An infectious disease such as ringworm is caused by various types of fungi, most often of the Microsporum or Trichophyton genus.
Cost of services in our clinic
| Appointment with a dermatologist, candidate of medical sciences | 1500 rub. |
| Consultation with a dermatologist (KMS) when removing 2 tumors | 0 rub. |
| Removal of a neoplasm (wart, mole) using the radio wave method | 500 rub. |
| Make an appointment by phone: 8-800-707-15-60 (toll-free) |
| *The clinic is licensed to remove tumors |
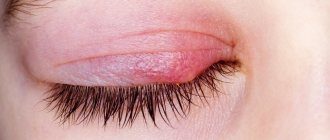
The disease manifests itself in the form of pinkish, scaly, rounded spots on the skin. The incubation period is one to two weeks from the moment of infection.
Ringworm
Ringworm (also known as microsporia) is a highly contagious fungal disease caused by the Microsporum fungus. It affects the skin, scalp and vellus hair, and rarely nails. Ringworm on the skin develops in animals and humans. The source of infection is most often a sick animal. At the same time, children are more susceptible to the disease, since they are more likely to come into contact with stray cats and dogs, which may be carriers of the fungus. In addition, the pH of the skin of adults is shifted to the “acidic” side, which prevents the fungus from actively multiplying. According to statistics, symptoms of ringworm are 5 times more common in boys than in girls.
Hygiene measures when in contact with a sick person
If you or your child have touched a sick animal or interacted with a sick person, then you need to take immediate action.
- The sooner you wash away particles containing fungus from your skin, the less likely you are to become infected.
- Wash your hands several times with antifungal soap. The simplest remedy, which is available in almost every store, is cinnamon laundry soap, or better yet, soap with birch tar.
- Wash your entire body with this soap. Suddenly, particles of the patient’s skin got under his clothes. Do not use a hard washcloth. It leaves micro-scratches on the skin, into which fungus easily penetrates.
- To wash your hair, you must use an antifungal shampoo. For example, Nizoral. You can also use it as a shower gel.
- A modern remedy with a powerful antifungal effect is Citeal. Dilute it in a small container five times. You will end up with a foaming liquid that can be used to wash your hands and entire body.
- Lavender oil, tea tree oil and turpentine have an antifungal effect. They can be used to treat small areas of skin.
Also, five days after contact, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist. He examines the body with a Wood's lamp. If you do become infected, the disease can be detected in the early stages. This will help you quickly treat her at home and avoid going to the hospital.
Reasons for development
The main causes of ringworm are contact with the pathogen:
- A child aged 4–11 years whose sweat reaction is predominantly alkaline.
- A child or adult with reduced immunity, the presence of scratches, scabs, microtraumas that can become infected.
Most often the carrier is an animal, less often a person. Infection also occurs through objects or personal belongings on which infected hairs, hairs or skin scales remain. Infection is possible through undisinfected hairdressing tools, through soil on which the causative agent of the disease can persist for up to 3 months, during processing of hay. According to statistics, up to 70–80% of cases of the disease occur as a result of contact with stray young cats and kittens.
Symptoms
Ringworm on the face and body appears in the form of pink or red circles raised 1-3 mm above the surface of the skin. The lesions are characterized by clear boundaries, while pale areas of skin with red dots are visible inside. These spots quickly increase in size. Their number is growing over time.
The skin inside the lesions becomes covered with a white crust, which peels and itches. Ringworm on the scalp is characterized by split hair and hair loss. As the number of lesions increases, they begin to connect and overlap each other. Ringworm on the body occurs with increased symptoms when the pathogen gets inside existing lesions, and new fungal rings form in them.
Diagnostics
It is not difficult to make a primary diagnosis if you know what ringworm looks like. To clarify the diagnosis use:
- analysis of clinical data;
- results of luminescent analysis;
- microscopic studies;
- sowing material.
