Inflammation of the intestine is a collective term that unites diseases that are diverse in their manifestations and etiology. All of them affect one or more parts of the intestine, affecting its mucous membrane and disrupting such an important function as food digestion. The inflammatory process causes hyperemia of the affected area of the mucosa, which disrupts the production of digestive enzymes and the processing of nutrients. How to treat intestinal inflammation?
Types of inflammatory bowel diseases
Intestinal inflammation cannot go away on its own
Among all gastrointestinal diseases, intestinal inflammation ranks second in frequency of occurrence, it affects all age and social groups, and occurs with equal frequency in men and women. According to the location of inflammation, it is divided into the following diseases:
- Enteritis is an inflammatory process that affects the small intestine.
- Duodenitis - inflammation affects the duodenum.
- Colitis – inflammation occurs in the large intestine.
- Enterocolitis - inflammation spreads to almost the entire intestine.
These diseases can be acute or chronic, depending on this there should be a completely different approach and treatment method to them.
Diffuse form of the disease
This form has a number of manifestation features: Unclear localization of pain in the abdominal area, pain can radiate to the sternum - this is one of the most characteristic symptoms of the diffuse form; the coating on the tongue becomes very strong, bad breath occurs, peristalsis disturbances, vomiting, and a false urge to go to the toilet.
This disease affects the entire intestine and has a very bright and intense manifestation of symptoms in a person from the moment of onset.
Enteritis - symptoms, causes
Acute and chronic inflammation of the small intestine (enteritis) have different causes and symptoms, so it makes sense to consider them separately. The causes of acute enteritis can be:
- Infections (typhoid fever, cholera, salmonellosis, rarely influenza).
- Banal overeating, as well as too spicy or too rough food.
- Poisoning with arsenic or sublimate, other poisons, poisonous mushrooms (fly agaric, toadstool, false mushrooms).
- Consumption of toxically unhealthy foods: stone fruits, mackerel caviar, pike liver, burbot.
- Hypothermia of the body, drinking very cold drinks (directly in accordance with the popular saying “Don’t drink cold things - you’ll catch a cold”).
- Polyhypovitaminosis.
Acute enteritis begins with nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, accompanied by cramps, and strong rumbling in the stomach.
A little later, general weakness and a feeling of malaise appear, the patient breaks into a cold sweat, and the temperature steadily rises. After a few hours, manifestations of intoxication increase: severe headache, increased vomiting and nausea. Acute enteritis has several other causes:
- Irregular and poor nutrition.
- Alcoholism.
- Work in hazardous industries.
- Abuse of spicy seasonings.
- Chronic household intoxication, laxative abuse.
- Uncontrolled and prolonged use of antibiotics.
- Giardiasis, helminthiasis.
- Food allergies.
The symptoms of chronic enteritis are not as bright as in the acute form, but they cause a lot of discomfort. Immediately after eating, there is a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, nausea, dull cramping pain around the navel, rumbling and transfusion in the intestines. During the day there may be 15-20 urges to defecate, which is expressed in foul-smelling, mushy stool with gas bubbles and pieces of undigested food.
The stool has a clay-like consistency and is light yellow in color. After defecation, there may be severe weakness, trembling of the hands, and the person breaks into a cold sweat. Almost always with enteritis, milk intolerance is observed; bloating and diarrhea after taking it are common.
Features of the manifestation of signs of colitis
Colitis causes discomfort in the stomach.
Many of the signs of colitis can be confused with other diseases that are of a completely different nature.
They can be either very serious or minor digestive disorders caused by various reasons. With colitis, the following features of these symptoms can be noted:
- Growing character. As a rule, colitis begins with minor changes in digestion and often many people ignore these changes. In this case, after a few weeks or months, colitis begins to manifest itself more and more clearly, the symptoms begin to increase in intensity, and more and more discomfort appears in a person’s daily life.
