Compound
The active component of the drug is tetracycline hydrochloride . The medicine in tablets contains the following additional ingredients: sucrose, talc, potato starch, calcium stearate, gelatin. The shell includes: hypromellose, polysorbate, petroleum jelly , acid red 2C.
Tetracycline eye ointment, in addition to the active component, contains sodium sulphate pyro, anhydrous lanolin , petroleum jelly , ceresin, and paraffin.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
According to the classification, this drug is included in the tetracycline group of antibiotics . It is active against many gram-positive microbes : Clostridium spp., Staphylococcus spp., Listeria spp., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Bacillus anthracis, Actinomyces israelii. In addition, this product can be used against many gram-negative microorganisms : Haemophilus ducreyi, Salmonella spp., Acinetobacter spp., Yersinia pestis, Haemophilus influenzae, Bartonella bacilliformis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Enterobacter spp., Bordetella pertussis, Klebsiella spp., Vibrio fetus, Shigella spp., Francisella tularensis, Vibrio cholerae, Rickettsia spp., Escherichia coli, Brucella spp.
The medicine is also active against Chlamydia psittaci, Treponema spp., Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
The degree of absorption of the drug when taken on an empty stomach is 75-77%; if taken with food, absorption decreases. plasma proteins by 55-65%. When orally , maximum plasma concentrations occur after 2-3 hours. It gradually decreases over 8 hours.
Once in the body, the active substance accumulates in the liver, lungs, kidneys, as well as in organs that are distinguished by a developed reticuloendothelial system . The content in bile is approximately 5-10 times higher than in blood serum . Tetracycline hydrochloride also accumulates in bone tissue, dentin, tumor , and enamel of baby teeth. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into milk during lactation .
The half-life is 6-11 hours. 20-50% of the drug is excreted through the intestines.
Tetracycline, 20 pcs., 100 mg, film-coated tablets
Tetracycline is active against gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus, including penicillinase-producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Listeria spp., Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., Actinomyces israelii; gram-negative microorganisms: Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella pertussis, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes), Acinetobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis, Bartonella bacilliformis, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio fetus, Rickettsia spp., Borrelia burgdorferi, Brucella spp. (in combination with streptomycin); with contraindications to the use of penicillins - Clostridium spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Actinomyces spp.; also active against Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Treponema spp. Resistant to tetracycline: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp., Serratia spp., most strains of Bacteroides spp. and fungi, viruses, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus faecalis.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption - 75-77%, decreases with food intake, binding to plasma proteins - 55-65%. The time to reach the maximum concentration of the drug in plasma (TCmax) when taken orally is 2-3 hours (2-3 days may be required to achieve therapeutic concentrations). Over the next 8 hours, the concentration gradually decreases. The maximum concentration of the drug in plasma is 1.5-3.5 mg/l (a concentration of 1 mg/l is sufficient to achieve a therapeutic effect).
It is distributed unevenly in the body: the maximum concentration of the drug is determined in the liver, kidneys, lungs and in organs with a well-developed reticuloendothelial system - the spleen, lymph nodes. The concentration in bile is 5-10 times higher than in blood serum. In the tissues of the thyroid and prostate glands, the concentration of tetracycline corresponds to that found in plasma; in pleural, ascitic fluid, saliva, milk of lactating women - 60-100% of the concentration in plasma. It accumulates in large quantities in bone tissue, tumor tissue, dentin and enamel of baby teeth. Penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. With intact meninges, it is not detected in the cerebrospinal fluid or is detected in small quantities (5-10% of the plasma concentration). In patients with diseases of the central nervous system, especially with inflammatory processes in the meninges, the concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid is 8-36% of the concentration in plasma. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. Volume of distribution - 1.3-1.6 l/kg.
Slightly metabolized in the liver. The half-life of the drug (T1/2) is 6-11 hours, with anuria - 57-108 hours. It is found in urine in high concentration 2 hours after administration and persists for 6-12 hours; in the first 12 hours, up to 10-20% of the dose is excreted by the kidneys. In smaller quantities (5-10% of the total dose) it is excreted with bile into the intestine, where partial reabsorption occurs, which promotes long-term circulation of the active substance in the body (enterohepatic circulation). Excretion through the intestines is 20-50%. During hemodialysis it is removed slowly.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of this drug are as follows:
- pneumonia , tracheitis , bronchitis , pleural empyema ;
- purulent soft tissue infections ;
- pyelonephritis;
- endocarditis;
- prostatitis;
- whooping cough;
- rickettsial diseases;
- osteomyelitis;
- conjunctivitis , blepharitis ;
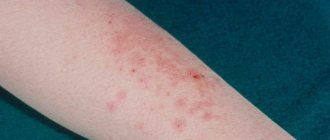
- furunculosis , acne , infected eczema , folliculitis ;
- cholecystitis;
- intestinal infections;
- endometritis;
- syphilis , gonorrhea ;
- trachoma;
- brucellosis;
- tonsillitis , pharyngitis , otitis .
