Published: 05/27/2021 11:45:00 Updated: 05/28/2021
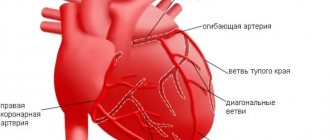
Coronary heart disease is a chronic or acutely developing disease characterized by partial or complete cessation of blood supply to the heart muscle.
The cause of this phenomenon is spasm and thrombosis of the coronary arteries, usually due to their atherosclerotic changes.
Organ ischemia is most often manifested by paroxysmal chest pain - angina pectoris; with a sharp and pronounced disturbance of blood flow in the vessels, myocardial infarction develops.
Prevalence of the disease
In Russia, about 5.1-5.3% of the population suffers from ischemic heart disease.
At the same time, coronary heart disease remains the main cause of mortality and disability in the population. Worldwide, deaths from pathologies of the cardiovascular system account for a third of diagnosed cases. In Russia, this figure is higher and amounts to 57%, of which 29% are deaths due to myocardial ischemia. Myocardial ischemia mainly affects people over 40 years of age. In young and middle age, coronary heart disease is more often detected in men; with increasing age, the ratio of cases evens out.
Herbal medicine for the prevention of heart disease
Herbal medicines and various traditional medicines are available to everyone. It is important to remember that herbal remedies are only good as part of comprehensive prevention - they cannot replace a balanced diet or quitting smoking. In addition, individual intolerance or contraindications may also occur to herbal remedies. Among the “folk” remedies for the heart are:
- garlic - it should be consumed raw with food, as well as in the form of tincture, garlic oil;
- chokeberry, ground with honey;
- a mixture of persimmon and turnip juices with honey;
- a mixture of radish, carrot, beet juices with honey;
- a mixture of carrot juice with vegetable oil;
- a mixture of honey and royal jelly;
- hawthorn in the form of tea, tincture.
Risk factors for the development of myocardial ischemia
Factors predisposing to this disease are conventionally divided into two groups – modifiable and non-modifiable.
By eliminating or correcting the former, the risk of coronary heart disease is significantly reduced. This group includes situations in which the myocardium needs more oxygen than usual (or oxygen delivery is reduced without increasing its consumption):
- sedentary lifestyle;
- excess weight;
- unhealthy diet – a large amount of fatty and high-calorie foods in the diet;
- psycho-emotional stress;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- high levels of “bad” cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood;
- high blood pressure – arterial hypertension;
- diabetes;
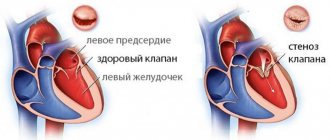
- endocarditis and heart defects;
- decrease in the concentration of high-density lipoproteins in the blood.
Factors that cannot be changed:
- male gender;
- age over 65 years;
- IHD, especially myocardial infarction in the past in close relatives of the patient;
- the onset of menopause.
The likelihood of coronary heart disease in women increases significantly with the onset of menopause.
How to help with acute pain in the heart?
It is no coincidence that when pain appears in the heart area, they do not know what to do until the doctor arrives. Call the hotline number +7 (863) 226-18-17 , which is best entered into the phone’s memory in advance. Experienced private medical doctors help in emergency situations and transport the patient to the hospital. Emergency medical care is provided in clinics, hospitals and at home.
Before the doctor arrives, you should stop moving and take a lying position, and be sure to call a specialized ambulance. If your heart hurts, self-medication can end sadly and lead to death.
In case of high or low blood pressure, take the tablet as indicated. The patient is prescribed sedative drops , Corvalol, motherwort, valerian, and nitroglycerin. If the pain has passed, there is no need for nitroglycerin; it is also contraindicated for low blood pressure. You can put validol under your tongue. Treatment of cardiac pathologies is prescribed by a doctor according to indications.
Symptoms and forms of IHD
With different forms of coronary heart disease, symptoms may differ. There are several forms of the disease.
