Progesterone
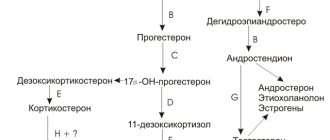
One of the most important hormones in the body is progesterone. This is a steroid hormone that is synthesized in women and men. In the male body, small amounts of progesterone are produced by the adrenal glands and testes. In a woman’s body, progesterone is involved in regulating the functioning of the reproductive system.
Progesterone is sometimes called the pregnancy hormone. This name did not appear by chance. Progesterone is required for the successful attachment of a fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus, and is also responsible for many processes that occur during pregnancy.
The main functions of progesterone in the female body
In a woman’s body, progesterone controls the following processes:
- Stimulates the growth of the endometrium of the uterus so that the egg can implant.
- It prevents contraction of the uterine muscles and, as a consequence, miscarriage, which often occurs in the early stages.
- Helps stop menstruation in pregnant women.
- Regulates the enlargement of the uterus during pregnancy.
- Stimulates the functioning of the sebaceous glands.
- Necessary for the formation and transformation of fetal tissue.
Since progesterone plays a huge role not only in the onset of pregnancy, but also in its course, its level increases several times immediately after implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall.
Hormone functions
The amount of the hormone determines whether a woman will be able to conceive a child and fully carry it to term. The level of progesterone in women is important from days 14 to 20 of the cycle, since ovulation occurs during this time period. If there is not enough substance, the walls of the uterus do not become loose enough to accept the embryo - it will not have the opportunity to attach.
Subsequently, the corpus luteum begins to produce a substance to carry out the following functions:
- preparing a woman’s reproductive system for bearing a child;
- control over the full process of gestation and delivery;
- ensuring high-quality implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterine layer;
- preventing the death of the uterine endothelium and the onset of menstruation;
- preparing the nervous system for the upcoming processes of childbirth, lactation and breastfeeding;
- control of the tone of the uterine walls to avoid spontaneous abortion;
- regulation of the growth and development of glandular breast tissue;
- reducing the risk of cystic growths in the mammary glands.
In addition to the fact that progesterone plays a major role in the functioning of the reproductive sphere, the hormone affects the functioning of almost all vital organs and systems:
- reduces blood viscosity;
- maintains sugar levels at normal levels;
- converts lipids (fats) into energy resources;
- increases blood pressure in hypotensive patients;
- supports libido.
With the help of a hormonal substance, the placenta is formed qualitatively, through which the embryo receives the substances necessary for development. If we talk about the norm of progesterone in the second phase of the cycle, then the indicators are very significant for the formation of the corpus luteum, its gain in volume, the growth of the endometrioid layer and fetal implantation.
Progesterone test
The concentration of progesterone depends on the phase of the cycle. So, during menstruation and until the middle of the cycle, its level is minimal, and after ovulation (usually on the 14th–15th day) the concentration increases. The maximum level is reached in the luteal phase: the egg transforms into the corpus luteum and synthesizes progesterone on its own.
The dependence of progesterone concentration on phase is due to the following:
1. At the beginning of the cycle, the body is preparing for ovulation, so it does not yet need the pregnancy hormone.
2. After ovulation, the female reproductive system rapidly prepares for the possible conception of a child, so the level of progesterone increases sharply, because it is necessary for the successful attachment of the egg to the uterus.
The level of progesterone in the body is determined by its content in the blood. This test is taken on an empty stomach (also acceptable 7 hours after eating). Since the concentration of progesterone depends on the phase of the cycle, the doctor needs to know the duration of the cycle to set a date for the test.
If the cycle lasts 28 days, then the analysis is prescribed on the 21st–22nd day: at this time you can get the most informative results.
For a 34-day cycle, the study is carried out on the 27th day. If the cycle is regular, then determining the date will not be difficult: you need to subtract 7 days from the approximate date of the start of menstruation (you can also add 7 days to the approximate date of ovulation).
If your cycle is irregular, a specialized test will help you calculate the date of ovulation. You can also resort to another method - measuring basal temperature and drawing up a schedule.
Normal progesterone level for a non-pregnant woman
Since progesterone concentrations fluctuate throughout the month, do not be surprised if you need to take a blood test several times. Hormone levels are measured in nanomoles per liter (abbreviated as nmol/l).
