The article was checked by an obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Lisichkina E.G., is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
The Clinical Hospital on Yauza identifies and confirms the diagnosis of “bacterial vaginosis” (gardnerellosis is the second name for this disease), as well as the causes that caused it. The treatment regimen for bacterial vaginosis is selected individually, taking into account the patient’s condition, concomitant pathologies, and etiological factors.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
About the disease
Bacterial vaginosis is not a sexually transmitted infection. Gardnerella vaginalis (gardnerella) refers to opportunistic microorganisms, that is, it can be present in small quantities in the normal microflora of the vagina. However, when dysbacteriosis occurs and a sharp decrease in the number of lactobacilli in the vagina, the acidity changes. The environment becomes more alkaline and gardnerella begins to actively multiply, provoking the development of characteristic symptoms. In other words, bacterial vaginosis is vaginal dysbiosis.
Why is bacterial vaginosis dangerous?
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a vaginal infection characterized by heavy discharge and an unpleasant fishy odor caused by an increase in the concentration of certain anaerobic bacteria. This leads to a decrease in a woman’s self-esteem, the development of complexes, and a deterioration in the quality of life.
The risk of contracting infections through sexual contact increases. Patients with a weak immune system are at risk of pelvic inflammation. The inflammatory process is accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse, bleeding after intimacy or between menstrual cycles. Gardnerellosis is dangerous during pregnancy.
Features of the bacterium
Gardnerella are bacteria that are constantly present in the female body. Microorganisms of the species Gardnerella vaginalis are present directly in the vagina. These microorganisms can maintain their activity in both anaerobic and aerobic environments, but the preferred condition is the absence of oxygen. Normally, the number of Gardenella is limited by the activity of lactobacilli, the content of which in the microflora reaches 95%, however, under certain pathological conditions, conditionally pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply. At the same time, gardenella creates optimal conditions for the spread of other infectious agents into the vagina.
Causes
The most common causes of vaginal dysbiosis:
- The use of topical contraceptive drugs, which include 9-nonoxynol (condoms with spermicidal lubricant, suppositories).
- Douching with solutions containing chlorine ions (Miramistin).
- Promiscuous sex life.
- A history of pathology for the treatment of which broad-spectrum antibiotics were used, as well as topical drugs with antimicrobial action.
- Decreased immunity.
- Use of intimate hygiene products (panty liners, gels, wet wipes).
- Wearing synthetic underwear.
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
Causes of gardnerellosis
Gardnerellosis in most cases is provoked by external factors or is activated during the course of any diseases that can affect the balance of vaginal flora. Among the reasons that can provoke the development of the disease, experts name the following factors:
- Infectious sexual diseases - with sexually transmitted diseases, a concomitant complication is dysbiosis of the vaginal flora, as a result of which a sharp increase in the number of Gardnerella bacteria can be observed;
- Failure to comply with the rules of intimate hygiene - regular use of panty liners can affect the condition of the microflora. Untimely replacement of personal hygiene products during menstruation can also lead to dysbacteriosis;
- Hormonal disorders - hormonal imbalance provokes changes in the flora of mucous tissues, disturbing the balance of microorganisms. Hormonal imbalances can be caused by various diseases or the targeted use of hormone-containing drugs during treatment;
- Taking medications - various antibiotics used to treat infectious diseases can act on the vaginal flora, reducing the number of beneficial bacteria and causing dysbiosis. The same applies to various means of contraception, birth control pills, oral condoms;
- Intestinal dysbiosis – disturbances of the intestinal flora can become a catalyst for vaginal dysbiosis;
- Promiscuity in intimate relationships , frequent change of partners;
- Decreased immunity due to various diseases or general weakening of the body in winter, vitamin deficiency, etc.;
- Carrying out operations and invasive cosmetic procedures that can affect the balance of microorganisms.
Classification and stages of development of bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is classified based on clinical manifestations and laboratory tests:
- Compensated – there is a decrease in lactobacterial flora and the risk of harmful bacteria entering the vagina from the external genitalia.
- Subcompensated - with a reduced level of lactobacilli, a significant increase in pathogenic flora is observed.
- Decompensated - smear studies show the absence of lactobacilli and an excessive increase in pathogens. The symptoms and signs of bacterial vaginosis are distinct.
