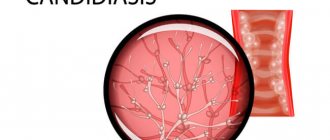
Thrush
is a disease caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida;
hence another name for this disease – candidiasis
.
Candida fungi are part of the natural microflora characteristic of the mucous membranes of the mouth, intestines and vagina. Normally, their activity is balanced by the activity of other microorganisms. But if this balance is disturbed, the fungi begin to multiply in quantities significantly higher than normal.
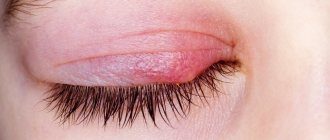
Thrush most often occurs in women and affects the vaginal mucosa and its vestibule. This localization of the disease is called vaginal candidiasis
.
Vaginal candidiasis occurs in the following forms:
- asymptomatic candidiasis (there are no manifestations of the disease, Candida fungi are found in small quantities. This form of the disease does not require treatment);
- acute candidiasis (symptoms manifested);
- chronic candidiasis. Candidiasis is considered chronic if the disease lasts more than 2 months. However, symptoms may appear only during periods of exacerbation.
The danger of candidiasis
Thrush is not a dangerous condition, since it does not relate to any particular disease and cannot affect the condition of the cervix and vaginal walls in women. The occurrence of a condition such as candidiasis indicates a disruption in the functioning of the body. Therefore, recurring thrush requires an examination to find out the cause of its occurrence. If you get rid of the cause, you can forget about the further appearance of candidiasis.
Causes
Reasons why thrush may occur in women:
- pregnancy;
- microflora disturbance;
- weakened immunity;
- endocrine diseases;
- use of contraceptives;
- failure to comply with hygiene standards.
Causes of thrush in men:
- failure to comply with hygiene standards;
- the result of unprotected sexual intercourse, transmission of the candida pathogen from a partner with thrush;
- sudden change in climatic conditions;
- use of aggressive detergents;
- weakened immunity;
- long-term use of antibiotics.
Risk factors
In many healthy women, VC develops sporadically. However, there are risk factors for candidiasis. Behavioral factors include frequent sexual intercourse and oral sex, as well as the use of spermicides.
Tight clothing and underwear usually do not cause illness. However, among women with recurrent VC (RVC), wearing tight tights and panty liners is positively associated with recurrence.
Biological risk factors for VC include:
- use of antibiotics;
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- genetic predisposition;
- high levels of sex hormones;
- taking oral contraceptives containing high doses of estrogen;
- pregnancy.
Antibacterial drugs help reduce the number of lacto- and bifidobacteria, a shift in pH in the vagina and the growth of Candida spp.
Tetracyclines, cephalosporins and ampicillin are more likely than other broad-spectrum antibiotics to provoke the development of candidiasis.
Pregnancy is one of the most common predisposing factors. According to studies, a third of pregnant women develop VK. High levels of sex hormones increase the glycogen content in the vagina, which in turn provides a constant source of carbon necessary for the growth of fungi.
Additionally, the increased acidity of the vaginal flora during pregnancy may inhibit the growth of other microorganisms that naturally inhibit Candida. Although the initial attachment of fungal cells occurs at higher pH values (6–7), an acidic environment favors mycelial development.
In the pathogenesis of vaginal candidiasis (VC), two main phases are distinguished: the adhesion phase, that is, the attachment of fungal cells to epithelial cells, and the mycelial phase. The mycelial phase begins with the entry of Candida spp. into epithelial cells. The growing pseudomycelium of fungi penetrates into the deep layers of the cervical and vaginal epithelium.
Candida are able to penetrate cells without violating the integrity of their mannoprotein membrane (this is the fibrillar coating of the cell wall of the fungus involved in adhesion processes). As a result, Candida resists defense factors and survives in the macroorganism.
Groups at risk for infection with non-albicans Candida species include:
- women with recurrent VK;
- HIV-infected women;
- women over 50 years of age;
- women with uncontrolled diabetes.
In all of the above groups, the most common species is C. glabrata.
The percentage of cases of non-albicans Candida-associated infection increases with women's age.
Features of RVC
Most women with VK respond quickly to therapy, but some may develop a relapsing form, characterized by four or more episodes of infection per year. Predisposing factors:
- uncontrolled diabetes mellitus;
- taking immunosuppressants;
- deviations in the local vaginal immunity of the mucous membranes;
- genetic predisposition.
Studies have proven that patients with RVC have a higher frequency of specific gene polymorphisms compared to the control group. In addition, these patients have certain Lewis system antigens in their blood.