If a woman is healthy, then the following norms are relevant:
The given values are relevant only for women of childbearing age. During menopause, the normal progesterone concentration is approximately 0.64 nmol/L.
Progesterone standards for a pregnant woman
The level of progesterone in the blood of a woman carrying a child is higher. In the first trimester, this hormone is actively secreted by the corpus luteum. It is needed to ensure that the uterus does not contract and a miscarriage does not occur. From the 16th week, the placenta also synthesizes this hormone.
The following indicators are considered normal for a pregnant woman:
Of course, during each trimester the concentration changes slightly. Therefore, gynecologists resort to additional methods and use special tables that divide the level by week of pregnancy.
Various factors, including certain medications, can affect the concentration of progesterone in the blood. Therefore, it is necessary to inform your doctor that you are taking any medications both before the test and at the appointment.
Reasons for changes in progesterone levels
High or low concentrations of the hormone should be under the close attention of a doctor, as they indicate the presence of gynecological diseases and serious hormonal imbalance. A one-time deviation of a small number of points can be attributed to the influence of external unfavorable factors.
Low levels of the hormone are provoked by:
- long-term abuse of antibacterial and hormonal drugs;
- amenorrhea (lack of menstruation);
- infertility;
- tumor processes in the pituitary gland or hypothalamus;
- chronic pathologies of the small pelvis;
- ovarian dysfunction.
A low level of progesterone in the 1st trimester of pregnancy is dangerous and can cause miscarriage, so monitoring the indicators over time is important.
A significant increase is just as dangerous as a decrease, and it can occur for several reasons:
- dysfunctional bleeding;
- tumor process in the adrenal glands, appendages;
- use of OCs and progesterone analogues;
- liver diseases;
- kidney failure;
- Corpus luteum cyst.
In pregnant women, due to inflated indicators, improper development of the placenta may occur; this requires the attention of specialists.
Low progesterone
If there is not enough progesterone produced, the menstrual cycle is disrupted, and women who want to become pregnant often experience problems conceiving or early miscarriages. Moreover, low concentrations of this hormone can be detected even in apparently healthy women.
A decrease in progesterone levels occurs for a number of reasons:
Also, low progesterone levels may be due to the fact that you incorrectly determined the day of your cycle.
However, low concentrations may have more serious reasons:
Signs of low progesterone levels:
If a woman is planning a child, she must understand that with reduced progesterone, pregnancy will not occur in the vast majority of cases or the risk of spontaneous abortion will be very high.
Low progesterone levels can be corrected. Doctors recommend starting treatment 2–3 months before the planned conception. This is hormone replacement therapy, that is, the woman is recommended to take hormones. Moreover, such treatment is also possible throughout pregnancy to reduce the risk of miscarriage. In addition, it is necessary to review your diet to stimulate the natural synthesis of hormones. You should add dairy products, protein, and nuts to your diet.
To normalize progesterone levels, you must first identify and eliminate the cause of the decrease in its concentration. If a woman is already expecting a child, the search for the cause is postponed until after childbirth.
Norm for those receiving OK
In women taking contraceptives, the levels of the substance in the blood will differ from those obtained in patients who are not protected with hormones.
| Phase | Normal (nmol/l) |
| Follicular | No more than 3.6 |
| Ovulatory | 1,52–5,45 |
| Luteal | 3,01–66,8 |
| Postmenopause | Up to 3.19 |
Women who are not yet pregnant, but are planning to conceive in the near future, need to monitor progesterone levels over time.
When to take a blood test
It is important to consider that progesterone begins to rise on day 5 of the cycle and reaches a maximum at the luteal stage, on days 20–21. It is during this time period that it is recommended to go to see a doctor if the cycle is standard and does not exceed 28–30 days.
With an extended and shortened cycle, a number of factors must be taken into account:
- the onset of ovulation - with an irregular cycle, you have to determine its day by measuring basal temperature;
- It is better to donate blood 4–5 days after ovulation;
- ideally, do a couple of test samples - from the 19th to the 23rd day of the cycle, so that the doctor can comment on the growth of the hormone level and its compliance with the norm;
- donate blood on an empty stomach, eating is prohibited for the last 12 hours before going to the treatment room;
- abstain from sexual activity for the same time.