Angina pectoris
The condition is characterized by attacks of squeezing or burning pain behind the sternum, which usually appears during physical and emotional stress.
It can radiate to the left arm, neck, shoulder, lower jaw, subscapular region, upper abdomen. For this reason, angina pectoris is also called “angina pectoris.” The duration of pain is usually several minutes. Depending on the stability of the course of the disease, stable and unstable forms of angina are distinguished. The first occurs only after physical or psycho-emotional stress, with increased blood pressure, tachycardia. As the disease progresses, the amount of activity available to a person decreases, and in the fourth class of pathology, he can no longer make any movement without developing attacks of chest pain.
Unstable angina can be new - a month or less after the onset of symptoms, progressive and early post-infarction. Progressive angina is characterized by a decrease in the load tolerated, for example, a decrease in the distance that a person can walk without the appearance of symptoms.
Unstable angina requires examination and treatment in a hospital; the risk of myocardial infarction is high.
Myocardial infarction
Develops acutely.
Due to a prolonged decrease in blood flow or its complete cessation to certain areas of the heart muscle, necrosis of the area of the heart muscle occurs - necrosis. The affected area can be of different sizes depending on the diameter of the affected vessel, which is why the disease is often called large-focal or small-focal myocardial infarction. The pain in this condition is intense, pressing and squeezing in nature, and attacks of burning “dagger” pain are also common. In many patients, it has a typical localization in the retrosternal region, but it can also involve the area to the left of the sternum or spread to the entire surface of the chest. In this case, the patient experiences “fear of death”, melancholy, a feeling of doom arises, and may be restless and very excited.
The localization of pain during myocardial infarction can be almost any; for example, sometimes pain occurs even in the abdomen. There is also a painless form.
With small focal lesions, the symptoms may be blurred, and diagnosis by ECG can be difficult.
Spontaneous Prinzmetal ischemia
Substernal pain occurs against the background of spasm of the coronary vessels and is not associated with exercise. Most often, the condition develops at night, between midnight and eight o'clock in the morning. Spastic angina is characterized by regularity and cyclicity, often repeating several attacks in a row with a short interval.
Post-infarction cardiosclerosis
After a heart attack, dead muscle cells are replaced with connective tissue. In this case, conductivity in the myocardium is disrupted, which may be accompanied by sensations of interruptions in the work or prolonged cardiac arrest, periodic fainting and dizziness. There may also be attacks of rapid heartbeat, chest pain, shortness of breath, pale or blue discoloration of the skin.
Heart failure
A disease in which the heart cannot fully perform its function of providing the tissues of various organs with a sufficient amount of blood. The condition is manifested by shortness of breath, swelling, fatigue, and poor tolerance to physical activity.
Heart rhythm disturbances
Arrhythmias are of various types. Accompanied by a feeling of palpitations or a decrease in heart rate. The patient may experience severe weakness, dizziness, nausea, and possible loss of consciousness. There are also asymptomatic forms of pathology, which become an accidental finding on the ECG.
Silent myocardial ischemia
It occurs without characteristic attacks of angina pectoris. It is usually detected accidentally on an ECG and after special diagnostic exercise tests.
Sudden cardiac death
More often it occurs due to ventricular fibrillation or flutter - erratic contraction of the heart muscle at high frequency. The condition develops unexpectedly and is manifested by the following symptoms:
- weakness;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- noisy and rapid breathing;
- dilated pupils;
- decrease in respiratory rate;
- absence of heart contractions.
Sometimes the heart can be returned to the correct rhythm, but if this was not done in the first minutes, then the brain cells die from hypoxia, and an irreversible coma develops.
What are the symptoms of pain in different diseases?
Often, pain in the heart area when inhaling is attributed to purely heart diseases, without even suspecting that the real reason lies in something completely different.
