Fibrates are a group of drugs that lower the levels of triglycerides, low and very low density lipoproteins (LDL, VLDL), cholesterol and increase the levels of high density lipoproteins (HDL). Before the invention of statins, they were widely used to treat atherosclerosis. Currently, these drugs are used to treat patients with high triglycerides, low HDL.
The first drug in this group was clofibrate, which was widely used in the 60s and 70s. Then they were replaced by second and third generation drugs: fenofibrate, bezafibrate, ciprofibrate, gemfibrozil.
What are fibrates - principle of action
Fibrates are classified as lipid-lowering drugs - drugs that reduce the value of certain lipid fractions, lipid-like substances (cholesterol). These drugs are derivatives of fenofibric acid, which gives them their name. The mechanism of action of fibrates is based on their ability to:
- Increase the activity of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase, which activates the breakdown of chylomicrons and LDL containing triglycerides;
- an increase in the number of liver receptors that take up and process LDL
- increase the excretion of cholesterol with bile, slightly reduce the synthesis of sterols
- Stimulation of apolipoprotein A1, synthesis of apolipoprotein A1.
Triglycerides (neutral fats), HDL, LDL and cholesterol decrease, and HDL increases. Changing the concentration of various products of fat metabolism has a positive effect on the prevention of the progression of atherosclerosis, as well as the development of its complications - coronary heart disease, heart attack, cerebral aneurysm, stroke.
Medicines also reduce:
- dietary dyslipidemia;
- fibrinogen (blood clotting factor);
- uric acid;
- GGT activity, alkaline phosphatase;
- reduces blood viscosity.
Fibrates are well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Unlike statins, they are eliminated primarily by the kidneys.
Pharmacology of statins
Statins are first-line drugs for the treatment of hyperlipidemia, which have the highest lipolytic activity among all subgroups of lipid-lowering drugs [3, 4]. The first representatives of statins were obtained from mold cultures. We are talking about lovastatin - it was isolated in 1980 from the mold Aspergillus terreus
. Lovastatin began to be used in clinical practice in 1987, marking the beginning of the era of the most powerful lipid-lowering drugs [5].
Subsequent drugs in this subgroup are of semi-synthetic (simvastatin, pravastatin) and synthetic origin (fluvastatin, atorvastatin, rosuvastatin).
Mechanism of action of statins
Statins reduce the synthesis of cholesterol and very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) in the liver by inhibiting the activity of a key enzyme involved in the early stage of cholesterol synthesis ( HMG-CoA reductase - editor's note).
). As a result, a chain of changes occurs [3]:
- cholesterol levels decrease in liver cells;
- cholesterol synthesis increases in liver cells for several hours (compensatory);
- for several days, the number of specific receptors that bind LDL and reduce their concentration in the blood increases on the hepatocyte membrane;
- the number of liver lipoprotein receptors increases compensatoryly;
- the concentration of LDL, VLDL, and apolipoprotein decreases; triglyceride levels decrease to a lesser extent;
- HDL content increases.
It is important to note that the lipid-lowering effect of statins appears quickly, within approximately a week after the start of therapy.
In addition, statins are characterized by non-lipid pleiotropic effects, among which the following should be highlighted:
- improvement of vascular endothelial function;
- suppression of inflammatory activity in the vascular wall;
- suppression of LDL oxidation processes;
- depletion and stabilization of the core of the atherosclerotic plaque;
- inhibition of thrombus formation;
- anti-inflammatory effect.
Statins also have a preventive effect against cardiovascular diseases. They have been proven to reduce the risk of mortality from major cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke) and the development of cardiovascular diseases [4]. A Cochrane review suggests that statins reduce the risk of recurrent stroke [4].
Resistance does not develop to statins (as well as to lipid-lowering drugs of other subgroups).
The safety of statins in pregnancy has not been studied, so it is important for women of reproductive age to use effective contraception during treatment. During lactation, statins are also contraindicated [5].
Side effects
As a rule, statins are well tolerated, but negative reactions when taking them are possible. Among the most common are dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, loss of appetite), neurological (dizziness, irritability). While taking statins, muscle pain and associated muscle weakness may be felt: they occur in 10% of patients [4].
A rare serious side effect of statins is the breakdown of muscle tissue called rhabdomyolysis. It manifests itself with a combination of unfavorable factors, for example, taking statins along with the use of immunosuppressants [4].
What should I warn the client about?
Statins quickly have a lipid-lowering effect, however, even if tests show normalization of lipid levels, the drugs cannot be discontinued without a doctor’s recommendation. When they are discontinued, lipid levels often rise again. The drugs are used for a long time, sometimes for life.