- Uneven manifestation of symptoms. With colitis, diagnosis is complicated by the fact that symptoms and signs of the disease often do not appear simultaneously. At first, increased gas formation and constipation may occur; after some time, these symptoms change to frequent urge to go to the toilet, and then pain and problems with other organs may occur.
- Various pain sensations that can be confused with other diseases and manifestations. Thus, with acute pain in the right side, many assume the presence of appendicitis, and with soft and tingling pain, colitis can be confused with preovulatory syndrome.
Causes and symptoms of duodenitis
Inflammation of the duodenum most often occurs in men. The acute form of the disease often occurs in combination with gastritis and enteritis, and can be complicated by bleeding, peritonitis (due to intestinal perforation) and acute pancreatitis. Chronic duodenitis is combined with food allergies, giardiasis, chronic pancreatitis, ulcerative lesions of the intestines and stomach. With duodenitis, the patient feels the following manifestations of the disease:
- Pain in the pit of the stomach.
- Nausea and vomiting, decreased or lack of appetite.
- Distension and feeling of fullness in the upper abdomen after eating.
If you do not follow the diet and the treatment prescribed by your doctor, the disease lasts a very long time, with frequent exacerbations.
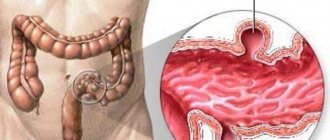
Ulcerative form of colitis
Ulcerative colitis can be accompanied by severe pain and bleeding.
Ulcerative colitis is a serious and severe disease that has both a hereditary transmission route and a bacterial origin.
Ulcerative colitis is characterized by severe and prolonged pain, fever, a constant urge to urinate, and sometimes severe bleeding.
The ulcerative form is complicated by poor nutrition, lack of treatment, and other intestinal diseases. This type of colitis is the most serious and dangerous, and, as a rule, is diagnosed quite quickly, due to the bright and intense signs of manifestation.
Diagnosis of intestinal inflammation
Gastroenterologist is a doctor who treats gastrointestinal diseases
A gastroenterologist should treat intestinal inflammation and should be contacted if the above symptoms appear in any degree of their manifestation. To clarify the diagnosis and to exclude diseases of a different profile with similar symptoms (oncology, infections), the doctor prescribes an examination. This may include:
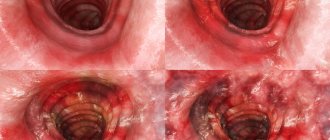
- Endoscopy of the stomach and duodenum with a biopsy of the mucous membrane, if necessary - the condition of the mucous membrane is analyzed.
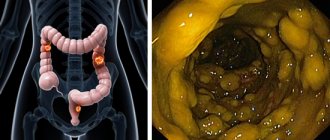
- Colonoscopy – using a colonoscope inserted through the rectum, the localization of inflammation in the large intestine is assessed.
- Blood test for ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) - the intensity of the inflammatory process is assessed.
- Coprogram – assessment of intestinal enzymatic function.
- Examination of stool for the absence or presence of bacteria, their sensitivity to groups of antibiotics.
Etiology and pathogenesis
The cause of chronic colitis is quite often the causative agents of intestinal infections - Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia, Clostridia, etc. Chronic colitis can be caused by helminths, protozoa (amoebas, Giardia, Trichomonas, Balantidia), as well as opportunistic and saprophytic flora. When chronic colitis occurs, the pathogen may not be detected, but dysbacteriosis remains, changes not only in the motor and enzyme-secreting functions of the intestine, but also in the structure of the mucous membrane, intensify, which contributes to the chronicity of the process.
Colitis of nutritional origin is quite common. They are caused by a violation of the diet, a monotonous diet containing a large amount of carbohydrates or proteins, a diet devoid of vitamins, frequent consumption of indigestible and spicy foods, and alcohol abuse. There are also “drug-induced colitis”, which occur with prolonged and uncontrolled use of a number of medications (laxatives containing anthraglycosides, antibiotics, salicylates, digitalis preparations, etc.).
Colitis of an allergic nature is possible (with food and drug allergies), and the allergic component is also inherent in the so-called post-infectious colitis, in which there is increased sensitivity to certain representatives of the intestinal microflora, the products of their vital activity and decay.