How the pain syndrome manifests itself depends on the causes and level of progression of the disease. For example, with heartburn, a burning sensation also occurs in the sternum area. They occur when gastric juice enters the esophagus. Heartburn is also characterized by the appearance of belching and an unpleasant sour taste. These symptoms appear after eating, when bending the body, or in a lying position. In this case, antacid medications are prescribed for relief. When heartburn occurs and pain radiates to the heart area, the cause does not always lie in the esophagus.
- These may be symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is also characterized by heartburn;
- Spasm of the esophagus with disruption of muscle function, which leads to problems with swallowing and moving food in the stomach;
- With achalasia, this pathology manifests itself in disruption of the valve between the stomach and esophagus, with food retention and the appearance of pain in the chest.
Depending on the nature of the pain in the heart area, inflammatory diseases can be diagnosed:
- Gall bladder with the development of cholecystitis;
- Pancreas and acute manifestations of pancreatitis;
- Gallstone disease (GSD).
Painful symptoms in these diseases can radiate into the chest cavity and resemble heart pain.
Pulmonary diseases can also be accompanied by sharp and dull pain in the chest. These signs can occur with pneumonia, pleurisy , with characteristic inflammation of the lungs and tissues that line the chest cavity, respectively. These diseases are characterized by increased pain when inhaling, the appearance of a cough, and an increase in temperature to critical values. Also, diseases can accompany each other and after pneumonia complications arise, which manifest themselves in the form of pleurisy.
Diagnosis of coronary heart disease
Usually, complaints and symptoms characteristic of coronary heart disease help to suspect the disease.
To confirm myocardial ischemia, instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods are used. Tests for coronary heart disease may include:
- Leukocytosis and decreased hemoglobin in a general blood test.
- Increased cholesterol and glucose, changes in the lipid profile according to biochemical blood tests.
- An increase in specific enzymes formed during the destruction of cardiomyocytes - creatine phosphokinase (its special fraction - MB) during the first 3-4 hours of a heart attack (lasts 48-72 hours), troponin-I, troponin-T (their level increases 6 hours after a heart attack and remains elevated for 7-14 days), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (exceeds the normal level 8-12 hours after the onset of pain, normalizes within 3-4 days), lactate dehydrogenase (begins to exceed the normal level 14-48 hours after the onset of symptoms, returns to normal on days 7-14), myoglobin (increases 2 hours after the onset of symptoms and normalizes within 24 hours) in the blood.
- Elevated C-reactive protein and homocysteine levels are a risk for sudden cardiovascular events.
- Increased blood clotting according to the results of a coagulogram may also increase the risk of developing certain forms of coronary artery disease.
Instrumental research methods can be invasive or non-invasive. In the latter case, the following is used to diagnose coronary heart disease:
- electrocardiography;
- ultrasound examination of the heart - Echo-CG;
- Holter ECG monitoring;
- stress ECG tests: treadmill and bicycle ergometry;
- PET/CT of the heart.
Functional load tests are widely used.
They are used, among other things, to detect the early stages of coronary artery disease or a painless form of the pathology, when the disorders cannot be determined at rest. Walking, climbing stairs, exercises on exercise machines (an exercise bike, a treadmill), accompanied by ECG recording of current indicators, are used as stress tests for suspected coronary heart disease. The standard and most accurate method for this is diagnostics using a treadmill (treadmill) and an exercise bike (bicycle ergometry). Positron emission tomography (PET) is used to diagnose viable cardiac muscle cells. Radiopharmaceuticals are used, the accumulation of which in heart cells reveals viable and necrotic areas.
Among the invasive techniques, coronary angiography is used - x-ray examination of blood vessels using a contrast agent.
Exercise tests
There is another very interesting method for identifying the degree of decrease in blood circulation (this is the so-called myocardial ischemia) these are tests with physical activity: veloergometry (the patient with the ECG electrodes connected is on a bicycle and pedals). The state of the heart and blood vessels is assessed in response to physical activity. A similar method is the treadmill test (only the patient is on a treadmill). Thus, we see that thanks to the combination of all examination methods, it is possible to collect a detailed picture about this disease. Thus, the cardiologist has a clear picture of the disease and is already moving along the precisely planned path of treatment for this disease.
