Tachycardia is one of the most common heart rhythm disorders. The main mechanism for the development of pathology is to increase the automaticity of the sinus node. In this case, the heart rate increases to more than 90 beats per minute. Tachycardia may not have subjective manifestations. Most often it is felt as increased heartbeat. In the presence of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, this type of arrhythmia can worsen the general condition and provoke the development of complications. Therefore, treatment of tachycardia should be prescribed and strictly monitored by a specialist.
Causes of tachycardia
An increased or increased heart rate does not always mean there are problems with the cardiovascular system. For example, in preschool age it is considered normal and does not require special help. Symptoms of cardiac tachycardia can also appear in practically healthy people as a result of activation of physiological compensatory mechanisms, that is, as the body’s response to the influence of one or another external factor. The reaction of the nervous and cardiovascular systems, accompanied by the release of adrenaline into the blood, causes increased heart rate. The occurrence of tachycardia can be provoked by the following factors:
- stress, physical activity and emotional arousal;
- increase in ambient temperature;
- consumption of caffeinated drinks, alcohol, and certain medications;
- sudden change in body position, etc.
When the action of the provoking factor ceases, the heart rhythm gradually returns to normal.
However, tachycardia often accompanies the presence of certain pathological conditions. It can be a manifestation of various cardiovascular diseases - arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction, heart disease (rheumatic or congenital), cardiosclerosis, etc. In addition, tachycardia can be neurogenic in nature, that is, associated with disturbances in the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and brain. Other causes include fever that develops against the background of an infectious-inflammatory process (pneumonia, tonsillitis, etc.).
Prevention
In order not to face the question of how to treat tachycardia in the future, doctors recommend:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol;
- control blood pressure;
- include more vegetables and fruits in the diet and limit the consumption of animal fats;
- control blood cholesterol levels;
- be examined annually by a cardiologist
.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Symptoms of the disease
Tachycardia, which is a sign of a disease, is characterized by the following symptoms.
- A feeling of interruptions and/or “failures” in the functioning of the heart is the most common manifestation.
- Shortness of breath (lack of air), which occurs with little physical activity or even at rest.
- Pain in the heart (accompanies an attack of tachycardia in vegetative-vascular dystonia and some other diseases).
- Dizziness and darkening of the eyes, lightheadedness and even fainting (this is due to impaired blood supply to the brain).
In general, the manifestation of clinical symptoms of tachycardia depends on the nature of the underlying disease, as well as on the severity and duration of the arrhythmia itself.
How to correctly calculate your pulse?
For self-counting, the most common method is palpation (palpation) of the radial artery of the wrist. You need to count your pulse at rest, no earlier than 2 hours after eating, bathing, or massage. The accuracy of the result depends on the correct counting technique.
First, you need to take a watch or stopwatch. Sit down with your hand on a horizontal surface, palm up. Place the index, middle and ring fingers of the opposite hand on the wrist approximately 3 centimeters from the base of the thumb;
When you feel the pulsation, you need to lightly press the artery to the inside of the radius. There is no need to press with force, as the pulse wave may disappear under pressure.
Then you need to count the number of blood pulses within 1 minute. Pulse waves should follow each other at regular intervals; then count the pulse on the second hand.
An increase in heart rate at rest greater than 90 beats per minute is considered tachycardia.
Consequences of tachycardia
Physiological tachycardia, which occurs in healthy people even in the presence of pronounced subjective manifestations, is not life-threatening and has a good prognosis. For patients suffering from heart disease, the consequences can be quite serious. The main and severe complications are the development of heart failure, states of loss of consciousness and even sudden death. In addition, the presence of tachycardia increases the risk of blood clots, which in turn leads to frequent heart attacks and stroke. Therefore, timely provision of assistance for tachycardia is so important.
What is the danger
In addition to unpleasant and uncomfortable sensations, tachycardia can lead to conditions that are more dangerous to health and life. As a result of inadequate work, the heart muscle wears out faster, which entails a number of complications. These include:
- Acute and chronic left ventricular failure (cardiogenic edema and cardiac asthma).
- Arrhythmias of various origins.
- Cardiac conduction disorders.
- Arrhythmic shock.
- Transient cerebrovascular accidents and strokes.
- Increased thrombus formation, which, in turn, can provoke myocardial infarction and pulmonary embolism.
Diagnosis of tachycardia
Electrocardiography
The ECG plays a leading role in the differential diagnosis of tachycardia and in helping to identify its causes. This method allows you to determine the type of pathology, as well as the rhythm and heart rate. If the severity of symptoms of cardiac tachycardia increases, it is advisable to conduct daily Holter ECG monitoring. This method is highly informative. It allows you to identify and analyze any heart rhythm disturbances within 24 hours. Holter monitoring helps detect ischemic changes during normal physical activity.
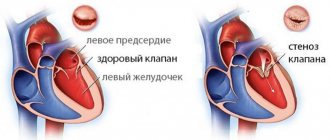
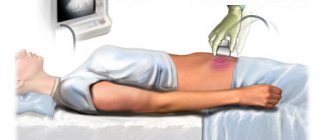
Echocardiography
It is a standard examination method to exclude heart pathology in case of any rhythm disturbances. Thanks to echocardiography, the doctor receives data on the size of the heart chambers, the thickness of the myocardial walls, and changes in the valve apparatus. This examination allows you to identify violations of local contractility.