Intermittent VK may also be associated with decreased in vivo concentrations of mannose-binding lectin. The latter, by binding to sugars on the surface of the Candida cell, triggers the pathway of activation of the complement system and leads to the death of the fungus through complement-mediated phagocytosis.
With this disease, an increased concentration of interleukin-4 is also recorded, which inhibits local protective mechanisms.
The Lewis antigen system depends on a group of genes that are expressed in the glandular epithelium. Lewis antigens, unlike erythrocyte antigens, are components of exocrine epithelial secretions, including vaginal ones.
The role of sexual transmission remains unproven. However, most studies indicate the need for treatment of sexual partners. Thus, an experiment by Dr. Horowitz, UK, demonstrated the presence of Candida species in the ejaculate of men whose partners suffered from RVC.
However, the same Horowitz conducted another study, which studied the results of therapy in 54 women, divided into two groups. Partners from the first group were subjected to antifungal therapy, but those from the second were not. There were no significant differences in the rate of relapse among women in these groups.
Relapses can also be caused by other Candida species that are not equally sensitive to first-line therapy.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of thrush in women are:
- Pain that occurs during sexual intercourse.
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membranes.
- Pain with cutting when urinating.
- Pain with the release of cheesy contents from the genital tract, without odor.
- There is itching and burning in the vagina, which can periodically or regularly intensify during sleep, after sexual intercourse, after swimming and during menstruation.
In men, there is a burning sensation and pain during emptying of the bladder, constant or periodic itching, and a white coating on the head of the genital organ.
How to cure thrush during pregnancy?
Statistics say that Candida fungi are detected in 80% of expectant mothers. Before giving birth, you must say goodbye to them. If this event is postponed until later, the baby will become infected during childbirth. Transmission of the fungus is also possible after - during feeding or hygiene procedures. This is fraught with thrush in the mouth, in girls - on the genitals, and a series of subsequent problems with the baby’s health.
To treat expectant mothers, gynecologists prefer to use topical medications - suppositories, tablets, creams. Suppositories Pimafucin and Primafungin can be used in any trimester of pregnancy, Terzhinan tablets - in the second. Systemic drugs are prescribed if the disease cannot be cured locally. Only the doctor prescribes medications and outlines the treatment regimen, depending on the clinical picture; amateur activity is unacceptable here.
Self-medication of candidiasis is unacceptable
Diagnostics
To determine the presence of candidiasis, you will need to take a scraping and send it for further research to a laboratory to identify pathogenic microflora.
The main goal of laboratory diagnostics is to determine the presence of candida fungus. If the diagnosis is carried out in women, then the diagnosis of thrush is established only when there is a large number of yeast-like fungi, as well as additional symptoms of vaginal dysbiosis.
Candidiasis in men is diagnosed when there is a small number of fungi, which indicates the presence of infection. Severe symptoms will allow the urologist to conduct a more detailed examination.
Which doctor should I contact?
If symptoms appear that indicate candidiasis, a woman should consult a gynecologist, and a man should consult a urologist.
Bibliography
- Gynecology textbook. IV edition ed. Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Professor G.M. Savelyeva; prof. V.G. Breusenko 2012
- Urogenital candidiasis. Clinical recommendations. Moscow, 2016 – 22 p.
- Vulvovaginal candidiasis: pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment tactics. Bayramova G.R., Amirkhanyan A.S., Chernova V.F. //Doctor.Ru 2018. No. 10 (154). pp. 32-36
- Sherry L., Kean R., McKloud E., O'Donnell LE, Metcalfe R., Jones BL et al. Biofilms formed by isolates from recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis patients are heterogeneous and insensitive to fluconazole. Antimicrob. Agents. Chemother. 2017; 61(9): e01065-17
- Prilepskaya V.N. Vulvovaginal candidiasis. Clinic, diagnosis, principles of therapy: manual / V.N. Prilepskaya, G.R. Bayramova - M 2008 - 50s
- Atlas of pathogens of fungal infections/E.N. Moskvitina and others - Moscow GEOTAR-Media, 2022 208p
- Zordan R., Cormack B. Adgesis on opportunistic fungal pathogens In: Calderone RA, Clancy CJ, ed Candada and candidiasis/ Washington: ASM press; 2012: 243-259)
- Zhang Y., Li W., Chu M., Chen H., Yu H., Fang C. et al. The AAA AT Pase Vps4 plays important roles in Candida albicans hyphal formation and is inhibited by DBeQ. Mycopathology 2016; (5-6) 329-39
- Murciano C., Moyes DL, Runglall M., Yobouti P., Islam A., Hoyer LL et al. Evaluation of the role of Candida albicans agglutinin-like sequence (Als) proteins in human oral epithelial cell interactions. Plos one 2012.