Expert electrocardiographers
Professional cardiographic systems designed specifically for cardiology clinics and departments. Manufactured using the latest technical advances, electrocardiographs are distinguished by their modern ergonomic design, functionality and ease of use. The high-resolution touch screen displays all 12 leads. The quality of electrocardiogram printing will satisfy even the most demanding cardiologist.
Treatment of coronary artery disease
Treatment for coronary heart disease includes lifestyle changes, medications and, in some cases, surgery.
All patients are advised to give up bad habits, spend more time in the fresh air, and reduce excess body weight. In your diet, you must avoid foods high in fat, very salty and sweet foods. Smoking and unauthorized discontinuation of prescribed medications are strictly prohibited. All this can lead to a sharp deterioration in the patient's condition. To stop an attack of angina, you need to immediately stop physical activity, provide access to fresh air and take nitroglycerin under the tongue or use nitrate in the form of a spray.
Basic drug therapy includes the following drugs:
- antiplatelet agents – drugs that thin the blood;
- beta blockers;
- ACE inhibitors or sartans;
- statins.
Long-acting nitrates can be used to prevent attacks.
In the presence of concomitant diseases, especially diabetes mellitus and hypertension, their treatment and achievement of target blood pressure and glucose levels are required.
To restore cardiac blood flow, surgical intervention is necessary in some cases:
- Coronary artery bypass surgery is the creation of a bypass for blood at the site of narrowing of the coronary arteries using vascular prostheses.
- Coronary angioplasty and stenting - restoration of the diameter of the vessel, and, accordingly, the blood flow in it, by installing a special dilator.
How are heart diseases treated?
Causal therapy is not always possible. However, as a rule, they try to eliminate the cause of the violation. In the case of coronary artery disease, acute symptomatic, long-term medicinal and surgical measures are distinguished. Acute measures involve reducing the heart's oxygen demand. In the long term, in addition, cholesterol levels and heart rate must be reduced, and oxygen supply must be improved.
If drug therapy is insufficient, an attempt is made to widen the narrowing using a cardiac catheter , in many cases a stent (vascular support) is used. The so-called bypass operation (from the English “bridge, bypass”) remains an open surgical intervention with the aim of replacing damaged vessels with another implant, for example, the own vein of the legs or an artery of the chest.
Measures to prevent cardiovascular pathology
To avoid developing heart disease, you need to stop smoking and reduce your alcohol consumption.
Severe stress is also one of the predisposing factors to the occurrence of IHD. It is impossible to remove stress from life, but you can react to it correctly: humans are evolutionarily designed in such a way that muscle work is necessary after any stress. If you are worried or upset, then you need to squat, jog, or walk – the muscles should get tired. In case of severe anxiety, you may need to use sedatives, for the selection of which you need to consult a doctor.
Regular exercise with moderate physical activity is useful for the prevention of ischemia. You also need to monitor your weight and blood pressure. All persons over 40 years of age must be examined annually - take a biochemical blood test to check the level of cholesterol in the blood, and do an ECG.
Vascular lesions
Vascular diseases include diseases such as varicose veins, atherosclerosis, aneurysm, etc. All these diseases develop against the background of deteriorating vascular condition and arise due to various factors.
The cause of vascular diseases can be age, poor diet, smoking and drinking alcohol, and a sedentary lifestyle. Some diseases can lead to serious complications. With atherosclerosis of the vessels of the extremities, gangrene may develop, while aortitis leads to a more severe form of the disease - aortic aneurysm.
In the Medicenter clinic network, it is possible to undergo a complete examination of the circulatory system and identify any cardiovascular disease.
How is differential diagnosis carried out?
If chest pain occurs, you should immediately call an emergency doctor. Before the specialist arrives, if possible, relieve emotional and physical stress, calm down, lie down and understand the nature of the pain in order to properly notify the doctors.