Colitis can be caused by congenital enzyme deficiency, in particular disaccharidase deficiency, due to constant irritation of the colon mucosa by products of incomplete breakdown of food. A similar mechanism, along with viscero-visceral reflexes, underlies some “secondary” colitis, such as colitis accompanying atrophic gastritis, pancreatitis with impaired exocrine function of the pancreas, and chronic enteritis. Developing dysbiosis contributes to the occurrence of an inflammatory process in the colon, but can also be its consequence, as is secondary disaccharidase deficiency.
In the pathogenesis of the disease, damage to the mucous membrane of the colon as a result of prolonged exposure to mechanical, toxic, and allergic factors is essential. The nervous apparatus of the intestine is involved in the pathological process, which leads to disruption of the motor and secretory functions of the colon and aggravates trophic disorders in the intestinal wall. Dysbacteriosis is of great importance, characterized by a decrease in the number of microorganisms constantly present in the intestine (bifidobacteria, E. coli, lactobacteria), a violation of the ratio of bacteria in various parts of the intestine, increased proliferation of opportunistic flora and the appearance of pathogenic flora. Secondary fermentopathy occurs. All this leads to the development of intestinal dyspepsia, immune disorders with the appearance of autoantibodies to antigens of the colon mucosa. The likelihood of autoimmunization in the progression and chronicity of the process is quite high.
Treatment with modern medicines
In case of acute enteritis, hospitalization is necessary; in a hospital setting, gastric lavage with a tube and bowel cleansing with laxatives are required. Acute intoxication is treated by drip administration of Ringer's solution, Trisol, and glucose. The intestinal flora is restored with the help of Intestopan, Bifikol, Colibacterin, Enteroseptol.
In case of chronic enteritis, antibacterial agents are not used to avoid dysbacteriosis. The flora is restored with the help of Linex, Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin. Panzinorm, Meksaza, Abomin, analogues of Enteroseptol, Intestopan are used. Diarrhea is stopped with drugs such as Imodium, Loperamide.
Acute colitis of infectious origin is treated in a specialized department of the hospital, where patients undergo a course of antibacterial therapy. For other forms of colitis, enveloping drugs (Kaolin), astringents (Bismuth drugs), and enzyme drugs (Bifikol, Colibacterin, Linex) are prescribed.
In chronic colitis, the main focus of therapy is aimed at normalizing the intestinal microflora. The patient is first given the shortest possible short course of antibiotics to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Then treatment with eubiotics and probiotics occurs.
Classification
There are several types of colitis:
- Ulcerative. Experts still find it difficult to name specific mechanisms for the development of this disease. It is known that the risk is increased by hereditary predisposition, as well as infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Infectious. Develops after infection with pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms.
- Ischemic - occurs against the background of damage to blood vessels - the branches of the abdominal aorta, and the blood supply to the intestine is disrupted.
- Toxic. Occurs against the background of poisoning with various chemicals, including uncontrolled use of medications.
- Radiation is a consequence of radiation sickness. Anyone who works in an area of high radiation exposure, as well as patients receiving radiation therapy, are at risk.
- Spastic - the exact causes have not been established.
- Microscopic – lymphocytic, collagen. Inflammatory changes are diagnosed only by histological examination.
Symptoms and treatment of colitis depend on the type of colitis diagnosed.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Sigmoidoscopy | 2 500 |
| Colonoscopy (video colonoscopy) | 7 000 |
| Irrigoscopy | 7 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Methods for diagnosing the disease and preparing for them
Human thick intestine
In order to make an accurate diagnosis of colitis and its type, I use special methods of examining the large intestine. The data obtained make it possible to determine the severity of the disease as accurately as possible and prescribe the most appropriate treatment accordingly. There are two methods for diagnosing colitis.
The first method includes laboratory blood tests, which show the presence of inflammation in the body. For reliable results, blood is donated on an empty stomach.