Today, there is no specific stage differentiation of bacterial vaginosis.
Symptoms
Gardnerellosis is not an inflammatory disease, since changes in the microbiome do not cause a specific immune response. Symptoms of the disease may appear within a few days after the microflora balance is disrupted. In this case, some signs of bacterial vaginosis may resemble inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Pale grey, white or greenish vaginal discharge.
- The appearance of an unpleasant odor reminiscent of rotten fish.
- Itching and burning in the vaginal area.
- Redness of the vaginal mucosa.
- Discomfort during urination.
- Pain in the lower abdomen.
Other symptoms may be due to complications of gardnerellosis or the proliferation of other pathogenic bacteria in the genitourinary tract.
How is BV transmitted?
If the lactobacillary flora is unable to prevent an excessive increase in anaerobes, the number of lactobacilli decreases. The predominance of anaerobic flora with the introduction of harmful bacteria is manifested by the appearance of symptoms of bacterial vaginosis.
The condition is not spread through toilet lids, bedding, or swimming in a pool.
The influence of vaginosis on the process of conception and pregnancy
Numerous studies have shown that if left untreated, bacterial vaginosis can affect female fertility and make it more difficult to conceive through changes in the pH environment, causing problems with pregnancy, including the possibility of premature birth or rupture of membranes in the very early stages of pregnancy.
Symptoms of gardnerellosis
How does bacterial vaginosis manifest? Symptoms, it turns out, are not always present. There are two forms of the disease:
- asymptomatic;
- with a characteristic clinical picture.
In the first case, women do not subjectively feel discomfort in the genital area, and the disease is diagnosed by chance during one of the preventive examinations.
If the patient has the second variant of the development of the disease, then the most characteristic of bacterial vaginosis is the appearance of discharge - abundant, white, with a rotten smell of fish. This smell is typical of gardnerellosis. There is also itching at the entrance to the vagina, a burning sensation that intensifies after sexual intercourse.
Despite the rather simple, at first glance, symptoms, gardnerellosis is dangerous due to the possibility of secondary infection - microorganisms such as mycoplasma, ureaplasma, chlamydia, candida, etc. and the development of inflammatory complications (endometritis, vaginitis/colpitis, salpingoophoritis). Then, symptoms of inflammation such as pain in the lower abdomen during sexual intercourse may be added to the clinical picture of bacterial vaginosis.
35% of all visits to the gynecologist are related to bacterial vaginosis. 50% of women on the planet suffer from this disease asymptomatically. The presence of pathology can only be ruled out by visiting a doctor. Make an appointment with a specialist now. Make sure you are healthy and receive adequate treatment if the disease is diagnosed.
Treatment of the disease
The goal of doctors is to eliminate the cause of the disease, eliminate a large volume of pathogenic microorganisms, restore normal microflora and strengthen the immune system. First of all, specialists prescribe medications:
- Antibiotics orally or intravaginally;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Painkillers;
- Antipruritic.
Next, creams and suppositories are prescribed that normalize the vaginal microflora.
A woman is advised to take foods with a high content of pro- and prebiotics. The basis of the diet is fermented milk products. Fried, pickled, and salty foods should be excluded from the diet. The patient also needs to take a course of vitamins to strengthen her immune system.
Bacterial vaginosis during pregnancy
Bacterial vaginosis can cause serious complications:
- miscarriage in the first half of pregnancy;
- development of postpartum endometritis;
- risk of premature rupture of the membranes;
- giving birth to an underweight child;
- penetration of infection into the amniotic fluid and into the membranes of the fetal bladder.
If symptoms of vaginosis appear during pregnancy, you should consult a doctor to exclude the possible development of complications.
Monitoring the vaginal microflora when registering a pregnant woman will allow you to identify imbalances in time and take preventive measures.
Bacterial vaginosis is one of the main causes of problems with conception and subsequent pregnancy. Often the disease is asymptomatic, which makes diagnosis difficult. Sick women do not feel discomfort and do not consult a doctor. To be examined for the presence of pathology, make an appointment with a gynecologist at the clinical center. This will help to identify and treat the disease in time.