In some cases, the source of infection is difficult to determine, since the incubation period ranges from 2 to 45 days. Symptoms may appear on the head, neck, arms, legs, including the palms, soles of the feet, groin areas and folds. Fungal infection causes itching, discomfort in the area of inflammation, and creates psychological discomfort.
Incubation period of the disease
The incubation period of the fungal infection that causes the appearance of ringworm ranges from several days to 6–8 weeks and depends on the type of pathogen that has entered the body.
Superficial lichen may appear as the first symptoms within 5-7 days after infection. Infiltrative-suppurative lichen does not give any clinical manifestations for several months. The first signs of the disease appear no earlier than 6-8 weeks after the pathogen enters the body.
Treatment
If you notice the first symptoms of ringworm, you should immediately go to the hospital. The effectiveness of treatment and the patient’s quality of life during it depend on the timely initiation of treatment.
Prescribed against ringworm:
- antifungal drugs of systemic or local action. For large areas it is better to use ringworm preparations in the form of sprays, for small areas - ointments and creams;
- hormonal drugs. They are prescribed for severe inflammation of the skin in combination with antimycotic agents;
- glucocorticosteroids are necessary in cases where a secondary infection is associated with inflammation.
The main part of treatment is the use of local drugs. The decision on the need to use tablet forms of drugs is made by the doctor based on the clinical picture of the individual patient.
Microsporia: why is it important to see a doctor in time?
There are factors that cause difficulties in treatment:
• Dermatophyte fungi of the genus Microsporum penetrate deeply into the skin and hair follicles.
• Fungi remain viable for a long time under environmental conditions.
• There are no quick ways to get rid of microsporia. It has been proven that the growth of the fungus stops on the 14-20th day of treatment. Both you and the child will have to be patient.
• In the presence of chronic diseases, it is more difficult to defeat the fungus: a suppurative form often develops, recovery is delayed due to a weakened immune system.
• Insufficient dosage of drugs or self-cessation of treatment leads to a rapid return of the disease - relapse. What are the consequences? The emergence of addiction of the fungus to drugs, the long course of the disease and/or the development of complications.
When prescribing treatment, the doctor takes into account all these factors, selecting an individual management plan for each patient.
Prevention
The main measures to prevent ringworm are careful adherence to hygiene procedures:
- Using only your own towels and combs, preventing the child or adult from sharing them and using other people’s hygiene items.
- After visiting swimming pools, bathhouses, and water parks, you should immediately wash with soap, wash and wash the items you used.
- If someone in your home shows signs of ringworm, further infestation should be prevented. His bedding and underwear must be washed separately. All items are thoroughly washed and treated with disinfectants.
- Preventing contact with stray animals, especially cats. According to statistics, about 50% of them are infected with microsporia or are its carriers.
- The patient should be isolated from the team until complete recovery.
- If there is a sick animal in the house, all surfaces must be treated with disinfectant solutions.
With careful prevention, ringworm may not appear in other household members.
How to protect your baby from infection?
Instill in your child the rules of personal hygiene and make sure they follow them: wash your hands after playing outside or with animals, keep your shoes clean, and much more.
Explain to your child that you cannot use other people's things - for example, clothes, a hat or a comb.
Try to exclude your child from contact with stray animals: explain that you cannot pet a street kitten or puppy.
Have you decided to get a pet: a cat, a dog, a hamster or a parrot? Wonderful! However, be sure to visit a veterinarian first so that he can examine the new family member.
If you already have a pet, regularly examine it yourself and take it to the veterinarian.
Do not leave baby strollers on the landing or outside. Homeless, sick animals, having settled comfortably in them for the night, can leave behind a “gift” in the form of fungus.
Abrasions, scratches, puncture or incised wounds are an easy way for pathogens to enter. Therefore, treat any wounds with antiseptics containing iodine, which has a detrimental effect on both bacteria and fungi.
Popular questions about ringworm
How does ringworm manifest in children?