If during the period of the test a woman is taking medications, drinking alcohol in large quantities, or has recently suffered a severe cold, the doctor should be warned about this. Otherwise, she will not be able to obtain a properly reliable transcript of the analysis.
Normal levels of gonadotropins
The secretion of FSH and LH is characterized not so much by a circadian rhythm (daily) as by an hourly rhythm (circhoral). Their level depends on the time of day, phase of the cycle, woman’s age, and estrogen production.
| Age period, cycle phases | Reference (average) values of FSH, IU/ml | Reference values of LH, IU/ml | Estradiol reference values |
| Girls before puberty (up to 9 years) | 0,11-1,6 | 0,7-1,3 | |
| Teenage girls (12-16 years old) | Up to 3.5 | ||
| Women of reproductive age (up to 40 years), follicular phase | 2,8-11,3 | 1,1-11,6 | 57-226 pg/ml |
| Ovulatory phase | 5,8-21 | 17-77, ovulatory peak – up to 150 | 127-476 pg/ml |
| Luteal phase | 1,7-9,0 | 2-17 | 77-226 pg/ml |
| Menopause | Up to 150 | 0,03-3,9 | |
| Postmenopause | 21,7-153 | 11,3-40 |
TSH remains stable - 0.4-4.0 µIU/ml, prolactin - 400-1000 IU/l.
Indications for taking hormone tests
Norm of progesterone when taking oral contraceptives
Oral contraceptives are one of the most effective ways to protect against unwanted pregnancy if used correctly. With the help of hormonal contraceptives, ovulation is suppressed in the body, so that the egg cannot attach to the wall of the uterine mucosa.
There are two types of oral contraceptives - mini-pills and combined pills. The first type contains only progesterone, they are more gentle. Combined ones also contain estrogen. With the help of combined contraceptives, a certain amount of estrogen and progesterone are present in the body, which helps inhibit the production of other hormones. Ovulation is blocked and sperm are unable to fertilize the egg.
What is the menstrual cycle?
To better understand how progesterone is produced and when it is best to determine it in the blood, we suggest first understanding what the menstrual cycle is.
The menstrual cycle is a sign of puberty in women, which indicates that a woman can perform reproductive functions.
The normal duration of the menstrual cycle is from 25 to 33 days.
This period is usually divided into four phases, namely:
- menstrual (from 1 to 5-7 days of the cycle), when the decidual layer of the endometrium is rejected;
- follicular (from 6-8 to 12-14 days of the cycle), which is characterized by the maturation of the dominant follicle in the ovary;
- ovulatory (days 13-15 of the cycle), during which the dominant follicle ruptures and the egg is released into the abdominal cavity;
- luteal, which begins on the day of ovulation and lasts until the next menstruation. In this phase, the decidual layer of the endometrium prepares to fall off and exit with menstrual blood.
Preparing for the study
The hormone is given as prescribed by the attending physician on a specific day of the cycle:
- For a cycle of 28 days - on days 20-23. In this case, the progesterone rate on day 21 of the cycle is the most highly concentrated in the body.
- With a duration of 32-35 days, it is worth visiting the laboratory on days 28-29.
- Pregnant women can take the test any day. This also applies to women going through menopause.
If you have an irregular cycle, you should take an ovulation test to determine the right day. In this case, the study is carried out 6-7 days after it.
How to get tested
A couple of days before the blood draw, do not eat fatty foods. Avoid alcohol, refrain from intimate relationships and take medications 24 hours before donating the biomaterial. A blood test is taken on an empty stomach from 8 to 10 am (in the morning the concentration of the steroid hormone reaches its peak in women). Before donating blood, an hour before the test, do not smoke, refrain from tea, coffee and other stimulants. You can drink water.
Important information: Table of hCG growth in the blood during pregnancy by days and weeks from conception
Before taking the biomaterial, the nurse will ask you about your last period, taking hormonal medications, cycle length - the norm in this case may differ. Most often, the hormone is most concentrated in the blood of women on the 21st day of the cycle - the health worker should also clarify this.
Cycle dependency
The concentration is never stable or the same.
The numbers depend on many factors:
- day of the menstrual cycle;
- age;
- pregnancy;
- taking hormonal contraceptives.