Electrophysiological study
This is an invasive method of examining patients with cardiac pathology. Electrophysiological testing is used when appropriate before surgery to treat arrhythmia. Used to diagnose different types of tachycardia in a limited number of patients. This method boils down to determining the nature of the propagation of an electrical impulse throughout the myocardium, making it possible to determine the mechanisms of tachycardia or cardiac conduction disorders.
Additional examinations
Additional research methods are used to identify the causes of cardiac pathology. The specialist may prescribe a blood test (general and thyroid hormone tests) and electroencephalography. In rare cases, an MRI of the heart is performed, usually to detect congenital abnormalities.
Slow heartbeat - bradycardia
Bradycardia is a condition where the heart beats so slowly that it cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. If bradycardia is left untreated, it can lead to extreme fatigue, dizziness, or fainting because not enough blood is supplied to the brain. This condition can be corrected by using an electronic pacemaker, which makes the heart beat normally.
Bradycardia occurs for various reasons:
- Sick sinus syndrome
The appearance of sinus bradycardia as a result of a “malfunction” in the sinus node (the natural pacemaker of the heart) occurs when discharges for contractions occur too infrequently. A weak sinus node can develop with age or be a consequence of illness. Some medications may also cause or worsen bradycardia. This arrhythmia may be temporary or permanent. It can be treated with medications or an electronic pacemaker.
- Blockage of the heart pathways
Heart block is a slowing or interruption of the electrical signal to the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) that cause the heart muscle to contract. The heart's electrical conduction system typically sends signals from the upper chambers of the heart (atria) to the lower chambers (ventricles), which causes coordinated contractions of the heart muscle. Complete blockade of the atrioventricular node can manifest as a sudden loss of consciousness, since the ventricles contract very rarely without stimulus from the sinus node. An artificial pacemaker can eliminate this problem and normalize heart function.
Treatment of tachycardia
Medicinal
To treat tachycardia, drugs belonging to the following groups are used.
- Antiarrhythmic. These are drugs with different mechanisms of action. Only the attending physician can prescribe them, based on clinical data. Self-medication is dangerous, since the same medications can be effective for one type of tachycardia and contraindicated for another.
- Sedatives. Most often these are synthetic drugs or herbal products. They are prescribed for the treatment of tachycardia associated with vegetative-vascular dystonia. Such drugs help normalize the functioning of the nervous system and, as a result, reduce the frequency of arrhythmia attacks.
If tachycardia is accompanied by a drop in blood pressure, pressor amines are usually prescribed to increase it to a level of 100-110 mmHg. Art.
Surgical
Common radical methods of treating tachycardia include minimally invasive surgery. It is performed under local anesthesia. This could be radiofrequency catheter ablation, installation of an artificial pacemaker, etc. Among the main reasons requiring serious surgical care are the following.
- Hormonal disorders. Common causes of tachycardia are thyrotoxicosis (excess thyroid hormones) and pheochromocytoma (a hormonally active tumor in the kidney or adrenal gland). In such cases, surgical removal of the tumor or part of the gland that produces excess hormones is usually recommended.
- Structural and functional changes. Cardiac surgery is performed in the presence of severe congenital heart defects, severe circulatory disorders (IBC), to eliminate the consequences of rheumatism, etc.
In some cases, arrhythmia does not require special treatment if it is a symptom of anemia, is caused by the presence of a malignant blood disease (for example, leukemia), occurs against the background of fever, etc. For tachycardia caused by such causes, treatment is the elimination of the underlying disease.
How to relieve an attack of tachycardia?
Unbutton your clothing collar, open a window or balcony, inhale deeply and exhale very slowly; breathe like this for 5-10 minutes. Then hold your breath and, as it were, “push” the air into the lower abdomen - this stimulates the vagus nerve, as a result of which the heartbeat will slow down;
Take Corvalol or Valocordin: dissolve 15-20 drops of the drug in half a glass of water at room temperature;
Wash your face with cold water, lie down on a high pillow, place a towel soaked in cold water on your forehead, try to relax;
Close your eyes and simultaneously press on your eyeballs for 2-3 minutes: press for 10 seconds, break for 10 seconds;
Find the right carotid artery (immediately under the jaw, at this point it connects to the cervical artery) and gently, without pressure, massage it. This technique also stimulates the vagus nerve and slows the heart rate.
If the condition does not improve, the heart rate does not decrease, dizziness appears, a feeling of shortness of breath, darkened vision, call an ambulance.
Sources
- Utsumueva M.D., Mironov N.Yu., Shlevkov N.B., Kiktev V.G., Gupalo E.M., Kashtanova S.Yu., Mironova N.A., Golitsyn S.P. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in a patient with dilated cardiomyopathy and concomitant cardiac conduction disorders. Clinical case and discussion of the problem. Cardiovascular therapy and prevention. 2020;19(3):2368.
- Salami Kh.F., Shlevkov N.B., Sokolov S.F. Possibilities and limitations of standard electrocardiography for the differential diagnosis of tachycardias with widened QRS complexes. Almanac of Clinical Medicine. 2019;47(4):350-360.
Forecast
Cardiac arrhythmias are dangerous because they can lead to sudden cardiac arrest due to complete blockade of conduction. In severe arrhythmia, there is a high risk of ventricular fibrillation, which can be fatal. Atrial fibrillation leads to the formation of blood clots in the atria and their transfer to other organs with the development of stroke and gangrene of the extremities. The probability of an unfavorable outcome in patients with arrhythmias depends on the form of rhythm disturbance and is more than 20% per year. You should not rely on folk remedies - arrhythmia is very dangerous and requires correction by a professional cardiologist.