Of the listed diseases, eye ointment is used, and tablets are infectious diseases For which ointment can be used in each individual case, it is advisable to consult a doctor. It is often prescribed instead of eye drops.
Regarding Tetracycline tablets (for what and in what dose to use), it is also better to consult a specialist. In some cases it is prescribed, for example, for sore throat . In addition, experts sometimes recommend using Tetracycline for acne.
Rules of application
Features of using the product:
- Tetracycline ophthalmic ointment, in a column no more than 1 cm long, is placed intraconjunctivally into the conjunctival sac (under the lower eyelid). A sterile stick is used for this. It is important to then distribute the product correctly using a cotton-gauze swab, performing gentle massaging movements.
- Ointment for external use 3% is applied to the affected areas of the skin in a thin layer. In this case, you need to capture a small area around the problem area. Additionally, a bandage is applied to enhance the therapeutic effect. If there is no damage to the skin, the product is practically not absorbed.
The course of treatment and its duration are determined by the attending doctor depending on the type of disease. For eye diseases, procedures are carried out 2-3 times a day. When using a 3% product to treat skin diseases, the dressing should be changed every 12-24 hours. Tetracycline ointment, the instructions for use provide this, can be used for acne. In this case, it is applied pointwise. The product can be used for 3 weeks in the absence of negative reactions from the body. If no improvement is observed within 2 weeks, then you should stop using the ointment and consult a doctor.
Side effects
Possible adverse reactions:
- organs of the digestive system: dysphagia , increased sensitivity of the papillae of the tongue, dullness of hunger, diarrhea , glossitis , gastritis , hepatotoxic effect , pancreatitis , enterocolitis , vomiting, nausea, esophagitis , stomach and duodenal ulcers , increased activity of liver transaminases , dysbacteriosis ;
- hematopoietic organs: hemolytic anemia , neutropenia , thrombocytopenia , eosinophilia ;
- allergies and immunopathological reactions: skin hyperemia angioedema , maculopapular rash , systemic lupus erythematosus , anaphylactoid reactions , photosensitivity ;
- CNS: headache , increased HF pressure , dizziness ;
- urinary system: azotemia , hypercreatininemia ;
- other: superinfection , hypovitaminosis B , discoloration of the enamel of baby teeth, candidiasis , stomatitis .
Instructions for use of Tetracycline (Method and dosage)
For those who have been prescribed Tetracycline ointment, the instructions for use indicate that the medicine should be used externally. It is applied in small quantities to the affected areas 1-2 times daily.
Tetracycline tablets are prescribed for oral administration; the instructions for use indicate that it is advisable to take them with liquid. Two application schemes are possible:
- 0.25-0.5 g 4 times/day;
- 0.5-1 g every 12 hours.
You should not take more than 2 g of medication per day. For children aged 8 years and older, two application regimens are also possible:
- 6.25-12.5 mg/kg every 6 hours;
- 12.5-25 mg/kg every 12 hours.
Instructions for use of Tetracycline for acne indicate that the dosage should be approximately 0.5-2.0 g per day in divided doses. When the condition improves (usually after 21 days), the dose is gradually reduced to 0.125-1 g. Then it is advisable to use the drug every other day. When using ointment, apply a thin layer exactly to the inflamed areas 2 times daily. The course of application is 3-14 days.
For brucellosis, tetracycline hydrochloride is taken 0.5 g every 6 hours. The course is designed for 3 weeks, with intramuscular injections of Streptomycin at a dosage of 1 g every 12 hours and once a day during the second week of therapy.
In the case of uncomplicated gonorrhea, the initial single dosage is 1.5 g. After this, you need to take 0.5 g every 6 hours for 4 days. The total dose is 9 g.
For syphilis you need to take 0.5 g every 6 hours. At the early stage of the disease, the medicine is taken for 15 days, in the late stage - for a month.
In case of uncomplicated urethral, rectal and endocervical infections , which are provoked by Chlamydia trachomatis, you need to take 0.5 g 4 times a day. Therapy is designed for at least a week.