Gardnerellosis during pregnancy
The greatest danger is a sharp exacerbation of gardnerellosis during pregnancy. Statistics show that pathology occurs in approximately 20% of women during pregnancy. Thanks to the body's natural defense mechanisms, actively stimulated during pregnancy, infectious processes are often suppressed at the initial stages by the body's immune system. However, if the immune system is weakened, the disease may develop, which in the future may have the following negative consequences:
- Complicated pregnancy;
- Increase or decrease in uterine tone;
- Damage to amniotic fluid by Gardnerella bacteria;
- Premature birth.
Considering all the risks, when planning a pregnancy, as well as during the period of bearing a child, it is worth regularly taking tests for gardnerellosis and other pathogenic microorganisms that can cause vaginal dysbiosis and other complications.
Also, it is worth remembering that gardnerellosis can be transmitted from mother to child (girl) during childbirth. Therefore, you should monitor your own health extremely carefully and take the necessary measures in a timely manner.
Is bacterial vaginosis possible in men?
No. Gardnerellosis usually does not develop in men, since gardnerella is not typical for male microflora. But is bacterial vaginosis transmitted to men through sexual intercourse?
Indeed, a microorganism can enter the mucous membranes of men during sexual contact, but normally, after a couple of days, its growth is suppressed, and there are no pathological symptoms.
In some cases, against the background of reduced immune defense, gardnerella can linger in the male body. Then he will become a carrier of the microbe and may contribute to the recurrence of gardnerellosis in his sexual partner. In such cases, to cure bacterial vaginosis, simultaneous treatment of both sexual partners is recommended. If gardnerella in men is combined with other pathogenic organisms, an inflammatory process in the genitourinary system (urethritis, prostatitis, cystitis, etc.) may develop.
How to diagnose and how to treat gardnerellosis in women
It is impossible to diagnose gardnerellosis based on symptoms and gynecological examination - similar complaints and discharge for many diseases. Laboratory tests will be required to detect Gardenerella vaginalis and its concentration. The doctor will also pay attention to a decrease in the number of lactobacilli and a decrease in leukocytes. To clarify the diagnosis, the following is carried out:
- microbiological analysis of a vaginal smear;
- immunofluorescence reaction;
- PCR test.
Based on the test results, the doctor decides how to treat gardnerellosis. Applicable:
- antibacterial drugs that act on pathogenic microorganisms;
- preparations for normalizing vaginal microflora - vaginal suppositories, tablets;
- immunomodulators;
- prebiotics for the prevention of intestinal dysbiosis.
It is recommended to treat gardnerellosis for a sexual partner who may become a carrier of the infection.
After completing the course, the effectiveness of therapy is checked by tests. Treatment of gardnerellosis in women has a favorable prognosis. Share:
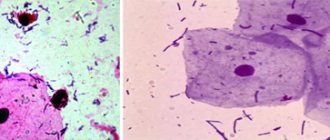
Diagnosis of gardnerellosis
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, the diagnosis of this disease is carried out according to a characteristic symptom complex with laboratory confirmation, which eliminates the very possibility of making an incorrect diagnosis.
Bacterial vaginosis can be suspected already at the stage of a gynecological examination based on typical signs - a specific smell and consistency of discharge. However, the decisive role belongs to microscopic and bacteriological examination of the vaginal smear.
The following changes in tests will be characteristic of vaginosis:
- A sharp decrease in the number of Doderlein bacillus (lactic acid bacteria).
- The presence of actively reproducing gardnerella, hemophilus (opportunistic microflora).
- The presence of “key” cells - desquamated vaginal epithelium, surrounded by bacteria from the coccus family.
Make an appointment
What indicators are important for diagnosing BV?
Clinical diagnosis is made when at least three of the following four features are present:
- watery and homogeneous appearance of discharge;
- pH above 4.5;
- fishy odor after alkalizing discharge with 10% potassium hydroxide (KOH);
- the presence of more than 20% of guide cells in a wet expanded state, which are vaginal epithelial cells covered with bacteria.
Cue cells (bacteria attached to epithelial cells) are identified by microscopic examination of fresh slides in saline. The presence of white blood cells suggests concomitant infection. In this case, further diagnosis is necessary.
Differential diagnosis with trichomoniasis, candidiasis and ureaplasmosis
Bacterial vaginosis requires differential diagnosis. Therefore, when discharge appears in women who are sexually active, it is necessary to undergo examination to identify the causative agents of the infection. An erroneous diagnosis leads to irrational treatment and possible relapse of the disease.