- Center for Disease Control (CDC) Sexually Transmitted Disease Treatment Guidelines, 2015.
- Donders GG, Bellen G., Mendling W. Management of recurrent vulvovaginal candidosis as a chronic illness. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest 2010 70(4):306-21
- Ankirskaya A.S. Muravyova V.V. Microbiological characteristics of vaginal infections caused by fungi of the genus Candida // sexually transmitted diseases 2001. pp. 12-14
- Eschenbach DA Chronic vulvovaginal candidosis N Engl. J Med 2004; 351(9)
- Tikhomirov A.L. Oleinik Ch.G. Optimization of treatment of recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis // effective therapy in obstetrics and gynecology. 2007 No. 3 from 22-27
- Bayramova G.R. Recurrent vaginal candidiasis. Clinic, diagnosis, treatment. dis. Doctor of Medical Sciences M. 2013 (46s)
- Prilepskaya V.N. Bayramova G.R. Vulvovaginal candidiasis, modern ways to solve the problem. Difficult patient 2006 (from 33-36)
Treatment
All medical procedures related to candidiasis should be carried out only under the supervision of the attending physician. If you try to treat yourself, thrush may transform into an acute form, into a chronic form, and there is also a possibility of an exacerbation of the condition, which will lead to further difficult treatment.
Treatment for thrush includes:
- Antibiotic therapy, personal hygiene, support and protection of the immune system.
- Adhering to a diet that will require limiting carbohydrate intake.
- Complete cessation of bad habits.
- Use of prescribed medications to combat thrush.
Medicines
In the treatment of thrush, which occurs in a mild stage, it will be enough to use local remedies such as vaginal ointments, suppositories and tablets. The most popular drugs include:
- Natamycin;
- Nystatin;
- Miconazole;
- Clotrimazole;
- Isoconazole;
- Ketoconazole.
Doctors most often prescribe drugs with clotrimazole, and avoid the use of vaginal tablets, as they can suppress the normal microflora of the vagina.
Experts prescribe tablets for candidiasis in more advanced cases, as well as in chronic cases of thrush. Almost all medicines have fluconazole as their active ingredient; itraconazole may be an alternative.
Compared to women, thrush in men occurs more easily, and as a treatment, an experienced specialist will prescribe local treatment in the form of ointments, which will need to be applied to the affected areas. In more severe cases, oral medications such as Diflucan and Fluconazole may be prescribed.
Suppositories Livarol
Suppositories for the treatment of fungal vulvovaginitis have ketoconazole as the active substance. This substance stops the vital activity of not only fungi, but also some bacteria, including staphylococcus and streptococcus. The substance helps well with primary infections. In the case of a chronic form of thrush, Livarol will not have the expected effect, because ketoconazole is a substance to which Candida fungi become resistant over time.
Livarol will cope with a mild form of thrush in 5 days. In special cases, the doctor may prescribe a 10-day course. The drug is sold in appropriate dosages: 5 and 10 suppositories per package.
The suppositories, once in the vagina, quickly take on a liquid form and envelop the mucous membranes of the organ. To achieve the maximum duration of contact of the substance with the contaminated surface, it is better to place suppositories at night. So that when the medicine becomes liquid, it does not leak out of the vagina.
Diet
For thrush in women, the diet plan should be based on consuming foods that have antibacterial and antifungal effects. These include:
- garlic;
- seafood;
- parsley;
- buckwheat;
- White rice;
- broccoli;
- natural yoghurts;
- oatmeal;
- cucumbers
For men, when diagnosing candidiasis, the diet should be followed for up to 12 months, the minimum is 4 months. During this time you should:
- Avoid consumption of spicy foods and various sauces.
- Completely abstain from alcohol for the entire period of treatment.
- There are only low-fat dishes, those that are steamed, boiled or stewed.
Prevention
Prevention of thrush:
- It is important to wear underwear made exclusively from natural fabrics. It should be such that it does not rub anywhere;
- when playing sports, it is recommended to wash your sports uniform as often as possible;
- in order to maintain hygiene of the genital organs, they should be washed only with water, using a special mild soap;
- Hygiene products should not contain dyes or fragrances;
- for those who suffer from diabetes, blood sugar control should be constant;
- adhere to proper nutrition and actively walk in the fresh air to support your immune system.