The doctor's examination includes consultations with specialized specialists, instrumental studies, and an electrocardiogram. It shows how the heart works, detecting signs of a heart attack depending on the stage and location.
Medical care and consultations can be prescribed by various specialists, a neurologist, cardiac surgeon, infectious disease specialist, pulmonologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, psychiatrist. In case of nervous experiences, you may need the help of a psychologist.
What signs confirm heart pain?
Critical conditions are caused by cardiac pathologies, which can be determined using simple manipulations. It is necessary to understand whether the pain intensifies when inhaling, when raising your arms, bending your torso, or whether you can take a deep breath. An increase in pain may indicate the presence of intercostal neuralgia or osteochondrosis.
The pain may intensify with physical exertion and decrease at rest when angina pectoris , with insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle in an active state.
Cardiac pathologies are often accompanied by sharp pressing pain, difficulty breathing, stress, discomfort in the chest, cold sweat, irradiation to the left shoulder, arm and under the left shoulder blade.
An emergency call to a private medical ambulance allows you to help in emergency situations, do an ECG, a rapid blood test for the protein troponin to determine myocardial infarction, and transport the patient to the hospital.
Rate this article
Article rating 4.26 out of 5. Votes: 74.
Latest articles
Sexual transmission of infections
Sexually transmitted infections or STIs are dangerous diseases that can undermine health and lead to dire consequences. Most of the diseases in this group are…
Hormonal disorders
A woman’s well-being largely depends on the endocrine system. Any hormonal imbalance can cause a sharp deterioration in health, weakening the immune system...
Cervical dysplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition expressed by pathological changes in cells. In most...
What diseases cause pain in the heart?
Acute pain syndrome can also appear with pulmonary diseases such as bronchial asthma and pneumothorax. Asthma attacks cause pain throughout the chest cavity. An equally severe form and painful condition is characterized by pneumothorax , in which air penetrates from the outside into the chest cavity and the lungs can collapse with the appearance of pain.
Among the main causes of painful attacks in the sternum area is also pathology of the peripulmonary vessels. They intensify when inhaling with the formation of a cough with pulmonary embolism , pulmonary hypertension with increased pressure in the vascular system supplying blood to the lungs.
Painful vascular diseases include dissecting aortic aneurysm with characteristic damage to large vessels. This emergency condition can be life-threatening. In this case, the pain is initially felt in the heart area and gradually moves down the abdomen. The patient's blood pressure drops sharply, tachycardia occurs and he loses consciousness.
A classic example of the appearance of pain in the chest area is osteochondrosis , which occurs in the thoracic and cervical spine. The pain is reminiscent of angina attacks with radiation to the left shoulder blade and arm. The difference lies in the intensification when moving, raising arms, turning the head, bending the body.
Sharp stabbing pain is characteristic of intercostal neuralgia, Tietze syndrome . It occurs at the joints and spaces between the ribs and becomes more intense when inhaling. The patient cannot take a deep breath, shallow breathing is observed. In case of pathology, strong anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed.
An extremely painful condition in the heart area is characterized by inflammation of the muscle fibers of the chest and back . It resembles similar acute pain in intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis.
Shingles , which occurs as a result of infection of the body with the herpes virus, is no less painful In this case, the nerve endings are affected, characteristic rashes appear on the skin, which becomes sensitive, and this whole clinical picture is accompanied by acute pain in the chest.
Painful attacks can occur during panic attacks, nervous disorders of various etiologies. This category of patients is often young, with an unstable nervous system, and in a depressed state after stress. In this case, pain can appear spontaneously or be systematic.
Instrumental studies
In addition to an electrocardiogram (ECG), in case of cardiac pathology, various instrumental diagnostic studies .
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- FEGDS examination of the digestive organs;
- Ultrasound of the heart, pulmonary vessels and aorta;
- FVD, examination of external respiration functions;
- Chest X-ray;
- CT, computed tomography;
- MRI, magnetic resonance imaging;
- EchoCG, echocardiography and others.