Tetracycline tab 100 mg N20 (Belmedprep)
Tetracycline is active against gram-positive microorganisms: Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus, including penicillinase-producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Listeria spp., Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., Actinomyces israelii; gram-negative microorganisms: Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella pertussis, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes), Acinetobacter spp., Klebsiella spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp., Yersinia pestis, Francisella tularensis, Bartonella bacilliformis, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio fetus, Rickettsia spp., Borrelia burgdorferi, Brucella spp. (in combination with streptomycin); with contraindications to the use of penicillins - Clostridium spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Actinomyces spp.; also active against Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Treponema spp. Resistant to tetracycline: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp., Serratia spp., most strains of Bacteroides spp. and fungi, viruses, Streptococcus pyogenes, Streptococcus faecalis. Pharmacokinetics Absorption - 75-77%, decreases with food intake, binding to plasma proteins - 55-65%. The time to reach the maximum concentration of the drug in plasma (TCmax) when taken orally is 2-3 hours (2-3 days may be required to achieve therapeutic concentrations). Over the next 8 hours, the concentration gradually decreases. The maximum concentration of the drug in plasma is 1.5-3.5 mg/l (a concentration of 1 mg/l is sufficient to achieve a therapeutic effect). It is unevenly distributed in the body: the maximum concentration of the drug is determined in the liver, kidneys, lungs and in organs with a well-developed reticuloendothelial system - spleen, lymph nodes. The concentration in bile is 5-10 times higher than in blood serum. In the tissues of the thyroid and prostate glands, the concentration of tetracycline corresponds to that found in plasma; in pleural, ascitic fluid, saliva, milk of lactating women - 60-100% of the concentration in plasma. It accumulates in large quantities in bone tissue, tumor tissue, dentin and enamel of baby teeth. Penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. With intact meninges, it is not detected in the cerebrospinal fluid or is detected in small quantities (5-10% of the plasma concentration). In patients with diseases of the central nervous system, especially with inflammatory processes in the meninges, the concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid is 8-36% of the concentration in plasma. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. Volume of distribution - 1.3-1.6 l/kg. Slightly metabolized in the liver. The half-life of the drug (T1/2) is 6-11 hours, with anuria - 57-108 hours. It is found in urine in high concentration 2 hours after administration and persists for 6-12 hours; in the first 12 hours, up to 10-20% of the dose is excreted by the kidneys. In smaller quantities (5-10% of the total dose) it is excreted with bile into the intestine, where partial reabsorption occurs, which promotes long-term circulation of the active substance in the body (enterohepatic circulation). Excretion through the intestines is 20-50%. During hemodialysis it is removed slowly.
Interaction
The degree of absorption of the drug is reduced when taking antacids , which include aluminum, calcium and magnesium, as well as medicines with iron and cholestyramine .
The use of the drug also reduces the effect of bactericidal antibiotics that interfere with cell wall synthesis.
Combination with Chymotrypsin leads to an increase in the active substance of Tetracycline and the duration of circulation.
The drug reduces the effect of estrogen-containing oral contraceptives and increases the likelihood of breakthrough bleeding. In combination with Retinol, intracranial pressure increases .
Read more about using Tetracin
Tetracin has a pronounced insecticidal effect against cockroaches, ants, bedbugs, fleas, flies, and mosquitoes. The residual effect of the drug lasts about 1 month.
For self-treatment, use a pump sprayer or a household sprayer.
To prepare working emulsions, the product is diluted with water at room temperature, stirring evenly. Calculation of the amount of concentrate required to prepare the working emulsion is given in the table.
| Insect type | Concentration of ADV, (%) | Amount of product (ml) per 1 liter of water |
| Cockroaches | 0,25 | 22 |
| flies | 0,20 | 17,5 |
| Fleas | 0,15 | 13 |
| Bed bugs | 0,10 | 10 |
| Red house ants | 0,10 | 10 |
| Mosquitoes: adult larvae | 0,15 | 13 |
| 0,10 | 10 |
The consumption rate of the working solution is 50 ml/m2 for non-moisture-absorbing surfaces and 100 ml/m2 for moisture-absorbing surfaces. Remove the product from treated surfaces using a wet method - with a rag and a soap-soda solution 24 hours after application, but no later than 3 hours before the start of the working day.