When lichen develops on the skin, pink round spots appear on the infected areas, which rise slightly above the rest of the surface. These spots itch and become covered with a whitish crust that begins to peel off. If the spots are located on the scalp, the hair within their radius breaks off and falls out.
How does lichen manifest itself in a child?
Ringworm is manifested by the development of spots of fungal infection, the number of which is constantly increasing. The spots increase in size and merge into asymmetrical patterns. A flaky crust forms inside the spots, from which scales infected with the fungus fall off. Secondary infection is possible when one spot begins to develop another.
What does ringworm look like in its early stages?
At the initial stage, ringworm looks like a pink spot of regular shape, raised above the surface of the skin by 1-3 mm. The spots can be localized on any part of the body - head, neck, arms, legs, stomach, back and even in the groin.
Main menu
Microsporia "ringworm"
(from ancient Greek Μικρός - small and σπόρος - seed, sowing), is an infectious disease (mycosis) caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum, characterized by damage to the skin and its derivatives (hair and nails). Both humans and animals suffer from microsporia.
Epidemiology of microsporia "ringworm"
A person becomes infected when hair or wool contaminated with the pathogen comes into contact with his skin. The pathogen can be transmitted through hats, bedding, hairdressing tools, and household items.
People's natural sensitivity is high.
Microsporia is widespread. The incidence predominates in urban areas. Mostly children get sick.
Unsatisfactory hygienic conditions, an abundance of homeless animals, as well as high temperature and humidity contribute to the spread of microsporia. There is an increase in incidence in the autumn-winter period.
The duration of the incubation period is 5-7 days for zoonotic microsporia, 4-6 weeks for anthroponotic microsporia.
Among animals, microsporia most often affects cats, dogs, fur-bearing animals, rabbits, and less often horses, sheep, goats, pigs, deer, monkeys, and tigers. The source of the infectious agent is sick animals, which release it into the external environment with affected hair and scales. Transmission factors are care items, equipment, protective clothing, feed, bedding contaminated with the hair of sick animals. The main carriers of microsporia are cats, especially stray ones. In fur-bearing animals, microsporia does not have a seasonality; Young animals get sick more often.
Diagnosis of ringworm
To confirm the diagnosis of microsporia, fluorescent, microscopic and cultural studies are used.
Luminescent study of microsporia "ringworm"
The method is based on identifying a bright green glow in hair affected by fungi of the genus Microsporum when examined under a Wood's lamp. The reason for this phenomenon has not yet been established.
Luminescence testing must be carried out in a darkened room. The lesions are first cleaned of crusts, ointments, etc. When examining fresh lesions, there may be no glow, which is due to insufficient hair damage. In such situations, the hair should be removed from the suspected site of the fungus, and the glow can be detected in its root part. When the fungus dies, the glow in the hair remains.
The luminescent method is used for:
- pathogen identification;
- identifying affected hair;
- evaluation of therapy results;
- control over persons in contact with the patient;
- determination of infection or carriage in animals.
Microscopic examination of microsporia "ringworm"
To confirm the fungal origin of the disease, scales from lesions of smooth skin lesions are subjected to microscopic examination, and if the scalp is involved in the process, hair fragments are subjected to microscopic examination. In scales from lesions on smooth skin, twisted threads of mycelium are found. A microscopic examination of the affected hair reveals many small spores on its surface.
Cultural study of microsporia "ringworm"
Carrying out cultural diagnostics with positive results of luminescent and microscopic studies is required to identify the causative fungus. The method allows you to determine the genus and type of pathogen and, therefore, carry out adequate therapy and prevention of the disease. The material (scales, hair) is placed on a nutrient medium. The growth of Microsporum colonies (the main pathogen of microsporia) is observed on the 3rd day after sowing.