Indications for use
Fibrate drugs are most effective in reducing triglyceride levels (20-55%), increasing HDL levels (10-30%) and reducing cholesterol (10-25%) and LDL (10-35%). Therefore, they are most actively used in the treatment of conditions accompanied by an increase in neutral fats.
The use of fibrates is justified when triglyceride levels are above 10 mmol/l, as well as in patients with rare type III hyperlipidemia. Also, drugs are prescribed when diet is ineffective as a replacement for statins for hyperlipidemia types A, B, V, V.
Due to the low effectiveness of drugs in lowering LDL cholesterol, they are rarely used on their own. If the neutral fat level is high, the HDL level is low, the patient may be prescribed fenofibrate in addition to statin therapy.
If triglyceride levels are greater than 5.6 mmol, the risk of pancreatitis increases. Taking fibric acid derivatives prevents the development of pancreatitis.
Prescribing fenofibrate and gemfibrozil to patients with coronary heart disease and patients after arterial surgery reduces cardiovascular mortality and slows the progression of coronary atherosclerosis. These two drugs improve the prognosis of patients with diabetes by preventing the development of some of its complications.
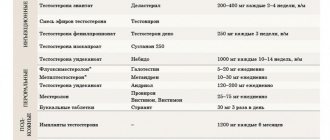
Doses and treatment regimens depend on the active substance:
- gemfibrozil - 2 times a day, 600 mg;
- bezafibrate 3 times a day, 200 mg;
- ciprofibrate 1 time/day 100 mg;
- fenofibrate 1 time/day 200 mg;
- etofibrate 500 mg once daily.
Tablets or capsules are best taken once daily with breakfast. The most active, fatty, neutral lipoproteins are synthesized in the morning. The tablets must not be chewed, crushed, dissolved or the contents of capsules opened.
The effectiveness of the drug is assessed after 4 weeks. By that time they had reached maximum efficiency.
It is recommended to supplement the medications with non-drug methods of reducing triglycerides and cholesterol: healthy eating, exercise, quitting smoking, and avoiding stress.
Group representatives
Fibrates, a long list of drugs, are classified as medicines and are sold through a network of pharmacies.
A well-known component of this group is Clofibrate. The composition is often used as a component for the treatment of atherosclerosis, but patients should remember to be careful, side effects often occur when using it
- bezafibrate;
- fenofibrate;
- gemfibrozil.
Currently, third-generation drugs, which are representatives of this category, are often used. This is due to the fact that they are relatively safe and do not have a negative effect on the human body.
Gemfibrozil
The medicinal composition is included in the list of low-toxic drugs. As a result of clinical trials, its effectiveness in reducing very low density lipoprotein levels in the blood of patients of various age groups has been confirmed.
The use of the medicinal substance during lactation and pregnancy is strictly prohibited. The drug is not recommended for use:
- patients with renal and liver failure;
- for cholecystitis and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- cirrhosis of the liver.
- headache;
- depressive states;
- dizziness ending in fainting;
- abdominal pain;
- lack of appetite;
- constant feeling of thirst;
- muscle pain;
- manifestations of allergies.
Cancellation of use of the product is indicated in the following situations:
- if a decrease in the concentration of bad cholesterol does not occur after 2-3 months;
- if side effects occur;
- in the presence of malfunctions of the liver and other internal organs;
- the appearance of muscle pain;
- in the presence of intolerance to the drug.
Fibrates are serious medicinal substances that can only be used as prescribed by a specialist. The manifestation of any deviations in the functioning of the body while taking the compositions always requires diagnosis.
Bezafibrate
The drug works in a similar way to the previous drug - it stops the process of synthesizing triglycerides in the liver and reduces the concentration of very low-density lipoproteins.
Bezafibrate acts on the human body as follows:
- inhibits the process of formation of atherosclerotic formations;
- improves blood circulation;
- relieves pressure in the coronary vessels.
The composition can be recommended to patients with the following pathologies:
- cardiac ischemia;
- diabetes;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland;
- hypertonic disease.
Like other anti-atherosclerotic drugs, the medicinal component is contraindicated in women during pregnancy and nursing mothers. It is prohibited to use in pediatrics, to reduce cholesterol in the blood of adolescents during puberty. During this period, preference should be given to gentle treatment methods. Attempts should be made to correct the indicators by rationalizing nutrition, introducing dietary supplements and normalizing the rhythm of life.
The drug is included in the list of not recommended for use in patients with gastrointestinal pathologies
The medicine can be used, but with extreme caution; if side effects occur, stop taking it
- a feeling of heaviness and a feeling of fullness in the abdomen;
- manifestations of iron deficiency anemia;
- partial muscle atrophy;
- destruction of muscle tissue;
- decreased potency in men;
- lack of sexual desire in both sexes;
- manifestation of allergic reactions in the form of rashes on various areas of the skin.