Treatment of gardnerellosis
Granderellosis is quite treatable and the microflora can be normalized within 1.5-2 weeks, depending on the severity of the case and individual characteristics. Treatment takes place in two main stages:
- Taking antibiotics to kill gardnerella bacteria . Antibiotics are selected by a specialist. When choosing, individual contraindications, the effectiveness of a particular drug, as well as general health are taken into account. You should not take any medications on your own; be sure to consult a doctor. A specialist can prescribe various types of antibiotic drugs. To increase effectiveness, topical antibiotics are used in the form of vaginal suppositories. Depending on the severity of the case, tablets may also be prescribed. An important point is the fact that when taking antibiotics, thrush may develop and a specialist, taking this into account, will prescribe suppositories to prevent it;
- At the second stage, the microflora is restored. To do this, colonies of lactobacilli are colonized in the vagina, normalizing the environment and restoring the condition of the mucous membranes. Suppositories or douching are prescribed, which can also be prescribed by a specialist. The second stage begins only after the gardenerelles have been successfully destroyed; after a course of antibiotics, you will need to take the necessary tests.
During the treatment process, the specialist will prescribe a diet that will help stabilize the flora. In particular, it is recommended to consume lactic acid products, kefir, biokefir, yoghurts, etc.
It is strictly recommended to limit the use of:
- Spicy food;
- Fried food;
- Alcohol and tobacco.
The doctor may also prescribe medications to boost immunity. After all, a weakened immune system is unable to fight infections and inflammation.
During the entire treatment period, you should refrain from intimacy and ask your partner to also take tests and be checked for the presence of bacteria. A man can act as a carrier and after treatment it is quite possible to become infected again.
At the end of the course of treatment, repeated tests are taken, a control smear is done after 2 months. In most cases, drug treatment allows you to completely get rid of the problem. To prevent the disease in the future, you should be attentive to personal intimate hygiene, give preference to underwear made from natural materials, and be tested annually for pathogenic microflora. At the first signs of illness, discomfort, change in color or smell of discharge, you should immediately contact a gynecologist.
Treatment of bacterial vaginosis
Effective therapy for this pathology consists of three stages:
- Elimination of the cause of dysbiosis: normalization of intestinal microflora, use of linen made from natural fabrics, avoidance of products containing 9-nonoxynol.
- Antimicrobial treatment of bacterial vaginosis, aimed at reducing the pathogen population: general (tablets) and local (suppositories, ointments) drugs containing an antibiotic are prescribed. The treatment regimen for gardnerellosis (dosage, course duration) is determined individually.
- Restoring local immunity and normal microflora in the vagina: for this, modern immunomodulators are used, as well as products that contain live lactobacilli. At the same time, with the help of probiotics, they try to restore normal intestinal microflora, which is important for maintaining good immunity.
If necessary, patients are consulted by related specialists, for example, an immunologist (to determine the causes of malfunctions in the immune system and eliminate them).
With properly selected therapy, bacterial vaginosis can be successfully treated. However, recovery does not guarantee that the disease will not appear again. The reasons for the development of the pathology have not yet been precisely established. It is important to regularly visit a gynecologist and undergo preventive examinations. If you feel symptoms of illness, make an appointment with a doctor before the disease takes effect.
Treatment
The main goal of treatment is the destruction of opportunistic microorganisms and restoration of the natural microflora of the vagina. For effective therapy, it is recommended to first test the sensitivity of the microbiome to antibiotics. Treatment uses not only oral antibiotics, but also topical medications.
Recommended destinations:
- Antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agents: metronidazole, ornidazole and secnidazole. Medicines are used in the form of tablets and ointments.
- Semisynthetic antibiotic clindamycin (oral).
- Antiseptics. Chlorhexidine is usually prescribed.
- Preparations containing lactic acid.
Only a doctor can prescribe a specific drug therapy regimen after studying the test results. Some antibiotics should not be taken by pregnant women. During treatment, it is important to consume enough lactic acid products. During therapy, doctors clarify the patient’s condition and re-examine laboratory parameters.
Is it possible to have sex with bacterial vaginosis?