Microsporia of smooth skin
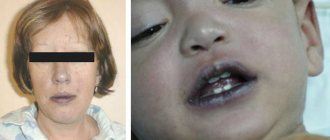
At the site where the fungus has invaded, a swollen, raised red spot with clear boundaries appears. Gradually the spot increases in diameter. A continuous raised ridge is formed along the edge, represented by small nodules, bubbles and crusts. In the central part of the spot, inflammation resolves, as a result of which it acquires a pale pink color, with pityriasis-like peeling on the surface. Thus, the focus has the appearance of a ring. The number of foci with microsporia of smooth skin is usually small (1-3). Their diameter ranges from 0.5 to 3 cm. Most often, lesions are located on the skin of the face, neck, forearms and shoulders. There are no subjective sensations or moderate itching.
In newborns and young children, as well as in young women, severe inflammation and minimal peeling are often observed.
In people prone to allergic reactions (in particular, in patients with atopic dermatitis), the fungus is often masked by manifestations of the underlying process and is not always diagnosed in a timely manner. The use of local hormonal drugs only increases the spread of fungal infection.
A rare type of microsporia includes damage to the skin of the palms, soles and nail plates. Nail lesions are characterized by isolated lesions of the nail, usually its outer edge. Initially, a dull spot is formed, which becomes white over time. The nail in the area of whitening becomes softer and more fragile, and may subsequently collapse.
Microsporia of the scalp
Damage to the scalp by microsporia occurs mainly in children 5-12 years old. It is generally accepted that the rarity of this form in adults is explained by the presence of organic acids in their hair, which slow down the growth of the fungus. This fact indirectly confirms the independent recovery of children during puberty, when the composition of sebum changes. Interestingly, microsporia of the scalp is practically never found in children with red hair.
Foci of microsporia of the scalp are located mainly on the crown, in the parietal and temporal regions. Usually there are 1-2 large lesions ranging from 2 to 5 cm in size, with round or oval outlines and clear boundaries. Along the edges of large lesions there may be screenings - small lesions with a diameter of 0.5–1.5 cm. At the beginning of the disease, a peeling area forms at the site of infection. In the first days, the fungus is located only at the mouth of the hair follicle. Upon closer inspection, you will notice a whitish ring-shaped scale surrounding the hair like a cuff. On the 6-7th day, microsporia spreads to the hair itself, which becomes brittle, breaks off above the level of the surrounding skin by 4-6 mm and looks as if it has been trimmed (hence the name “ringworm”). The remaining stumps look dull and are covered with a grayish-white sheath, which is the spores of a fungus. If you “stroke” the stumps, they deviate in one direction and, unlike healthy hair, do not restore their original position. The skin in the affected area is usually slightly reddened, swollen, and its surface is covered with grayish-white small scales.
In the suppurative form of microsporia, against the background of significant inflammation, soft bluish-red nodes form, the surface of which is covered with pustules. When pressed, pus is released through the holes. The formation of a suppurative form of microsporia is facilitated by irrational (usually local) therapy, the presence of serious concomitant diseases, and late consultation with a doctor.
Treatment of microsporia "ringworm"
Treatment of patients with microsporia seems to be an important, socially significant problem. This disease usually affects not only children, but also their parents. Due to the high contagiousness of mycosis, children are prohibited from attending kindergartens and schools. They miss school classes and find themselves separated from the children's group for a long time. Parents are forced to interrupt work and take sick leave for care. Thus, the family suffers significant moral and material damage.
A speedy recovery of patients with microsporia is achieved with timely recognition of mycosis and adequate treatment. It includes the combined use of systemic and external antifungal agents along with pathogenetic drugs. The latter increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce the frequency and severity of adverse reactions and complications.
Prevention of microsporia “ringworm”
Prevention of microsporia consists of timely identification, isolation and treatment of patients with microsporia. In children's institutions, periodic medical examinations should be carried out. A child diagnosed with microsporia must be isolated from other children and sent for treatment to a specialized hospital. Things belonging to a patient with microsporia must be disinfected. Relatives and people in contact with the patient must be examined. Particular attention should be paid to pets, since they are often the source of infection. Animals with microsporia are either destroyed or given full antifungal treatment.