Liver function must be monitored throughout the entire period of therapy. If side effects occur, the use of the composition is canceled. In cases where it is impossible to do without the use of medicinal components, drugs from other groups are used.
One should not think that fibrate drugs, the list of which is quite extensive, are the only medicinal component in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Of course, such compositions are distinguished by high efficiency criteria, but if adverse reactions occur in a patient, a replacement can be found
Patients should pay attention to the fact that atherosclerosis is a complicated disease, which cannot be eliminated without an integrated approach. A person must direct all his efforts to correcting indicators, because the progress of recovery largely depends on his attitude towards his own health
List of the best fibrates
Modern fibrates come in three generations:
- The first is clofibrate;
- 2. gemfibrozil, bezafibrate;
- 3. fenofibrate, ciprofibrate.
The once popular clofibrate is now practically not used. This drug has been shown to promote the development of malignant tumors of the bile ducts and some types of gastrointestinal cancers. Microbeads have been found to be the most effective form of fibrate. It is better absorbed by the body and much more effective.
Gemfibrozil
Structurally, gemfibrozil is closely related to clofibrate, which is less toxic. Effectively reduces triglycerides and LDL in patients who do not respond to diet or other lipid-lowering drugs. In case of hereditary lipoprotein lipase deficiency, do not use. Gemfibrozil is rarely prescribed these days. Gradually it was replaced by more effective drugs.
Fenofibrate
Fenobrate is the most commonly prescribed fenofibric acid derivative. Compared to other fibrates, it has the additional property of reducing uric acid levels. This action of the drug is used to treat patients with gout. Fenofibrate reduces the likelihood of diabetes complications: polyneuropathy, kidney and retinal diseases. Sold under the trademarks Traicor (France), Lipantil 200 M (France), Fenofibrate Canon (Russia), Exlip (Turkey).
When should you take statins?
As you know, you cannot self-medicate. Only a specialist can prescribe medications according to a regimen individually selected for the patient. And before including lipid-lowering drugs in the treatment protocol, he needs to know the state of the patient’s fat metabolism. Therefore, the examination plan necessarily includes determining the lipid profile.
Absolute indications for the use of statins are atherosclerosis of any stage and any location. First of all, they are prescribed for damage to the blood vessels of the heart and brain:
- acute forms of coronary heart disease (acute coronary syndrome, myocardial infarction);
- states after them;
- with chronic ischemic heart disease (diffuse or post-infarction cardiosclerosis, angina pectoris);
- atherosclerotic encephalopathy;
- in the post-stroke period;
- after surgical interventions on the heart and blood vessels.
Taking statins is indicated for metabolic and endocrine pathologies - obesity, diabetes mellitus. Some of them are used in pediatric practice in children over 10 years of age and adolescents with high blood cholesterol levels caused by various reasons. And in adults with a significant risk of developing atherosclerosis, lipid metabolism is corrected with statin drugs.
At what cholesterol level do doctors prescribe statins? There are no clear boundaries here.
- For preventive purposes, you should start taking statins if your blood plasma cholesterol exceeds 7 mmol/l. Is it necessary? No: lipid metabolism can be corrected through diet, moderate physical activity, and a ban on drinking alcoholic beverages and smoking.
- If a patient has a lipid imbalance for a long time and has already manifested itself as atherosclerosis, statins are indicated regardless of the degree of increase in the level of low-density lipoproteins. The control of fat-protein complexes affects only the dosage and duration of the course. And the goal of therapy in this case is to prevent further growth of plaques, thrombosis, and, accordingly, the development of vascular complications.
According to statistics, rarely does anyone live to the age of 60 or 70 years, having a cholesterol level of 6 mmol/l, and not suffering from atherosclerosis, but even in this situation, whether a person takes statins is decided by the doctor.
Contraindications
Fibrates are not prescribed to patients with liver or kidney disease. This does not apply to mild forms of pathology. Most tablets or capsules contain lactose. For this reason, the drug is contraindicated in patients with lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency, and galactosemia.
Fibrates should not be prescribed to patients suffering from alcoholism or biliary tract diseases.
Besafibrate and ciprofibrate are contraindicated in pregnant women. Fenofibrate and gemfibrozil are rated fetal exposure category C. This means that animal studies have shown a risk to the developing baby, but there have been no adequate studies in women. Therefore, drugs in this category are not recommended for pregnant women, unless the benefit to their body outweighs the possible harm to the fetus.
These drugs are prescribed only to adults. Their safety for children has not been confirmed by studies.
When taking tablets, you should check the level of liver enzymes, creatine phosphokinase and blood creatinine at least once every 3 months.