If concomitant sexually transmitted infections are not identified, then it is possible, with condom protection. A sexual partner in the absence of any symptoms and pathogenic microflora does not need treatment. However, if bacterial vaginosis in a woman is difficult to treat, a course of therapy can be prescribed to both partners, since the man may be a carrier of Gardnerella for some time.
The Yauza Clinical Hospital guarantees its patients a delicate and individual approach in each specific case. If there are reasons for concern, do not put off solving health problems for later, make an appointment with a gynecologist right now!
Prevention
Eliminating negative external and endogenous influences helps prevent the development of gardnerellosis. Doctors recommend that women pay attention to their diet, personal hygiene and the health of their sexual partners. First of all, it is necessary to treat existing infectious diseases of the genitourinary system.
Other prevention methods:
- Using a condom.
- Exclusion of casual sexual relations.
- Refusal to take oral contraceptives.
- Proper use of antibacterial agents.
Thus, gardnerellosis is a common form of vaginal microflora disorder. This disease rarely causes dangerous complications, but prolonged vaginosis can negatively affect the patient’s quality of life. Complex treatment helps to destroy pathogenic microorganisms and restore the natural genital microbiome.
Complications of bacterial vaginosis
Complications arising from BV are associated with late diagnosis. An important point is the non-use of modern laboratory research.
Complications of bacterial vaginosis include:
- development of inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system: vulvovaginia, salpingoophoritis, endometritis;
- the risk of cystitis, urethritis in women and sexual partners;
- reduced resistance to STDs, also HIV, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis.
Gardnerellosis is a complex vaginal dysbiosis that does not have a clear and absolutely effective treatment method. Clinical recommendations, both in Russia and in other countries, need to be revised and supplemented. The genetic composition, pathogenesis and antibiotic resistance of pathogens have not been fully studied. Recently, there has been a tendency for BV to increase, which requires additional attention.
Prognosis and prevention
Bacterial vaginosis goes away on its own in about 1/3 of cases. In most patients, therapy is successful. However, the risk of recurrence is high, especially if there is an existing biofilm, i.e. a layer of mucus that contains bacteria. It cannot be completely eliminated with antibiotics. Up to 60% of patients may experience recurrence of the disease within 6 months after completion of primary treatment.
Bacterial vaginosis is not a sexually transmitted disease (STD), but frequent changes of sexual partners, sex with multiple partners, and risky sexual behavior increase the likelihood of developing BV. Fluids, bacteria and microorganisms that make up the genital flora of other people can change the number of bacteria in the vagina.
To prevent the development of BV, as well as any other STDs (trichomoniasis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, HIV, herpes), it is recommended to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid changing sexual partners frequently.
- Use a condom, especially with a new sexual partner.
- Avoid sexual intercourse if you have symptoms of infection.
- Avoid douching, which alters the population of healthy bacteria and disrupts normal pH levels.
- Do not use antibiotics without a doctor's prescription.
- Never self-administer medications to treat unusual vaginal symptoms. This is because other infections can cause symptoms similar to bacterial vaginosis, but their origin and treatment are different.
- The soap should be mild, without a lot of fragrances and with a neutral pH.
- Chemicals found in feminine hygiene products can cause irritation and disrupt the acid balance of the vagina (bubble baths, strongly scented soaps and deodorants, laundry detergents, scented toilet paper, scented tampons).
- Avoid wearing underwear or clothing that is too tight, as this can cause excess moisture in the vagina and create an ideal environment for harmful bacteria to grow.
- Avoid synthetic fabrics and choose cotton underwear.
You should know that smoking suppresses the immune system, promotes the accumulation of toxins and the proliferation of bacteria throughout the body. To prevent diseases, women are recommended to undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist, treat chronic diseases, and strengthen the immune system.
Which specialist should I contact for the treatment of gardnerellosis?
Gardnerellosis is not a sexually transmitted disease. This means that if symptoms appear, you should contact a gynecologist who will conduct an initial examination and take a smear for analysis. If the course of the disease is accompanied by an intestinal disorder, it is worth contacting a gastroenterologist, since gardnerellosis can be the cause of intestinal dysbiosis. Men with gardnerellosis should see a urologist.
If there is a suspicion that a sexual partner is also a carrier of Gardnellera bacteria, then the man should be examined by a urologist and also undergo the necessary tests to identify pathogenic bacteria.