To destroy cockroaches , the working solution is used to treat places where insects accumulate, nest and move, paying special attention to the following places: cracks and holes in floors and walls, door frames, thresholds, floor and ceiling skirting boards, ventilation holes, pipe joints, cladding, kitchen furniture . If there are a large number of insects, the entire room should be treated at once (even those rooms where there were no insects). This is carried out in order to prevent the migration of cockroaches to other territories and their further spread. When insects appear, re-treatment is carried out.
When treating bedbugs , the entire room is often not treated. If the number of parasites is insignificant, only their habitats are treated with the working solution. If there is a high infestation of bed bugs, the areas where wallpaper has peeled off, baseboards, window frames, door frames and ventilation holes, cracks in walls, back walls of furniture, carpets, and mattresses should also be treated. It is not recommended to treat bed linen with the working solution; it must be washed at high temperatures. After 5-7 days, it is recommended to re-treat, as young offspring may appear from the larvae that you may have missed.
To destroy ants , the working solution is sprayed on the places of accumulation and movement (paths) of insects.
When treating fleas , the working solution should expose walls (up to a height of 1 meter from the floor), the entire floor surface, various floor coverings, baseboards and cracks. When processing basements, it is necessary to get rid of garbage and clutter and thoroughly treat the entire room. Pet beds should also be treated and washed well after 24 hours.
When treating against flies and mosquitoes , insect landing sites, as well as external walls, garbage chutes and garbage containers should be treated with a working solution. To destroy mosquito larvae with a working solution, it is necessary to treat the surfaces of closed reservoirs, basements, and large containers with standing water.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Oxytetracycline
The following drugs are known, which are indicated as analogues of Tetracycline:
- Tetracycline Akos ointment ;
- Tetracycline Lect tablets .
In Latin recipes you will notice that all medicines have the same active substance. However, why Tetracycline Akos and other analogues can be used in each individual case, it is better to consult a doctor.
Composition of Tetracin
The product has a moderate level of danger, so it is important to carefully read the instructions before using it and use the substance exclusively in accordance with its instructions. The composition includes the following substances:
- Cypermethrin (10%);
- PPB (10%);
- Surfactant (7%);
- Tetramethrin (1.5%);
- Solvent;
- Stabilizer.
The instructions for use indicate the required proportions and concentration for dissolving the insecticide, as well as an approximate list of places that may be dangerous for impregnation.
During pregnancy (and lactation)
This drug is contraindicated during pregnancy . Passing through the placenta, tetracyclines accumulate in the bones and tooth buds of the developing fetus. They can disrupt mineralization and cause severe disorders in bone tissue.
The medicine should not be used not only during pregnancy , but also during lactation . It can penetrate into breast milk and negatively affect the condition of the baby’s bones and teeth, provoke photosensitivity , as well as candidiasis of the mouth and vagina .
Tetracycline-lect tablet p/o film 100 mg 20 pcs
Pharmacological group:
Antibacterial agents.
Pharmacodynamics:
Bacteriostatic antibiotic from the tetracycline group. It disrupts the formation of the complex between transfer RNA and the ribosome, which leads to suppression of protein synthesis. Active against gram-positive microorganisms - Staphylococcus spp. (including Staphylococcus aureus, including penicillinase-producing strains), Streptococcus spp. (some strains, including Streptococcus pneumoniae), Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus anthracis, Clostridium spp., Actinomyces spp., Propionibacterium acnes, Bacillus fusiformis; - gram-negative microorganisms - Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus ducreyi, Bordetella pertussis, Escherichia coli, Enterobacter spp. (including Enterobacter aerogenes), Klebsiella spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Shigella spp., Yersinia pestis, Bartonella bacilliformis, Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio fetus, Rickettsia prawazekii, Rickettsia reckettsii, Rickettsia akari, Borrelia Vinceni, Borrelia recurrentis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Brucella spp. (in combination with streptomycin); Calymmatobacterium granulomatis, Francisella tularensis, Treponema pallidum, Treponema pertenue; - with contraindications to the use of penicillins - Clostridium spp., Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Actinomyces spp.; — active against Chlamydia trachomatis; Chlamydia psittaci, Entamoeba histolytica; — microorganisms resistant to tetracycline: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus spp., Serratia spp., most strains of Bacteroides spp. and fungi, viruses, group A beta-hemolytic streptococci (including 44% of Streptococcus pyogenes strains and 74% of Streptococcus faecalis strains).
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption - 75 - 77%, decreases with food intake, connection with plasma proteins - 55 - 65%. The time to reach maximum concentration when taken orally is 2-3 hours (it may take 2-3 days to reach therapeutic concentrations). Over the next 8 hours, the concentration gradually decreases. The maximum concentration is 1.5 - 3.5 mg/l (a concentration of 1 mg/l is sufficient to achieve a therapeutic effect).
