels. Getting mycoplasma into the body does not mean that a person will necessarily get sick. About 15% of people are carriers of the infection, but do not suffer from mycoplasmosis.
What is Mycoplasma hominis?
The content of the article
Mycoplasma hominis
- atypical bacteria, belong to the genus
Mycoplasma.
These are microorganisms that lack a cell wall, which makes them resistant to many antibiotics.
Mycoplasma hominis
- can colonize the genitourinary tract. Colonization by these bacteria is most often accompanied by hormonal changes in women, for example, during menopause, as well as with frequent unprotected sexual intercourse.
Diagnosis of the disease
Our clinic uses several tests that allow the doctor to accurately diagnose mycoplasmosis and prescribe the most correct treatment option. Of all the possible tests (PCR-DNA diagnostic method, culture of secretions, determination of antibodies in the blood and others), the most highly qualified specialists in St. Petersburg will choose the optimally suitable and reliable ones. The diagnostic accuracy of these modern methods reaches 100%. Thanks to the high level of staff at our clinic, conducting research will not cause you any inconvenience or discomfort.
Mycoplasmosis: prevention
Such an area as the prevention of mycoplasmosis is preferable in gynecological practice rather than the treatment of the disease itself and its complications.
- Avoid unprotected sexual intercourse. Only the use of barrier methods of contraception (condom) can protect almost 100% from the transmission of sexually transmitted infections.
- Support of the immune system, which can be achieved by eliminating low-quality and unhealthy foods from the diet and giving up bad habits.
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene.
- Regularly scheduled examinations with a gynecologist.
Treatment of mycoplasmosis
Treatment of mycoplasmosis is carried out based on research results, taking into account the identified characteristics of the disease, the patient, and may include
- physiotherapeutic procedures,
- taking antibiotics and vitamins,
- herbal treatment.
The doctor at our clinic will prescribe a set of measures that will lead to recovery without side effects. Treatment of genitourinary mycoplasmosis should be carried out not only in the patient, but also in his sexual partner. If mycoplasmosis is detected during pregnancy, our doctors will help you begin treatment in a timely manner, using drugs and procedures that do not harm the fetus.
It is difficult to find another clinic in St. Petersburg with such extensive and successful experience in treating infectious diseases. We always take care of the health of our clients first.
See also : Appointment with a urologist, Analysis for tumor markers for men, Urological programs.
Complications after mycoplasmosis
- Endometritis. In the absence of competent and timely therapy, the infection can ascend into the uterine cavity and cause endometritis (an inflammatory process of the uterine mucosa). Endometritis can subsequently affect a woman’s fertility, causing infertility.
- Salpingo-oophoritis. Inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. After suffering salpingo-oophoritis, adhesions can form, due to which obstruction of the fallopian tubes is formed, causing tubal infertility.
- Diseases of a rheumatic nature (Reiter's disease).
- With the development of a tubo-ovarian formation filled with purulent contents and a violation of its integrity, peritonitis can develop, which threatens not only the health, but also the life of the woman.
Mycoplasma hominis during pregnancy
Presence of Mycoplasma hominis
in a smear from the cervical canal is observed in approximately 10% of pregnant women. Mycoplasma infection can cause inflammation of the urethra and cervix; as the disease progresses, complications develop: inflammation of the placenta and membranes. Inflammation of the membranes can lead to their rupture, resulting in miscarriage or premature birth.
In addition, infection with Mycoplasma hominis
can lead to intrauterine infection, resulting in intrauterine infection, the fetus may develop pneumonia, inflammation of the meninges or bacteremia.
Why is mycoplasma dangerous?
A disease such as mycoplasmosis is very often asymptomatic, but it cannot be cured on its own. The latent infection continues to progress and pose a possible threat. If left untreated, mycoplasmosis can cause consequences such as pyelonephritis and infertility. The infection can remain in the body for a long time, which leads to the following dangerous conditions:
- decreased immune defense;
- addition of other pathogens;
- spread of the infectious process to the bladder, kidneys, genitals, with the development of foci of chronic infection and infertility.
That is why treatment of mycoplasmosis is necessary, of course, under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of infection
Treatment of infection caused by the bacterium Mycoplasma hominis
requires the use of antibiotics. The most commonly used are tetracyclines and macrolides. Prescribe Unidox Solutab (doxycycline) 100 mg twice a day for 10 days. Vilprafen (josamycin) at a dosage of 500 mg three times a day, course - 10 days.
Macropen (midecamycin) 400 mg three times a day, course of treatment for 14 days. The use of the drug Sumamed (azithromycin) is effective; on the first day, take 500 mg once, then 250 mg in the next four days, also once a day. Treatment is accompanied by the use of means to normalize the microflora, stimulate the immune system, and vitamins.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Pathways of pathogen transmission
Mycoplasma pathogens are highly contagious (infectious). The cause of mycoplasmosis is infection during unprotected intimacy. The danger of infection is posed by vaginal contact, since the mucous membrane of the genitourinary organs is a favorable environment for mycoplasma. The risk of transmission of infection through oral and anal sex is negligible.