In addition to the above mentioned nuances, there are others that indirectly affect the fact of an increase/decrease in the hormone. This is stress, an exhausting diet, gynecological diseases, intense physical activity, and taking medications. Firstly, it depends on the phase and day of the menstrual period.
How to normalize hormone levels
In case of serious deviations from the norm, the indicators are restored by treating the underlying disease or long-term hormonal treatment with the following drugs:
- Duphaston;
- Utrozhestan;
- gels, suppositories, injections containing progesterone.
If there is a slight deviation from the norm, it will be enough to change your lifestyle - give up bad habits, eat a balanced diet, and avoid excessive physical and mental stress. It is necessary to keep your weight under control, get plenty of rest and sleep, and protect yourself from stress.
Normal hormone levels on days 20–23 of the cycle indicate the absence of chronic gynecological diseases and a calm hormonal background. Determining its level in the blood is necessary for women who cannot get pregnant for a long time, have a history of several miscarriages, and are planning to undergo an IVF procedure. It is important to inform your doctor about any deviations or changes in tests so that the necessary therapy can be prescribed.
Sources: https://adella.ru/health/norma-progesterona-u-zhenshhin.html https://www.wantbaby.ru/ru/kalkulatory/progesteron-po-dnjam-cikla/ https://DetStrana.ru /article/planirovanie/podgotovka-k-zachatiyu/normy-progesterona/ https://www.BabyBlog.ru/theme/normy-progesterona-po-dnyam-cikla https://FB.ru/article/428389/den- tsikla-kakaya-faza-norma-progesterona https://helix.ru/kb/item/08-112 https://www.babyblog.ru/community/post/conception/1831502
Drugs to increase progesterone levels
Utrozhestan® (Utrogectan)
The basis of the composition is micronized progesterone. One capsule contains 100 or 200 mg (depending on the dosage of the medicine). The shape of the capsule 100 mg is round, 200 mg is oval. The filling of the gelatin shell is an oily homogeneous suspension.
The main directions for using pharmaceuticals internally:
- infertility due to luteal insufficiency;
- threat of miscarriage;
- premenstrual syndrome;
- fibrocystic mastopathy;
- menstrual irregularities due to infertility or failure of the ovulation process;
- Hormone replacement therapy during the menopausal transition or postmenopause.
The intravaginal method of using the product is also practiced.
It is recommended for the following problems:
- non-functioning or absent ovaries;
- threat of abortion;
- premature menopause;
- infertility (cause - luteal insufficiency).
Utrozhestan is used in preparation for in vitro fertilization to support the luteal phase.
The pharmacological product has a number of restrictions on its use. The doctor must take them into account when developing a treatment regimen.
Among the contraindications:
- allergy to the components of the composition;
- problems with veins (thrombosis);
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- stroke, heart attack;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown etiology;
- oncology of the mammary glands, genital organs;
- incomplete abortion;
- genetic pathology of the liver (porphyria), other diseases of the organ;
- lactation period;
- age up to 18 years.
The treatment regimen is determined individually.
The annotation offers the following options:
- if there is a threat of miscarriage, take a daily dose of 200 to 600 mg/day. (prescribed in the third trimester only after assessing clinical data);
- during the menopausal transition – daily dose – 200 mg, course duration – 12 days;
- after menopause - the daily dose is from 100 to 200 mg, the duration of treatment is determined individually;
- to maintain the luteal phase - the daily norm is 200-400 mg, administration begins from the 17th to 26th day of the month, a ten-day course is proposed.
Progesterone
The product is available in the form of an injection solution of different concentrations: 10 and 25 mg. The active compound is progesterone.
The main direction of application of the pharmaceutical product:
- metrorrhagia;
- recurrent miscarriage;
- uterine bleeding associated with genital dysfunction;
- amenorrhea.
The treatment regimen is determined individually, taking into account the characteristics of the body and clinical trial data. The maximum daily allowance is 0.025 g.
Please read the restrictions before using the product. The medicine should not be used in the presence of kidney or liver dysfunction.
The manufacturer also identifies the following contraindications:
- breast carcinoma;
- hepatitis;
- vaginal bleeding of unknown origin;
- thromboembolic pathologies.