It is distributed unevenly in the body: in maximum concentration it is found in the liver, kidneys, lungs and in organs with a well-developed reticuloendothelial system - the spleen, lymph nodes. The concentration in bile is 5-10 times higher than in blood serum. In the tissues of the thyroid and prostate glands, the content of tetracycline is the same as in plasma; in pleural, ascitic fluid, saliva, milk of lactating women - 60 - 100% concentration in plasma. It accumulates in large quantities in bone tissue, tumor tissue, dentin and enamel of baby teeth. Penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier. With intact meninges, it is not detected in the cerebrospinal fluid or is detected in small quantities (5 - 10% of the plasma concentration). In patients with diseases of the central nervous system, especially with inflammatory processes in the meninges, the concentration in the cerebrospinal fluid is 8 - 36% of the concentration in plasma. Penetrates through the placental barrier and into breast milk. Volume of distribution - 1.3 - 1.6 l/kg.
Slightly metabolized in the liver. The half-life is 6 - 11 hours, with anuria - 57 - 108 hours. It is found in urine in high concentration 2 hours after administration and persists for 6 - 12 hours; in the first 12 hours, up to 10-20% of the dose is excreted by the kidneys. In smaller quantities (5 - 10% of the total dose) it is excreted with bile into the intestine, where partial reabsorption occurs, which promotes long-term circulation of the active substance in the body (enterohepatic circulation). Excretion through the intestines - 20 - 50%. During hemodialysis it is removed slowly.
Tetracycline price, where to buy
The price of Tetracycline tablets is about 80 rubles. This is the most expensive dosage form of this drug. The price of Tetracycline ointment is about 40 rubles.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Tetracycline eye ointment 1% 3gAO Tatkhimfarmpreparaty
54 rub. order - Tetracycline eye ointment 1% 5g JSC Tatkhimfarmpreparaty
68 RUR order
- Tetracycline tablets p.p.o. 100mg 20pcsBiokhimik OJSC
83 RUR order
- Tetracycline ointment 3% 15g BiosintezPAO Biosintez
92 rub. order
- Tetracycline-lect tab. p.p.o. 100 mg 20 pcs JSC "Tyumen Chemical Plant"
82 RUR order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Tetracycline ointment (tube 1% 5g (l.)) TCPP
68 RUR order
- Tetracycline (100 mg tablet No. 20) Biosynthesis OJSC
81 RUR order
- Tetracycline (100 mg tablet No. 20)Biokhimik JSC
77 RUR order
- Tetracycline ointment (tube 3% 15g) Sintez (Kurgan) OJSC
82 RUR order
- Tetracycline + nystatin (tablet 100 mg + 22.2 mg No. 10) Biosynthesis OJSC
84 rub. order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Tetracycline hydrochloride 0.1g No. 20 tablets PAT NEC "Borshchagivsky chemical and pharmaceutical plant", Kiev, Ukraine
15 UAH. order - Tetracycline ointment 3% 15 g VAT "Nizhpharm", Nizhny Novgorod, Russian Federation
52 UAH order
- Tetracycline 0.1g No. 20 tablets PAT "Vitamin" Ukraine
12 UAH order
PaniPharmacy
- TETRACYCLINE tablets Tetracycline film-coated tablets 0.1g No. 20 Ukraine, Vitamins PJSC
16 UAH order
- TETRACYCLINE ointment Tetracycline ointment 3% 15g Russia, Nizhpharm
60 UAH.order
- Oxytetracycline ointment 1% 30g Ukraine, Ukrzoovetprompostach vet.
24 UAH order
show more
Mode of application
Tetracin performs exceptionally well both in domestic and professional use. People note its high speed of action, long-lasting effect, and lack of addiction in insects. The use of the substance leads to the fact that insects stop coming to the treated area, even if they have lived there for years.
The amount of Tetracin required for the preparation of working aqueous emulsions:
| Insect type | Concentration by DV, (%) | Amount of product (ml) for 1 liter of water |
| Cockroaches | 0,25 | 22 |
| flies | 0,20 | 17,5 |
| Fleas | 0,15 | 13 |
| Bed bugs | 0,10 | 10 |
| Red house ants | 0,10 | 10 |
| Mosquito larvae Mosquito imago | 0,15 | 13 |
| 0,10 | 10 |