Unidentified or unresolved mycoplasmas in a pregnant woman are transmitted to the child during delivery. Infection occurs when the baby passes through the birth canal and the baby’s skin comes into contact with female biological secretions.
The hypothesis of infection through household contact is unfounded. Mycoplasma genitalium, Mycoplasma hominis are anaerobes that are unable to live and reproduce in an oxygen environment.
Symptoms of mycoplasmosis
Symptoms of mycoplasmosis are largely indirect. In this situation, the most typical complaints include the occurrence of light transparent discharge, discomfort or slight burning during urination, and nagging pain in the groin and lower abdomen, which intensifies during sexual intercourse.
Mycoplasmosis in women often occurs against the background of bacterial vaginosis and inflammatory lesions of the genitourinary organs (endometritis, salpingitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis, etc.). The presence of this infection can lead to the development of such serious complications as menstrual irregularities, miscarriage, polyhydramnios, placental abnormalities, and secondary infertility.
Mycoplasmosis in men most often occurs in a latent form and is detected only during a diagnostic examination. Lack of treatment leads to the development of complications, accompanied by typical symptoms of inflammation of the urogenital tract, pain in the scrotum, perineum and rectum.
Mycoplasma hominis - diagnosis
To diagnose mycoplasmosis, laboratory tests are necessary. The main and most informative method for detecting mycoplasma is PCR (polymerase chain reaction). PCR detects the genetic material of a bacterium. A smear from the urethra, cervical canal is analyzed, and urine testing is possible. Before smear analysis, patient preparation is necessary. Two days before the study, you must abstain from sexual activity and refuse vaginal irrigation. Before submitting urine for analysis, it is not recommended to wash the genitals; it is better to take morning urine.
PCR analysis
Serological blood testing is much less common. The serological test determines the level of immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies. Their presence in the blood indicates a fresh infection and persists for up to 1-2 months. The material for serological testing is blood taken strictly on an empty stomach; the preliminary period of fasting should be at least 10-12 hours.
Treatment of mycoplasma in women
Treatment of mycoplasmosis in women primarily depends on the form of the disease, severity, complications, if any, and concomitant diseases. Depending on the diagnostic results, the gynecologist prescribes individual therapy for each patient. The cost of developing a treatment regimen starts from 1000 rubles.
It should be noted that the bacterium Mycoplasma hominis, as a rule, does not cause severe pathological manifestations. It is mainly associated with bacterial vaginosis. Complex therapy with antibiotics is carried out when Mycoplasma genitalium is detected. A course of treatment is also required if a woman is planning a pregnancy or suffers from infertility. Antibacterial therapy is mandatory if minimally invasive intrauterine interventions or gynecological surgery are planned.
For mixed infections, clinic doctors use a combination of antibiotics with antiparasitic and antifungal drugs. Not only the patient, but also her sexual partner should undergo appropriate treatment.
Adjuvant therapy
The effectiveness of antibacterial treatment is increased by immunomodulators - drugs that stimulate the immune system to fight infection. Therapy is supplemented with vitamin complexes with a high content of ascorbic acid, retinol, and B vitamins.
To normalize the vaginal microflora and prevent the side effects of antibiotics, our doctors use topical agents - vaginal suppositories. Oral probiotics help restore the microenvironment of the urogenital and gastrointestinal tract. The duration of probiotic therapy is 10 days after discontinuation of antibacterial medications.
Nutrition during antibacterial therapy
Part of the complex therapy of mycoplasma infection is diet. During the treatment period, our specialists help you adjust your diet. Products that inhibit the effect of medications are eliminated from the daily menu. They are replaced with healthy foods that speed up recovery.
| Forbidden | Healthy |
| pickled vegetables, mushrooms | fresh vegetables, fruits, berries |
| smoked fish, meat, lard | olive oil |
| hot sauces, seasonings, spices | grains and legumes |
| fermented milk products | nuts |
| fast food |
The consumption of alcoholic beverages, including weak alcohol, is strictly prohibited.
Prevention of mycoplasma infection in women
Preventive measures are aimed at reducing risk factors for infection with mycoplasma microorganisms. Gynecologists at our center recommend:
- exclude accidental unprotected sexual intercourse;
- maintain a high level of immunity;
- regularly be examined by a gynecologist and undergo laboratory tests for STDs;
- promptly treat gynecological and urological inflammations.
The gynecologists at our clinic have many years of experience in the successful treatment of mycoplasmosis. We practice an individual approach to treating each patient. The activities of the medical center are licensed, the qualifications of doctors are confirmed by certificates.