Side effects of latest generation fibrates
Side effects of fibrates are usually minimal and short-lived. The most common complaints are gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, headache and rash. Such symptoms occur in 5-10% of patients.
Each representative of the fibrate group has its own list of side effects. But there are a number of complications that are typical for most medications:
- changes in the composition of bile, which increases the risk of developing cholelithiasis (1st-2nd generation drugs);
- hepatitis;
- flatulence;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- renal failure;
- photosensitivity;
- arrhythmia;
- muscle inflammation;
- myopathies;
- rhabdomyolysis;
- General weakness;
- decreased potency (very common when taking cyclofibrate).
Fibrate analogues
Fibrates are not the only drugs that are intended to normalize fat metabolism products. The group of lipid-lowering drugs includes:
- Statins (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are the most powerful drugs with versatile effects. They block cholesterol synthesis, thereby reducing the concentration of sterols, LDL, triglycerides and increasing HDL. Statins reduce the size of atherosclerotic deposits;
- Bile acid sequestrants (cholestyramine, colestipol) are drugs that bind bile acids in the intestine. They block the absorption of bile acids back into the blood. The body must synthesize new bile acids from cholesterol, which leads to a decrease in the concentration of sterol, as well as LDL containing it;
- Ezetimibe, a drug that slows down the absorption of cholesterol from the gastrointestinal tract. It can be used together with statins or as a standalone drug if it is contraindicated;
- Vitamin PP (vitamin B3, nicotinic acid) - stops the synthesis of LDL, reduces the concentration of triglycerides in the blood, increases the concentration of HDL. The action of the vitamin is relatively fast - after 4-5 days. It is rarely used due to many side effects;
- Omega-3 fatty acids (omacor) - used to normalize triglyceride levels as an alternative to fibrates in addition to statin treatment.
All these drugs can replace each other, but not all diseases. The most universal drugs are statins (Table 1).
Table 1: Treatment of primary hyperlipoproteinemia.
What to choose: fibrates or statins?
Before the advent of statins, fibrates were considered effective in lowering “bad” LDL cholesterol by increasing con HDL. However, HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors turned out to be so effective that they quickly replaced fibric acid derivatives from practice.
According to modern views on the treatment of atherosclerosis, statins are the first choice drugs for lowering LDL cholesterol levels. On the other hand, fibrates are used as adjuvant drugs in patients with high triglycerides, low HDL. However, there are three rare diseases for which fibric acid derivatives are more effective than statins: familial dysbetalipoproteinemia, familial hypertriglyceridemia, and familial mixed hypertriglyceridemia.
Therefore, when choosing between fibrates and statins, it should be remembered that the optimal decision depends primarily on the type of fat metabolism disorder.
Specificity and mechanism of action
What is dyslipidemia
Fibrates are lipid-lowering drugs, derivatives of fibric acid, which act on liver cells, blocking the synthesis of triglycerides, and enhance their catabolism and excretion from the body.
This group of medications is also actively used in restoring lipid metabolism, like statins. But you should not equate these two groups of drugs, because they have slightly different directions in normalizing lipid metabolism. Tablets are prescribed in the same way as statins, individually with a clearly prescribed treatment regimen.
Action of fibrates
The mechanism of action of fibrates is aimed at increasing one of the enzymes of lipid metabolism - lipoprotein lipase. This enzyme is responsible in the lipid process for the breakdown of lipoproteins of low molecular density and very low molecular density. The activity of lipoprotein lipase prevents the development of systemic pathologies, including atherosclerosis.
Proper breakdown of low-density lipoproteins reduces their concentration in the blood and increases the level of high-density lipoprotein molecules, which cleanse the bloodstream of free cholesterol molecules.
Fibrates have a beneficial effect on metabolism in liver cells and block the increase in the synthesis of cholesterol molecules and the increase in the LDL fraction in the blood.
As a result of the effect of fibrates on liver cells, the following processes occur:
- the triglyceride fraction decreases from 20 to 50%;
- the total cholesterol index decreases by 10-15%;
- LDL fraction decreases – 20-30.0%;
- the concentration of high-density cholesterol (HDL) increases by 10-12%.
Also, this group of medications relieves inflammation in the arterial membranes, strengthens the intima of the arteries and increases the elasticity of blood vessels.
Most often, fibrates are prescribed in complex drug therapy with vitamin PP (Niacin), which reduces by several times the risks of mortality from complicated vascular pathologies and cardiac complications - cerebral and cardiac infarction.
It is not often that bile sequestrants are prescribed in combination to lower the cholesterol index, and even more rarely, in combination with fibric acid derivatives, statin drugs are prescribed.